Zyloprim
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZYLOPRIM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZYLOPRIM. ZYLOPRIM (allopurinol) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval:1966
07d71f52-bafb-4307-a7cc-b52724151d42
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 25, 2023
Casper Pharma LLC
DUNS: 080025838
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
allopurinol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
allopurinol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
allopurinol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
ZYLOPRIM® (allopurinol)
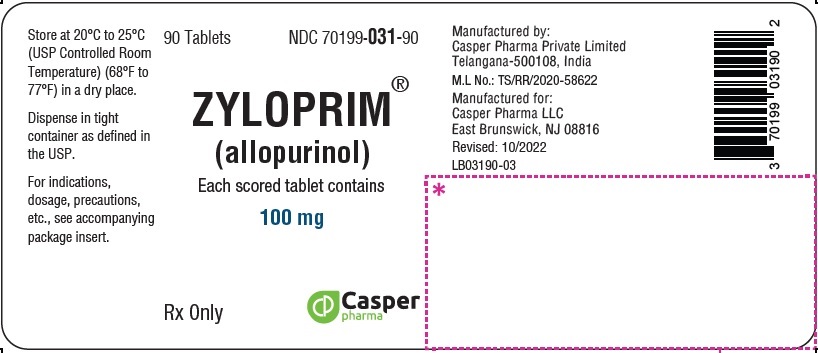
100 mg 90 Tablets Bottle
NDC 70199-031-90
Rx Only
ZYLOPRIM® (allopurinol)
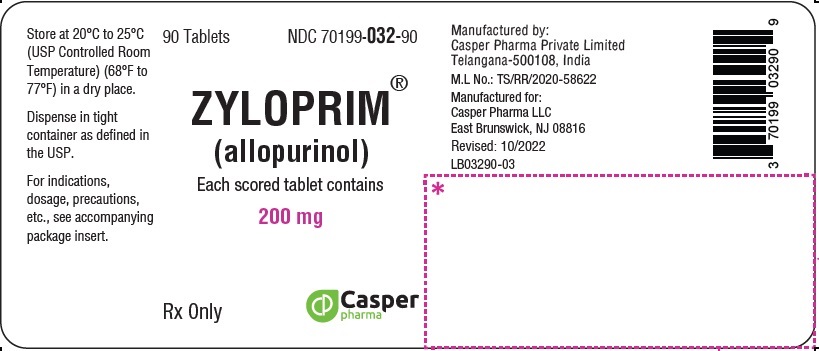
200 mg 90 Tablets Bottle
NDC 70199-032-90
Rx Only
ZYLOPRIM® (allopurinol)
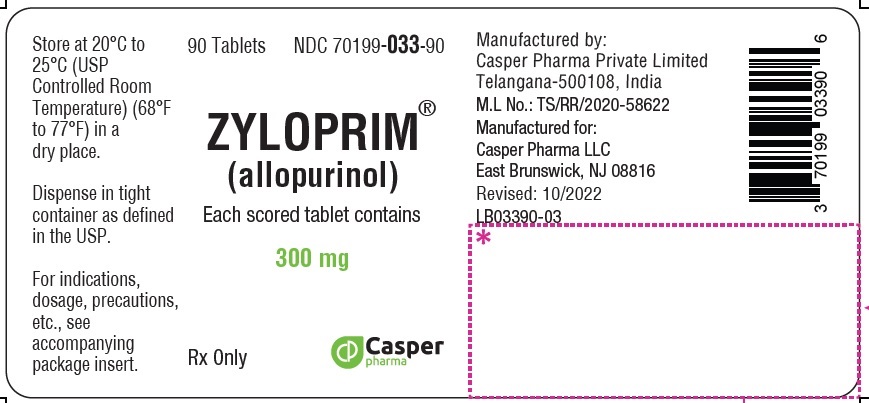
300 mg 90 Tablets Bottle
NDC 70199-033-90
Rx Only
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals, ZYLOPRIM may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Adverse developmental outcomes have been described in exposed animals (see Data). Allopurinol and its metabolite oxypurinol have been shown to cross the placenta following administration of maternal allopurinol.
Available limited published data on allopurinol use in pregnant women do not demonstrate a clear pattern or increase in frequency of adverse developmental outcomes. Among approximately 50 pregnancies described in published literature, 2 infants with major congenital malformations have been reported with following maternal allopurinol exposure. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Experience with ZYLOPRIM during human pregnancy has been limited partly because women of reproductive age rarely require treatment with ZYLOPRIM. A case report published in 2011 described the outcome of a full-term pregnancy in a 35-year-old woman who had recurrent kidney stones since age 18 who took allopurinol throughout the pregnancy. The child had multiple complex birth defects and died at 8 days of life. A second report in 2013 provided data on 31 prospectively ascertained pregnancies involving mothers exposed to allopurinol for varying durations during the first trimester. The overall rate of major fetal malformations and spontaneous abortions was reported to be within the normal expected range; however, one child had severe malformations similar to those described in the cited earlier case report.
Animal Data
There was no evidence of fetotoxicity or teratogenicity in rats or rabbits
treated during the period of organogenesis with oral allopurinol at doses up
to 200 mg/kg/day and up to 100 mg/kg/day, respectively (about 2.4 times the
human dose on a mg/m2 basis). However, there is a published report in pregnant
mice that single intraperitoneal doses of 50 mg/kg or 100 mg/kg (about 0.3 or
0.6 times the human dose on a mg/m2 basis) of allopurinol on gestation days 10
or 13 produced significant increases in fetal deaths and teratogenic effects
(cleft palate, harelip, and digital defects). It is uncertain whether these
findings represented a fetal effect or an effect secondary to maternal
toxicity.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Allopurinol and oxypurinol are present in human milk. Based on information
from a single case report, allopurinol and its active metabolite, oxypurinol,
were detected in the milk of a mother receiving 300 mg of allopurinol daily at
5 weeks postpartum. The estimated relative infant dose were 0.14 mg/kg and 0.2
mg/kg of allopurinol and between 7.2 mg/kg to 8 mg/kg of oxypurinol daily.
There was no report of effects of allopurinol on the breastfed infant or on
milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a
breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatments with
ZYLOPRIM and for one week after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Hyperuricemia Associated with Cancer Therapy
The safety and effectiveness of allopurinol for the management of pediatric
patients with leukemia, lymphoma and solid tumor malignancies who are
receiving cancer therapy which causes elevations of serum and urinary uric
acid levels have been established in approximately 200 pediatric patients. The
efficacy and safety profile observed in this patient population were similar
to that observed in adults.
Primary or Secondary Gout
The safety and effectiveness of ZYLOPRIM have not been established for the
treatment of signs and symptoms of primary or secondary gout in pediatric
patients.
Recurrent Calcium Oxalate Calculi
The safety and effectiveness of ZYLOPRIM have not been established for the
management of pediatric patients with recurrent calcium oxalate calculi.
Inborn Errors of Metabolism
The safety and effectiveness of ZYLOPRIM have not been established in
pediatric patients with rare inborn errors of purine metabolism.
8.6 Renal Impairment
ZYLOPRIM and its primary active metabolite, oxipurinol, are eliminated by the kidneys; therefore, changes in renal function have a profound effect on exposure. In patients with decreased renal function or who have concurrent illnesses which can affect renal function, perform periodic laboratory parameters of renal function and reassess the patient's dosage of ZYLOPRIM [see Dosage and Administration (2.6), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male or female mice or rats that
received oral allopurinol for the majority of their life spans (greater than
88 weeks) at doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (0.1 and 0.2 times the MRHD on a mg/m2
basis in mice and rats, respectively).
Allopurinol tested negative in the following genotoxicity assays: the in vitro
Ames assay, in vitro mouse lymphoma assay, and in vivo rat bone marrow
micronucleus assay. Allopurinol administered intravenously to rats (50 mg/kg)
was not incorporated into rapidly replicating intestinal DNA. No evidence of
clastogenicity was observed in lymphocytes taken from patients treated with
allopurinol (mean duration of treatment 40 months), or in an in vitro assay
with human lymphocytes.
Allopurinol oral doses of 20 mg/kg/day had no effect on male or female
fertility in rats or rabbits (approximately 0.2 or 0.5 times the MRHD on a
mg/m2 basis, respectively).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
ZYLOPRIM (allopurinol) is available in multiple tablet strengths with functional scoring and package sizes (bottles with child-resistant caps) as listed in Table 4.
TABLE 4: ZYLOPRIM Presentations|
Tablet Strength |
Tablet Description |
Package Sizes (NDC) |
|
100 mg |
Flat-faced raised hexagon, beveled edge, white tablet, one side engraved “ZYLOPRIM 100” with a score bar, and plain on the other side |
Bottles of:
|
|
200 mg |
Biconvex, round, white scored tablets, imprinted ZYLOPRIM about the upper periphery, and 200 on the lower half, below the score, and plain on the other side |
Bottles of:
|
|
300 mg |
Flat-faced raised hexagon, beveled edge, peach tablet, one side engraved “ZYLOPRIM 300” with a score bar, and plain on the other side |
Bottles of:
|
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (USP Controlled Room Temperature) (68°F to 77°F) in a
dry place. Dispense in a tight container as defined in the USP.
