Stiolto Respimat
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use STIOLTO RESPIMAT safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for STIOLTO RESPIMAT. STIOLTO RESPIMAT (tiotropium bromide and olodaterol inhalation spray), for oral inhalation use Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
01e15aee-40e0-23f3-537f-c96dd63e2cb1
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
May 23, 2023
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals Inc.
DUNS: 603175944
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
DUNS: 603175944
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
tiotropium bromide and olodaterol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
Drug Labeling Information
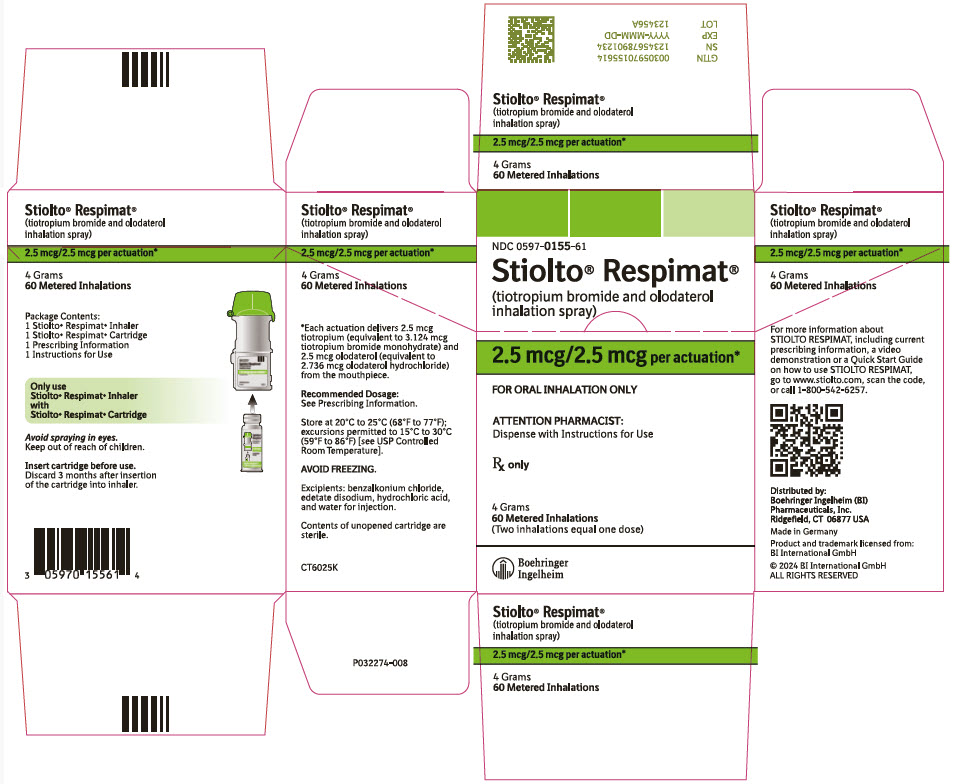
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2.5 mcg/2.5 mcg Cartridge Carton
NDC 0597-0155-61
Stiolto® Respimat®
(tiotropium bromide and olodaterol
inhalation spray)
2.5 mcg/2.5 mcg per actuation*
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
ATTENTION PHARMACIST:
Dispense with Instructions for Use
Rx only
4 Grams
60 Metered Inhalations
(Two inhalations equal one dose)
Boehringer
Ingelheim
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Maintenance Treatment of COPD
STIOLTO RESPIMAT is a combination of tiotropium bromide and olodaterol indicated for long-term, once-daily maintenance treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema.
Important Limitations of Use
- STIOLTO RESPIMAT is not indicated to treat acute deteriorations of COPD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- STIOLTO RESPIMAT is not indicated to treat asthma. The safety and effectiveness of STIOLTO RESPIMAT in asthma have not been established.
STIOLTO RESPIMAT is a combination of tiotropium bromide, an anticholinergic and olodaterol, a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist (LABA) indicated for the long-term, once-daily maintenance treatment of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). (1.1)
Important limitations:
- STIOLTO RESPIMAT is NOT indicated to treat acute deterioration of COPD. (1.1)
- STIOLTO RESPIMAT is NOT indicated to treat asthma. (1.1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Use of a LABA, including STIOLTO RESPIMAT, without an inhaled corticosteroid is contraindicated in patients with asthma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. STIOLTO RESPIMAT is not indicated for the treatment of asthma.
STIOLTO RESPIMAT is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to tiotropium, ipratropium, olodaterol, or any component of this product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
In clinical trials and postmarketing experience with tiotropium, immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema (including swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat), itching, or rash have been reported. Hypersensitivity reactions were also reported in clinical trials with STIOLTO RESPIMAT.
- Use of a LABA, including STIOLTO RESPIMAT, without an inhaled corticosteroid is contraindicated in patients with asthma. (4)
- Hypersensitivity to tiotropium, ipratropium, olodaterol, or any component of this product. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Asthma-Related Events – Hospitalizations, Intubations, Death
- The safety and efficacy of STIOLTO RESPIMAT in patients with asthma have not been established. STIOLTO RESPIMAT is not indicated for the treatment of asthma [see Contraindications (4)].
- Use of long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists (LABA) as monotherapy [without inhaled corticosteroids (ICS)] for asthma is associated with an increased risk of asthma-related death. Available data from controlled clinical trials also suggest that use of LABA as monotherapy increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. These findings are considered a class effect of LABA monotherapy. When LABA are used in fixed-dose combination with ICS, data from large clinical trials do not show a significant increase in the risk of serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death) compared with ICS alone.
- A 28-week, placebo-controlled US study comparing the safety of another LABA (salmeterol) with placebo, each added to usual asthma therapy, showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in patients receiving salmeterol (13/13,176 in patients treated with salmeterol vs. 3/13,179 in patients treated with placebo; RR 4.37, 95% CI 1.25, 15.34). The increased risk of asthma-related death is considered a class effect of LABA, including olodaterol, one of the active ingredients in STIOLTO RESPIMAT.
- No study adequate to determine whether the rate of asthma-related death is increased in patients treated with STIOLTO RESPIMAT has been conducted.
- Available data do not suggest an increased risk of death with use of LABA in patients with COPD.
5.2 Deterioration of Disease and Acute Episodes
STIOLTO RESPIMAT should not be initiated in patients with acutely deteriorating COPD, which may be a life-threatening condition. STIOLTO RESPIMAT has not been studied in patients with acutely deteriorating COPD. The use of STIOLTO RESPIMAT in this setting is inappropriate.
STIOLTO RESPIMAT should not be used for the relief of acute symptoms, i.e., as rescue therapy for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm. STIOLTO RESPIMAT has not been studied in the relief of acute symptoms and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Acute symptoms should be treated with an inhaled short-acting beta2-agonist.
When beginning STIOLTO RESPIMAT, patients who have been taking inhaled, short- acting beta2-agonists on a regular basis (e.g., four times a day) should be instructed to discontinue the regular use of these drugs and use them only for symptomatic relief of acute respiratory symptoms. When prescribing STIOLTO RESPIMAT, the healthcare provider should also prescribe an inhaled, short- acting beta2-agonist and instruct the patient on how it should be used. Increasing inhaled beta2-agonist use is a signal of deteriorating disease for which prompt medical attention is indicated.
COPD may deteriorate acutely over a period of hours or chronically over several days or longer. If STIOLTO RESPIMAT no longer controls symptoms of bronchoconstriction, or the patient's inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist becomes less effective or the patient needs more inhalation of short-acting beta2-agonist than usual, these may be markers of deterioration of disease. In this setting, a re-evaluation of the patient and the COPD treatment regimen should be undertaken at once. Increasing the daily dosage of STIOLTO RESPIMAT beyond the recommended dosage is not appropriate in this situation.
5.3 Excessive Use of STIOLTO RESPIMAT and Use With Other Long-Acting
Beta2-Agonists
As with other inhaled drugs containing beta2-adrenergic agents, STIOLTO RESPIMAT should not be used more often than recommended, at higher doses than recommended, or in conjunction with other medications containing long-acting beta2-agonists, as an overdose may result. Clinically significant cardiovascular effects and fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs.
5.4 Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including urticaria, angioedema (including swelling of the lips, tongue or throat), rash, bronchospasm, anaphylaxis, or itching may occur after administration of STIOLTO RESPIMAT. If such a reaction occurs, therapy with STIOLTO RESPIMAT should be stopped at once and alternative treatments should be considered. Given the similar structural formula of atropine to tiotropium, patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to atropine or its derivatives should be closely monitored for similar hypersensitivity reactions to STIOLTO RESPIMAT.
5.5 Paradoxical Bronchospasm
As with other inhaled medicines, STIOLTO RESPIMAT may cause paradoxical bronchospasm that may be life-threatening. If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, STIOLTO RESPIMAT should be stopped immediately and alternative therapy instituted.
5.6 Cardiovascular Effects
Olodaterol, like other beta2-agonists, can produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by increases in pulse rate, systolic or diastolic blood pressure, and/or symptoms. If such effects occur, STIOLTO RESPIMAT may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta-agonists have been reported to produce ECG changes, such as flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Long acting beta2-adrenergic agonists should be administered with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, and hypertension.
5.7 Coexisting Conditions
Olodaterol, like other sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with convulsive disorders or thyrotoxicosis, in patients with known or suspected prolongation of the QT interval, and in patients who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines. Doses of the related beta2-agonist albuterol, when administered intravenously, have been reported to aggravate pre-existing diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis.
5.8 Worsening of Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
STIOLTO RESPIMAT should be used with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma. Prescribers and patients should be alert for signs and symptoms of acute narrow-angle glaucoma (e.g., eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos or colored images in association with red eyes from conjunctival congestion and corneal edema). Instruct patients to consult a physician immediately should any of these signs or symptoms develop.
5.9 Worsening of Urinary Retention
STIOLTO RESPIMAT should be used with caution in patients with urinary retention. Prescribers and patients should be alert for signs and symptoms of prostatic hyperplasia or bladder-neck obstruction (e.g., difficulty passing urine, painful urination), especially in patients with prostatic hyperplasia or bladder neck obstruction. Instruct patients to consult a physician immediately should any of these signs or symptoms develop.
5.10 Renal Impairment
Because tiotropium is a predominantly renally excreted drug, patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance of <60 mL/min) treated with STIOLTO RESPIMAT should be monitored closely for anticholinergic side effects [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.11 Hypokalemia and Hyperglycemia
Beta-adrenergic agonists may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Inhalation of high doses of beta2-adrenergic agonists may produce increases in plasma glucose.
In patients with severe COPD, hypokalemia may be potentiated by hypoxia and concomitant treatment [see Drug Interactions (7.2)], which may increase the susceptibility for cardiac arrhythmias.
Clinically notable decreases in serum potassium or changes in blood glucose were infrequent during clinical studies with long-term administration of olodaterol with the rates similar to those for placebo controls. Olodaterol has not been investigated in patients whose diabetes mellitus is not well controlled.
- LABA as monotherapy (without an inhaled corticosteroid) for asthma increases the risk of serious asthma-related events. (5.1)
- Do not initiate STIOLTO RESPIMAT in acutely deteriorating COPD patients. (5.2)
- Do not use for relief of acute symptoms. Concomitant short-acting beta2-agonists can be used as needed for acute relief. (5.2)
- Do not exceed the recommended dosage. Excessive use of STIOLTO RESPIMAT, or use in conjunction with other medications containing LABA can result in clinically significant cardiovascular effects and may be fatal. (5.3)
- Immediate hypersensitivity reactions: Discontinue STIOLTO RESPIMAT at once and consider alternatives if immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema, urticaria, rash, bronchospasm, or anaphylaxis, occur. (5.4)
- Life-threatening paradoxical bronchospasm can occur. Discontinue STIOLTO RESPIMAT immediately. (5.5)
- Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular or convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, or sensitivity to sympathomimetic drugs. (5.6, 5.7)
- Worsening of narrow-angle glaucoma may occur. Use with caution in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma and instruct patients to consult a physician immediately if this occurs. (5.8)
- Worsening of urinary retention may occur. Use with caution in patients with prostatic hyperplasia or bladder-neck obstruction and instruct patients to consult a physician immediately if this occurs. (5.9)
- Be alert to hypokalemia and hyperglycemia. (5.11)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
STIOLTO RESPIMAT contains both tiotropium bromide and olodaterol; therefore, the risks associated with overdosage for the individual components described below apply to STIOLTO RESPIMAT.
Tiotropium
High doses of tiotropium may lead to anticholinergic signs and symptoms. However, there were no systemic anticholinergic adverse effects following a single inhaled dose of up to 282 mcg tiotropium in 6 healthy volunteers. In a study of 12 healthy volunteers, bilateral conjunctivitis and dry mouth were seen following repeated once-daily inhalation of 141 mcg of tiotropium. Dry mouth/throat and dry nasal mucosa occurred in a dose-dependent [10-40 mcg daily] manner, were observed following 14-day dosing of up to 40 mcg tiotropium bromide inhalation solution in healthy subjects.
Olodaterol
The expected signs and symptoms with overdosage of olodaterol are those of excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation and occurrence or exaggeration of any of the signs and symptoms, e.g., myocardial ischemia, angina pectoris, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia, arrhythmias, palpitations, dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, anxiety, headache, tremor, dry mouth, muscle spasms, nausea, fatigue, malaise, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, and metabolic acidosis. As with all inhaled sympathomimetic medications, cardiac arrest and even death may be associated with an overdose of olodaterol.
Treatment of overdosage consists of discontinuation of STIOLTO RESPIMAT together with institution of appropriate symptomatic and supportive therapy. The judicious use of a cardioselective beta-receptor blocker may be considered, bearing in mind that such medication can produce bronchospasm. There is insufficient evidence to determine if dialysis is beneficial for overdosage of STIOLTO RESPIMAT. Cardiac monitoring is recommended in cases of overdosage.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
STIOLTO RESPIMAT
No studies of the carcinogenicity, in vitro mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility were conducted with STIOLTO RESPIMAT, however, studies are available for the individual components, tiotropium and olodaterol.
Tiotropium
No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in a 104-week inhalation study in rats at tiotropium doses up to 59 mcg/kg/day, in an 83-week inhalation study in female mice at doses up to 145 mcg/kg/day, and in a 101-week inhalation study in male mice at doses up to 2 mcg/kg/day. These doses correspond to approximately 30, 40, and 0.5 times the recommended human daily inhalation dose (RHDID) on a mcg/m2 basis, respectively.
Tiotropium bromide demonstrated no evidence of mutagenicity or clastogenicity in the following assays: the bacterial gene mutation assay, the V79 Chinese hamster cell mutagenesis assay, the chromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes in vitro, the mouse micronucleus assay in vivo, and the unscheduled DNA synthesis assay in primary rat hepatocytes in vitro.
In rats, decreases in the number of corpora lutea and the percentage of implants were noted at inhalation tiotropium doses of 78 mcg/kg/day or greater (approximately 35 times the RHDID on a mcg/m2 basis). No such effects were observed at 9 mcg/kg/day (approximately 4 times than the RHDID on a mcg/m2 basis). The fertility index; however, was not affected at inhalation doses up to 1,689 mg/kg/day (approximately 760 times the RHDID on a mcg/m2 basis).
Olodaterol
Two-year inhalation studies were conducted in rats and mice to assess the carcinogenic potential of olodaterol. Lifetime treatment of female rats induced leiomyomas of the mesovarium at doses of 25.8 and 270 mcg/kg/day (approximately 18- and 198-fold, respectively, the RHDID on an AUC basis). No tumor findings were observed in male rats at doses up to 270 mcg/kg/day (approximately 230-fold the RHDID on an AUC basis). Lifetime treatment of female mice induced leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas of the uterus at doses ≥76.9 mcg/kg/day (approximately 106-fold the RHDID on an AUC basis). No tumor findings were observed in male mice at doses up to 255 mcg/kg/day (approximately 455-fold the RHDID on an AUC basis). Increases in leiomyomas and leiomyosarcomas of the female rodent reproductive tract have been similarly demonstrated with other beta2-adrenergic agonist drugs. The relevance of these findings to human use is unknown.
Olodaterol was not mutagenic in the in vitro Ames test or in the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay. Olodaterol produced increased frequency of micronuclei in rats after intravenous doses. The increased frequency of micronuclei was likely related to drug enhanced (compensatory) erythropoiesis. The mechanism for induction of micronuclei formation is likely not relevant at clinical exposures.
Olodaterol did not impair male or female fertility in rats at inhalation doses up to 3,068 mcg/kg/day (approximately 2,322 times the RHDID on an AUC basis).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
STIOLTO RESPIMAT Inhalation Spray is supplied in a labeled carton containing one STIOLTO RESPIMAT cartridge and one STIOLTO RESPIMAT inhaler.
The STIOLTO RESPIMAT cartridge is provided as an aluminum cylinder with a tamper protection seal on the cap. The STIOLTO RESPIMAT cartridge is only intended for use with the STIOLTO RESPIMAT inhaler and should not be interchanged with any other RESPIMAT device delivered product.
The STIOLTO RESPIMAT inhaler is a cylindrical shaped plastic inhalation device with a gray colored body and a clear base. The clear base is removed to insert the cartridge. The inhaler contains a dose indicator. The light green-colored cap and the written information on the label of the gray inhaler body indicate that it is labeled for use with the STIOLTO RESPIMAT cartridge.
STIOLTO RESPIMAT Inhalation Spray is available as:
- STIOLTO RESPIMAT Inhalation Spray: 60 metered actuations (NDC 0597-0155-61)
- STIOLTO RESPIMAT Inhalation Spray: 10 metered actuations (NDC 0597-0155-70) (institutional pack)
The STIOLTO RESPIMAT cartridge has a net fill weight of at least 4 grams and when used with the STIOLTO RESPIMAT inhaler, is designed to deliver the labeled number of metered actuations after preparation for use.
When the labeled number of actuations has been dispensed from the inhaler, the RESPIMAT locking mechanism will be engaged and no more actuations can be dispensed.
After assembly, the STIOLTO RESPIMAT inhaler should be discarded at the latest 3 months after first use or when the locking mechanism is engaged, whichever comes first.
Keep out of reach of children. Do not spray into eyes.
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Avoid freezing.
