Risedronate Sodium
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RISEDRONATE SODIUM TABLETS safely and effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for RISEDRONATE SODIUM TABLETS. RISEDRONATE SODIUM tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
89896dfe-f69d-4cb3-bb71-7a7c611071fa
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 31, 2024
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
DUNS: 650082092
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Risedronate Sodium
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (12)
Risedronate Sodium
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Risedronate Sodium
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 35 mg Blister Carton - 4 Week Supply
(4 Tablets)
NDC 65862-519-04
Rx only
Once-a-week
Risedronate Sodium
** Tablets, USP
** 35 mg
PHARMACIST: Dispense theaccompanying****** Medication Guide to
each patient.**
AUROBINDO 4 Week Supply (4 Tablets)
****
Indications & Usage Section
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Risedronate sodium tablets are indicated for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. In postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, risedronate sodium tablets reduce the incidence of vertebral fractures and a composite endpoint of nonvertebral osteoporosis-related fractures [see Clinical Studies (14.1, 14.2)].
1.2 Osteoporosis in Men
Risedronate sodium tablets are indicated for treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis.
1.3 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Risedronate sodium tablets are indicated for the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women who are either initiating or continuing systemic glucocorticoid treatment (daily dosage of greater than or equal to 7.5 mg of prednisone or equivalent) for chronic diseases. Patients treated with glucocorticoids should receive adequate amounts of calcium and vitamin D.
1.4 Paget's Disease
Risedronate sodium tablets are indicated for treatment of Paget’s disease of bone in men and women.
1.5 Important Limitations of Use
The optimal duration of use has not been determined. The safety and effectiveness of risedronate sodium tablets for the treatment of osteoporosis are based on clinical data of three years duration. All patients on bisphosphonate therapy should have the need for continued therapy re-evaluated on a periodic basis. Patients at low-risk for fracture should be considered for drug discontinuation after 3 to 5 years of use. Patients who discontinue therapy should have their risk for fracture re-evaluated periodically.
Risedronate sodium tablets are a bisphosphonate indicated for:
- Treatment and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis (1.1)
- Treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis (1.2)
- Treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (1.3)
- Treatment of Paget’s disease (1.4)
Limitations of Use
Optimal duration of use has not been determined. For patients at low-risk for
fracture, consider drug discontinuation after 3 to 5 years of use. (1.5)
Contraindications Section
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Risedronate sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay esophageal emptying such as stricture or achalasia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Known hypersensitivity to risedronate sodium tablets or any of its excipients. Angioedema, generalized rash, bullous skin reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]
- Abnormalities of the esophagus which delay esophageal emptying such as stricture or achalasia (4, 5.1)
- Inability to stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes (4, 5.1)
- Hypocalcemia (4, 5.2)
- Known hypersensitivity to any component of this product (4, 6.2)
Warnings And Precautions Section
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Drug Products with the Same Active Ingredient
Risedronate sodium tablets contains the same active ingredient found in Atelvia®. A patient being treated with Atelvia should not receive risedronate sodium tablets.
5.2 Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Risedronate, like other bisphosphonates administered orally, may cause local irritation of the upper gastrointestinal mucosa. Because of these possible irritant effects and a potential for worsening of the underlying disease, caution should be used when risedronate is given to patients with active upper gastrointestinal problems (such as known Barrett’s esophagus, dysphagia, other esophageal diseases, gastritis, duodenitis or ulcers) [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Information for Patients (17.1)].
Esophageal adverse experiences, such as esophagitis, esophageal ulcers and esophageal erosions, occasionally with bleeding and rarely followed by esophageal stricture or perforation, have been reported in patients receiving treatment with oral bisphosphonates. In some cases, these have been severe and required hospitalization. Physicians should therefore be alert to any signs or symptoms signaling a possible esophageal reaction and patients should be instructed to discontinue risedronate and seek medical attention if they develop dysphagia, odynophagia, retrosternal pain or new or worsening heartburn.
The risk of severe esophageal adverse experiences appears to be greater in patients who lie down after taking oral bisphosphonates and/or who fail to swallow it with the recommended full glass (6 to 8 ounces) of water, and/or who continue to take oral bisphosphonates after developing symptoms suggestive of esophageal irritation. Therefore, it is very important that the full dosing instructions are provided to, and understood by, the patient [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. In patients who cannot comply with dosing instructions due to mental disability, therapy with risedronate should be used under appropriate supervision.
There have been post-marketing reports of gastric and duodenal ulcers with oral bisphosphonate use, some severe and with complications, although no increased risk was observed in controlled clinical trials.
5.3 Mineral Metabolism
Hypocalcemia has been reported in patients taking risedronate. Treat hypocalcemia and other disturbances of bone and mineral metabolism before starting risedronate therapy. Instruct patients to take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if their dietary intake is inadequate. Adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D is important in all patients, especially in patients with Paget’s disease in whom bone turnover is significantly elevated [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Information for Patients (17.1)].
5.4 Jaw Osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ), which can occur spontaneously, is generally associated with tooth extraction and/or local infection with delayed healing, and has been reported in patients taking bisphosphonates, including risedronate. Known risk factors for osteonecrosis of the jaw include invasive dental procedures (for example, tooth extraction, dental implants, boney surgery), diagnosis of cancer, concomitant therapies (for example, chemotherapy, corticosteroids, angiogenesis inhibitors), poor oral hygiene, and co-morbid disorders (for example, periodontal and/or other pre-existing dental disease, anemia, coagulopathy, infection, ill-fitting dentures). The risk of ONJ may increase with duration of exposure to bisphosphonates.
For patients requiring invasive dental procedures, discontinuation of bisphosphonate treatment may reduce the risk for ONJ. Clinical judgment of the treating physician and/or oral surgeon should guide the management plan of each patient based on individual benefit/risk assessment.
Patients who develop osteonecrosis of the jaw while on bisphosphonate therapy should receive care by an oral surgeon. In these patients, extensive dental surgery to treat ONJ may exacerbate the condition. Discontinuation of bisphosphonate therapy should be considered based on individual benefit/risk assessment [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5.5 Musculoskeletal Pain
In postmarketing experience, there have been reports of severe and occasionally incapacitating bone, joint, and/or muscle pain in patients taking bisphosphonates [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. The time to onset of symptoms varied from one day to several months after starting the drug. Most patients had relief of symptoms after stopping medication. A subset had recurrence of symptoms when rechallenged with the same drug or another bisphosphonate. Consider discontinuing use if severe symptoms develop.
5.6 Atypical Subtrochanteric and Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures
Atypical, low-energy, or low trauma fractures of the femoral shaft have been reported in bisphosphonate-treated patients. These fractures can occur anywhere in the femoral shaft from just below the lesser trochanter to above the supracondylar flare and are traverse or short oblique in orientation without evidence of comminution. Causality has not been established as these fractures also occur in osteoporotic patients who have not been treated with bisphosphonates.
Atypical femur fractures most commonly occur with minimal or no trauma to the affected area. They may be bilateral and many patients report prodromal pain in the affected area, usually presenting as dull, aching thigh pain, weeks to months before a complete fracture occurs. A number of reports note that patients were also receiving treatment with glucocorticoids (for example, prednisone) at the time of fracture.
Any patient with a history of bisphosphonate exposure who presents with thigh or groin pain should be suspected of having an atypical fracture and should be evaluated to rule out an incomplete femur fracture. Patients presenting with an atypical fracture should also be assessed for symptoms and signs of fracture in the contralateral limb. Interruption of bisphosphonate therapy should be considered, pending a risk/benefit assessment, on an individual basis.
5.7 Renal Impairment
Risedronate is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min).
5.8 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Before initiating risedronate treatment for the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, the sex steroid hormonal status of both men and women should be ascertained and appropriate replacement considered.
5.9 Laboratory Test Interactions
Bisphosphonates are known to interfere with the use of bone-imaging agents. Specific studies with risedronate have not been performed.
-
Products Containing Same Active Ingredient: Patients receiving Atelvia should not be treated with risedronate sodium tablets (5.1)
-
Upper Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions can occur. Instruct patients to follow dosing instructions. Discontinue use if new or worsening symptoms occur (5.2)
-
Hypocalcemia may worsen and must be corrected prior to use (5.3)
-
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw has been reported (5.4)
-
Severe Bone, Joint, Muscle Pain may occur. Discontinue use if severe symptoms develop (5.5, 6.2)
-
Atypical Femur Fractures have been reported. Patients with new thigh or groin pain should be evaluated to rule out a femoral fracture (5.6)
Adverse Reactions Section
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Daily Dosing
The safety of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg once daily in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in four randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multinational trials of 3232 women aged 38 to 85 years with postmenopausal osteoporosis. The duration of the trials was up to three years, with 1619 patients exposed to placebo and 1613 patients exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg. Patients with pre-existing gastrointestinal disease and concomitant use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 antagonists were included in these clinical trials. All women received 1000 mg of elemental calcium plus vitamin D supplementation up to 500 international units per day if their 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 level was below normal at baseline.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was 2% in the placebo group and 1.7% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 24.6% in the placebo group and 27.2% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 15.6% in the placebo group and 14.8% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. The most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 10 percent of subjects were: back pain, arthralgia, abdominal pain and dyspepsia. Table 1 lists adverse events from the Phase 3 postmenopausal osteoporosis trials reported in greater than or equal to 5% of patients. Adverse events are shown without attribution of causality.
|
Table 1 | ||
|
Body System |
Placebo |
5 mg Risedronate Sodium Tablets |
|
% |
% | |
|
Body as a Whole | ||
|
Infection |
29.9 |
31.1 |
|
Back Pain |
26.1 |
28 |
|
Accidental Injury |
16.8 |
16.9 |
|
Pain |
14 |
14.1 |
|
Abdominal Pain |
9.9 |
12.2 |
|
Flu Syndrome |
11.6 |
10.5 |
|
Headache |
10.8 |
9.9 |
|
Asthenia |
4.5 |
5.4 |
|
Neck Pain |
4.7 |
5.4 |
|
Chest Pain |
5.1 |
5 |
|
Allergic Reaction |
5.9 |
3.8 |
|
Cardiovascular System | ||
|
Hypertension |
9.8 |
10.5 |
|
Digestive System | ||
|
Constipation |
12.6 |
12.9 |
|
Diarrhea |
10 |
10.8 |
|
Dyspepsia |
10.6 |
10.8 |
|
Nausea |
11.2 |
10.5 |
|
Metabolic & Nutritional Disorders | ||
|
Peripheral Edema |
8.8 |
7.7 |
|
Musculoskeletal System | ||
|
Arthralgia |
22.1 |
23.7 |
|
Arthritis |
10.1 |
9.6 |
|
Traumatic Bone Fracture |
12.3 |
9.3 |
|
Joint Disorder |
5.3 |
7 |
|
Myalgia |
6.2 |
6.7 |
|
Bone Pain |
4.8 |
5.3 |
|
Nervous System | ||
|
Dizziness |
5.7 |
7.1 |
|
Depression |
6.1 |
6.8 |
|
Insomnia |
4.6 |
5 |
|
Respiratory System | ||
|
Bronchitis |
10.4 |
10 |
|
Sinusitis |
9.1 |
8.7 |
|
Rhinitis |
5.1 |
6.2 |
|
Pharyngitis |
5 |
6 |
|
Increased Cough |
6.3 |
5.9 |
|
Skin and Appendages | ||
|
Rash |
7.1 |
7.9 |
|
Special Senses | ||
|
Cataract |
5.7 |
6.5 |
|
Urogenital System | ||
|
Urinary Tract Infection |
10.4 |
11.1 |
Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: The incidence of adverse events in the placebo and risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily groups were: abdominal pain (9.9% versus 12.2%), diarrhea (10% versus 10.8%), dyspepsia (10.6% versus 10.8%), and gastritis (2.3% versus 2.7%). Duodenitis and glossitis have been reported uncommonly in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group (0.1% to 1%). In patients with active upper gastrointestinal disease at baseline, the incidence of upper gastrointestinal adverse events was similar between the placebo and risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily groups.
Musculoskeletal Adverse Events: The incidence of adverse events in the placebo and risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily groups were: back pain (26.1% versus 28%), arthralgia (22.1% versus 23.7%), myalgia (6.2% versus 6.7%), and bone pain (4.8% versus 5.3%).
Laboratory Test Findings: Throughout the Phase 3 studies, transient decreases from baseline in serum calcium (less than 1%) and serum phosphate (less than 3%) and compensatory increases in serum PTH levels (less than 30%) were observed within 6 months in patients in osteoporosis clinical trials treated with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg once daily. There were no significant differences in serum calcium, phosphate, or PTH levels between placebo and risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg once daily at 3 years. Serum calcium levels below 8 mg/dL were observed in 18 patients, 9 (0.5%) in each treatment arm (placebo and risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg once daily). Serum phosphorus levels below 2 mg/dL were observed in 14 patients, 3 (0.2%) treated with placebo and 11 (0.6%) treated with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg once daily. There have been rare reports (less than 0.1%) of abnormal liver function tests.
Endoscopic Findings: In the risedronate clinical trials, endoscopic evaluation was encouraged in any patient with moderate-to-severe gastrointestinal complaints, while maintaining the blind. Endoscopies were performed on equal numbers of patients between the placebo and treated groups [75 (14.5%) placebo; 75 (11.9%) risedronate]. Clinically important findings (perforations, ulcers, or bleeding) among this symptomatic population were similar between groups (51% placebo; 39% risedronate).
Once-a-Week Dosing
The safety of risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in a 1-year, double-blind, multicenter study comparing risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week in postmenopausal women aged 50 to 95 years. The duration of the trials was one year, with 480 patients exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and 485 exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week. Patients with pre-existing gastrointestinal disease and concomitant use of non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 antagonists were included in these clinical trials. All women received 1000 mg of elemental calcium plus vitamin D supplementation up to 500 international units per day if their 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 level was below normal at baseline.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was 0.4% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 1% in the risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once- a-week group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 7.1% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 8.2% in the risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 11.9% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 11.5% in the risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week group. The overall safety and tolerability profiles of the two dosing regimens were similar.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse events was similar between the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and the risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week group: dyspepsia (6.9% versus 7.6%), diarrhea (6.3% versus 4.9%), and abdominal pain (7.3% versus 7.6%).
Musculoskeletal Adverse Events: Arthralgia was reported in 11.5% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 14.2% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week group. Myalgia was reported by 4.6% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 6.2% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week group.
Laboratory Test Findings: The mean percent changes from baseline at 12 months were similar between the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week groups, respectively, for serum calcium (0.4% versus 0.7%), phosphate (-3.8% versus -2.6%) and PTH (6.4% versus 4.2%).
Monthly Dosing
Two Consecutive Days per Month
The safety of risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg administered on two consecutive days per month for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in a double-blind, multicenter study in postmenopausal women aged 50 to 86 years. The duration of the trial was two years; 613 patients were exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and 616 were exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month. Patients with pre- existing gastrointestinal disease and concomitant use of non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 antagonists were included in this clinical trial. All women received 1000 mg of elemental calcium plus 400 to 800 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was 1% for the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 0.5% for the risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 10.8% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 14.4% in the risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from treatment due to adverse events was 14.2% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group and 13% in the risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month group. The overall safety and tolerability profiles of the two dosing regimens were similar.
Acute Phase Reactions: Symptoms consistent with acute phase reaction have been reported with bisphosphonate use. The overall incidence of acute phase reaction was 3.6% of patients on risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and 7.6% of patients on risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month. These incidence rates are based on reporting of any of 33 acute phase reaction-like symptoms within 5 days of the first dose. Fever or influenza- like illness with onset within the same period were reported by 0% of patients on risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and 0.6% of patients on risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: The risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month group resulted in a higher incidence of discontinuation due to vomiting (1% versus 0.2%) and diarrhea (1% versus 0.3%) compared to the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. Most of these events occurred within a few days of dosing.
Ocular Adverse Events: None of the patients treated with risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month reported ocular inflammation such as uveitis, scleritis, or iritis; 1 patient treated with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily reported uveitis.
Laboratory Test Findings: When risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month were compared in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, the mean percent changes from baseline at 24 months were 0.2% and 0.8% for serum calcium, -1.9% and -1.3% for phosphate, and -10.4% and -17.2% for PTH, respectively. Compared to the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group, risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month resulted in a slightly higher incidence of hypocalcemia at the end of the first month of treatment (4.5% versus 3%). Thereafter, the incidence of hypocalcemia with these regimens was similar at approximately 2%.
Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Daily Dosing
The safety of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily in the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. In one study of postmenopausal women aged 37 to 82 years without osteoporosis, the use of estrogen replacement therapy in both placebo- and risedronate-treated patients was included. The duration of the trial was one year, with 259 exposed to placebo and 261 patients exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg. The second study included postmenopausal women aged 44 to 63 years without osteoporosis. The duration of the trial was one year, with 125 exposed to placebo and 129 patients exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg. All women received 1000 mg of elemental calcium per day.
In the trial with estrogen replacement therapy, the incidence of all-cause mortality was 1.5% for the placebo group and 0.4% for the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 8.9% in the placebo group and 5.4% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from treatment due to adverse events was 18.9% in the placebo group and 10.3% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. Constipation was reported by 1.9% of the placebo group and 6.5% of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group.
In the second trial, the incidence of all-cause mortality was 0% for both groups. The incidence of serious adverse events was 17.6% in the placebo group and 9.3% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from treatment due to adverse events was 6.4% in the placebo group and 5.4% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. Nausea was reported by 6.4% of patients in the placebo group and 13.2% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group.
Once-a-Week Dosing
There were no deaths in a 1-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week for prevention of bone loss in 278 postmenopausal women without osteoporosis. More treated subjects on risedronate reported arthralgia (placebo 7.8%; risedronate 13.9%), myalgia (placebo 2.1%; risedronate 5.1%), and nausea (placebo 4.3%; risedronate 7.3%) than subjects on placebo.
Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
In a 2-year, double-blind, multicenter study, 284 men with osteoporosis were treated with placebo (N = 93) or risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week (N = 191). The overall safety and tolerability profile of risedronate in men with osteoporosis was similar to the adverse events reported in the risedronate postmenopausal osteoporosis clinical trials, with the addition of benign prostatic hyperplasia (placebo 3%; risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg 5%), nephrolithiasis (placebo 0%; risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg 3%), and arrhythmia (placebo 0%; risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg 2%).
Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
The safety of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily in the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis was assessed in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled multinational trials of 344 patients [male (123) and female (221)] aged 18 to 85 years who had recently initiated oral glucocorticoid therapy (less than or equal to 3 months, prevention study) or were on long-term oral glucocorticoid therapy (greater than or equal to 6 months, treatment study). The duration of the trials was one year, with 170 patients exposed to placebo and 174 patients exposed to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily. Patients in one study received 1000 mg elemental calcium plus 400 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day; patients in the other study received 500 mg calcium supplementation per day.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was 2.9% in the placebo group and 1.1% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 33.5% in the placebo group and 30.5% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 8.8% in the placebo group and 7.5% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. Back pain was reported in 8.8% of patients in the placebo group and 17.8% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. Arthralgia was reported in 14.7% of patients in the placebo group and 24.7% of patients in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group.
Treatment of Paget’s Disease
Risedronate has been studied in 392 patients with Paget’s disease of bone. As in trials of risedronate for other indications, the adverse experiences reported in the Paget’s disease trials have generally been mild or moderate, have not required discontinuation of treatment, and have not appeared to be related to patient age, gender, or race.
The safety of risedronate was assessed in a randomized, double-blind, active- controlled study of 122 patients aged 34 to 85 years. The duration of the trial was 540 days, with 61 patients exposed to risedronate and 61 patients exposed to Didronel®. The adverse event profile was similar for risedronate and Didronel: 6.6% (4/61) of patients treated with risedronate sodium tablets 30 mg daily for 2 months discontinued treatment due to adverse events, compared to 8.2% (5/61) of patients treated with Didronel 400 mg daily for 6 months. Table 2 lists adverse events reported in greater than or equal to 5% of risedronate-treated patients in Phase 3 Paget's disease trials. Adverse events shown are considered to be possibly or probably causally related in at least one patient.
|
Table 2 | ||
|
Body System |
30 mg/day x 2 months Risedronate |
400 mg/day x 6 months Didronel |
|
Body as a Whole | ||
|
Flu Syndrome |
9.8 |
1.6 |
|
Chest Pain |
6.6 |
3.3 |
|
Gastrointestinal | ||
|
Diarrhea |
19.7 |
14.8 |
|
Abdominal Pain |
11.5 |
8.2 |
|
Nausea |
9.8 |
9.8 |
|
Constipation |
6.6 |
8.2 |
|
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders | ||
|
Peripheral Edema |
8.2 |
6.6 |
|
Musculoskeletal | ||
|
Arthralgia |
32.8 |
29.5 |
|
Nervous | ||
|
Headache |
18 |
16.4 |
|
Dizziness |
6.6 |
4.9 |
|
Skin and Appendages | ||
|
Rash |
11.5 |
8.2 |
|
*Considered to be possibly or probably causally related in at least one patient. |
Gastrointestinal Adverse Events: During the first year of the study (treatment and nontreatment follow-up), the proportion of patients who reported upper gastrointestinal adverse events was similar between the treatment groups; no patients reported severe upper gastrointestinal adverse events. The incidence of diarrhea was 19.7% in the risedronate group and 14.8% in the Didronel group; none were serious or resulted in withdrawal.
Ocular Adverse Events: Three patients who received risedronate sodium tablets 30 mg daily experienced acute iritis in 1 supportive study. All 3 patients recovered from their events; however, in 1 of these patients, the event recurred during risedronate treatment and again during treatment with pamidronate. All patients were effectively treated with topical steroids.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity and skin reactions have been reported, including angioedema, generalized rash, bullous skin reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Events
Events involving upper gastrointestinal irritation, such as esophagitis and esophageal or gastric ulcers, have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Musculoskeletal Pain
Bone, joint, or muscle pain, described as severe or incapacitating, have been reported rarely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Eye Inflammation
Reactions of eye inflammation including iritis and uveitis have been reported rarely.
Jaw Osteonecrosis
Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported rarely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Pulmonary
Asthma exacerbations
Most common adverse reactions reported in greater than 10% of patients treated with risedronate and with a higher frequency than placebo are: back pain, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and dyspepsia (6.1)
Hypersensitivity reactions (angioedema, generalized rash, bullous skin reactions, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis), and eye inflammation (iritis, uveitis) have been reported rarely (6.2)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or****www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Drug Interactions Section
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No specific drug-drug interaction studies were performed. Risedronate is not metabolized and does not induce or inhibit hepatic microsomal drug- metabolizing enzymes (for example, Cytochrome P450).
7.1 Calcium Supplements/Antacids
Co-administration of risedronate and calcium, antacids, or oral medications containing divalent cations will interfere with the absorption of risedronate.
7.2 Hormone Replacement Therapy
One study of about 500 early postmenopausal women has been conducted to date in which treatment with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily plus estrogen replacement therapy was compared to estrogen replacement therapy alone. Exposure to study drugs was approximately 12 to 18 months and the primary endpoint was change in BMD. If considered appropriate, risedronate may be used concomitantly with hormone replacement therapy.
7.3 Aspirin/Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Of over 5700 patients enrolled in the risedronate Phase 3 osteoporosis studies, aspirin use was reported by 31% of patients, 24% of whom were regular users (3 or more days per week). Forty-eight percent of patients reported NSAID use, 21% of whom were regular users. Among regular aspirin or NSAID users, the incidence of upper gastrointestinal adverse experiences in placebo- treated patients (24.8%) was similar to that in risedronate-treated patients (24.5%).
7.4 H2 Blockers and Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
Of over 5700 patients enrolled in the risedronate Phase 3 osteoporosis studies, 21% used H2 blockers and/or PPIs. Among these patients, the incidence of upper gastrointestinal adverse experiences in the placebo-treated patients was similar to that in risedronate-treated patients.
Calcium, antacids, or oral medications containing divalent cations interfere with the absorption of risedronate
(7.1)
Dosage Forms & Strengths Section
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 5 mg yellow colored, circular, beveled edge, film-coated biconvex tablets debossed with ‘X’ on one side and ‘61’ on the other side.
- 30 mg white to off-white, circular, film-coated biconvex tablets debossed with ‘L’ on one side and ‘30’ on the other side.
- 35 mg light orange colored, circular, film-coated biconvex tablets debossed with ‘F27’ on one side and plain on the other side.
Tablets: 5 mg, 30 mg, and 35 mg (3)
Use In Specific Populations Section
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data on the use of risedronate in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Discontinue risedronate when pregnancy is recognized.
In animal reproduction studies, daily oral administration of risedronate to pregnant rats during organogenesis decreased neonatal survival and body weight at doses approximately 5 and 26 times, respectively, the highest recommended human daily dose of 30 mg (based on body surface area, mg/m2). A low incidence of cleft palate was observed in fetuses of dams treated at doses approximately equal to the 30 mg human daily dose. Delayed skeletal ossification was observed in fetuses of dams treated at approximately 2.5 to 5 times the 30 mg human daily dose. Periparturient mortality due to maternal hypocalcemia occurred in dams and neonates upon daily oral administration of risedronate to pregnant rats during mating and/or gestation starting at doses equivalent to the 30 mg daily human dose.
Bisphosphonates are incorporated into the bone matrix, from which they are gradually released over a period of years. The amount of bisphosphonate incorporated into adult bone and available for release into the systemic circulation is directly related to the dose and duration of bisphosphonate use. Consequently, based on the mechanism of action of bisphosphonates, there is a potential risk of fetal harm, predominantly skeletal, if a woman becomes pregnant after completing a course of bisphosphonate therapy. The impact of variables such as time between cessation of bisphosphonate therapy to conception, the particular bisphosphonate used, and the route of administration (intravenous versus oral) on this risk has not been studied.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In animal studies, pregnant rats received risedronate sodium during organogenesis at doses equivalent to 1 to 26 times the 30 mg human daily dose (based on body surface area, mg/m2). Survival of neonates was decreased in dams treated during gestation with oral doses approximately 5 times the human dose, and body weight was decreased in neonates of dams treated with approximately 26 times the human dose. A low incidence of cleft palate was observed in fetuses of dams treated with oral doses approximately equal to the human dose. The number of fetuses exhibiting incomplete ossification of sternebrae or skull of dams treated with approximately 2.5 times the human dose was significantly increased compared to controls. Both incomplete ossification and unossified sternebrae were increased in fetuses of dams treated with oral doses approximately 5 times the human dose.
No significant ossification effects were seen in fetuses of rabbits treated with oral doses approximately 7 times the human dose (the highest dose tested). However, 1 of 14 litters were aborted and 1 of 14 litters were delivered prematurely.
Periparturient mortality due to maternal hypocalcemia occurred in dams and neonates when pregnant rats were treated daily during mating and/or gestation with oral doses equivalent to the human dose or higher.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of risedronate in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. A small degree of lacteal transfer occurred in nursing rats. The concentration of the drug in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk. However, when a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for risedronate and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from risedronate or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data
Risedronate was detected in neonates of lactating rats given a single oral dose of risedronate at 24-hours post-dosing, indicating a small degree of lacteal transfer.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Risedronate is not indicated for use in pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of risedronate was assessed in a one-year, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 143 pediatric patients (94 received risedronate) with osteogenesis imperfecta (OI). The enrolled population was predominantly patients with mild osteogenesis imperfecta (85% Type-I), aged 4 to less than 16 years, 50% male and 82% Caucasian, with a mean lumbar spine BMD Z-score of -2.08 (2.08 standard deviations below the mean for age-matched controls). Patients received either a 2.5 mg (less than or equal to 30 kg body weight) or 5 mg (greater than 30 kg body weight) daily oral dose. After one year, an increase in lumbar spine BMD in the risedronate group compared to the placebo group was observed. However, treatment with risedronate did not result in a reduction in the risk of fracture in pediatric patients with osteogenesis imperfecta. In risedronate-treated subjects, no mineralization defects were noted in paired bone biopsy specimens obtained at baseline and month 12.
The overall safety profile of risedronate in OI patients treated for up to 12 months was generally similar to that of adults with osteoporosis. However, there was an increased incidence of vomiting compared to placebo. In this study, vomiting was observed in 15% of children treated with risedronate and 6% of patients treated with placebo. Other adverse events reported in greater than or equal to 10% of patients treated with risedronate and with a higher frequency than placebo were: pain in the extremity (21% with risedronate versus 16% with placebo), headache (20% versus 8%), back pain (17% versus 10%), pain (15% versus 10%), upper abdominal pain (11% versus 8%), and bone pain (10% versus 4%).
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the patients receiving risedronate in postmenopausal osteoporosis studies [see Clinical Studies (14)], 47% were between 65 and 75 years of age, and 17% were over 75. The corresponding proportions were 26% and 11% in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis trials, and 40% and 26% in Paget’s disease trials. No overall differences in efficacy between geriatric and younger patients were observed in these studies. In the male osteoporosis trial, 28% of patients receiving risedronate were between 65 and 75 years of age and 9% were over 75. The lumbar spine BMD response for risedronate compared to placebo was 5.6% for subjects less than 65 years and 2.9% for subjects greater than or equal to 65 years. No overall differences in safety between geriatric and younger patients were observed in the risedronate trials, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Risedronate is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) because of lack of clinical experience. No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with a creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL/min.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No studies have been performed to assess risedronate’s safety or efficacy in patients with hepatic impairment. Risedronate is not metabolized in human liver preparations. Dosage adjustment is unlikely to be needed in patients with hepatic impairment.
- Pregnancy: Discontinue when pregnancy is recognized (8.1)
- Risedronate is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) (5.6, 8.6, 12.3)
- Risedronate is not indicated for use in pediatric patients (8.4)
Overdosage Section
10 OVERDOSAGE
Decreases in serum calcium and phosphorus following substantial overdose may be expected in some patients. Signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia may also occur in some of these patients. Milk or antacids containing calcium should be given to bind risedronate and reduce absorption of the drug.
In cases of substantial overdose, gastric lavage may be considered to remove unabsorbed drug. Standard procedures that are effective for treating hypocalcemia, including the administration of calcium intravenously, would be expected to restore physiologic amounts of ionized calcium and to relieve signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia.
Lethality after single oral doses was seen in female rats at 903 mg/kg and male rats at 1703 mg/kg. The minimum lethal dose in mice and rabbits was 4000 mg/kg and 1000 mg/kg, respectively. These values represent 320 to 620 times the 30 mg human dose based on surface area (mg/m2).
Nonclinical Toxicology Section
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a 104-week carcinogenicity study, rats were administered daily oral doses up to approximately 8 times the maximum recommended human daily dose. There were no significant drug-induced tumor findings in male or female rats. The high dose male group was terminated early in the study (Week 93) due to excessive toxicity, and data from this group were not included in the statistical evaluation of the study results. In an 80-week carcinogenicity study, mice were administered daily oral doses approximately 6.5 times the human dose. There were no significant drug-induced tumor findings in male or female mice.
Mutagenesis
Risedronate did not exhibit genetic toxicity in the following assays: In vitro bacterial mutagenesis in Salmonella and E. coli (Ames assay), mammalian cell mutagenesis in CHO/HGPRT assay, unscheduled DNA synthesis in rat hepatocytes and an assessment of chromosomal aberrations in vivo in rat bone marrow. Risedronate was positive in a chromosomal aberration assay in CHO cells at highly cytotoxic concentrations (greater than 675 mcg/mL, survival of 6% to 7%). When the assay was repeated at doses exhibiting appropriate cell survival (29%), there was no evidence of chromosomal damage.
Impairment of Fertility
In female rats, ovulation was inhibited at an oral dose approximately 5 times the human dose. Decreased implantation was noted in female rats treated with doses approximately 2.5 times the human dose. In male rats, testicular and epididymal atrophy and inflammation were noted at approximately 13 times the human dose. Testicular atrophy was also noted in male rats after 13 weeks of treatment at oral doses approximately 5 times the human dose. There was moderate-to-severe spermatid maturation block after 13 weeks in male dogs at an oral dose approximately 8 times the human dose. These findings tended to increase in severity with increased dose and exposure time.
Dosing multiples provided above are based on the recommended human dose of 30 mg/day and normalized using body surface area (mg/m2). Actual doses were 24 mg/kg/day in rats, 32 mg/kg/day in mice, and 8, 16 and 40 mg/kg/day in dogs.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Risedronate demonstrated potent anti-osteoclast, antiresorptive activity in ovariectomized rats and minipigs. Bone mass and biomechanical strength were increased dose-dependently at daily oral doses up to 4 and 25 times the human recommended oral dose of 5 mg for rats and minipigs, respectively. Risedronate treatment maintained the positive correlation between BMD and bone strength and did not have a negative effect on bone structure or mineralization. In intact dogs, risedronate induced positive bone balance at the level of the bone remodeling unit at oral doses ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 times the 5 mg/day human daily dose.
In dogs treated with an oral dose approximately 5 times the human daily dose, risedronate caused a delay in fracture healing of the radius. The observed delay in fracture healing is similar to other bisphosphonates. This effect did not occur at a dose approximately 0.5 times the human daily dose.
The Schenk rat assay, based on histologic examination of the epiphyses of growing rats after drug treatment, demonstrated that risedronate did not interfere with bone mineralization even at the highest dose tested, which was approximately 3500 times the lowest antiresorptive dose in this model (1.5 mcg/kg/day) and approximately 800 times the human daily dose of 5 mg. This indicates that risedronate administered at the therapeutic dose is unlikely to induce osteomalacia.
Dosing multiples provided above are based on the recommended human dose of 5 mg/day and normalized using body surface area (mg/m2).
Information For Patients Section
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide before starting therapy with risedronate and to re-read it each time the prescription is renewed.
Instruct patients that Atelvia and risedronate sodium tablets contain the same active ingredient and if they are taking Atelvia, they should not take risedronate sodium tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Instruct patients to pay particular attention to the dosing instructions as clinical benefits may be compromised by failure to take the drug according to instructions. Specifically, risedronate should be taken at least 30 minutes before the first food or drink of the day other than water.
Instruct patients to take risedronate while in an upright position (sitting or standing) with a full glass of plain water (6 to 8 ounces) to facilitate delivery to the stomach, and thus reduce the potential for esophageal irritation.
Instruct patients not to lie down for 30 minutes after taking the medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Instruct patients not to chew or suck on the tablet because of a potential for oropharyngeal irritation.
Instruct patients that if they develop symptoms of esophageal disease (such as difficulty or pain upon swallowing, retrosternal pain or severe persistent or worsening heartburn) they should consult their physician before continuing risedronate.
Instruct patients about missing risedronate doses as follows:
- If a dose of risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week is missed, they should take 1 tablet on the morning after they remember and return to taking 1 tablet once-a-week, as originally scheduled on their chosen day. Patients should not take 2 tablets on the same day.
- If one or both tablets of risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month are missed, and the next month’s scheduled doses are more than 7 days away, the patient should be instructed as follows:
- If both tablets are missed, take one risedronate sodium tablet 75 mg in the morning after the day it is remembered and then the other tablet on the next consecutive morning.
- If only one risedronate sodium tablet 75 mg is missed, take the missed tablet in the morning after the day it is remembered.
- Patients should then return to taking their risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month as originally scheduled. Patients should not take more than two 75 mg tablets within 7 days.
- If one or both tablets of risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month are missed, and the next month’s scheduled doses are within 7 days, patients should wait until their next month’s scheduled doses and then continue taking risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month as originally scheduled.
Instruct patients to take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if dietary intake is inadequate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Weight-bearing exercise should be considered along with the modification of certain behavioral factors, such as excessive cigarette smoking, and/or alcohol consumption, if these factors exist.
Instruct patients to take calcium supplements or calcium-, aluminum-, and magnesium-containing medications at a different time of the day than risedronate as these medications may interfere with the absorption of risedronate.
Remind patients to give all of their healthcare providers an accurate medication history. Instruct patients to tell all of their healthcare providers that they are taking risedronate. Patients should be instructed that any time they have a medical problem they think may be from risedronate, they should talk to their doctor.
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.aurobindousa.com/medication-guides
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
****279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
****Hyderabad-500 032, India
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Aurobindo Pharma Limited.
Revised: 10/2021
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
Medication Guide
Risedronate Sodium Tablets, USP
** (ris'' e droe' nate soe' dee um)**
Read the Medication Guide that comes with risedronate sodium tablets before you start taking them and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. Talk to your doctor if you have any questions about risedronate sodium tablets, there may be new information about them.
What is the most important information I should know about risedronate sodium tablets?
Risedronate sodium tablets can cause serious side effects including:
1. Esophagus problems
2. Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia)
3. Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis)
4. Bone, joint, or muscle pain
5. Unusual thigh bone fractures
1. Esophagus problems.
Some people who take risedronate sodium tablets may develop problems in the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth and the stomach). These problems include irritation, inflammation, or ulcers of the esophagus which may sometimes bleed.
*It is important that you take risedronate sodium tablets exactly as prescribed to help lower your chance of getting esophagus problems. (See the section “How should I take risedronate sodium tablets?”) *Stop taking risedronate sodium tablets and call your doctor right away if you get chest pain, new or worsening heartburn, or have trouble or pain when you swallow.
**2.**Low calcium levels in your blood (hypocalcemia).
Risedronate sodium tablets may lower the calcium levels in your blood. If you have low blood calcium before you start taking risedronate sodium tablets, it may get worse during treatment. Your low blood calcium must be treated before you take risedronate sodium tablets. Most people with low blood calcium levels do not have symptoms, but some people may have symptoms. Call your doctor right away if you have symptoms of low blood calcium such as:
- Spasms, twitches, or cramps in your muscles
- Numbness or tingling in your fingers, toes, or around your mouth
Your doctor may prescribe calcium and vitamin D to help prevent low calcium levels in your blood, while you take risedronate sodium tablets. Take calcium and vitamin D as your doctor tells you to.****
** 3.**Severe jaw bone problems (osteonecrosis).
Severe jaw bone problems may happen when you take risedronate sodium tablets. Your doctor should examine your mouth before you start risedronate sodium tablets. Your doctor may tell you to see your dentist before you start risedronate sodium tablets. It is important for you to practice good mouth care during treatment with risedronate sodium tablets.****
** 4.**Bone, joint, or muscle pain.
Some people who take risedronate sodium tablets develop severe bone, joint, or muscle pain.****
** 5.**Unusual thigh bone fractures.
Some people have developed unusual fractures in their thigh bone. Symptoms of a fracture may include new or unusual pain in your hip, groin, or thigh.****
** Call your doctor right away if you have any of these side effects.**
What arerisedronate sodium tablets?
****Risedronate sodium tablets are a prescription medicine used to:
- Treat or prevent osteoporosis in women after menopause. Risedronate sodium tablets help increase bone mass and helps reduce the chance of having a spinal or non-spinal fracture (break).
- Increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis.
- Treat or prevent osteoporosis in either men or women who are taking corticosteroid medicines.
- Treat certain men and women who have Paget’s disease of the bone.
It is not known how long risedronate sodium tablets work for the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis. You should see your doctor regularly to determine if risedronate sodium tablets are still right for you.
Risedronate sodium tablets are not for use in children.
Who should not takerisedronate sodium tablets?
****Do not takerisedronate sodium tablets if you:
- Have certain problems with your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth with your stomach
- Cannot stand or sit upright for at least 30 minutes
- Have low levels of calcium in your blood
- Are allergic to risedronate sodium or any of their ingredients. A list of ingredients is at the end of this leaflet.
What should I tell my doctor before takingrisedronate sodium tablets?
Before you start****risedronate sodium tablets, be sure to talk to your doctor if you:
- Have problems with swallowing
- Have stomach or digestive problems
- Have low blood calcium
- Plan to have dental surgery or teeth removed
- Have kidney problems
- Have been told you have trouble absorbing minerals in your stomach or intestines (malabsorption syndrome)
- Are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or suspect that you are pregnant.If you become pregnant while taking risedronate sodium tablets, stop taking it and contact your doctor. It is not known if risedronate sodium tablets can harm your unborn baby.
- Are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if risedronate sodium passes into your milk and may harm your baby.
Especially tell your doctor if you take:
- antacids
- aspirin
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory (NSAID) medicines
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. Certain medicines may affect how risedronate sodium tablets work.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your doctor and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take risedronate sodium tablets?
- Take risedronate sodium tablets exactly as your doctor tells you. Your doctor may change your dose of risedronate sodium tablets if needed. *Risedronate sodium tablets work only if taken on an empty stomach.
- Take 1 risedronate sodium tablet, after you get up for the day and before taking your first food, drink, or other medicine.
- Take risedronate sodium tablets while you are sitting or standing. *Do not chew or suck on a tablet of risedronate sodium.
- Swallow risedronate sodium tablet with a full glass (6 to 8 ounces) of plain water only.
- Donot take risedronate sodium tablets with mineral water, coffee, tea, soda, or juice.
After swallowing risedronate sodium tablet, wait at least 30 minutes:
- Before you lie down. You may sit, stand or walk, and do normal activities like reading.
- Before you take your first food or drink except for plain water.
- Before you take other medicines, including antacids, calcium, and other supplements and vitamins.
Do not lie down for at least 30 minutes after you take****risedronate sodium tablets and after you eat your first food of the day.
If you miss a dose of risedronate sodium tablets, do not take it later in the day. Take your missed dose the next morning and then return to your normal schedule. Do not take 2 doses at the same time.
If you miss more than 2 doses of risedronate sodium tablets in a month, call your doctor for instructions.
If you take too much risedronate sodium, call your doctor. Do not try to vomit. Do not lie down.
** What are the possible side effects ofrisedronate sodium tablets?**
****Risedronate sodium tablets may cause serious side effects:
- See** “What is the most important information I should know about****risedronate sodium tablets?”**
The most common side effects of risedronate sodium tablets are:
- pain, including back and joint pain
- stomach area (abdominal) pain
- heartburn
You may get allergic reactions, such as hives, swelling of your face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of risedronate sodium tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store risedronate sodium tablets?
- Store risedronate sodium tablets at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep****risedronate sodium tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use ofrisedronate sodium tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use risedronate sodium tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give risedronate sodium tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. They may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about risedronate sodium tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about risedronate sodium tablets that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876.
What are the ingredients inrisedronate sodium tablets?
****Active ingredient: risedronate sodium
Inactive ingredients in all dose strengths: crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
Inactive ingredients specific to a dose strength: 5 mg—colloidal silicon dioxide and iron oxide yellow; 35 mg—colloidal silicon dioxide, iron oxide red, and iron oxide yellow.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
**Dispense with Medication Guide available at: **www.aurobindousa.com/medication-guides
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Aurobindo Pharma Limited
Hyderabad-500 032, India
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Aurobindo Pharma Limited.
Revised: 10/2021
Dosage & Administration Section
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
[see Indications and Usage (1.1)]
The recommended regimen is:
- one 5 mg tablet orally, taken daily
or
- one 35 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-week
or
- one 75 mg tablet orally, taken on two consecutive days for a total of two tablets each month
2.2 Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
[see Indications and Usage (1.1)]
The recommended regimen is:
-
one 5 mg tablet orally, taken daily
or -
one 35 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-week
or -
alternatively, one 75 mg tablet orally, taken on two consecutive days for a total of two tablets each month may be considered
2.3 Treatment to Increase Bone Mass in Men with Osteoporosis
[see Indications and Usage (1.2)]
The recommended regimen is:
- one 35 mg tablet orally, taken once-a-week
2.4 Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
[see Indications and Usage (1.3)]
The recommended regimen is:
- one 5 mg tablet orally, taken daily
2.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease
[see Indications and Usage (1.4)]
The recommended treatment regimen is 30 mg orally once daily for 2 months. Retreatment may be considered (following post-treatment observation of at least 2 months) if relapse occurs, or if treatment fails to normalize serum alkaline phosphatase. For retreatment, the dose and duration of therapy are the same as for initial treatment. No data are available on more than 1 course of retreatment.
2.6 Important Administration Instructions
Instruct patients to do the following:
- Take risedronate sodium tablets at least 30 minutes before the first food or drink of the day other than water, and before taking any oral medication or supplementation, including calcium, antacids, or vitamins to maximize absorption and clinical benefit, [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Avoid the use of water with supplements, including mineral water, because they may have a higher concentration of calcium.
- Swallow risedronate sodium tablets whole with a full glass of plain water (6 to 8 ounces). Avoid lying down for 30 minutes after taking the medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Do not chew or suck the tablet because of a potential for oropharyngeal ulceration.
- Do not eat or drink anything except plain water, or take other medications for at least 30 minutes after taking risedronate sodium tablets.
2.7 Recommendations for Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
Instruct patients to take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if their dietary intake is inadequate; and to take calcium supplements, antacids, magnesium- based supplements or laxatives, and iron preparations at a different time of the day as they interfere with the absorption of risedronate sodium tablets.
2.8 Administration Instructions for Missed Doses
Instruct patients about missing risedronate sodium tablets dose as follows:
- If a dose of risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week is missed:
- Take 1 tablet on the morning after they remember and return to taking 1 tablet once-a-week, as originally scheduled on their chosen day.
- Do not take 2 tablets on the same day.
- If one or both tablets of risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month are missed, and the next month’s scheduled doses are more than 7 days away:
- If both tablets are missed, take one risedronate sodium tablet 75 mg in the morning after the day it is remembered and then the other tablet on the next consecutive morning.
- If only one risedronate sodium tablet 75 mg is missed, take the missed tablet in the morning after the day it is remembered
- Return to taking their risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month as originally scheduled.
- Do not take more than two 75 mg tablets within 7 days.
- If one or both tablets of risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month are missed, and the next month’s scheduled doses are within 7 days:
- Wait until their next month’s scheduled doses and then continue taking risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg on two consecutive days per month as originally scheduled.
Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: 5 mg daily, 35 mg once-a-week, 75 mg
two consecutive days each month (2.1)
Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: 5 mg daily, 35 mg once-a-week (2.2)
Men with Osteoporosis: 35 mg once-a-week (2.3)
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis: 5 mg daily (2.4)
Paget’s Disease: 30 mg daily for 2 months (2.5)
Instruct patients to:
- Swallow tablet whole with 6 to 8 ounces of plain water, at least 30 minutes before the first food, beverage, or medication of the day
- Avoid lying down for 30 minutes (2)
- Take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if dietary intake is inadequate (2.7)
Description Section
11 DESCRIPTION
Risedronate sodium tablets, USP are a pyridinyl bisphosphonate that inhibits osteoclast-mediated bone resorption and modulates bone metabolism. Each risedronate sodium tablet, USP for oral administration contains the equivalent of 5 mg, 30 mg, or 35 mg of anhydrous risedronate sodium in the form of the hemi-pentahydrate with small amounts of monohydrate. The molecular formula for risedronate sodium hemi-pentahydrate is C7H10NO7P2Na •2.5 H2O. The chemical name of risedronate sodium is [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis[phosphonic acid] monosodium salt. The chemical structure of risedronate sodium hemi-pentahydrate is the following:
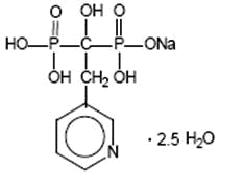
Molecular Weight:
Anhydrous: 305.10
Hemi-pentahydrate: 350.13
Risedronate sodium is a white to off-white, crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and in aqueous solutions, and essentially insoluble in common organic solvents.
Inactive Ingredients
All dose strengths contain: crospovidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide.
Dose strength-specific ingredients include: 5 mg—colloidal silicon dioxide and iron oxide yellow; 35 mg—colloidal silicon dioxide, iron oxide red, and iron oxide yellow.
Clinical Pharmacology Section
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Risedronate has an affinity for hydroxyapatite crystals in bone and acts as an antiresorptive agent. At the cellular level, risedronate inhibits osteoclasts. The osteoclasts adhere normally to the bone surface, but show evidence of reduced active resorption (for example, lack of ruffled border). Histomorphometry in rats, dogs, and minipigs showed that risedronate treatment reduces bone turnover (activation frequency, that is, the rate at which bone remodeling sites are activated) and bone resorption at remodeling sites.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Risedronate treatment decreases the elevated rate of bone turnover that is typically seen in postmenopausal osteoporosis. In clinical trials, administration of risedronate to postmenopausal women resulted in decreases in biochemical markers of bone turnover, including urinary deoxypyridinoline/creatinine and urinary collagen cross-linked N-telopeptide (markers of bone resorption) and serum bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (a marker of bone formation). At the 5 mg dose, decreases in deoxypyridinoline/creatinine were evident within 14 days of treatment. Changes in bone formation markers were observed later than changes in resorption markers, as expected, due to the coupled nature of bone resorption and bone formation; decreases in bone-specific alkaline phosphatase of about 20% were evident within 3 months of treatment. Bone turnover markers reached a nadir of about 40% below baseline values by the sixth month of treatment and remained stable with continued treatment for up to 3 years. Bone turnover is decreased as early as 14 days and maximally within about 6 months of treatment, with achievement of a new steady-state that more nearly approximates the rate of bone turnover seen in premenopausal women. In a 1-year study comparing daily versus weekly oral dosing regimens of risedronate for the treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week decreased urinary collagen cross-linked N-telopeptide by 60% and 61%, respectively. In addition, serum bone-specific alkaline phosphatase was also reduced by 42% and 41% in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily and risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week groups, respectively. When postmenopausal women with osteoporosis were treated for 1 year with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily or risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month, urinary collagen cross-linked N-telopeptide was decreased by 54% and 52%, respectively, and serum bone-specific alkaline phosphatase was reduced by 36% and 35%, respectively.
Osteoporosis in Men
In a 2-year study of men with osteoporosis, treatment with risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week resulted in a mean decrease from baseline compared to placebo of 16% (placebo 20%; risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg 37%) for the bone resorption marker urinary collagen cross-linked N-telopeptide, 45% (placebo -6%; risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg 39%) for the bone resorption marker serum C-telopeptide, and 27% (placebo -2%; risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg 25%) for the bone formation marker serum bone-specific alkaline phosphatase.
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis with glucocorticoid use occurs as a result of inhibited bone formation and increased bone resorption resulting in net bone loss. Risedronate decreases bone resorption without directly inhibiting bone formation.
In two 1-year clinical trials in the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg decreased urinary collagen cross-linked N-telopeptide (a marker of bone resorption), and serum bone-specific alkaline phosphatase (a marker of bone formation) by 50% to 55% and 25% to 30%, respectively, within 3 to 6 months after initiation of therapy.
Paget’s Disease
Paget’s disease of bone is a chronic, focal skeletal disorder characterized by greatly increased and disordered bone remodeling. Excessive osteoclastic bone resorption is followed by osteoblastic new bone formation, leading to the replacement of the normal bone architecture by disorganized, enlarged, and weakened bone structure.
In pagetic patients treated with risedronate sodium tablets 30 mg daily for 2 months, bone turnover returned to normal in a majority of patients as evidenced by significant reductions in serum alkaline phosphatase (a marker of bone formation), and in urinary hydroxyproline/creatinine and deoxypyridinoline/creatinine (markers of bone resorption).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Based on simultaneous modeling of serum and urine data, peak absorption after an oral dose is achieved at approximately 1 hour (Tmax) and occurs throughout the upper gastrointestinal tract. The fraction of the dose absorbed is independent of dose over the range studied (single dose, from 2.5 mg to 30 mg; multiple dose, from 2.5 mg to 5 mg). Steady-state conditions in the serum are observed within 57 days of daily dosing. Mean absolute oral bioavailability of the 30 mg tablet is 0.63% (90% CI: 0.54% to 0.75%) and is comparable to a solution.
Food Effect
The extent of absorption of a 30 mg dose (three 10 mg tablets) when administered 0.5 hours before breakfast is reduced by 55% compared to dosing in the fasting state (no food or drink for 10 hours prior to or 4 hours after dosing). Dosing 1 hour prior to breakfast reduces the extent of absorption by 30% compared to dosing in the fasting state. Dosing either 0.5 hours prior to breakfast or 2 hours after dinner (evening meal) results in a similar extent of absorption. Risedronate is effective when administered at least 30 minutes before breakfast.
Distribution
The mean steady-state volume of distribution for risedronate is 13.8 L/kg in humans. Human plasma protein binding of drug is about 24%. Preclinical studies in rats and dogs dosed intravenously with single doses of [14C] risedronate indicate that approximately 60% of the dose is distributed to bone. The remainder of the dose is excreted in the urine. After multiple oral dosing in rats, the uptake of risedronate in soft tissues was in the range of 0.001% to 0.01%.
Metabolism
There is no evidence of systemic metabolism of risedronate.
Excretion
In young healthy subjects, approximately half of the absorbed dose of risedronate was excreted in urine within 24 hours, and 85% of an intravenous dose was recovered in the urine over 28 days. Based on simultaneous modeling of serum and urine data, mean renal clearance was 105 mL/min (CV = 34%) and mean total clearance was 122 mL/min (CV = 19%), with the difference primarily reflecting nonrenal clearance or clearance due to adsorption to bone. The renal clearance is not concentration dependent, and there is a linear relationship between renal clearance and creatinine clearance. Unabsorbed drug is eliminated unchanged in feces. In osteopenic postmenopausal women, the terminal exponential half-life was 561 hours, mean renal clearance was 52 mL/min (CV = 25%), and mean total clearance was 73 mL/min (CV = 15%).
Specific Populations
Pediatric: Risedronate is not indicated for use in pediatric patients [see Pediatric Use (8.4)].
Gender: Bioavailability and pharmacokinetics following oral administration are similar in men and women.
Geriatric: Bioavailability and disposition are similar in elderly (greater than 60 years of age) and younger subjects. No dosage adjustment is necessary.
Race: Pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied.
Renal Impairment: Risedronate is excreted unchanged primarily via the kidney. As compared to persons with normal renal function, the renal clearance of risedronate was decreased by about 70% in patients with creatinine clearance of approximately 30 mL/min. Risedronate is not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min) because of lack of clinical experience. No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with a creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 30 mL/min.
Hepatic Impairment: No studies have been performed to assess risedronate’s safety or efficacy in patients with hepatic impairment. Risedronate is not metabolized in rat, dog, and human liver preparations. Insignificant amounts (less than 0.1% of intravenous dose) of drug are excreted in the bile in rats. Therefore, dosage adjustment is unlikely to be needed in patients with hepatic impairment.
Drug Interactions: No specific drug-drug interaction studies were performed. Risedronate is not metabolized and does not induce or inhibit hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing enzymes (Cytochrome P450) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Clinical Studies Section
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The fracture efficacy of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was demonstrated in 2 large, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind studies that enrolled a total of almost 4000 postmenopausal women under similar protocols. The Multinational study (VERT MN) (risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 408) was conducted primarily in Europe and Australia; a second study was conducted in North America (VERT NA) (risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 821). Patients were selected on the basis of radiographic evidence of previous vertebral fracture, and therefore, had established disease. The average number of prevalent vertebral fractures per patient at study entry was 4 in VERT MN, and 2.5 in VERT NA, with a broad range of baseline BMD levels. All patients in these studies received supplemental calcium 1000 mg/day. Patients with low 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 levels (approximately 40 nmol/L or less) also received supplemental vitamin D 500 international units/day.
Effect on Vertebral Fractures
Fractures of previously undeformed vertebrae (new fractures) and worsening of pre-existing vertebral fractures were diagnosed radiographically; some of these fractures were also associated with symptoms (that is, clinical fractures). Spinal radiographs were scheduled annually and prospectively planned analyses were based on the time to a patient’s first diagnosed fracture. The primary endpoint for these studies was the incidence of new and worsening vertebral fractures across the period of 0 to 3 years. Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily significantly reduced the incidence of new and worsening vertebral fractures and of new vertebral fractures in both VERT NA and VERT MN at all time points (Table 3). The reduction in risk seen in the subgroup of patients who had 2 or more vertebral fractures at study entry was similar to that seen in the overall study population.
|
Table 3 | ||||
|
VERT NA |
Proportion of Patients with Fracture (%)a | |||
|
Placebo |
Risedronate Sodium Tablets 5 mg |
Absolute Risk Reduction (%) |
Relative Risk Reduction (%) | |
|
New and Worsening |
7.2 |
3.9 |
3.3 |
49 |
|
New |
6.4 |
2.4 |
4 |
65 |
|
VERT MN |
Placebo |
Risedronate Sodium Tablets 5 mg |
Absolute Risk Reduction (%) |
Relative Risk Reduction (%) |
|
New and Worsening |
15.3 |
8.2 |
7.1 |
50 |
|
New |
13.3 |
5.6 |
7.7 |
61 |
|
a Calculated by Kaplan-Meier methodology. |
Effect on Osteoporosis-Related Nonvertebral Fractures
In VERT MN and VERT NA, a prospectively planned efficacy endpoint was defined consisting of all radiographically confirmed fractures of skeletal sites accepted as associated with osteoporosis. Fractures at these sites were collectively referred to as osteoporosis-related nonvertebral fractures. Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily significantly reduced the incidence of nonvertebral osteoporosis-related fractures over 3 years in VERT NA (8% versus 5%; relative risk reduction 39%) and reduced the fracture incidence in VERT MN from 16% to 11%. There was a significant reduction from 11% to 7% when the studies were combined, with a corresponding 36% reduction in relative risk. Figure 1 shows the overall results as well as the results at the individual skeletal sites for the combined studies.
** Figure 1****Nonvertebral Osteoporosis-Related Fractures Cumulative Incidence Over 3 Years Combined VERT MN and VERT NA**
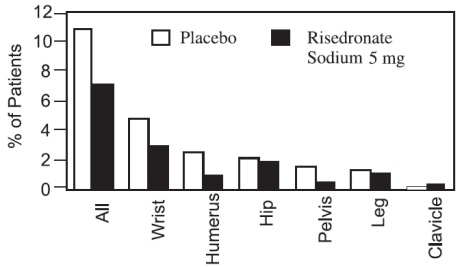
Effect on Bone Mineral Density
The results of 4 randomized, placebo-controlled trials in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis (VERT MN, VERT NA, BMD MN, BMD NA) demonstrate that risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily increases BMD at the spine, hip, and wrist compared to the effects seen with placebo. Table 4 displays the significant increases in BMD seen at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, femoral trochanter, and midshaft radius in these trials compared to placebo. In both VERT studies (VERT MN and VERT NA), risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily produced increases in lumbar spine BMD that were progressive over the 3 years of treatment and were statistically significant relative to baseline and to placebo at 6 months and at all later time points.
|
Table 4 | ||||||||
|
VERT MNb |
VERT NAb |
BMD MNc |
BMD NAc | |||||
|
Placebo |
5 mg |
Placebo |
5 mg |
Placebo |
5 mg |
Placebo |
5 mg | |
|
Lumbar Spine |
1 |
6.6 |
0.8 |
5 |
0 |
4 |
0.2 |
4.8 |
|
Femoral Neck |
-1.4 |
1.6 |
-1 |
1.4 |
-1.1 |
1.3 |
0.1 |
2.4 |
|
Femoral |
-1.9 |
3.9 |
-0.5 |
3 |
-0.6 |
2.5 |
1.3 |
4 |
|
Trochanter | ||||||||
|
Midshaft Radius |
-1.5* |
0.2* |
-1.2* |
0.1* |
ND |
ND | ||
|
a The endpoint value is the value at the study's last time point for all
patients who had BMD measured at that time; otherwise the last post-baseline
BMD value prior to the study's last time point is used.
|
Risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week (N = 485) was shown to be non- inferior to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily (N = 480) in a 1-year, double-blind, multicenter study of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. In the primary efficacy analysis of completers, the mean increases from baseline in lumbar spine BMD at 1 year were 4% (3.7, 4.3; 95% confidence interval [CI]) in the 5 mg daily group (N = 391) and 3.9% (3.6, 4.3; 95% CI) in the 35 mg once-a-week group (N = 387) and the mean difference between 5 mg daily and 35 mg once-a-week was 0.1% (-0.4, 0.6; 95% CI). The results of the intent-to- treat analysis with the last observation carried forward were consistent with the primary efficacy analysis of completers. The 2 treatment groups were also similar with regard to BMD increases at other skeletal sites.
In a double-blind, multicenter study of postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, treatment with risedronate sodium tablets 75 mg two consecutive days per month (N = 616) was shown to be non-inferior to risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily (N = 613). In the primary efficacy analysis of completers, the mean increases from baseline in lumbar spine BMD at 1 year were 3.6% (3.3, 3.9; 95% CI) in the 5 mg daily group (N = 527) and 3.4% (3.1, 3.7; 95% CI) in the 75 mg two days per month group (N = 524) with a mean difference between groups being 0.2% (-0.2, 0.6; 95% CI). The results of the intent-to-treat analysis with the last observation carried forward were consistent with the primary efficacy analysis of completers. The 2 treatment groups were also similar with regard to BMD increases at other skeletal sites.
Histology/Histomorphometry
Bone biopsies from 110 postmenopausal women were obtained at endpoint. Patients had received placebo or daily risedronate sodium tablets (2.5 mg or 5 mg) for 2 to 3 years. Histologic evaluation (N = 103) showed no osteomalacia, impaired bone mineralization, or other adverse effects on bone in risedronate- treated women. These findings demonstrate that bone formed during risedronate administration is of normal quality. The histomorphometric parameter mineralizing surface, an index of bone turnover, was assessed based upon baseline and post-treatment biopsy samples from 21 treated with placebo and 23 patients treated with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg. Mineralizing surface decreased moderately in risedronate-treated patients (median percent change: placebo, -21%; risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, -74%), consistent with the known effects of treatment on bone turnover.
Effect on Height
In the two 3-year osteoporosis treatment studies, standing height was measured yearly by stadiometer. Both risedronate and placebo-treated groups lost height during the studies. Patients who received risedronate had a statistically significantly smaller loss of height than those who received placebo. In VERT MN, the median annual height change was -2.4 mm/yr in the placebo group compared to -1.3 mm/yr in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group. In VERT NA, the median annual height change was -1.1 mm/yr in the placebo group compared to -0.7 mm/yr in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily group.
14.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The safety and effectiveness of risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily for the prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis were demonstrated in a 2-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 383 postmenopausal women (age range 42 to 63 years) within three years of menopause (risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 129). All patients in this study received supplemental calcium 1000 mg/day. Increases in BMD were observed as early as 3 months following initiation of risedronate treatment. Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily produced significant mean increases in BMD at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and trochanter compared to placebo at the end of the study (Figure 2). Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily was also effective in patients with lower baseline lumbar spine BMD (more than 1 SD below the premenopausal mean) and in those with normal baseline lumbar spine BMD. Bone mineral density at the distal radius decreased in both risedronate and placebo-treated women following 1 year of treatment.
Figure 2****Change in BMD from Baseline 2-Year Prevention Study
****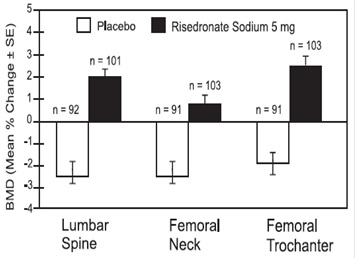
The safety and effectiveness of risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week for the prevention postmenopausal osteoporosis were demonstrated in a 1-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 278 patients (risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg, N = 136). All patients were supplemented with 1000 mg elemental calcium and 400 international units vitamin D per day. The primary efficacy measure was the percent change in lumbar spine BMD from baseline after 1 year of treatment using LOCF (last observation carried forward). Risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week resulted in a statistically significant mean difference from placebo in lumbar spine BMD of +2.9% (least square mean for placebo -1.05%; risedronate +1.83%). Risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a- week also showed a statistically significant mean difference from placebo in BMD at the total proximal femur of +1.5% (placebo -0.53%; risedronate +1.01%), femoral neck of +1.2% (placebo -1%; risedronate +0.22%), and trochanter of +1.8% (placebo -0.74%; risedronate +1.07%).
Combined Administration with Hormone Replacement Therapy
The effects of combining risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily with conjugated estrogen 0.625 mg daily (N = 263) were compared to the effects of conjugated estrogen alone (N = 261) in a 1-year, randomized, double-blind study of women ages 37 to 82 years, who were on average 14 years postmenopausal. The BMD results for this study are presented in Table 5.
|
Table 5 | ||
|
Estrogen 0.625 mg |
Risedronate Sodium Tablets | |
|
Lumbar Spine |
4.6 ± 0.2 |
5.2 ± 0.23 |
|
Femoral Neck |
1.8 ± 0.25 |
2.7 ± 0.25 |
|
Femoral Trochanter |
3.2 ± 0.28 |
3.7 ± 0.25 |
|
Midshaft Radius |
0.4 ± 0.14 |
0.7 ± 0.17 |
|
Distal Radius |
1.7 ± 0.24 |
1.6 ± 0.28 |
|
Values shown are mean (±SEM) percent change from baseline. |
Histology/Histomorphometry
Bone biopsies from 53 postmenopausal women were obtained at endpoint. Patients had received risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg plus estrogen or estrogen-alone once daily for 1 year. Histologic evaluation (N = 47) demonstrated that the bone of patients treated with risedronate plus estrogen was of normal lamellar structure and normal mineralization. The histomorphometric parameter mineralizing surface, a measure of bone turnover, was assessed based upon baseline and post-treatment biopsy samples from 12 patients treated with risedronate plus estrogen and 12 treated with estrogen-alone. Mineralizing surface decreased in both treatment groups (median percent change: Risedronate plus estrogen, -79%; estrogen-alone, -50%), consistent with the known effects of these agents on bone turnover.
14.3 Men with Osteoporosis
The effects of risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week on BMD were examined in a 2-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational study in 285 men with osteoporosis (Risedronate, N = 192). The patients had a mean age of 61 years (range 36 to 84 years) and 95% were Caucasian. At baseline, mean lumbar spine T-score was -3.2 and mean femoral neck T-score was -2.4. All patients in the study had either, 1) a BMD T-score less than or equal to -2 at the femoral neck and less than or equal to -1 at the lumbar spine, or 2) a BMD T-score less than or equal to -1 at the femoral neck and less than or equal to -2.5 at the lumbar spine. All patients were supplemented with calcium 1000 mg/day and vitamin D 400 to 500 international units/day. Risedronate sodium tablets 35 mg once-a-week produced significant mean increases in BMD at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, trochanter, and total hip compared to placebo after 2 years of treatment (treatment difference: lumbar spine, 4.5%; femoral neck, 1.1%; trochanter, 2.2%; total proximal femur, 1.5%).
14.4 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Bone Mineral Density
Two 1-year, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in patients who were taking greater than or equal to 7.5 mg/day of prednisone or equivalent demonstrated that risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg daily was effective in the prevention and treatment of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women who were either initiating or continuing glucocorticoid therapy. The efficacy of risedronate therapy for glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis beyond one year has not been studied.
The prevention study enrolled 228 patients (risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 76) (18 to 85 years of age), each of whom had initiated glucocorticoid therapy (mean daily dose of prednisone 21 mg) within the previous 3 months (mean duration of use prior to study 1.8 months) for rheumatic, skin, and pulmonary diseases. The mean lumbar spine BMD was normal at baseline (average T-score -0.7). All patients in this study received supplemental calcium 500 mg/day. By the third month of treatment, and continuing through the year-long treatment, the placebo group experienced losses in BMD at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and trochanter, while BMD was maintained or increased in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group. At each skeletal site there were statistically significant differences between the placebo group and the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group at all timepoints (Months 3, 6, 9, and 12). The treatment differences increased with continued treatment. Although BMD increased at the distal radius in the risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg group compared to the placebo group, the difference was not statistically significant. The differences between placebo and risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg after 1 year were 3.8% at the lumbar spine, 4.1% at the femoral neck, and 4.6% at the trochanter, as shown in Figure 3. The results at these skeletal sites were similar to the overall results when the subgroups of men and postmenopausal women, but not premenopausal women, were analyzed separately. Risedronate was effective at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and trochanter regardless of age (less than 65 vs. greater than or equal to 65), gender, prior and concomitant glucocorticoid dose, or baseline BMD. Positive treatment effects were also observed in patients taking glucocorticoids for a broad range of rheumatologic disorders, the most common of which were rheumatoid arthritis, temporal arteritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica.
The treatment study of similar design enrolled 290 patients (risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg, N = 100) (19 to 85 years of age) with continuing, long- term (greater than or equal to 6 months) use of glucocorticoids (mean duration of use prior to study 60 months; mean daily dose of prednisone 15 mg) for rheumatic, skin, and pulmonary diseases. The baseline mean lumbar spine BMD was low (1.63 SD below the young healthy population mean), with 28% of the patients more than 2.5 SD below the mean. All patients in this study received supplemental calcium 1000 mg/day and vitamin D 400 international units/day.
After 1 year of treatment, the BMD of the placebo group was within 1% of baseline levels at the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and trochanter. Risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg increased BMD at the lumbar spine (2.9%), femoral neck (1.8%), and trochanter (2.4%). The differences between risedronate and placebo were 2.7% at the lumbar spine, 1.9% at the femoral neck, and 1.6% at the trochanter as shown in Figure 4. The differences were statistically significant for the lumbar spine and femoral neck, but not at the femoral trochanter. Risedronate was similarly effective on lumbar spine BMD regardless of age (less than 65 vs. greater than or equal to 65), gender, or pre-study glucocorticoid dose. Positive treatment effects were also observed in patients taking glucocorticoids for a broad range of rheumatologic disorders, the most common of which were rheumatoid arthritis, temporal arteritis, and polymyalgia rheumatica.
Figure 3****Change in BMD from Baseline Patients Recently Initiating
Glucocorticoid Therapy
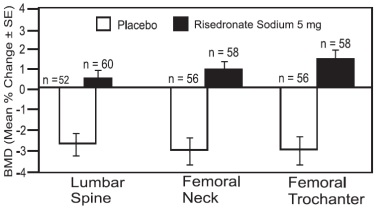
Figure 4Change in BMD from Baseline Patients on Long-Term
Glucocorticoid Therapy
********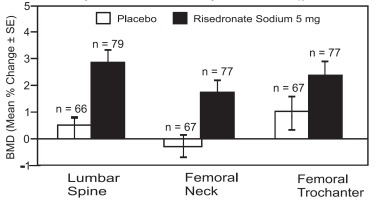
Vertebral Fractures
In the prevention study of patients initiating glucocorticoids, the incidence of vertebral fractures at 1 year was reduced from 17% in the placebo group to 6% in the risedronate group. In the treatment study of patients continuing glucocorticoids, the incidence of vertebral fractures was reduced from 15% in the placebo group to 5% in the risedronate group (Figure 5). The statistically significant reduction in vertebral fracture incidence in the analysis of the combined studies corresponded to an absolute risk reduction of 11% and a relative risk reduction of 70%. All vertebral fractures were diagnosed radiographically; some of these fractures also were associated with symptoms (that is, clinical fractures).
Figure 5****Incidence of Vertebral Fractures in Patients Initiating or
Continuing Glucocorticoid Therapy
****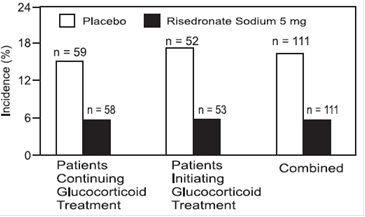
Histology/Histomorphometry
Bone biopsies from 40 patients on glucocorticoid therapy were obtained at endpoint. Patients had received placebo or daily risedronate sodium tablets (2.5 mg or 5 mg) for 1 year. Histologic evaluation (N = 33) showed that bone formed during treatment with risedronate was of normal lamellar structure and normal mineralization, with no bone or marrow abnormalities observed. The histomorphometric parameter mineralizing surface, a measure of bone turnover, was assessed based upon baseline and post-treatment biopsy samples from 10 patients treated with risedronate sodium tablets 5 mg. Mineralizing surface decreased 24% (median percent change) in these patients. Only a small number of placebo-treated patients had both baseline and post-treatment biopsy samples, precluding a meaningful quantitative assessment.
14.5 Treatment of Paget's Disease
The efficacy of risedronate was demonstrated in 2 clinical studies involving 120 men and 65 women. In a double-blind, active-controlled study of patients with moderate-to-severe Paget’s disease (serum alkaline phosphatase levels of at least 2 times the upper limit of normal), patients were treated with risedronate sodium tablets 30 mg daily for 2 months or Didronel (etidronate disodium) 400 mg daily for 6 months. At Day 180, 77% (43/56) of risedronate- treated patients achieved normalization of serum alkaline phosphatase levels, compared to 10.5% (6/57) of patients treated with Didronel (p less than 0.001). At Day 540, 16 months after discontinuation of therapy, 53% (17/32) of risedronate-treated patients and 14% (4/29) of Didronel-treated patients with available data remained in biochemical remission.
During the first 180 days of the active-controlled study, 85% (51/60) of risedronate-treated patients demonstrated a greater than or equal to 75% reduction from baseline in serum alkaline phosphatase excess (difference between measured level and midpoint of the normal range) with 2 months of treatment compared to 20% (12/60) in the Didronel-treated group with 6 months of treatment (p less than 0.001). Changes in serum alkaline phosphatase excess over time (shown in Figure 6) were significant following only 30 days of treatment, with a 36% reduction in serum alkaline phosphatase excess at that time compared to only a 6% reduction seen with Didronel treatment at the same time point (p less than 0.01).
Figure 6****Mean Percent Change from Baseline in Serum Alkaline Phosphatase
Excess by Visit
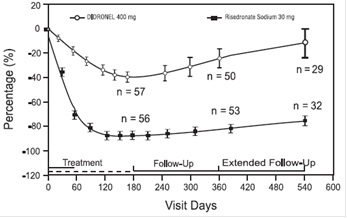
Response to risedronate therapy was similar in patients with mild to very severe Paget’s disease. Table 6 shows the mean percent reduction from baseline at Day 180 in excess serum alkaline phosphatase in patients with mild, moderate, or severe disease.
|
Table 6 | ||||||
|
Subgroup: Baseline Disease Severity (AP) |
Risedronate Sodium Tablets |
Didronel 400 mg | ||||
|
n |
Baseline Serum AP (U/L)* |
Mean % Reduction |
n |
Baseline Serum AP (U/L)* |
Mean % Reduction | |
|
greater than 2, less than 3x ULN |
32 |
271.6 ± 5.3 |
-88.1 |
22 |
277.9 ± 7.45 |
-44.6 |
|
greater than or equal to 3, less than 7x ULN |
14 |
475.3 ± 28.8 |
-87.5 |
25 |
480.5 ± 26.44 |
-35 |
|
greater than or equal to 7x ULN |
8 |
1336.5 ± 134.19 |
-81.8 |
6 |
1331.5 ± 167.58 |
-47.2 |
|
*Values shown are mean ± SEM; ULN = upper limit of normal. |
Response to risedronate therapy was similar between patients who had previously received anti-pagetic therapy and those who had not. In the active- controlled study, 4 patients previously non-responsive to 1 or more courses of anti-pagetic therapy (calcitonin, Didronel) responded to treatment with risedronate sodium tablets 30 mg daily (defined by at least a 30% change from baseline). Each of these patients achieved at least 90% reduction from baseline in serum alkaline phosphatase excess, with 3 patients achieving normalization of serum alkaline phosphatase levels.
Histomorphometry of the bone was studied in 14 patients with bone biopsies: 9 patients had biopsies from pagetic bone lesions and 5 patients from non- pagetic bone. Bone biopsy results in non-pagetic bone did not reveal osteomalacia, impairment of bone remodeling, or induction of a significant decline in bone turnover in patients treated with risedronate.
How Supplied Section
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Risedronate sodium tablets, USP are available as follows:
Risedronate Sodium Tablets USP, 5 mgare yellow colored, circular, beveled edge, film-coated biconvex tablets debossed with ‘X’ on one side and ‘61’ on the other side.
Bottles of 30 NDC 65862-517-30
Bottles of 2,000 NDC 65862-517-22
10 x 10 Unit-dose Tablets NDC 65862-517-78
Risedronate Sodium Tablets USP, 30 mgare white to off-white, circular, film-coated biconvex tablets debossed with ‘L’ on one side and ‘30’ on the other side.
Bottles of 30 NDC 65862-518-30
Bottles of 1,000 NDC 65862-518-99
10 x 10 Unit-dose Tablets NDC 65862-518-78
Risedronate Sodium Tablets USP, 35 mgare light orange colored, circular, film-coated biconvex tablets debossed with ‘F27’ on one side and plain on the other side.
Unit-of-use blister package of 4 NDC 65862-519-04
Unit-of-use blister package of 12 NDC 65862-519-08
** Store at** 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
