Isoproterenol Hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Isoproterenol hydrochloride safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Isoproterenol hydrochloride. Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1956
dfb97590-dcbf-47e7-bbfe-f01580eb6ed0
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 16, 2025
Nexus Pharmaceuticals Inc
DUNS: 620714787
Nexus Pharmaceuticals LLC
DUNS: 620714787
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
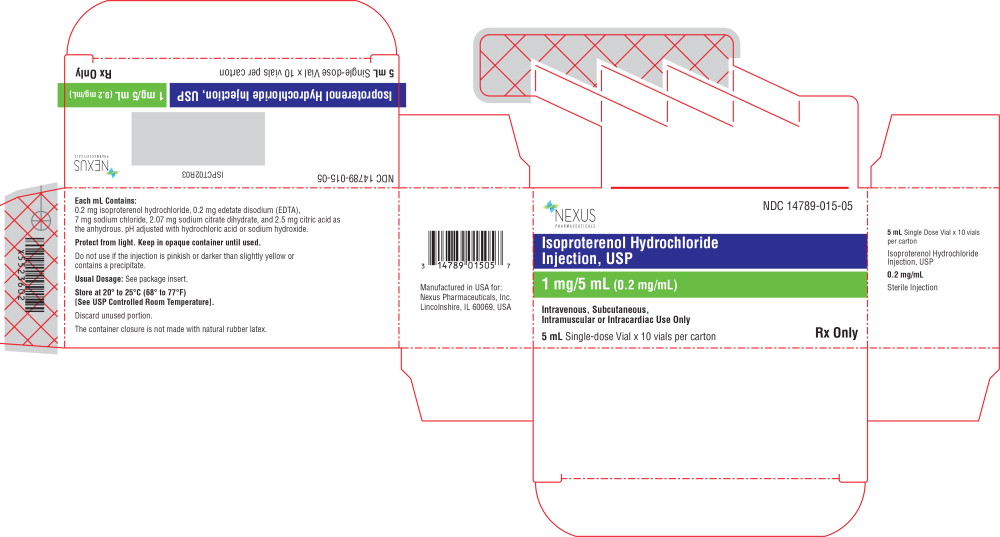
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel - 5 mL Carton Label
NDC 14789-015-05
NEXUS
PHARMACEUTICALS
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride
** Injection, USP**
1 mg/5 mL (0.2 mg/mL)
Intravenous, Subcutaneous
** Intramuscular or Intracardiac Use Only**
5 mLSingle Dose Vial x 10 vials per carton
Rx Only
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is indicated:
- To improve hemodynamic status in patients in distributive shock and shock due to reduced cardiac output
- For bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is a beta-adrenergic agonist indicated:
- To improve hemodynamic status in patients in distributive shock and shock due to reduced cardiac output ( 1)
- For treatment of bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia ( 1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4. CONTRAINDICATIONS
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with:
- tachycardia
- ventricular arrhythmias
- angina pectoris
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with:
- Tachycardia ( 4)
- Ventricular arrhythmias ( 4)
- Angina pectoris ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5. WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiac Arrhythmias and Ischemia
Isoproterenol may induce cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial ischemia in patients, especially patients with coronary artery disease, or cardiomyopathy.
5.2 Allergic Reactions associated with Sulfite
Isoproterenol hydrochloride contains sodium metabisulfite, which may cause mild to severe allergic reactions including anaphylaxis or asthmatic episodes, particularly in patients with a history of allergies. However, the presence of metabisulfite in this product should not preclude its use for treatment in emergency situations, even if the patient is sulfite-sensitive, as the alternatives to using isoproterenol in a life-threatening situation may not be satisfactory.
- Cardiac arrhythmias and ischemia may be induced by Isoproterenol hydrochloride ( 5.1)
- Sulfite: Isoproterenol hydrochloride contains metabisulfite, which may cause allergic reaction ( 5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been associated with use of isoproterenol. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Nervous system disorders:Nervousness, headache, dizziness, visual blurring
Cardiovascular:Tachycardia, tachyarrhythmias, palpitations, angina, ventricular arrhythmias, Adams-Stokes attacks, pulmonary edema
Respiratory:Dyspnea
Other:Flushing of the skin, sweating, mild tremors, pallor, nausea
Common adverse reactions with isoproterenol include tachycardia and palpitations ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lambda Therapeutics Limited at 1-855-642-2594 or email:safety.nexuspharma@lambda-cro.comor FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 orwww.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7. DRUG INTERACTIONS
Table 1. Clinically Relevant Interactions with Isoproterenol|
Epinephrine | |
|
Clinical Impact |
Both drugs are direct cardiac stimulants, and their combined effects may induce serious arrhythmias upon simultaneous administration. |
|
Intervention |
Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection and epinephrine should not be administered simultaneously. |
|
Drugs that may potentiate clinical response of Isoproterenol | |
|
Clinical Impact |
The effects of isoproterenol may be potentiated by tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, levothyroxine sodium, and certain antihistamines, notably chlorpheniramine, tripelennamine, and diphenhydramine. |
|
Intervention |
Monitor hemodynamic parameters in patients who concurrently are taking tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, levothyroxine sodium and certain antihistamines. Adjust doses appropriately. |
|
Drugs that may reduce clinical response of Isoproterenol | |
|
Clinical Impact |
The cardiostimulating and bronchodilating effects of isoproterenol are antagonized by beta-adrenergic blocking drugs, such as propranolol. |
|
Intervention |
Monitor for hemodynamic response and relief of bronchospasm and adjust dose appropriately |
- Do not administer Isoproterenol hydrochloride and epinephrine simultaneously due to combined effects may induce serious arrhythmias ( 7)
- Concomitant use of tricyclic antidepressants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, levothyroxine sodium and certain antihistamines; hemodynamic parameters may potentiate a clinical response of isoproterenol ( 7)
- Beta-adrenergic blocking drugs may reduce cardiostimulating and bronchodilating effects of isoproterenol ( 7)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection solution: single dose, clear glass vials containing isoproterenol in a clear, colorless solution;
- 1 mL containing 0.2 mg/1 mL (0.2 mg/mL)
- 5 mL containing 1 mg/5 mL (0.2 mg/mL)
Injection: 0.2 mg/mL and 1 mg/5 mL (0.2mg/mL) single dose vial ( 3)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Considerations
Inspect visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if the injection is pinkish or darker than slightly yellow or contains a precipitate. Discard any unused portion.
Diluted solution should be used immediately. Unused material should be discarded.
2.2 Recommended Dosage
Dosage should generally be started at the lowest recommended dose and increased gradually based on patient response.
Recommended dosage for adults with shock and hypoperfusion states:|
†Concentrations up to 10 times greater have been used when limitation of volume is essential. | ||
|
††Rates over 30 mcg per minute have been used in advanced stages of shock. Adjust the rate of infusion based on heart rate, central venous pressure, systemic blood pressure, and urine flow. If the heart rate exceeds 110 beats per minute, consider decreasing or temporarily discontinuing the infusion. | ||
|
Route of Administration |
Preparation of Dilution† |
Infusion Rate†† |
|
Intravenous infusion |
Dilute 5 mL (1 mg) in 500 mL of |
0.5 mcg to 5 mcg per minute (0.25 mL to |
|
Route of Administration |
Preparation of Dilution |
Initial Dose |
Subsequent Dose |
|
Bolus |
Dilute 1 mL (0.2 mg) |
10 mcg to 20 mcg per minute (0.5 mL to |
The initial dose may be repeated when necessary |
There are no well-controlled studies in children to establish appropriate dosing; however, the American Heart Association recommends an initial infusion rate of 0.1 mcg/kg/min, with the usual range being mcg/kg/min to 1 mcg/kg/min.
-
Initiate Isoproterenol hydrochloride at the lowest recommended dose and increase gradually based on patient response ( 2.2)
Recommended initial dosage: -
Shock: 0.5 mcg to 5 mcg per minute as an intravenous infusion ( 2.2)
-
Bronchospasm: 10 mcg to 20 mcg intravenous injection ( 2.2)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11. DESCRIPTION
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is 3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(isopropylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol hydrochloride, a beta-adrenergic agonist and a synthetic sympathomimetic amine that is structur ally related to epinephrine. The molecular formula is C 11H 17NO 3· HCl. It has a molecular weight of 247.72 and the following structural formula:
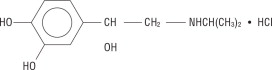
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is a racemic compound.
|
Each milliliter of the sterile solution contains: | |
|
Isoproterenol hydrochloride, USP |
0.2 mg |
|
Edetate Disodium (EDTA) mg |
0.2 |
|
Sodium Citrate Dihydrate mg |
2.07 |
|
Citric Acid, Anhydrous mg |
2.5 |
|
Sodium Chloride |
7.0 mg |
|
Water for Injection |
qs 1.0 mL |
The pH is adjusted between 3.5 and 4.5 with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide. The sterile solution is nonpyrogenic and can be administered by the intravenous route.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16. HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
|
NDC Number |
Container |
Concentration |
Fill |
Quantity |
|
14789-011-01 |
Single-dose vial |
0.2 mg/mL |
1 mL |
10 vials per carton |
|
14789-015-05 |
Single-dose vial |
1 mg/5 mL (0.2 mg/mL) |
5 mL |
10 vials per carton |
Protect from light.
Keep in opaque container until used. Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Do not use if the injection is pinkish or darker than slightly yellow or contains a precipitate.
Discard unused portion.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex.
Manufactured in the USA for:
Nexus Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Lincolnshire, IL 60069, USA
ISPPI01R03
Revised: 03/2023
NEXUS
PHARMACEUTICALS
