Rivelsa
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RIVELSA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RIVELSA. RIVELSA (levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol and ethinyl estradiol) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1982
822e56c6-562f-4299-bf4f-eaee0c0f2b7a
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 19, 2023
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
DUNS: 001627975
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Levonorgestrel/Ethinyl Estradiol and Ethinyl Estradiol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
Drug Labeling Information
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The sections below provide information on substances for which data on drug interactions with COCs are available. There is little information available about the clinical effect of most drug interactions that may affect COCs. However, based on the known pharmacokinetic effects of these drugs, clinical strategies to minimize any potential adverse effect on contraceptive effectiveness or safety are suggested.
Consult the approved product labeling of all concurrently used drugs to obtain further information about interactions with COCs or the potential for metabolic enzyme or transporter system alterations.
No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with RIVELSA.
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Combined Oral Contraceptives
Substances Decreasing the Plasma Concentrations of COCs and Potentially Diminishing the Efficacy of COCs:
Table 3 includes substances that demonstrated an important drug interaction with RIVELSA.
Table 3: Significant Drug Interactions Involving Substances That Affect COCs
|
Metabolic Enzyme Inducers | |
|
Clinical effect |
|
|
Prevention or management |
|
|
Examples |
Aprepitant, barbiturates, bosentan, carbamazepine, efavirenz, felbamate, griseofulvin, oxcarbazepine, phenytoin, rifampin, rifabutin, rufinamide, topiramate, products containing St. John’s worta, and certain protease inhibitors (see separate section on protease inhibitors below). |
|
Colesevelam | |
|
Clinical effect |
|
|
Prevention or management |
Administer 4 or more hours apart to attenuate this drug interaction. |
a Induction potency of St. John’s wort may vary widely based on preparation.
Substances increasing the systemic exposure of COCs:
Co-administration of atorvastatin or rosuvastatin and COCs containing ethinyl estradiol increase systemic exposure of ethinyl estradiol by approximately 20 to 25 percent. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase systemic exposure of ethinyl estradiol, possibly by inhibition of conjugation. CYP3A4 inhibitors such as itraconazole, voriconazole, fluconazole, grapefruit juice, or ketoconazole may increase systemic exposure of the estrogen and/or progestin component of COCs.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)/Hepatitis C virus (HCV) protease inhibitors and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors:
Significant decreases in systemic exposure of the estrogen and/or progestin have been noted when COCs are co-administered with some HIV protease inhibitors (e.g., nelfinavir, ritonavir, darunavir/ritonavir, (fos)amprenavir/ritonavir, lopinavir/ritonavir, and tipranavir/ritonavir), some HCV protease inhibitors (e.g., boceprevir and telaprevir), and some non- nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., nevirapine).
In contrast, significant increases in systemic exposure of the estrogen and/or progestin have been noted when COCs are co-administered with certain other HIV protease inhibitors (e.g., indinavir and atazanavir/ritonavir) and with other non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., etravirine).
7.2 Effects of Combined Oral Contraceptives on Other Drugs
Table 4 provides significant drug interaction information for drugs co- administered with RIVELSA.
Table 4: Significant Drug Interaction Information for Drugs Co-Administered With COCs
|
Lamotrigine | |
|
Clinical effect |
|
|
Prevention or management |
Dose adjustment may be necessary. Consult the approved product labeling for lamotrigine. |
|
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy or Corticosteroid Replacement Therapy | |
|
Clinical effect |
Concomitant use of COCs with thyroid hormone replacement therapy or corticosteroid replacement therapy may increase systemic exposure of thyroid- binding and cortisol-binding globulin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. |
|
Prevention or management |
The dose of replacement thyroid hormone or cortisol therapy may need to be increased. Consult the approved product labeling for the therapy in use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. |
|
Other Drugs | |
|
Clinical effect |
Concomitant use of COCs may decrease systemic exposure of acetaminophen, morphine, salicylic acid, and temazepam. Concomitant use with ethinyl estradiol-containing COCs may increase systemic exposure of other drugs (e.g., cyclosporine, prednisolone, theophylline, tizanidine, and voriconazole). |
|
Prevention or management |
The dosage of drugs that can be affected by this interaction may need to be increased. Consult the approved product labeling for the concomitantly used drug. |
7.3 Concomitant Use with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) Combination Therapy –
Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not co-administer RIVELSA with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)], and glecaprevir/pibrentasvir due to potential for ALT elevations.
7.4 Effect on Laboratory Tests
The use of COCs may influence the results of certain laboratory tests, such as coagulation factors, lipids, glucose tolerance, and binding proteins.
Enzyme inducers (e.g., CYP3A4): May decrease the effectiveness of RIVELSA or increase breakthrough bleeding. Counsel patients to use a back-up or alternative method of contraception when enzyme inducers are used with RIVELSA. (7.1)
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
FDA-approved Patient Labeling
PATIENT INFORMATION
RIVELSA**®**
(levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol and ethinyl estradiol tablets)
What is the most important information I should know about RIVELSA?
**Do not use RIVELSA if you smoke cigarettes and are over 35 years old. **Smoking increases your risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from birth control pills, including death from heart attack, blood clots or stroke. This risk increases with age and the number of cigarettes you smoke.
What is RIVELSA?
RIVELSA is a birth control pill (hormonal contraceptive) used by women to prevent pregnancy. It contains two female hormones, an estrogen called ethinyl estradiol, and a progestin called levonorgestrel.
How does RIVELSA work for contraception?
Your chance of getting pregnant depends on how well you follow the directions for taking your birth control pills. The more carefully you follow the directions, the less chance you have of getting pregnant.
Based on the results of a single clinical study lasting 12 months, 2 to 4 women out of 100 women may get pregnant during the first year they use RIVELSA.
The following chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who use different methods of birth control. Each box on the chart contains a list of birth control methods that are similar in effectiveness. The most effective methods are at the top of the chart. The box on the bottom of the chart shows the chance of getting pregnant for women who do not use birth control and are trying to get pregnant.
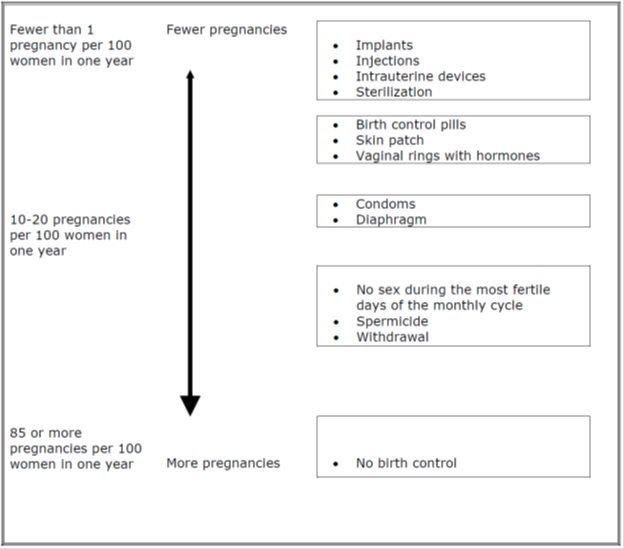
Who should not take RIVELSA?
Do not take RIVELSA if you:
- smoke and are over 35 years of age
- had blood clots in your arms, legs, eyes, or lungs
- have certain heart valve problems or heart rhythm abnormalities that can cause blood clots to form in the heart
- had a stroke
- had a heart attack
- have an inherited problem with your blood that makes it clot more than normal
- have liver disease, including liver tumors
- have high blood pressure that medicine can't control
- take any Hepatitis C drug combination containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme “alanine aminotransferase” (ALT) in the blood
- have diabetes with kidney, eye, nerve, or blood vessel damage
- have certain kinds of severe migraine headaches with aura, numbness, weakness or changes in vision, or have any migraine headaches if you are over age 35
- have any unexplained bleeding from the vagina
- had breast cancer which may be sensitive to female hormones
If any of these conditions happens to you while you are taking RIVELSA, stop taking RIVELSA right away and talk to your healthcare provider. Use non- hormonal contraception (such as condoms and spermicide) when you stop taking RIVELSA.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking RIVELSA?
Tell your healthcare provider if you:
- are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- are depressed now or have been depressed in the past
- had yellowing of your skin or eyes (jaundice) caused by pregnancy (cholestasis of pregnancy)
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. RIVELSA may decrease the amount of breast milk you make. A small amount of the hormones in RIVELSA may pass into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best birth control method for you while breastfeeding.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had any of the conditions listed in,“Who should not take RIVELSA” above. Your healthcare provider may recommend another method of birth control.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
RIVELSA may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how well RIVELSA works.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take RIVELSA?
Read the** Instructions for Use** at the end of this Patient Information**.**
What are the most serious risks of taking birth control pills?
Like pregnancy, birth control pills increase the risk of serious blood clots, especially in women who have other risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, or age greater than 35. This increased risk is highest when you first start taking birth control pills and when you restart the same or different birth control pills after not using them for a month or more.
It is possible to die from a problem caused by a blood clot, such as a heart attack or a stroke. Some examples of serious blood clots are blood clots in the:
- Legs (deep vein thrombosis)
- Lungs (pulmonary embolus)
- Eyes (loss of eyesight)
- Heart (heart attack)
- Brain (stroke)
Women who take birth control pills may get:
- High blood pressure
- Gallbladder problems
- Rare cancerous or noncancerous liver tumors
All of these events are uncommon in healthy women.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have:
- Persistent leg pain
- Sudden shortness of breath
- Sudden blindness, partial or complete
- Severe pain or pressure in your chest
- Sudden, severe headache unlike your usual headaches
- Weakness or numbness in an arm or leg, or trouble speaking
- Yellowing of the skin or eyeballs
What are common side effects of birth control pills?
The most common side effects of birth control pills are:
- Spotting or bleeding between menstrual periods
- Nausea
- Breast tenderness
- Headache
These side effects are usually mild and usually disappear with time.
Less common side effects are:
- Acne
- Less sexual desire
- Bloating or fluid retention
- Blotchy darkening of the skin, especially on the face
- High blood sugar, especially in women who already have diabetes
- High fat (cholesterol, triglyceride) levels in the blood
- Depression, especially if you have had depression in the past. Call your healthcare provider immediately if you have any thoughts of harming yourself.
- Problems tolerating contact lenses
- Weight gain
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider if you develop any side effects that concern you. You may report side effects to the FDA at 1‑800-FDA-1088.
No serious problems have been reported from a birth control pill overdose, even when accidentally taken by children.
What else should I know about taking RIVELSA?
Birth control pills donot protect you against any sexually transmitted infection, including HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
Do not skip any pills, even if you do not have sex often.
Birth control pills should not be taken during pregnancy. However, birth control pills taken by accident during pregnancy are not known to cause birth defects.
You should stop RIVELSA at least four weeks before you have major surgery and not restart it for at least two weeks after the surgery, due to an increased risk of blood clots.
If you are breastfeeding, consider another birth control method until you are ready to stop breastfeeding. Birth control pills that contain estrogen, like RIVELSA, may decrease the amount of milk you make. A small amount of the pill's hormones pass into breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all medicines and herbal products that you take. Some medicines and herbal products may make birth control pills less effective, including:
- barbiturates
- bosentan
- carbamazepine
- felbamate
- griseofulvin
- oxcarbazepine
- phenytoin
- rifampin
- St. John’s wort
- topiramate
Use a back-up or alternative birth control method when you take medicines that may make birth control pills less effective.
If you have vomiting or diarrhea, your birth control pills may not work as well. Use another birth control method, like condoms and spermicide, until you check with your healthcare provider.
Birth control pills may interact with lamotrigine, an anticonvulsant used for epilepsy. This may increase the risk of seizures, so your healthcare provider may need to adjust the dose of lamotrigine.
Women on thyroid hormone replacement therapy may need increased doses of thyroid hormone.
How should I store RIVELSA?
- Store RIVELSA at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep RIVELSA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about RIVELSA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use RIVELSA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give RIVELSA to anyone else.
If you have concerns or questions, ask your healthcare provider. You may also ask your healthcare provider for a more detailed label written for medical professionals.
Do birth control pills cause cancer?
It is not known if hormonal birth control pills cause breast cancer. Some studies, but not all, suggest that there could be a slight increase in the risk of breast cancer among current users with longer duration of use.
If you have breast cancer now, or have had it in the past, do not use hormonal birth control because some breast cancers are sensitive to hormones.
Women who use birth control pills may have a slightly higher chance of getting cervical cancer. However, this may be due to other reasons such as having more sexual partners.
What if I want to become pregnant?
You may stop taking the pill whenever you wish. Consider a visit with your healthcare provider for a pre-pregnancy checkup before you stop taking the pill.
What should I know about my period when taking RIVELSA?
When you take RIVELSA, which has a 91-day extended dosing cycle, you should expect to have 4 scheduled periods per year (bleeding when you are taking the 7 yellow pills). Each period is likely to last about 3-4 days. However, you will probably have more bleeding or spotting between your scheduled periods than if you were using a birth control pill with a 28-day dosing cycle. This bleeding or spotting tends to decrease with each additional cycle. Do not stop taking RIVELSA because of this bleeding or spotting. If the spotting continues for more than 7 consecutive days or if the bleeding is heavy, call your healthcare provider.
What if I miss my scheduled period when taking RIVELSA?
You should consider the possibility that you are pregnant if you miss your scheduled period (no bleeding on the days that you are taking yellow pills). Because scheduled periods are less frequent when you are taking RIVELSA, notify your healthcare provider that you have missed your period and that you are taking RIVELSA. Also notify your healthcare provider if you have symptoms of pregnancy such as morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness. It is important that your healthcare provider evaluates you to determine if you are pregnant. Stop taking RIVELSA if it is determined that you are pregnant.
What are the ingredients in RIVELSA?
Active ingredients:
Light pink tablets, pink tablets, purple tablets: levonorgestrel acetate and ethinyl estradiol
Yellow tablets: ethinyl estradiol
Inactive ingredients:
Light pink tablets: anhydrous lactose, D&C Red no. 27/phloxine aluminum lake, FD&C Blue no. 2/Indigo Carmine aluminum lake, FD&C Yellow no. 6/Sunset Yellow FCF aluminum lake, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
Pink tablets: anhydrous lactose, D&C Red no. 27/phloxine aluminum lake, FD&C Blue no. 2/Indigo Carmine aluminum lake, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, titanium dioxide and triacetin.
Purple tablets: anhydrous lactose, D&C Red no. 27/phloxine aluminum lake, FD&C Blue no. 1/Brilliant blue FCF aluminum lake, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, titanium dioxide and triacetin.
Yellow tablets: anhydrous lactose, D&C yellow no. 10 aluminum lake, FD&C Yellow no. 6/Sunset Yellow FCF aluminum lake, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polacrilin potassium, polyethylene glycol/macrogol, polysorbate 80 and titanium dioxide.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
RIVELSA**®**
(levonorgestrel/ethinyl estradiol and ethinyl estradiol tablets)
Important information about taking RIVELSA
- Take one pill every day at the same time. Take pills in the order directed on the Extended-Cycle Tablet Dispenser.
- Do not skip pills or delay taking your pills. If you miss pills (including starting the pack late), you could get pregnant. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant.
- You may have spotting or light bleeding or feel sick to your stomach during the first few months of taking RIVELSA. If you feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If it doesn't go away, check with your healthcare provider.
- If you vomit or have diarrhea within 4 hours after taking your pill, follow the instructions in,“What to do if you miss pills.”
- Missing pills can also cause spotting or light bleeding, even when you take the missed pills later. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
- If you have trouble remembering to take RIVELSA, talk to your healthcare provider about how to make pill-taking easier or about using another method of birth control.
Before** you start taking RIVELSA**
- Decide what time of day you want to take your pill. It is important to take it at about the same time every day.
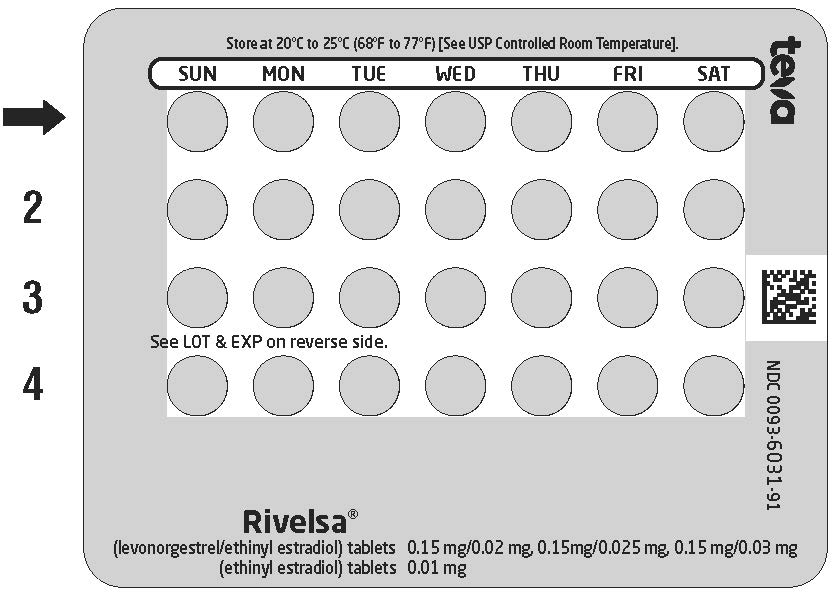
- Look at your Extended-Cycle Tablet Dispenser. Your Extended-Cycle Tablet Dispenser consists of 3 trays with cards that hold 91 individually sealed pills (a 13-week or 91-day cycle). The 91 pills consist of 42 light pink tablets, each containing 0.15 mg of levonorgestrel and 0.02 mg ethinyl estradiol, 21 pink tablets containing 0.15 mg of levonorgestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, 21 purple tablets containing 0.15 mg of levonorgestrel and 0.03 mg ethinyl estradiol, and 7 yellow tablets containing 0.01 mg of ethinyl estradiol.
Tray 1 contains 4 rows of 7 light pink pills.
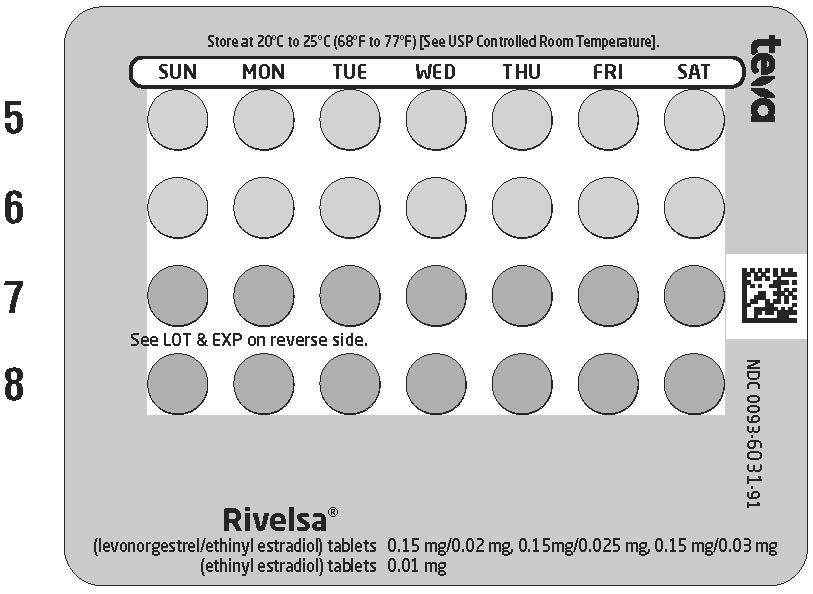
Tray 2 contains 2 rows of 7 light pink pills (a total of 14 light pink pills) followed by 2 rows of 7 pink pills (a total of 14 pink pills).
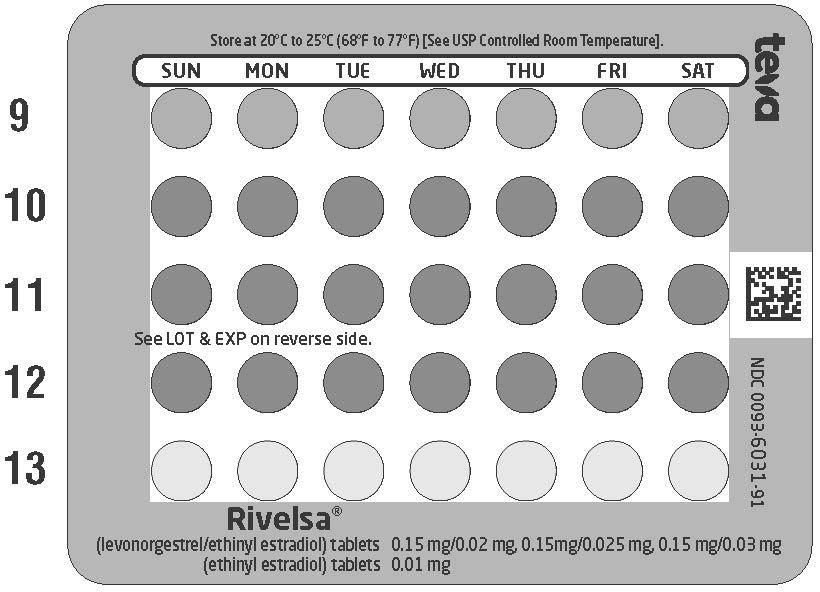
Tray 3 contains 1 row of 7 pink pills, followed by three rows of 7 purple pills (a total of 21 purple pills), followed by the last row, which contains 7 yellow pills.
-
Also find: * Where on the first tray in the pack to start taking pills (upper left corner at the start arrow) and * In what order to take the pills (follow the weeks and arrow).
-
Be sure you have another kind of birth control (such as condoms and spermicides) ready at all times, to use as a back-up in case you miss pills.
When to start RIVELSA
- Take the first light pink pill on the Sunday after your period starts, even if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the first light pink pill that same day.
- Use another method of birth control (such as condoms and spermicides) as a back-up method if you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first light pink pill until the next Sunday (first 7 days).
If you are switching from another birth control method:
If you have been using a different hormonal method of birth control (such as a different pill, the “patch,” or the “vaginal ring”), wait for your next period and begin taking RIVELSA on the Sunday after your period starts as instructed in steps 1 and 2 in,**“When to start RIVELSA”**above. You need to use another method of birth control (such as condoms and spermicides) each time you have sex after stopping your old method of birth control until you have taken RIVELSA for 7 days.
If you have recently given birth and have not yet had a period, use another method of birth control if you have sex (such as condoms and spermicides) as a back-up method until you have taken RIVELSA for 7 days.
How to take RIVELSA
- Take one pill at the same time every day until you have taken the last pill in the Extended-Cycle Tablet Dispenser.
* Do not skip pills even if you are experiencing spotting or bleeding or feel sick to your stomach (nausea).
* Do not skip pills even if you do not have sex very often.
* Do not skip the yellow pills because they are not placebo pills (“sugar pills”). They contain ethinyl estradiol.
2. When you finish a tablet dispenser
* After taking the last yellow pill, start taking the first light pink pill from a new Extended-Cycle Tablet Dispenser the very next day (this should be on a Sunday) regardless of when your period started.
3. If you miss your scheduled period when you are taking the yellow pills, contact your healthcare provider because you may be pregnant. If you are pregnant, you should stop taking RIVELSA.
What to do if you miss pills
If youMISS 1 light pink, pink or purple pill:
- Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills in 1 day.
- You do not need to use a back-up birth control method if you have sex.
If youMISS 2 light pink, pink or purple pills in a row:
- Take 2 pills on the day you remember, and 2 pills the next day.
- Then take 1 pill a day until you finish the pack.
- You could become pregnant if you have sex in the 7 days after you miss two pills. You MUST use another birth control method (such as condoms and spermicide) as a back-up for the 7 days after you restart your pills.
If youMISS 3 OR MORE light pink, pink or purple pills in a row:
- Do not take the missed pills. Keep taking 1 pill every day as indicated on the pack until you have completed all of the remaining pills in the pack. For example: If you resume taking the pill on Thursday, take the pill under “Thursday” and do not take the missed pills. You may experience bleeding during the week following the missed pills.
- You could become pregnant if you have sex during the days of missed pills or during the first 7 days after restarting your pills.
- You MUST use a non-hormonal birth control method (such as condoms and spermicide) as a back-up when you miss pills and for the first 7 days after you restart your pills. If you do not have your period when you are taking the yellow pills, call your healthcare provider because you may be pregnant.
If youMISS ANY of the 7 yellow pills:
- Throw away the missed pills.
- Take the next scheduled pill at the scheduled time.
- You do not need a back-up method of birth control.
Finally, if you are still not sure what to do about the pills you have missed
- Use a back-up method anytime you have sex.
- Keep taking one pill each day until you contact your healthcare provider.
If you have any questions or are unsure about the information in this leaflet, call your healthcare provider.
Manufactured for:
Teva Pharmaceuticals
Parsippany, NJ 07054
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 08/2022
RIVPL-004
©2022 Teva Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
