Enjaymo
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ENJAYMO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ENJAYMO. ENJAYMO (sutimlimab-jome) injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2022
281cf1d4-6296-4416-858e-9bff46d01b71
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
May 25, 2023
Bioverativ Therapeutics Inc.
DUNS: 080521844
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
sutimlimab-jome
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
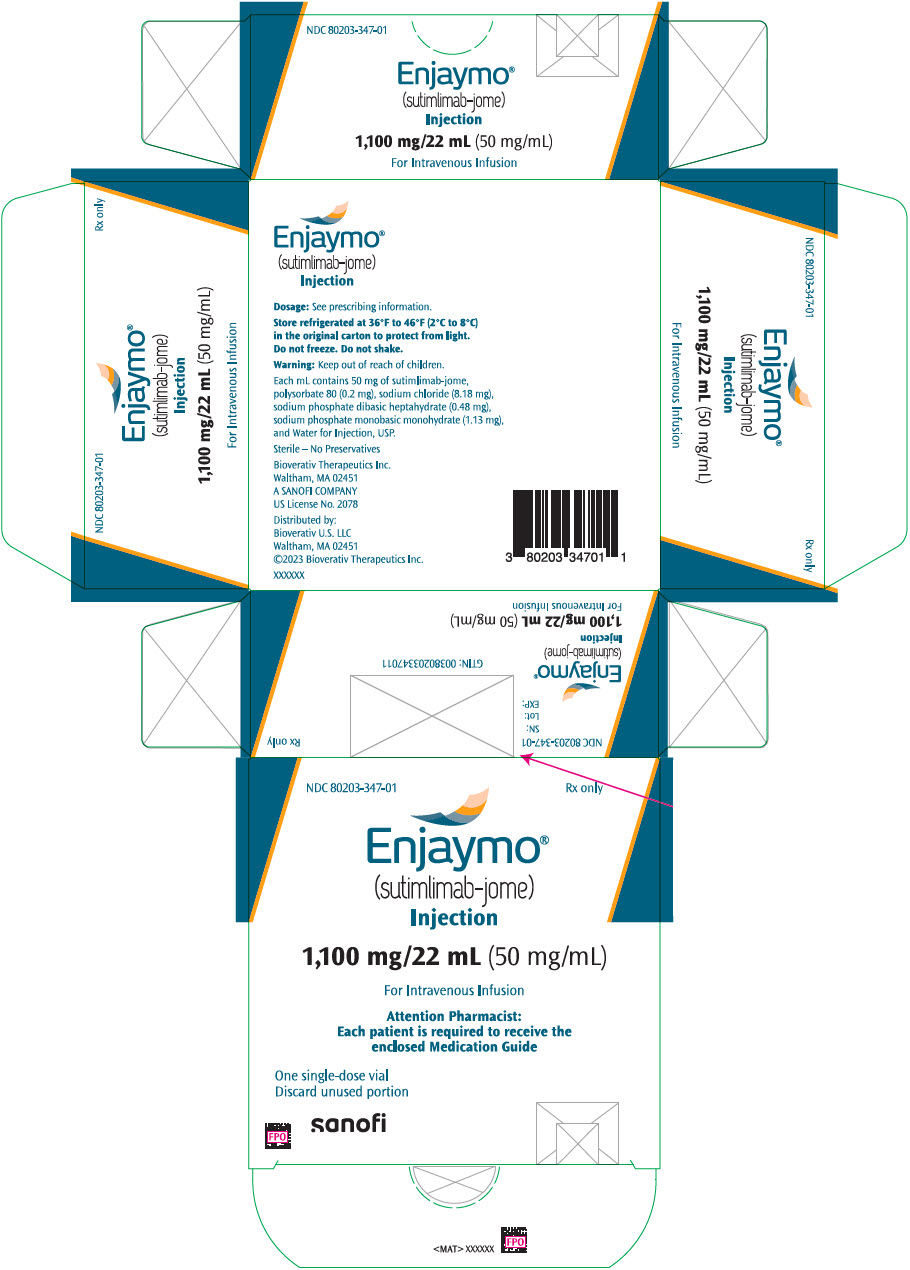
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1,100 mg/22 mL Vial Carton
NDC 80203-347-01
Rx only
Enjaymo ®
(sutimlimab-jome)
Injection
1,100 mg/22 mL (50 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion
Attention Pharmacist:
Each patient is required to receive the
enclosed Medication Guide
One single-dose vial
Discard unused portion
sanofi
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Infections
ENJAYMO may increase susceptibility to serious infections, including infections caused by encapsulated bacteria such as Neisseria meningitidis (any serogroup), Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae.
Serious infections (bacterial and viral) were reported in 15% (10/66) of patients receiving ENJAYMO from the two phase 3 studies. These infections included urinary tract infection with sepsis, respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, otomastoiditis, and skin infections One patient (1.5%) died due to klebsiella pneumonia.
Vaccinate patients for encapsulated bacteria according to the most current ACIP recommendations for patients with persistent complement deficiencies. Revaccinate patients in accordance with ACIP recommendations.
Immunize patients without a history of vaccination against encapsulated bacteria at least two weeks prior to receiving the first dose of ENJAYMO. If urgent ENJAYMO therapy is indicated in an unvaccinated patient, administer vaccine(s) as soon as possible.
Vaccination reduces, but does not eliminate, the risk of encapsulated bacterial infections.
If ENJAYMO treatment is administered to patients with active systemic infections, monitor closely for signs and symptoms of worsening infection. Some infections may become rapidly life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated promptly. Inform patients of these signs and symptoms and steps to be taken to seek immediate medical care. Consider interruption of ENJAYMO treatment in patients who are undergoing treatment for serious infection. ENJAYMO has not been studied in patients with chronic systemic infections such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, or HIV. Consider patients' immune status when initiating treatment with ENJAYMO.
5.2 Infusion-Related Reactions
ENJAYMO is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to sutimlimab-jome or any of the inactive ingredients [see Contraindications (4)] . Administration of ENJAYMO may result in infusion-related reactions. In the two phase 3 studies, 19 of 66 (29%) patients treated with ENJAYMO experienced infusion-related reactions (e.g., shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, nausea, flushing, headache, hypotension, chest discomfort, pruritus, rash, injection site reaction, and dizziness) were reported in patients from the two clinical studies. One patient permanently discontinued ENJAYMO due to an infusion-related reaction.
Monitor patients for infusion-related reactions and interrupt if a reaction occurs. Discontinue ENJAYMO infusion and institute appropriate supportive measures if signs of hypersensitivity reactions, such as cardiovascular instability or respiratory compromise, occur.
5.3 Risk of Autoimmune Disease
Based on its mechanism of action, ENJAYMO may potentially increase the risk for developing autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Development of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) has been associated with inherited classical complement deficiency. Patients with SLE or autoimmune disease with positive anti-nuclear antibody were excluded from clinical trials with ENJAYMO. In clinical trials, 3/66 (4.5%) patients developed a relapse or worsening of preexisting autoimmune disease. Monitor patients being treated with ENJAYMO for signs and symptoms and manage medically.
5.4 Recurrent Hemolysis After ENJAYMO Discontinuation
If treatment with ENJAYMO is interrupted, closely monitor patients for signs and symptoms of recurrent hemolysis, e.g., elevated levels of total bilirubin or lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) accompanied by a decrease in hemoglobin, or reappearance of symptoms such as fatigue, dyspnea, palpitations, or hemoglobinuria. Consider restarting ENJAYMO if signs and symptoms of hemolysis occur after discontinuation.
- Serious Infections: Ensure patients are vaccinated against encapsulated bacteria. Monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of infections. ( 5.1)
- Infusion-Related Reactions: Monitor patients for infusion-related reactions, interrupt if reaction occurs, and institute appropriate medical management as needed. ( 5.2)
- Risk of Autoimmune Disease: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms and manage medically. ( 5.3)
- Recurrent Hemolysis After ENJAYMO Discontinuation: Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hemolysis if treatment with ENJAYMO is interrupted. ( 5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Infusion-Related Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Risk of Autoimmune Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Recurrent Hemolysis After ENJAYMO Discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety of ENJAYMO in patients with a confirmed diagnosis of CAD was evaluated in a placebo-controlled study (CADENZA) in Part A (n=42) followed by an open-label single-arm study in Part B (n=39) and an open-label single-arm study (CARDINAL) (n=24) [see Clinical Studies (14)] . The median duration of treatment exposure to ENJAYMO was 104 weeks (patients randomized to ENJAYMO in CADENZA Part A) and 93 weeks (patients randomized to placebo in CADENZA Part A) and 143 weeks for CARDINAL.
CADENZA (Part A)
Serious adverse reaction occurred in 2/22 (9%) patients who received ENJAYMO. Serious adverse reactions included Raynaud's phenomenon (n=1) and febrile infection (n=1).
Permanent discontinuation of ENJAYMO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2/22 (9%) patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of ENJAYMO included Raynaud's phenomenon (n=1), acrocyanosis (n=1), and infusion related reactions (n=1).
Dosage interruptions of ENJAYMO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 3/22 patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption included nasopharyngitis (n=1) and infusion related reaction (n=1), including pruritis (n=1) and chest discomfort (n=1).
The most common adverse reactions (≥18%) reported in the CADENZA study were rhinitis, headache, hypertension, acrocyanosis, and Raynaud's phenomenon.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients Who Received ENJAYMO with a Difference Between Arms of >5% Compared to Placebo in the CADENZA Study (Part A)|
Adverse Reactions |
ENJAYMO |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Headache |
5 (23%) |
2 (10%) |
|
Hypertension |
5 (23%) |
0 |
|
Rhinitis |
4 (18%) |
0 |
|
Acrocyanosis |
4 (18%) |
0 |
|
Raynaud's phenomenon |
4 (18%) |
0 |
CARDINAL
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 10/24 (42%) patients who received ENJAYMO. The most common adverse reaction (>5%) was acrocyanosis (n=2). A fatal adverse reaction of pneumonia klebsiella occurred in one patient who received ENJAYMO.
Permanent discontinuation of ENJAYMO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2/24 (8%) patients. Adverse reactions which resulted in permanent discontinuation of ENJAYMO included pneumonia klebsiella (n=1) and acrocyanosis (n=2).
Dosage interruptions of ENJAYMO due to an adverse reaction occurred in 7/24 patients. Adverse reactions which required dosage interruption included pneumonia, COVID-19 pneumonia, abdominal pain upper, urinary tract infection bacterial, urosepsis, acrocyanosis, viral infection, blood creatinine increased and infusion-related reaction.
The most common adverse reaction (≥25%) reported in the CARDINAL study were urinary tract infection, respiratory tract infection, bacterial infection, dizziness, fatigue, peripheral edema, arthralgia, cough, hypertension, and nausea.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions (≥15%) in Patients Receiving ENJAYMO in the CARDINAL Study|
Adverse Reaction/Body System |
n (%) |
|---|---|
|
Please note: if a subject has multiple events in a grouped term the subject is only counted once. | |
|
The following terms were combined for the analysis: | |
Þ ß à è ð | |
|
INFECTIONS AND INFESTATIONS | |
|
Urinary tract infection * |
9 (38%) |
|
Respiratory tract infection † |
6 (25%) |
|
Bacterial infection ‡ |
6 (25%) |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
5 (21%) |
|
Viral infection § |
5 (21%) |
|
NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS | |
|
Dizziness ¶ |
7 (29%) |
|
Headache |
5 (21%) |
|
GENERAL DISORDERS | |
|
Fatigue # |
8 (33%) |
|
Peripheral edema Þ |
6 (25%) |
|
Pyrexia |
5 (21%) |
|
MUSCULOSKELETAL AND CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDERS | |
|
Arthralgia |
6 (25%) |
|
VASCULAR DISORDERS | |
|
Hypertension ß |
6 (25%) |
|
Acrocyanosis |
5 (21%) |
|
GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | |
|
Nausea |
6 (25%) |
|
Abdominal pain à |
5 (21%) |
|
RESPIRATORY, THORACIC, AND MEDIASTINAL DISORDERS | |
|
Cough è |
6 (25%) |
|
INJURY, POISONING AND PROCEDURAL COMPLICATIONS | |
|
Infusion-related reaction ð |
4 (17%) |
Most common adverse reactions in the CADENZA study (Part A) (incidence ≥18%) are rhinitis, headache, hypertension, acrocyanosis, and Raynaud's phenomenon. The most common adverse reactions in the CARDINAL study (incidence ≥25%) are urinary tract infection, respiratory tract infection, bacterial infection, dizziness, fatigue, peripheral edema, arthralgia, cough, hypertension, and nausea. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bioverativ Therapeutics Inc. (A SANOFI COMPANY) at 1-800-745-4447 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and mutagenicity studies have not been conducted with sutimlimab-jome.
Effects of sutimlimab-jome on male and female fertility have not been studied in animals. In repeat-dose studies in cynomolgus monkeys with sutimlimab-jome administered once-weekly at exposures 3 to 4 times the human exposures at the maximum recommended human doses of sutimlimab-jome, no effects on male or female reproductive tissues were observed.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Serious Infections
Advise patients of the potential increased risk of infections including infections caused by encapsulated bacteria such as Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae. These infections may be serious or life-threatening. Inform patients that they are required to receive vaccinations against these bacteria according to current medical guidelines prior to initiation of and during treatment with ENJAYMO. Educate patients on the symptoms of infections and advise them to seek immediate medical attention if any new symptoms of infection occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
Infusion-Related Reactions
Advise patients that administration of ENJAYMO may result in infusion-related reactions including hypersensitivity reactions. Hypersensitivity reactions may be serious or life-threatening (e.g., anaphylaxis). Educate patients on the symptoms of infusion-related reactions and advise them to seek medical attention if any new symptoms of infusion-related reactions occur [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
Risk of Autoimmune Disease
Educate patients that there may be an increased risk of developing an autoimmune disease such as SLE during ENJAYMO therapy. Advise patients on signs and symptoms of SLE and to report any new symptoms of SLE and seek medical attention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] .
Discontinuation
Inform patients with CAD that they may develop hemolysis due to CAD when ENJAYMO is discontinued and that they should be monitored by their healthcare provider following ENJAYMO discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] .
This product's labeling may have been updated. For the most recent prescribing information, please visit www.enjaymo.com.
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: January 2023 | ||||
|
MEDICATION GUIDE | |||||
|
What is the most important information I should know about ENJAYMO? | |||||
|
Serious infections. ENJAYMO is a prescription medicine that affects your immune system. ENJAYMO can lower the ability of your immune system to fight infections. People who are treated with ENJAYMO may have an increased risk of getting infections caused by certain kinds of bacteria such as Neisseria meningitidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and Haemophilus influenzae. These infections may be serious or life-threatening. Some infections may quickly become life-threatening or cause death if not recognized and treated early. | |||||
| |||||
|
| ||||
|
See**"What are the possible side effects of ENJAYMO?"** for more information about side effects. | |||||
|
What is ENJAYMO? | |||||
|
ENJAYMO is a prescription medicine used to treat the breakdown of red blood
cells (hemolysis) in adults with cold agglutinin disease (CAD). | |||||
|
Who should not receive ENJAYMO? | |||||
|
Do not receive ENJAYMO if you are allergic to sutimlimab-jome or any of the ingredients in ENJAYMO. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in ENJAYMO. | |||||
|
Before receiving ENJAYMO, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | |||||
| |||||
|
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | |||||
|
How will I receive ENJAYMO? | |||||
| |||||
|
| ||||
| |||||
|
What are the possible side effects of ENJAYMO?
| |||||
|
| ||||
|
*Risk of autoimmune disease. ENJAYMO may increase your risk for developing an autoimmune disease such as SLE. Tell your healthcare provider and get medical help if you develop any symptoms of SLE, including: * joint pain or swelling * rash on the cheeks and nose * unexplained fever | |||||
|
The most common side effects of ENJAYMO include: | |||||
|
| ||||
|
These are not all the possible side effects of ENJAYMO. | |||||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of ENJAYMO. | |||||
|
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about ENJAYMO that is written for health professionals. | |||||
|
What are the ingredients in ENJAYMO? | |||||
|
Active ingredient: sutimlimab-jome | |||||
|
Inactive ingredients: polysorbate 80, sodium chloride, sodium phosphate dibasic heptahydrate, sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate, and Water for Injection, USP. | |||||
|
Bioverativ Therapeutics Inc., Waltham, MA 02451. A SANOFI COMPANY. US License
No. 2078 |
