LISDEXAMFETAMINE DIMESYLATE
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LISDEXAMFETAMINE DIMESYLATE CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LISDEXAMFETAMINE DIMESYLATE CAPSULES. LISDEXAMFETAMINE DIMESYLATE capsules, for oral use, CII Initial U.S. Approval: 2007
d1f2093f-46b4-434d-ad6b-972434a8b0ff
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 25, 2023
Ascent Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
DUNS: 080938961
Products 7
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (13)
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (13)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Abuse and Dependence
CNS stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, other amphetamine-containing products, and methylphenidate, have a high potential for abuse and dependence. Assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing, and monitor for signs of abuse and dependence while on therapy [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)].
5.2 Serious Cardiovascular Reactions
Sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in adults with CNS stimulant treatment at recommended doses. Sudden death has been reported in pediatric patients with structural cardiac abnormalities and other serious heart problems taking CNS stimulants at recommended doses for ADHD. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, and other serious heart problems. Further evaluate patients who develop exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or arrhythmias during lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules treatment.
5.3 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
CNS stimulants cause an increase in blood pressure (mean increase about 2 to 4 mm Hg) and heart rate (mean increase about 3 to 6 bpm). Monitor all patients for potential tachycardia and hypertension.
5.4 Psychiatric Adverse Reactions
Exacerbation of Pre-existing Psychosis
CNS stimulants may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance and thought
disorder in patients with a pre-existing psychotic disorder.
Induction of a Manic Episode in Patients with Bipolar Disorder
CNS stimulants may induce a mixed/manic episode in patients with bipolar
disorder. Prior to initiating treatment, screen patients for risk factors for
developing a manic episode (e.g., comorbid or history of depressive symptoms
or a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression).
New Psychotic or Manic Symptoms
CNS stimulants, at recommended doses, may cause psychotic or manic symptoms
(e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania) in patients without a
prior history of psychotic illness or mania. If such symptoms occur, consider
discontinuing lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. In a pooled analysis of
multiple short-term, placebo-controlled studies of CNS stimulants, psychotic
or manic symptoms occurred in 0.1% of CNS stimulant-treated patients compared
to 0% in placebo-treated patients.
5.5 Suppression of Growth
CNS stimulants have been associated with weight loss and slowing of growth rate in pediatric patients. Closely monitor growth (weight and height) in pediatric patients treated with CNS stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. In a 4-week, placebo-controlled trial of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules in pediatric patients ages 6 to 12 years old with ADHD, there was a dose-related decrease in weight in the lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules groups compared to weight gain in the placebo group. Additionally, in studies of another stimulant, there was slowing of the increase in height [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients who are not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted. Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules is not approved for use in pediatric patients below 6 years of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon
Stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of drug. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with stimulants. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
5.7 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening reaction, may occur when amphetamines are used in combination with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John’s Wort [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. The co-administration with cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) inhibitors may also increase the risk with increased exposure to the active metabolite of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules (dextroamphetamine). In these situations, consider an alternative non-serotonergic drug or an alternative drug that does not inhibit CYP2D6 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
Concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with MAOI drugs is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Discontinue treatment with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if symptoms of serotonin syndrome occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with other serotonergic drugs or CYP2D6 inhibitors is clinically warranted, initiate lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules with lower doses, monitor patients for the emergence of serotonin syndrome during drug initiation or titration, and inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome.
- Serious Cardiovascular Reactions: Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulant treatment at recommended doses in pediatric patients with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. In adults, sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported. Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmia, or coronary artery disease (5.2)
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases: Monitor blood pressure and pulse. Consider benefits and risks before use in patients for whom blood pressure increases may be problematic (5.3)
- Psychiatric Adverse Reactions: May cause psychotic or manic symptoms in patients with no prior history, or exacerbation of symptoms in patients with pre-existing psychosis. Evaluate for bipolar disorder prior to stimulant use (5.4)
- Suppression of Growth: Monitor height and weight in pediatric patients during treatment (5.5)
- Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon: Stimulants are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with stimulants (5.6)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with serotonergic agents (e.g., SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans), but also during overdosage situations. If it occurs, discontinue lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and initiate supportive treatment (4, 5.7, 10)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules [see Contraindications (4)]
- Hypertensive Crisis When Used Concomitantly with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- Drug Dependence [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)]
- Serious Cardiovascular Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Psychiatric Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Suppression of Growth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
The safety data in this section is based on data from the 4-week controlled
parallel-group clinical studies of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules in
pediatric and adult patients with ADHD [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
Adverse Reactions Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment in ADHD
Clinical Trials
In the controlled trial in pediatric patients ages 6 to 12 years (Study 1), 8%
(18/218) of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules-treated patients discontinued
due to adverse reactions compared to 0% (0/72) of placebo-treated patients.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions (1% or more and twice rate of
placebo) were ECG voltage criteria for ventricular hypertrophy, tic, vomiting,
psychomotor hyperactivity, insomnia, decreased appetite and rash [2 instances for each adverse reaction, i.e., 2/218 (1%)].Less frequently reported adverse
reactions (less than 1% or less than twice rate of placebo) included abdominal
pain upper, dry mouth, weight decreased, dizziness, somnolence, logorrhea,
chest pain, anger and hypertension.
In the controlled trial in pediatric patients ages 13 to 17 years (Study 4), 3% (7/233) of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions compared to 1% (1/77) of placebo-treated patients. The most frequently reported adverse reactions (1% or more and twice rate of placebo) were decreased appetite (2/233; 1%) and insomnia (2/233; 1%). Less frequently reported adverse reactions (less than 1% or less than twice rate of placebo) included irritability, dermatillomania, mood swings, and dyspnea.
In the controlled adult trial (Study 7), 6% (21/358) of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules-treated patients discontinued due to adverse reactions compared to 2% (1/62) of placebo-treated patients. The most frequently reported adverse reactions (1% or more and twice rate of placebo) were insomnia (8/358; 2%), tachycardia (3/358; 1%), irritability (2/358; 1%), hypertension (4/358; 1%), headache (2/358; 1%), anxiety (2/358; 1%), and dyspnea (3/358; 1%). Less frequently reported adverse reactions (less than 1% or less than twice rate of placebo) included palpitations, diarrhea, nausea, decreased appetite, dizziness, agitation, depression, paranoia and restlessness.
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of ≥5% or More Among
Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Capsules Treated Patients with ADHD in Clinical
Trials
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at a rate at least twice
placebo) reported in pediatric patients ages 6 to 17 years, and/or adults were
anorexia, anxiety, decreased appetite, decreased weight, diarrhea, dizziness,
dry mouth, irritability, insomnia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, and vomiting.
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 2% or More Among
Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Capsules Treated Patients with ADHD in Clinical
Trials
Adverse reactions reported in the controlled trials in pediatric patients
ages, 6 to 12 years (Study 1), pediatric patients ages 13 to 17 years (Study
4), and adult patients (Study 7) treated with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
capsules or placebo are presented in Tables 1, 2 and 3 below.

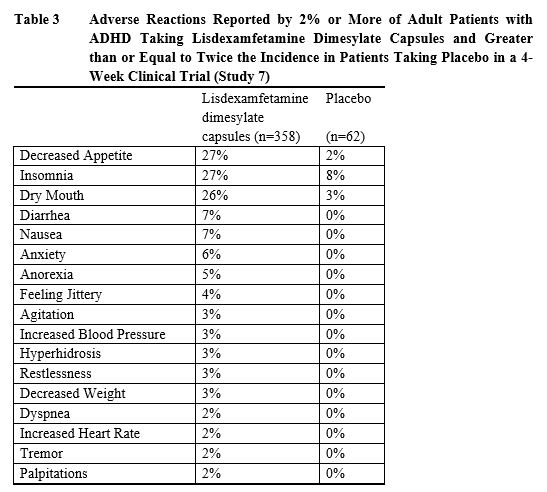
In addition, in the adult population erectile dysfunction was observed in 2.6% of males on lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and 0% on placebo; decreased libido was observed in 1.4% of subjects on lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and 0% on placebo.
Weight Loss and Slowing Growth Rate in Pediatric Patients with ADHD
In a controlled trial of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules in pediatric
patients ages 6 to 12 years (Study 1), mean weight loss from baseline after 4
weeks of therapy was -0.9, -1.9, and -2.5 pounds, respectively, for patients
receiving 30 mg, 50 mg, and 70 mg of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules,
compared to a 1 pound weight gain for patients receiving placebo. Higher doses
were associated with greater weight loss with 4 weeks of treatment. Careful
follow-up for weight in pediatric patients ages 6 to 12 years who received
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules over 12 months suggests that consistently
medicated pediatric patients (i.e., treatment for 7 days per week throughout
the year) have a slowing in growth rate, measured by body weight as
demonstrated by an age-and sex-normalized mean change from baseline in
percentile, of -13.4 over 1 year (average percentiles at baseline and 12
months were 60.9 and 47.2, respectively). In a 4-week controlled trial of
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules in pediatric patients ages 13 to 17
years, mean weight loss from baseline to endpoint was -2.7, -4.3, and -4.8
lbs., respectively, for patients receiving 30 mg, 50 mg, and 70 mg of
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, compared to a 2.0 pound weight gain for
patients receiving placebo.
Careful follow-up of weight and height in pediatric patients ages 7 to 10 years who were randomized to either methylphenidate or non-medication treatment groups over 14 months, as well as in naturalistic subgroups of newly methylphenidate-treated and non-medication treated pediatric patients over 36 months (to the ages of 10 to 13 years), suggests that consistently medicated pediatric patients ages 7 to 13 years (i.e., treatment for 7 days per week throughout the year) have a temporary slowing in growth rate (on average, a total of about 2 cm less growth in height and 2.7 kg less growth in weight over 3 years), without evidence of growth rebound during this period of development. In a controlled trial of amphetamine (d- to l-enantiomer ratio of 3:1) in pediatric patients ages 13 to 17 years, mean weight change from baseline within the initial 4 weeks of therapy was -1.1 pounds and -2.8 pounds, respectively, for patients receiving 10 mg and 20 mg of amphetamine. Higher doses were associated with greater weight loss within the initial 4 weeks of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Weight Loss in Adults with ADHD
In the controlled adult trial (Study 7), mean weight loss after 4 weeks of
therapy was 2.8 pounds, 3.1 pounds, and 4.3 pounds, for patients receiving
final doses of 30 mg, 50 mg, and 70 mg of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
capsules, respectively, compared to a mean weight gain of 0.5 pounds for
patients receiving placebo.
Binge Eating Disorder
The safety data in this section is based on data from two 12-week parallel
group, flexible-dose, placebo-controlled studies in adults with BED [see Clinical Studies 14.2]. Patients with cardiovascular risk factors other than
obesity and smoking were excluded.
Adverse Reactions Associated with Discontinuation of Treatment in BED Clinical
Trials
In controlled trials of patients ages 18 to 55 years, 5.1% (19/373) of
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules-treated patients discontinued due to
adverse reactions compared to 2.4% (9/372) of placebo-treated patients. No
single adverse reaction led to discontinuation in 1% or more of
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules-treated patients. Less commonly reported
adverse reactions (less than 1% or less than twice rate of placebo) included
increased heart rate, headache, abdominal pain upper, dyspnea, rash, insomnia,
irritability, feeling jittery and anxiety.
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 5% or More and At Least Twice
Placebo Among Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Capsules Treated Patients with BED
in Clinical Trials
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at a rate at least twice
placebo) reported in adults were dry mouth, insomnia, decreased appetite,
increased heart rate, constipation, feeling jittery, and anxiety.
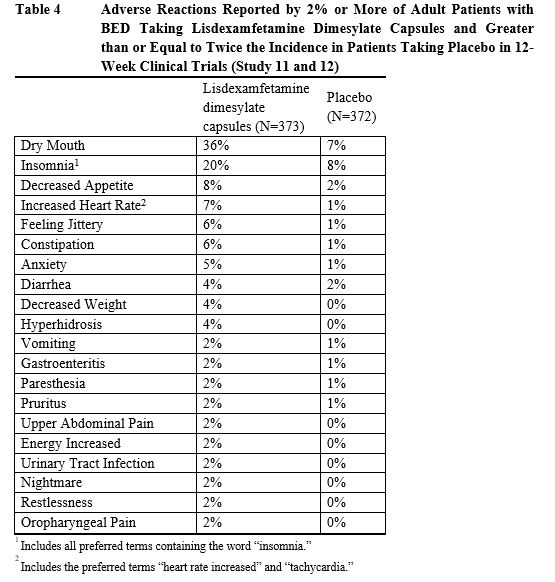
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 2% or More and At Least Twice
Placebo Among Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Capsules Treated Patients with BED
in Clinical Trials
Adverse reactions reported in the pooled controlled trials in adult patients
(Study 11 and 12) treated with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules or placebo
are presented in Table 4 below.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events are as follows: cardiomyopathy, mydriasis, diplopia, difficulties with visual accommodation, blurred vision, eosinophilic hepatitis, anaphylactic reaction, hypersensitivity, dyskinesia, dysgeusia, tics, bruxism, depression, dermatillomania, alopecia, aggression, Stevens- Johnson Syndrome, chest pain, angioedema, urticaria, seizures, libido changes, frequent or prolonged erections, constipation, rhabdomyolysis, and intestinal ischemia.
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5% and at a rate at least twice placebo) in pediatric patients ages 6 to 17 years, and/or adults with ADHD were anorexia, anxiety, decreased appetite, decreased weight, diarrhea, dizziness, dry mouth, irritability, insomnia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, and vomiting (6.1) (6)
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥ 5% and at a rate at least twice placebo) in adults with BED were dry mouth, insomnia, decreased appetite, increased heart rate, constipation, feeling jittery, and anxiety (6.1) (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ascent Pharmaceuticals, Inc., at 1-855-221-1622 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE SECTION
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules contains lisdexamfetamine, a prodrug of amphetamine, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
CNS stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, other amphetamine-containing products, and methylphenidate have a high potential for abuse. Abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, to achieve a desired psychological or physiological effect. Abuse is characterized by impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving. Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence. Both abuse and misuse may lead to addiction, and some individuals may develop addiction even when taking lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules as prescribed.
Signs and symptoms of amphetamine abuse may include increased heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, and/or sweating, dilated pupils, hyperactivity, restlessness, insomnia, decreased appetite, loss of coordination, tremors, flushed skin, vomiting, and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility, aggression, suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been seen. Abusers of CNS stimulants may chew, snort, inject, or use other unapproved routes of administration which can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)].
To reduce the abuse of CNS stimulants, including lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, assess the risk of abuse prior to prescribing. After prescribing, keep careful prescription records, educate patients and their families about abuse and on proper storage and disposal of CNS stimulants. Monitor for signs of abuse while on therapy, and re-evaluate the need for lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules use.
Studies of Lisdexamfetamine Dimesylate Capsules in Drug Abusers
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-control, cross-over, abuse liability study
in 38 patients with a history of drug abuse was conducted with single-doses of
50, 100, or 150 mg of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules, 40 mg of
immediate-release d-amphetamine sulphate (a controlled II substance), and 200
mg of diethylpropion hydrochloride (a controlled IV substance).
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 100 mg produced significantly less “Drug
Liking Effects” as measured by the Drug Rating Questionnaire-Subject score,
compared to d-amphetamine 40 mg; and 150 mg of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
capsules demonstrated similar “Drug-Liking Effects” compared to 40 mg of
d-amphetamine and 200 mg of diethylpropion.
Intravenous administration of 50 mg lisdexamfetamine dimesylate to individuals with a history of drug abuse produced positive subjective responses on scales measuring "Drug Liking", "Euphoria", "Amphetamine Effects", and "Benzedrine Effects" that were greater than placebo but less than those produced by an equivalent dose (20 mg) of intravenous d-amphetamine.
9.3 Dependence
Physical Dependence
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules may produce physical dependence from
continued therapy. Physical dependence is a state of adaptation manifested by
a withdrawal syndrome produced by abrupt cessation, rapid dose reduction, or
administration of an antagonist. Withdrawal symptoms after abrupt cessation
following prolonged high-dosage administration of CNS stimulants include
extreme fatigue and depression.
Tolerance
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules may produce tolerance from continued
therapy. Tolerance is a state of adaptation in which exposure to a specific
dose of a drug results in a reduction of the drug’s desired and/or undesired
effects over time.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies of lisdexamfetamine dimesylate have not been
performed. No evidence of carcinogenicity was found in studies in which d-,
l-amphetamine (enantiomer ratio of 1:1) was administered to mice and rats in
the diet for 2 years at doses of up to 30 mg/kg/day in male mice, 19 mg/kg/day
in female mice, and 5 mg/kg/day in male and female rats.
Mutagenesis
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate was not clastogenic in the mouse bone marrow
micronucleus test in vivo and was negative when tested in the E.coli and S.
typhimurium components of the Ames test and in the L5178Y/TK+/- mouse lymphoma
assay in vitro.
Impairment of Fertility
Amphetamine (d- to l-enantiomer ratio of 3:1) did not adversely affect
fertility or early embryonic development in the rat at doses of up to 20
mg/kg/day.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Acute administration of high doses of amphetamine (d- or d, l-) has been shown to produce long-lasting neurotoxic effects, including irreversible nerve fiber damage, in rodents. The significance of these findings to humans is unknown.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules:
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 10 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"3" Pink Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and Pink Opaque body
imprinted with 10 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 100 NDC 43602-306-01
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 20 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"3" Ivory Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and Ivory Opaque body
imprinted with 20 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 60 NDC 43602-307-60
Bottles of 500 NDC 43602-307-05
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 30 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"3" Orange Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and White Opaque body
imprinted with 30 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 60 NDC 43602-308-60
Bottles of 500 NDC 43602-308-05
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 40 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"3" Blue Green Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and White Opaque body
imprinted with 40 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 60 NDC 43602-309-60
Bottles of 500 NDC 43602-309-05
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 50 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"3" Blue Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and White Opaque body
imprinted with 50 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 60 NDC 43602-310-60
Bottles of 500 NDC 43602-310-05
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 60 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"2" Aqua Blue Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and Aqua Blue Opaque
body imprinted with 60 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 60 NDC 43602-311-60
Bottles of 500 NDC 43602-311-05
• Lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules 70 mg: Hard Gelatin Capsule Shell Size
"2" White Opaque Cap imprinted with AC in Black ink and Blue Transparent body
imprinted with 70 in black ink filled with White to Off-white powder.
Bottles of 60 NDC 43602-312-60
Bottles of 500 NDC 43602-312-05
16.2 Storage and Handling
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Store at room temperature, 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF). Excursions permitted between 15ºC and 30ºC (59 to 86ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Disposal
Comply with local laws and regulations on drug disposal of CNS stimulants.
Dispose of remaining, unused, or expired lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules
by a medicine take-back program.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Controlled Substance Status/High Potential for Abuse and Dependence
Advise patients that lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules is a controlled
substance and it can be abused and lead to dependence and not to give
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules to anyone else [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.1, 9.2, and 9.3)]. Advise patients to store lisdexamfetamine
dimesylate capsules in a safe place, preferably locked, to prevent abuse.
Advise patients to dispose of remaining, unused, or expired lisdexamfetamine
dimesylate capsules by a medicine take-back program.
Serious Cardiovascular Risks
Advise patients that there is a potential serious cardiovascular risk
including sudden death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and hypertension with
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules use. Instruct patients to contact a
healthcare provider immediately if they develop symptoms such as exertional
chest pain, unexplained syncope, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac
disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hypertension and Tachycardia
Instruct patients that lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules can cause
elevations of their blood pressure and pulse rate and they should be monitored
for such effects.
Psychiatric Risks
Advise patients that lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules at recommended doses
may cause psychotic or manic symptoms even in patients without prior history
of psychotic symptoms or mania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Suppression of Growth
Advise patients that lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules may cause slowing of
growth including weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Impairment in Ability to Operate Machinery or Vehicles
Advise patients that lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules may impair their
ability to engage in potentially dangerous activities such as operating
machinery or vehicles. Instruct patients to find out how lisdexamfetamine
dimesylate capsules will affect them before engaging in potentially dangerous
activities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
Circulation problems in fingers and toes [Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon]
Instruct patients beginning treatment with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
capsules about the risk of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s
phenomenon, and associated signs and symptoms: fingers or toes may feel numb,
cool, painful, and/or may change from pale, to blue, to red. Instruct patients
to report to their physician any new numbness, pain, skin color change, or
sensitivity to temperature in fingers or toes. Instruct patients to call their
physician immediately with any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on
fingers or toes while taking lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules. Further
clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for
certain patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Caution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome with concomitant use of
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules and other serotonergic drugs including
SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium,
tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, St. John’s Wort, and with drugs that impair
metabolism of serotonin (in particular MAOIs, both those intended to treat
psychiatric disorders and also others such as linezolid [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Advise
patients to contact their healthcare provider or report to the emergency room
if they experience signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome.
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to notify their physicians if they are taking, or plan to
take, any prescription or over-the-counter drugs because there is a potential
for interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients of the potential fetal effects from the use of
lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules during pregnancy. Advise patients to
notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become
pregnant during treatment with lisdexamfetamine dimesylate capsules [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed if they are taking lisdexamfetamine dimesylate
capsules [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Administration Instructions
- Advise patients to take the capsules whole or empty and mix the entire contents with yogurt, water, or orange juice. Advise patients to consume the mixture immediately and not to store for future use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Manufactured by:
Ascent Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Central Islip, NY 11722
Rev: 08/23
For more information call 1-855-221-1622.
The trademarks referenced herein are owned by their respective companies.
