fosaprepitant
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FOSAPREPITANT FOR INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FOSAPREPITANT FOR INJECTION. FOSAPREPITANT for injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
9b6d5ea3-2f7a-4501-9a4a-6fa1a7c2d50a
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 10, 2020
Mylan Institutional LLC
DUNS: 790384502
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
fosaprepitant
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
fosaprepitant
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with HEC in Adults
Fosaprepitant for Injection 115 mg (3-Day Dosing Regimen of Fosaprepitant for Injection)
Fosaprepitant 115 mg intravenous infused over 15 minutes can be substituted for 125 mg oral aprepitant on Day 1 of a 3-day regimen. Efficacy studies with the 3-day regimen were conducted with oral aprepitant.
In 2 multicenter, randomized, parallel, double-blind, controlled clinical studies, the aprepitant regimen (see Table 11) was compared with standard therapy in patients receiving a chemotherapy regimen that included cisplatin
50 mg/m2 (mean cisplatin dose = 80.2 mg/m2).
Of the 550 patients who were randomized to receive the aprepitant regimen, 42% were women, 58% men, 59% White, 3% Asian, 5% Black, 12% Hispanic American, and 21% Multi-Racial. The aprepitant-treated patients in these clinical studies ranged from 14 to 84 years of age, with a mean age of 56 years. 170 patients were 65 years or older, with 29 patients being 75 years or older.
Patients (N = 1,105) were randomized to either the aprepitant regimen (N = 550) or standard therapy (N = 555). The treatment regimens are defined in Table 11.
Table 11
Treatment Regimens Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy Trials*
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 | |
|
CINV Aprepitant Regimen | ||||
|
Aprepitant |
125 mg orally |
80 mg orally |
80 mg orally |
None |
|
Dexamethasone |
12 mg orally |
8 mg orally |
8 mg orally |
8 mg orally |
|
5-HT3 antagonist† |
See package insert |
none |
none |
none |
|
CINV Standard Therapy | ||||
|
Dexamethasone |
20 mg orally |
8 mg orally twice daily |
8 mg orally twice daily |
8 mg orally twice daily |
|
5-HT3 antagonist† |
See package insert |
none |
none |
none |
*Aprepitant placebo and dexamethasone placebo were used to maintain blinding.
†Ondansetron 32 mg I.V. was used in the clinical trials of aprepitant. Although this dose was used in clinical trials, this is no longer the currently recommended dose. Refer to the ondansetron package insert for the current dosing.
During these studies, 95% of the patients in the aprepitant group received a concomitant chemotherapeutic agent in addition to protocol-mandated cisplatin. The most common chemotherapeutic agents and the number of aprepitant patients exposed follow: etoposide (106), fluorouracil (100), gemcitabine (89), vinorelbine (82), paclitaxel (52), cyclophosphamide (50), doxorubicin (38), docetaxel (11).
The antiemetic activity of oral aprepitant was evaluated during the acute phase (0 to 24 hours post-cisplatin treatment), the delayed phase (25 to 120 hours post-cisplatin treatment) and overall (0 to 120 hours post-cisplatin treatment) in Cycle 1. Efficacy was based on evaluation of the following endpoints in which emetic episodes included vomiting, retching, or dry heaves:
Primary endpoint:
•
complete response (defined as no emetic episodes and no use of rescue therapy as recorded in patient diaries)
Other prespecified endpoints:
•
complete protection (defined as no emetic episodes, no use of rescue therapy, and a maximum nausea visual analogue scale [VAS] score <25 mm on a 0 to 100 mm scale)
•
no emesis (defined as no emetic episodes regardless of use of rescue therapy)
•
no nausea (maximum VAS <5 mm on a 0 to 100 mm scale)
•
no significant nausea (maximum VAS <25 mm on a 0 to 100 mm scale)
A summary of the key study results from each individual study analysis is shown in Table 12 and in Table 13.
Table 12
Percent of Patients Receiving Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy Responding by Treatment Group and Phase for Study 1 — Cycle 1
|
ENDPOINTS |
Aprepitant Regimen % |
Standard Therapy % |
p-Value |
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT | |||
|
Complete Response | |||
|
Overall‡ |
73 |
52 |
<0.001 |
|
OTHER PRESPECIFIED ENDPOINTS | |||
|
Complete Response | |||
|
Acute phase§ Delayed phase|| |
89 75 |
78 56 |
<0.001 <0.001 |
|
Complete Protection | |||
|
Overall Acute phase Delayed phase |
63 85 66 |
49 75 52 |
0.001 NS* <0.001 |
|
No Emesis | |||
|
Overall Acute phase Delayed phase |
78 90 81 |
55 79 59 |
<0.001 0.001 <0.001 |
|
No Nausea | |||
|
Overall Delayed phase |
48 51 |
44 48 |
NS** NS** |
|
No Significant Nausea | |||
|
Overall Delayed phase |
73 75 |
66 69 |
NS** NS** |
†N: Number of patients (older than 18 years of age) who received cisplatin, study drug, and had
at least one post-treatment efficacy evaluation.
‡Overall: 0 to 120 hours post-cisplatin treatment.
§Acute phase: 0 to 24 hours post-cisplatin treatment.
||Delayed phase: 25 to 120 hours post-cisplatin treatment.
*Not statistically significant when adjusted for multiple comparisons.
**Not statistically significant.
Visual analogue scale (VAS) score range: 0 mm = no nausea; 100 mm = nausea as bad as it could be.
Table 13
Percent of Patients Receiving Highly Emetogenic Chemotherapy Responding by Treatment Group and Phase for Study 2 — Cycle 1
|
ENDPOINTS |
Aprepitant Regimen (N = 261)† % |
Standard Therapy (N = 263)† % |
p-Value |
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT | |||
|
Complete Response | |||
|
Overall‡ |
63 |
43 |
<0.001 |
|
OTHER PRESPECIFIED ENDPOINTS | |||
|
Complete Response | |||
|
Acute phase§ Delayed phase|| |
83 68 |
68 47 |
<0.001 <0.001 |
|
Complete Protection | |||
|
Overall Acute phase Delayed phase |
56 80 61 |
41 65 44 |
<0.001 <0.001 <0.001 |
|
No Emesis | |||
|
Overall Acute phase Delayed phase |
66 84 72 |
44 69 48 |
<0.001 <0.001 <0.001 |
|
No Nausea | |||
|
Overall |
49 |
39 |
NS* |
|
Delayed phase |
53 |
40 |
NS* |
|
No Significant Nausea | |||
|
Overall |
71 |
64 |
NS** |
|
Delayed phase |
73 |
65 |
NS** |
†N: Number of patients (older than 18 years of age) who received cisplatin, study drug, and had at least one post-treatment efficacy evaluation.
‡Overall: 0 to 120 hours post-cisplatin treatment.
§Acute phase: 0 to 24 hours post-cisplatin treatment.
||Delayed phase: 25 to 120 hours post-cisplatin treatment.
*Not statistically significant when adjusted for multiple comparisons.
**Not statistically significant.
Visual analogue scale (VAS) score range: 0 mm = no nausea; 100 mm = nausea as bad as it could be.
In both studies, a statistically significantly higher proportion of patients (both p<0.001) receiving the aprepitant regimen in Cycle 1 had a complete response in the overall phase (primary endpoint), compared with patients receiving standard therapy. A statistically significant difference in complete response in favor of the aprepitant regimen was also observed when the acute phase and the delayed phase were analyzed separately.
In both studies, the estimated time to first emesis after initiation of cisplatin treatment was longer with the aprepitant regimen, and the incidence of first emesis was reduced in the aprepitant regimen group compared with standard therapy group as depicted in the Kaplan-Meier curves in Figure 2.
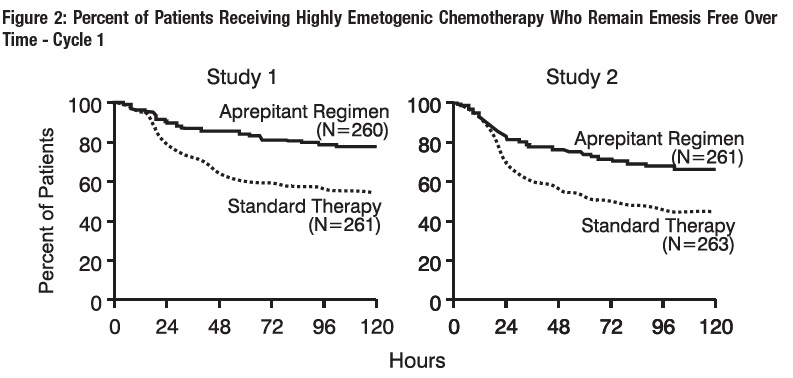
p-Value <0.001 based on a log rank test for Study 1 and Study 2; nominal p-values not adjusted for multiplicity.
Additional Patient-Reported Outcomes: The impact of nausea and vomiting on patients’ daily lives was assessed in Cycle 1 of both phase 3 studies using the Functional Living Index–Emesis (FLIE), a validated nausea- and vomiting- specific patient-reported outcome measure. Minimal or no impact of nausea and vomiting on patients’ daily lives is defined as a FLIE total score >108. In each of the 2 studies, a higher proportion of patients receiving the aprepitant regimen reported minimal or no impact of nausea and vomiting on daily life (Study 1: 74% versus 64%; Study 2: 75% versus 64%).
Multiple-Cycle Extension: In the same 2 clinical studies, patients continued into the Multiple-Cycle extension for up to 5 additional cycles of chemotherapy. The proportion of patients with no emesis and no significant nausea by treatment group at each cycle is depicted in Figure 3.
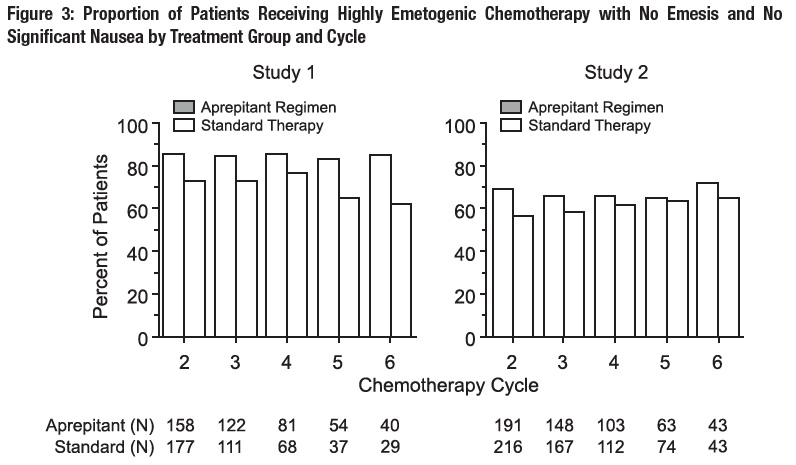
Fosaprepitant for Injection 150 mg
In a randomized, parallel, double-blind, active-controlled study, fosaprepitant for injection 150 mg as a single intravenous infusion (N=1,147) was compared to a 3-day oral aprepitant regimen (N=1,175) in patients receiving a HEC regimen that included cisplatin (≥70 mg/m2). All patients in both groups received dexamethasone and ondansetron (see Table 14). Patient demographics were similar between the two treatment groups. Of the total 2,322 patients, 63% were men, 56% White, 26% Asian, 3% American Indian/Alaska Native, 2% Black, 13% Multi-Racial, and 33% Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Patient ages ranged from 19 to 86 years of age, with a mean age of 56 years. Other concomitant chemotherapy agents commonly administered were fluorouracil (17%), gemcitabine (16%), paclitaxel (15%), and etoposide (12%).
Table 14
Treatment Regimens in Adult HEC Trial*****
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 |
Day 4 | |
|
Fosaprepitant Regimen | ||||
|
Fosaprepitant for injection |
150 mg intravenously over 20 to 30 minutes approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy |
none |
none |
none |
|
Oral dexamethasone† |
12 mg |
8 mg |
8 mg twice daily |
8 mg twice daily |
|
Ondansetron |
|
none |
none |
none |
|
Oral Aprepitant Regimen | ||||
|
Aprepitant capsules |
125 mg |
80 mg |
80 mg |
none |
|
Oral dexamethasone§ |
12 mg |
8 mg |
8 mg |
8 mg |
|
Ondansetron |
|
none |
none |
none |
*Fosaprepitant for injection placebo, aprepitant capsules placebo and dexamethasone placebo (in the evenings on Days 3 and 4) were used to maintain blinding.
†Dexamethasone was administered 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy treatment on Day 1 and in the morning on Days 2 through 4. Dexamethasone was also administered in the evenings on Days 3 and 4. The 12 mg dose of dexamethasone on Day 1 and the 8 mg once daily dose on Day 2 reflects a dosage adjustment to account for a drug interaction with the fosaprepitant for injection regimen [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
‡Ondansetron 32 mg intravenous was used in the clinical trials of fosaprepitant. Although this dose was used in clinical trials, this is no longer the currently recommended dose. Refer to the ondansetron prescribing information for the current recommended dose.
§Dexamethasone was administered 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy treatment on Day 1 and in the morning on Days 2 through 4. The 12 mg dose of dexamethasone on Day 1 and the 8 mg once daily dose on Days 2 through 4 reflects a dosage adjustment to account for a drug interaction with the oral aprepitant regimen [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The efficacy of fosaprepitant for injection was evaluated based on the primary and secondary endpoints listed in Table 15 and was shown to be non-inferior to that of the 3-day oral aprepitant regimen with regard to complete response in each of the evaluated phases. The pre-specified non-inferiority margin for complete response in the overall phase was 7%. The pre-specified non- inferiority margin for complete response in the delayed phase was 7.3%. The pre-specified non-inferiority margin for no vomiting in the overall phase was 8.2%.
Table 15
Percent of Adult Patients Receiving HEC Responding by Treatment Group and Phase — Cycle 1
|
ENDPOINTS |
Fosaprepitant for Injection Regimen (N = 1,106)***** % |
Oral Aprepitant Regimen (N = 1,134)***** % |
Difference**†** (95% CI) |
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT | |||
|
Complete Response‡ | |||
|
71.9 |
72.3 |
-0.4 (-4.1, 3.3) |
|
SECONDARY ENDPOINTS | |||
|
Complete Response‡ | |||
|
74.3 |
74.2 |
0.1 (-3.5, 3.7) |
|
No Vomiting | |||
|
72.9 |
74.6 |
-1.7 (-5.3, 2) |
*N: Number of patients included in the primary analysis of complete response.
†Difference and Confidence interval (CI) were calculated using the method proposed by Miettinen and
Nurminen and adjusted for Gender.
‡Complete Response = no vomiting and no use of rescue therapy.
§Overall = 0 to 120 hours post-initiation of cisplatin chemotherapy.
¶Delayed phase = 25 to 120 hours post-initiation of cisplatin chemotherapy.
14.2 Prevention of Nausea and Vomiting Associated with MEC in Adults
In a randomized, parallel, double-blind, active comparator-controlled study, fosaprepitant for injection 150 mg as a single intravenous infusion (N=502) in combination with ondansetron and dexamethasone (fosaprepitant regimen) was compared with ondansetron and dexamethasone alone (standard therapy) (N=498) (see Table 16) in patients receiving a MEC regimen. Patient demographics were similar between the two treatment groups. Of the total 1,000 patients included in the efficacy analysis, 41% were men, 84% White, 4% Asian, 1% American Indian/Alaska Native, 2% Black, 10% Multi-Racial, and 19% Hispanic/Latino ethnicity. Patient ages ranged from 23 to 88 years of age, with a mean age of 60 years. The most commonly administered MEC chemotherapeutic agents were carboplatin (51%), oxaliplatin (24%), and cyclophosphamide (12%).
Table 16
Treatment Regimens in Adult MEC Trial*****
|
Day 1 |
Day 2 |
Day 3 | |
|
Fosaprepitant Regimen | |||
|
Fosaprepitant for injection |
150 mg intravenously over 20 to 30 minutes approximately 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy |
none |
none |
|
Oral Dexamethasone† |
12 mg |
none |
none |
|
Oral Ondansetron‡ |
8 mg for 2 doses |
none |
none |
|
Standard Therapy | |||
|
Oral Dexamethasone |
20 mg |
none |
none |
|
Oral Ondansetron‡ |
8 mg for 2 doses |
8 mg twice daily |
8 mg twice daily |
*Fosaprepitant for injection placebo and dexamethasone placebo (on Day 1) were used to maintain blinding.
†Dexamethasone was administered 30 minutes prior to chemotherapy treatment on Day 1. The 12 mg dose reflects a dosage adjustment to account for a drug interaction with the fosaprepitant for injection regimen [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
‡The first ondansetron dose was administered 30 to 60 minutes prior to chemotherapy treatment on Day 1 and the second dose was administered 8 hours after first ondansetron dose.
The primary endpoint was complete response (defined as no vomiting and no rescue therapy) in the delayed phase (25 to 120 hours) of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. The results by treatment group are shown in Table 17
Table 17
Percent of Adult Patients Receiving MEC Responding by Treatment Group
|
ENDPOINTS |
Fosaprepitant for Injection Regimen (N = 502)***** % |
Standard Therapy Regimen (N = 498)***** % |
P-Value |
Treatment Difference (95% CI) |
|
PRIMARY ENDPOINT | ||||
|
Complete Response† | ||||
|
Delayed phase‡ |
78.9 |
68.5 |
<0.001 |
10.4 (5.1, 15.9) |
*N: Number of patients included in the intention to treat population.
†Complete Response = no vomiting and no use of rescue therapy.
‡Delayed phase = 25 to 120 hours post-initiation of chemotherapy.
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
Patient Information
Fosaprepitant (FOS-a-PRE-pi-tant)
for Injection
Read this Patient Information before you start receiving fosaprepitant for injection and each time you are scheduled to receive fosaprepitant for injection. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is fosaprepitant for injection?
Fosaprepitant for injection is a prescription medicine used with other medicines that treat nausea and vomiting in patients 18 years of age and older to prevent nausea and vomiting caused by certain anti-cancer (chemotherapy) medicines.
•
Fosaprepitant for injection is not used to treat nausea and vomiting that you already have.
•
It is not known if fosaprepitant for injection is safe and effective in children less than 6 months of age.
Who should not receive fosaprepitant for injection?
Do not receive fosaprepitant for injection if you:
•
are allergic to fosaprepitant, aprepitant, or any of the ingredients in fosaprepitant for injection. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of the ingredients in fosaprepitant for injection.
•
are taking pimozide (ORAP®)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before receiving fosaprepitant for injection?
Before receiving fosaprepitant for injection, tell your healthcare provider if you:
•
have liver problems
•
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if fosaprepitant for injection can harm your unborn baby.
o
Women who use birth control medicines containing hormones to prevent pregnancy (birth control pills, skin patches, implants, and certain IUDs) should also use a backup method of birth control that does not contain hormones, such as condoms and spermicides, during treatment with fosaprepitant for injection and for 1 month after receiving fosaprepitant for injection
•
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if fosaprepitant for injection passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you receive fosaprepitant for injection.
**Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,**including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Fosaprepitant for injection may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect the way fosaprepitant for injection works, causing serious side effects.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider or pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How will I receive fosaprepitant for injection?
Adults 18 years of age and older:
Fosaprepitant for injection will be given on Day 1 of chemotherapy treatment. It will be given to you by intravenous (IV) infusion in your vein about 50 to 60 minutes before you start your chemotherapy treatment.
or
1. Fosaprepitant for injection 115 mg given along with capsules of aprepitant.
o
Day 1 (Day of chemotherapy): Fosaprepitant for injection 115 mg will be given to you by intravenous (IV) infusion in your vein about 30 minutes before you start your chemotherapy treatment.
o
You will get a prescription for two capsules of aprepitant
o
Day 2 and Day 3 (the two days after chemotherapy): Take one 80 mg capsule of aprepitant (white) by mouth, each morning for the 2 days after your chemotherapy treatment.
If you take the blood thinner medicine warfarin sodium (COUMADIN®, JANTOVEN®), your healthcare provider may do blood tests after you receive fosaprepitant for injection to check your blood clotting.
What are the possible side effects of fosaprepitant for injection?
Fosaprepitant for injection may cause serious side effects, including:
•
**Serious allergic reactions.**Allergic reactions can happen with fosaprepitant for injection and may be serious. Tell your doctor or nurse right away if you have hives, rash, itching, flushing or redness of your face or skin, trouble breathing or swallowing, dizziness, a rapid or weak heartbeat, or you feel faint during or soon after you receive fosaprepitant for injection, as you may need emergency medical care.
•
Severe skin reactions, which may include rash, skin peeling, or sores, may occur.
•
Infusion site reactions (ISR) at or near the infusion site have happened with fosaprepitant for injection.
Most severe ISR have happened with a certain type of chemotherapy medicine that can burn or blister your skin (vesicant) with side effects, including pain, swelling and redness. Death of skin tissue (necrosis) has happened in some people getting this type of chemotherapy medicine. Most ISR can happen with the first, second, or third dose and some can last up to 2 weeks or longer. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any infusion site side effects.
In adults, the most common side effects of fosaprepitant for injection include:
•
tiredness
•
diarrhea
•
low white blood cell and red blood cell counts
•
weakness
•
feeling weak or numb in your arms and legs
•
painful, difficult, or changes in your digestion (dyspepsia)
•
urinary tract infection
•
pain in your arms and legs
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of fosaprepitant for injection. For more information ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to Mylan at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
General information about the safe and effective use of fosaprepitant for injection.
If you would like more information about fosaprepitant for injection, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about fosaprepitant for injection that is written for health professionals.For more information about fosaprepitant for injection call 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
What are the ingredients in fosaprepitant for injection?
**Active ingredient:**fosaprepitant dimeglumine
**Inactive ingredients:**edetate disodium, polysorbate 80, lactose anhydrous, sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (for pH adjustment)
Pediatric use information is approved for Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.’s Emend (fosaprepitant) for injection. However, due to Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp., a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
The brands listed are the registered trademarks of their respective owners.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Mylan Institutional LLC
Rockford, IL 61103 U.S.A.
Manufactured by:
Mylan Laboratories Limited
Bangalore, India
MARCH 2020
