levetiracetam
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LEVETIRACETAM IN SODIUM CHLORIDE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LEVETIRACETAM IN SODIUM CHLORIDE INJECTION.LEVETIRACETAM IN SODIUM CHLORIDE injection, for intravenous useInitial U.S. Approval: 1999
3d88adda-9580-44bf-b75c-d615c973c1e1
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 16, 2023
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
DUNS: 005083209
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
levetiracetam
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
levetiracetam
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
levetiracetam
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package/Label Display Panel - (15 mg/mL)
NDC 36000-354-01
Rx only
Levetiracetam in 0.54% Sodium Chloride Injection
1500 mg/100 mL
(15 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion Only
100 mL
INFUSE OVER A PERIOD OF 15 MINUTES
Each 100 mL contains: 1500 mg levetiracetam, USP (15 mg/mL), water for injection, USP;540 mg sodium chloride, USP;7.5 mg of glacial acetic acid, USP and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid, USP and164****mg sodium acetate trihydrate, USP.
**Usual Dosage:**See package insert.
CAUTION: Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Levetiracetam in 0.54% Sodium Chloride Injection should not be further diluted prior to its use.
Use unit promptly once overwrap is removed.
**Recommended storage:**Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Single-dose bag only. Discard unused portion
VIAFLO container is not made with natural rubber latex, DEHP, or PVC.
Baxter
Manufactured for:
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
Made in Ireland
CB-35-05-547
EZPE8832

TO OPEN: TEAR AT NOTCH
NDC 36000-354-01
Rx only
Levetiracetam in 0.54% Sodium Chloride Injection
1500 mg/100 mL
(15 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion Only
1 x 100 mL
INFUSE OVER A PERIOD OF 15 MINUTES
Each 100 mL contains: 1500 mg levetiracetam, USP (15 mg/mL), water for injection, USP;540 mg sodium chloride, USP;7.5 mg of glacial acetic acid, USP and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid, USP and164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate, USP.
**Usual Dosage:**See package insert.
CAUTION: Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Levetiracetam in 0.54% Sodium Chloride Injection should not be further diluted prior to its use.
**TO OPEN: TEAR AT NOTCH.**Do not use if overwrap has been previously opened or damaged. Use unit promptly once overwrap is removed.
**Recommended storage:**Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Single-dose bag only with an aluminum overwrap. Discard unused portion.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Baxter
Manufactured for:
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
Made in Ireland
(See Solution Container for Lot and Exp)
CB-10-01-258
EZPE8832

CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
All clinical studies supporting the efficacy of levetiracetam utilized oral formulations. The finding of efficacy of levetiracetam injection is based on the results of studies using an oral formulation of levetiracetam, and on the demonstration of comparable bioavailability of the oral and parenteral formulations [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)].
14.1 Partial-Onset Seizures
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy (added to other antiepileptic drugs) in adults was established in three multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical studies in patients who had refractory partial-onset seizures with or without secondary generalization. The tablet formulation was used in all these studies. In these studies, 904 patients were randomized to placebo, 1000 mg, 2000 mg, or 3000 mg/day. Patients enrolled in Study 1 or Study 2 had refractory partial-onset seizures for at least two years and had taken two or more classical AEDs. Patients enrolled in Study 3 had refractory partial-onset seizures for at least 1 year and had taken one classical AED. At the time of the study, patients were taking a stable dose regimen of at least one and could take a maximum of two AEDs. During the baseline period, patients had to have experienced at least two partial-onset seizures during each 4-week period.
Study 1
Study 1 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study conducted at 41 sites in the United States comparing levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=97), levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=101), and placebo (N=95) given in equally divided doses twice daily. After a prospective baseline period of 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of the three treatment groups described above. The 18-week treatment period consisted of a 6-week titration period, followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED regimens were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency). The results of the analysis of Study 1 are displayed in Table 7.
Table 7: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial-Onset Seizures in Study 1
|
Placebo (N=95) |
Levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=97) |
Levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=101) | |
|
– |
26.1%* |
30.1%* |
- Statistically significant versus placebo
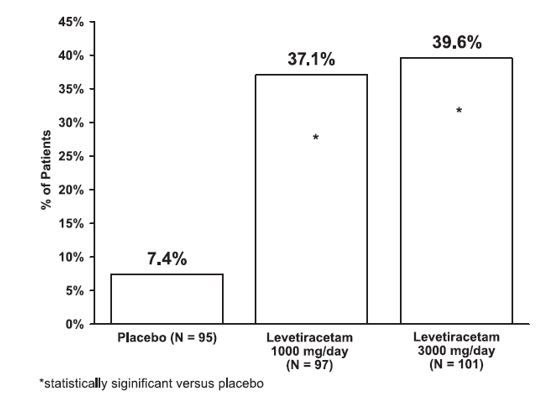
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the three treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Study 1
****
Study 2
Study 2 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study conducted at 62 centers in Europe comparing levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=106), levetiracetam 2000 mg/day (N=105), and placebo (N=111) given in equally divided doses twice daily.
The first period of the study (Period A) was designed to be analyzed as a parallel-group study. After a prospective baseline period of up to 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of the three treatment groups described above. The 16-week treatment period consisted of the 4-week titration period followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED regimens were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly partial seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency). The results of the analysis of Period A are displayed in Table 8.
Table 8: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial-Onset Seizures in Study 2: Period A
|
Placebo (N=111) |
Levetiracetam 1000 mg/day (N=106) |
Levetiracetam 2000 mg/day (N=105) | |
|
– |
17.1%* |
21.4%* |
- Statistically significant versus placebo
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the three treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Study 2: Period A
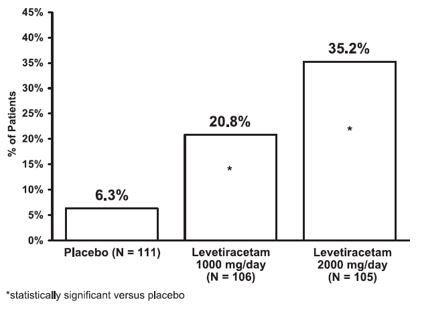
The comparison of levetiracetam 2000 mg/day to levetiracetam 1000 mg/day for responder rate was statistically significant (P=0.02). Analysis of the trial as a cross-over yielded similar results.
Study 3
Study 3 was a double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study conducted at 47 centers in Europe comparing levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=180) and placebo (N=104) in patients with refractory partial-onset seizures, with or without secondary generalization, receiving only one concomitant AED. Study drug was given in two divided doses. After a prospective baseline period of 12 weeks, patients were randomized to one of two treatment groups described above. The 16-week treatment period consisted of a 4-week titration period, followed by a 12-week fixed dose evaluation period, during which concomitant AED doses were held constant. The primary measure of effectiveness was a between group comparison of the percent reduction in weekly seizure frequency relative to placebo over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period). Secondary outcome variables included the responder rate (incidence of patients with ≥50% reduction from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency).
Table 9 displays the results of the analysis of Study 3.
Table 9: Reduction in Mean Over Placebo in Weekly Frequency of Partial-Onset Seizures in Study 3
|
Placebo (N=104) |
Levetiracetam 3000 mg/day (N=180) | |
|
– |
23.0%* |
- Statistically significant versus placebo
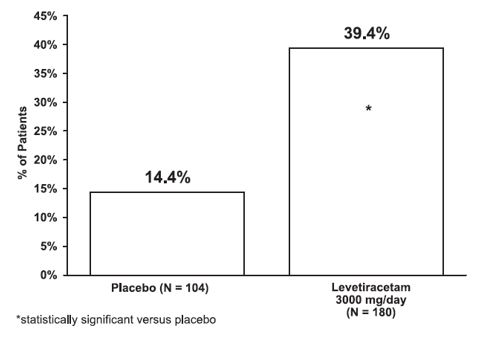
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in partial-onset seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Study 3
****
14.2 Myoclonic Seizures in Patients with Juvenile Myoclonic Epilepsy
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in patients with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME) experiencing myoclonic seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 37 sites in 14 countries. Of the 120 patients enrolled, 113 had a diagnosis of confirmed or suspected JME. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 antiepileptic drug (AED) experiencing one or more myoclonic seizures per day for at least 8 days during the prospective 8-week baseline period were randomized to either levetiracetam or placebo (levetiracetam N=60, placebo N=60). Patients were titrated over 4 weeks to a target dose of 3000 mg/day and treated at a stable dose of 3000 mg/day over 12 weeks (evaluation period).
Study drug was given in 2 divided doses. The primary measure of effectiveness was the proportion of patients with at least 50% reduction in the number of days per week with one or more myoclonic seizures during the treatment period (titration + evaluation periods) as compared to baseline. Table 10 displays the results for the 113 patients with JME in this study. Of 120 patients enrolled, 113 had a diagnosis of confirmed or suspected JME. The results are displayed in Table 10.
Table 10: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in Myoclonic Seizure Days Per Week For Patients With JME
|
Placebo (N=59) |
Levetiracetam (N=54) | |
|
23.7% |
60.4%* |
*Statistically significant versus placebo
14.3 Primary Generalized Tonic-Clonic Seizures
The effectiveness of levetiracetam as adjunctive therapy in patients with idiopathic generalized epilepsy experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic (PGTC) seizures was established in one multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, conducted at 50 sites in 8 countries. Eligible patients on a stable dose of 1 or 2 antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) experiencing at least 3 PGTC seizures during the 8-week combined baseline period (at least one PGTC seizure during the 4 weeks prior to the prospective baseline period and at least one PGTC seizure during the 4-week prospective baseline period) were randomized to either levetiracetam or placebo. The 8-week combined baseline period is referred to as “baseline” in the remainder of this section.
The population included 164 patients (levetiracetam N=80, placebo N=84) with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (predominately juvenile myoclonic epilepsy, juvenile absence epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy, or epilepsy with Grand Mal seizures on awakening) experiencing primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures. Each of these syndromes of idiopathic generalized epilepsy was well represented in this patient population. Patients were titrated over 4 weeks to a target dose of 3000 mg/day for adults or a pediatric target dose of 60 mg/kg/day and treated at a stable dose of 3000 mg/day (or 60 mg/kg/day for children) over 20 weeks (evaluation period). Study drug was given in 2 equally divided doses per day.
The primary measure of effectiveness was the percent reduction from baseline in weekly PGTC seizure frequency for levetiracetam and placebo treatment groups over the treatment period (titration + evaluation periods). There was a statistically significant decrease from baseline in PGTC frequency in the levetiracetam-treated patients compared to the placebo-treated patients.
Table 11: Median Percent Reduction from Baseline in PGTC Seizure Frequency per Week
|
Placebo (N=84) |
Levetiracetam (N=78) | |
|
44.6% |
77.6%* |
*Statistically significant versus placebo
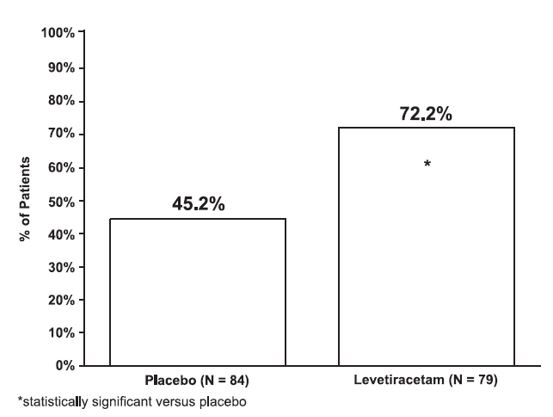
The percentage of patients (y-axis) who achieved ≥50% reduction in weekly seizure rates from baseline in PGTC seizure frequency over the entire randomized treatment period (titration + evaluation period) within the two treatment groups (x-axis) is presented in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Responder Rate (≥50% Reduction from Baseline) in PGTC Seizure Frequency per Week
****
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is an antiepileptic drug available as a clear, colorless, sterile solution for intravenous administration.
The chemical name of levetiracetam, a single enantiomer, is (-)-(S)-α-ethyl-2-oxo-1-pyrrolidine acetamide, its molecular formula is C8H14N2O2 and its molecular weight is 170.21 g/mol.
Levetiracetam is chemically unrelated to existing antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). It has the following structural formula:
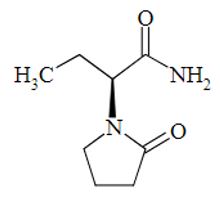
Levetiracetam is a white to almost white powder with a faint odor and a bitter taste. It is very soluble in water (104.0 g/100 mL). It is freely soluble in chloroform (65.3 g/100 mL) and in methanol (53.6 g/100 mL), soluble in ethanol (16.5 g/100 mL), sparingly soluble in acetonitrile (5.7 g/100 mL) and practically insoluble in n-hexane. (Solubility limits are expressed as g/100 mL solvent.)
Levetiracetam in Sodium Chloride Injection is a clear, colorless, sterile solution that is available in a single-dose VIAFLO bag with an one side aluminum and other side transparent over wrap. The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
500 mg/100 mL: One 100 mL bag contains 500 mg of levetiracetam, USP (5 mg/mL), water for injection, USP; 820 mg sodium chloride, USP; 5.5 mg of glacial acetic acid, USP and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid, USP and 164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate, USP.
1000 mg/100 mL: One 100 mL bag contains 1000 mg of levetiracetam, USP (10 mg/mL), water for injection, USP; 750 mg sodium chloride, USP; 6.5 mg of glacial acetic acid, USP and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid, USP and 164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate, USP.
1500 mg/100 mL: One 100 mL bag contains 1500 mg of levetiracetam, USP (15 mg/mL), water for injection, USP; 540 mg sodium chloride, USP; 7.5 mg of glacial acetic acid, USP and buffered at approximately pH 5.5 with glacial acetic acid, USP and 164 mg sodium acetate trihydrate, USP.
