Cetirizine Hydrochloride
Cetirizine Hydrochloride Oral Solution USP, 5 mg/5 mL (1 mg/mL)
6d81446e-f713-4ca4-af38-3d31cf618873
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 1, 2025
Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc.
DUNS: 146974886
Taro Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc.
DUNS: 145186370
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Cetirizine Hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
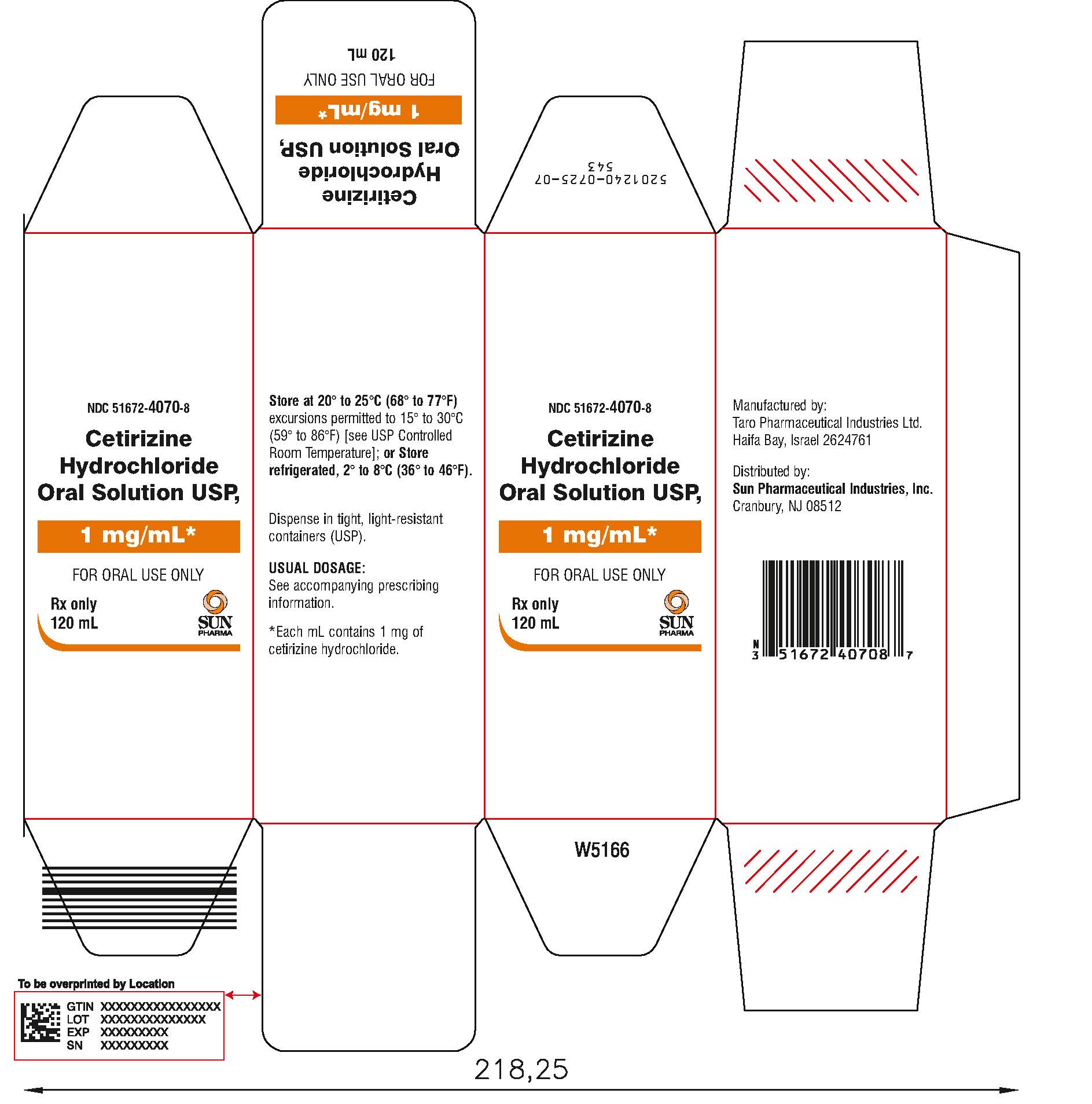
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 120 mL Bottle Carton
NDC 51672-4070-8
120 mL
Cetirizine
Hydrochloride
Oral Solution
USP,
1 mg/mL*
FOR ORAL USE ONLY
Rx only

ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Pediatric studies were also conducted with cetirizine hydrochloride. More than 1300 pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years with more than 900 treated with cetirizine hydrochloride at doses of 1.25 to 10 mg per day were included in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials conducted in the United States. The duration of treatment ranged from 2 to 12 weeks. Placebo-controlled trials up to 4 weeks duration included 168 pediatric patients aged 2 to 5 years who received cetirizine, the majority of whom received single daily doses of 5 mg. A placebo-controlled trial 18 months in duration included 399 patients aged 12 to 24 months treated with cetirizine (0.25 mg/kg bid), and another placebo- controlled trial of 7 days duration included 42 patients aged 6 to 11 months who were treated with cetirizine (0.25 mg/kg bid).
The majority of adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients aged 2 to 11 years with cetirizine hydrochloride were mild or moderate. In placebo- controlled trials, the incidence of discontinuations due to adverse reactions in pediatric patients receiving up to 10 mg of cetirizine hydrochloride was uncommon (0.4% on cetirizine hydrochloride vs. 1% on placebo).
Table 1 lists adverse experiences which were reported for cetirizine hydrochloride 5 and 10 mg in pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years in placebo- controlled clinical trials in the United States and were more common with cetirizine hydrochloride than placebo. Of these, abdominal pain was considered treatment-related and somnolence appeared to be dose-related, 1.3% in placebo, 1.9% at 5 mg and 4.2% at 10 mg. The adverse experiences reported in pediatric patients aged 2 to 5 years in placebo-controlled trials were qualitatively similar in nature and generally similar in frequency to those reported in trials with children aged 6 to 11 years.
In the placebo-controlled trials of pediatric patients 6 to 24 months of age, the incidences of adverse experiences, were similar in the cetirizine and placebo treatment groups in each study. Somnolence occurred with essentially the same frequency in patients who received cetirizine and patients who received placebo. In a study of 1 week duration in children 6 to 11 months of age, patients who received cetirizine exhibited greater irritability/fussiness than patients on placebo. In a study of 18 months duration in patients 12 months and older, insomnia occurred more frequently in patients who received cetirizine compared to patients who received placebo (9% v. 5.3%). In those patients who received 5 mg or more per day of cetirizine as compared to patients who received placebo, fatigue (3.6% v. 1.3%) and malaise (3.6% v. 1.8%) occurred more frequently.
Table 1. Adverse Experiences Reported in Pediatric Patients Aged 6 to 11 Years in Placebo-Controlled United States Cetirizine Hydrochloride Trials (5 or 10 mg Dose) Which Occurred at a Frequency of ≥ 2% in Either the 5-mg or the 10-mg Cetirizine Hydrochloride Group, and More Frequently Than in the Placebo Group|
Cetirizine hydrochloride | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Adverse Experiences |
Placebo |
5 mg |
10 mg |
|
Headache |
12.3% |
11% |
14% |
|
Pharyngitis |
2.9% |
6.2% |
2.8% |
|
Abdominal pain |
1.9% |
4.4% |
5.6% |
|
Coughing |
3.9% |
4.4% |
2.8% |
|
Somnolence |
1.3% |
1.9% |
4.2% |
|
Diarrhea |
1.3% |
3.1% |
1.9% |
|
Epistaxis |
2.9% |
3.7% |
1.9% |
|
Bronchospasm |
1.9% |
3.1% |
1.9% |
|
Nausea |
1.9% |
1.9% |
2.8% |
|
Vomiting |
1% |
2.5% |
2.3% |
The following events were observed infrequently (less than 2%), in either 3982 adults and children 12 years and older or in 659 pediatric patients aged 6 to 11 years who received cetirizine hydrochloride in U.S. trials, including an open adult study of six months duration. A causal relationship of these infrequent events with cetirizine hydrochloride administration has not been established.
**Autonomic Nervous System:**anorexia, flushing, increased salivation, urinary retention.
**Cardiovascular:**cardiac failure, hypertension, palpitation, tachycardia.
**Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems:**abnormal coordination, ataxia, confusion, dysphonia, hyperesthesia, hyperkinesia, hypertonia, hypoesthesia, leg cramps, migraine, myelitis, paralysis, paresthesia, ptosis, syncope, tremor, twitching, vertigo, visual field defect.
**Gastrointestinal:**abnormal hepatic function, aggravated tooth caries, constipation, dyspepsia, eructation, flatulence, gastritis, hemorrhoids, increased appetite, melena, rectal hemorrhage, stomatitis including ulcerative stomatitis, tongue discoloration, tongue edema.
**Genitourinary:**cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, micturition frequency, polyuria, urinary incontinence, urinary tract infection.
**Hearing and Vestibular:**deafness, earache, ototoxicity, tinnitus.
**Metabolic/Nutritional:**dehydration, diabetes mellitus, thirst.
**Musculoskeletal:**arthralgia, arthritis, arthrosis, muscle weakness, myalgia.
**Psychiatric:**abnormal thinking, agitation, amnesia, anxiety, decreased libido, depersonalization, depression, emotional lability, euphoria, impaired concentration, insomnia, nervousness, paroniria, sleep disorder.
**Respiratory System:**bronchitis, dyspnea, hyperventilation, increased sputum, pneumonia, respiratory disorder, rhinitis, sinusitis, upper respiratory tract infection.
**Reproductive:**dysmenorrhea, female breast pain, intermenstrual bleeding, leukorrhea, menorrhagia, vaginitis.
**Reticuloendothelial:**lymphadenopathy.
**Skin:**acne, alopecia, angioedema, bullous eruption, dermatitis, dry skin, eczema, erythematous rash, furunculosis, hyperkeratosis, hypertrichosis, increased sweating, maculopapular rash, photosensitivity reaction, photosensitivity toxic reaction, pruritus, purpura, rash, seborrhea, skin disorder, skin nodule, urticaria.
**Special Senses:**parosmia, taste loss, taste perversion.
**Vision:**blindness, conjunctivitis, eye pain, glaucoma, loss of accommodation, ocular hemorrhage, xerophthalmia.
**Body as a Whole:**accidental injury, asthenia, back pain, chest pain, enlarged abdomen, face edema, fever, generalized edema, hot flashes, increased weight, leg edema, malaise, nasal polyp, pain, pallor, periorbital edema, peripheral edema, rigors.
Occasional instances of transient, reversible hepatic transaminase elevations have occurred during cetirizine therapy. Hepatitis with significant transaminase elevation and elevated bilirubin in association with the use of cetirizine hydrochloride has been reported.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries,
Inc., at 1-866-923-4914 or FDA at 1-800-
FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Post-Marketing Experience
In the post-marketing period, the following additional rare, but potentially severe adverse events have been reported: aggressive reaction, anaphylaxis, cholestasis, convulsions, glomerulonephritis, hallucinations, hemolytic anemia, hepatitis, orofacial dyskinesia, severe hypotension, stillbirth, suicidal ideation, suicide, thrombocytopenia, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and new onset pruritus within a few days after discontinuation of cetirizine, usually after long-term use (e.g., few months to years) of cetirizine.
PRECAUTIONS SECTION
PRECAUTIONS
Activities Requiring Mental Alertness
In clinical trials, the occurrence of somnolence has been reported in some patients taking cetirizine hydrochloride; due caution should therefore be exercised when driving a car or operating potentially dangerous machinery. Concurrent use of cetirizine hydrochloride with alcohol or other CNS depressants should be avoided because additional reductions in alertness and additional impairment of CNS performance may occur.
Risk of New Onset Pruritus After Discontinuation of Cetirizine
Cases of pruritus after discontinuation of cetirizine have been reported in
the postmarketing setting in patients where pruritus was not
present before initiation of cetirizine. Pruritus occurred within a few days
of discontinuing cetirizine among patients who used
cetirizine long-term (e.g., few months to years). Reported cases of pruritus
were infrequent, but some were serious with patients
experiencing widespread severe pruritus. If pruritus occurs after
discontinuation of cetirizine, symptoms may improve with restarting
or tapering cetirizine.
Drug-Drug Interactions
No clinically significant drug interactions have been found with theophylline at a low dose, azithromycin, pseudoephedrine, ketoconazole, or erythromycin. There was a small decrease in the clearance of cetirizine caused by a 400-mg dose of theophylline; it is possible that larger theophylline doses could have a greater effect.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility
In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats, cetirizine was not carcinogenic at dietary doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 15 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m 2basis, or approximately 7 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in infants on a mg/m 2basis). In a 2-year carcinogenicity study in mice, cetirizine caused an increased incidence of benign liver tumors in males at a dietary dose of 16 mg/kg (approximately 6 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m 2basis, or approximately 3 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in infants on a mg/m 2basis). No increase in the incidence of liver tumors was observed in mice at a dietary dose of 4 mg/kg (approximately 2 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m 2basis, or approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended daily oral dose in infants on a mg/m 2basis). The clinical significance of these findings during long-term use of cetirizine hydrochloride is not known.
Cetirizine was not mutagenic in the Ames test, and not clastogenic in the human lymphocyte assay, the mouse lymphoma assay, and in vivomicronucleus test in rats.
In a fertility and general reproductive performance study in mice, cetirizine did not impair fertility at an oral dose of 64 mg/kg (approximately 25 times the maximum recommended daily oral dose in adults on a mg/m 2basis).
Pediatric Use
The safety of cetirizine hydrochloride has been demonstrated in pediatric patients aged 6 months to 5 years. The safety of cetirizine has been demonstrated in 168 patients aged 2 to 5 years in placebo controlled trials of up to 4 weeks duration. On a mg/kg basis, most of the 168 patients received between 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg of cetirizine hydrochloride. The safety of cetirizine in 399 patients aged 12 to 24 months has been demonstrated in a placebo-controlled 18-month trial, in which the average dose was 0.25 mg/kg bid, corresponding to a range of 4 to 11 mg/day. The safety of cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution has been demonstrated in 42 patients aged 6 to 11 months in a placebo-controlled 7-day trial. The prescribed dose was 0.25 mg/kg bid, which corresponded to a mean of 4.5 mg/day, with a range of 3.4 to 6.2 mg/day.
The effectiveness of cetirizine hydrochloride for the treatment of allergic rhinitis and chronic idiopathic urticaria in pediatric patients aged 6 months to 5 years is based on an extrapolation of the demonstrated efficacy of cetirizine hydrochloride in adults with these conditions and the likelihood that the disease course, pathophysiology and the drug's effect are substantially similar between these two populations. Efficacy is extrapolated down to 6 months of age for perennial allergic rhinitis because this disease is thought to occur down to these ages in children. The recommended doses for the pediatric population are based on cross-study comparisons of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cetirizine in adult and pediatric subjects and on the safety profile of cetirizine in both adult and pediatric patients at doses equal to or higher than the recommended doses. The cetirizine AUC and C maxin pediatric subjects aged 6 to 23 months who received a mean of 2.3 mg in a single dose and in subjects aged 2 to 5 years who received a single dose of 5 mg of cetirizine oral solution, was estimated to be intermediate between that observed in adults who received a single dose of 10 mg of cetirizine tablets and those who received a single dose of 20 mg of cetirizine tablets.
The safety and effectiveness of cetirizine in pediatric patients under the age of 6 months have not been established.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Mfd. by: Taro Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd., Haifa Bay, Israel 2624761
Dist. by:Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc., Cranbury, NJ 08512
Revised: June 2025
DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION
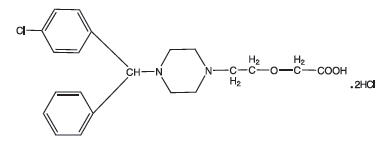
Cetirizine hydrochloride is an orally active and selective H 1-receptor antagonist. The chemical name is (±) - [2- [4- [ (4-chlorophenyl) phenylmethyl]-1-piperazinyl] ethoxy]acetic acid, dihydrochloride. Cetirizine hydrochloride is a racemic compound with an empirical formula of C 21H 25ClN 2O 3∙2HCl. The molecular weight is 461.82 and the chemical structure is shown below:
Cetirizine hydrochloride is a white, crystalline powder and is water soluble. Cetirizine hydrochloride oral solution is a colorless to slightly yellow oral solution containing cetirizine hydrochloride at a concentration of 1 mg/mL (5 mg/5 mL) for oral administration. The pH is between 4 and 5. The inactive ingredients of the oral solution are: artificial grape flavor, glacial acetic acid, glycerin, methylparaben, natural and artificial banana flavor, propylene glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium acetate (anhydrous), sucrose.
