Products (6)
Zubsolv
54123-929
NDA204242
NDA (C73594)
SUBLINGUAL
July 1, 2022
Zubsolv
54123-957
NDA204242
NDA (C73594)
SUBLINGUAL
July 1, 2022
Zubsolv
54123-914
NDA204242
NDA (C73594)
SUBLINGUAL
July 1, 2022
Zubsolv
54123-114
NDA204242
NDA (C73594)
SUBLINGUAL
July 1, 2022
Zubsolv
54123-986
NDA204242
NDA (C73594)
SUBLINGUAL
July 1, 2022
Zubsolv
54123-907
NDA204242
NDA (C73594)
SUBLINGUAL
July 1, 2022
Drug Labeling Information
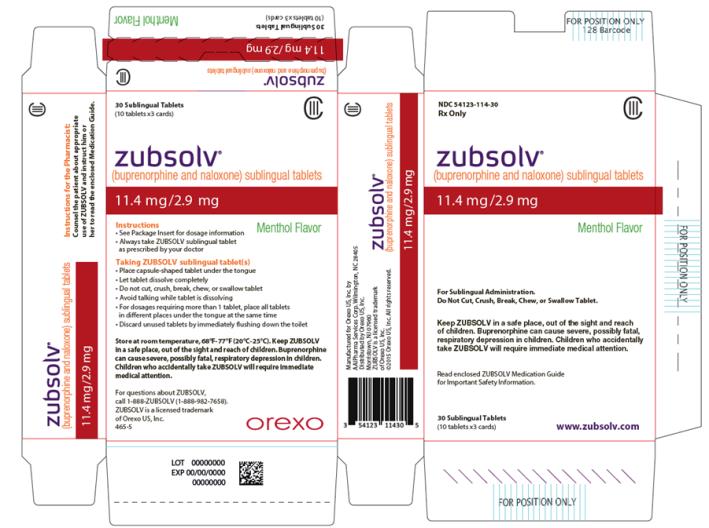
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 54123-114-30****
Rx Only
CIII
zubsolv**®**
(buprenorphine and naloxone) sublingual tablets
11.4 mg/2.9 mg
Menthol Flavor
For Sublingual Administration.****
Do Not Cut, Crush, Break, Chew, or Swallow Tablet.****
Keep ZUBSOLV in a safe place, out of the sight and reach of children.
Buprenorphine can cause severe, possibly fatal, respiratory depression in
children. Children who accidentally take ZUBSOLV will require immediate
medical attention.
Read enclosed ZUBSOLV Medication Guide for Important Safety Information.
30 Sublingual Tablets
(10 tablets x3 cards)
www.zubsolv.com
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
Highlight: Dosage and Administration (2.4) 05/2025
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration (2.4) 05/2025
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
1****INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2****DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
2.2 Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid
Overdose
2.3 Induction
2.4 Maintenance
2.5 Method of Administration
2.6 Clinical Supervision
2.7 Unstable Patients
2.8 Discontinuing Treatment
2.9 Switching between ZUBSOLV Sublingual Tablets and Other
Buprenorphine/Naloxone Combination Products
3****DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4****CONTRAINDICATIONS
5****WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Addiction, Abuse and Misuse
5.2 Risk of Life-Threatening Respiratory and Central Nervous System (CNS)
Depression
5.3 Managing Risks from Concomitant Use of Benzodiazepines or Other CNS
Depressants
5.4 Unintentional Pediatric Exposure
5.5 Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal Syndrome
5.6 Adrenal Insufficiency
5.7 Risk of Opioid Withdrawal with Abrupt Discontinuation
5.8 Risk of Hepatitis, Hepatic Events
5.9 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.10 Precipitation of Opioid Withdrawal Signs and Symptoms
5.11 Risk of Overdose in Opioid Naïve Patients
5.12 Use in Patients with Impaired Hepatic Function
5.13 Dental Adverse Events
5.14 QTc Prolongation
5.15 Impairment of Ability to Drive or Operate Machinery
5.16 Orthostatic Hypotension
5.17 Elevation of Cerebrospinal Fluid Pressure
5.18 Elevation of Intracholedochal Pressure
5.19 Effects in Acute Abdominal Conditions
6****ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
7DRUG INTERACTIONS
8****USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
9****DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10****OVERDOSAGE
11****DESCRIPTION
12****CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13****NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14****CLINICAL STUDIES
16****HOW SUPPLIED / STORAGE AND HANDLING
17****PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11****DESCRIPTION
ZUBSOLV (buprenorphine and naloxone) sublingual tablets are white menthol- flavored tablets in an oval shape for the dosage strength 0.7 mg/0.18 mg, a triangular shape for the dosage strength 1.4 mg /0.36 mg, a D shape for the dosage strength 2.9 mg/0.71 mg, a round shape for the dosage strength 5.7 mg/1.4 mg, a diamond shape for the dosage strength 8.6 mg/2.1 mg and a capsule shape for the dosage strength 11.4 mg/2.9 mg. They are debossed with the respective dosage strength of buprenorphine. They contain buprenorphine HCl, an opioid partial agonist and naloxone HCl dihydrate, an opioid antagonist, at a ratio of 4:1 (ratio of free bases). ZUBSOLV is intended for sublingual administration and is available in six dosage strengths, 0.7 mg buprenorphine with 0.18 mg naloxone, 1.4 mg buprenorphine with 0.36 mg naloxone, 2.9 mg buprenorphine with 0.71 mg naloxone, 5.7 mg buprenorphine with 1.4 mg naloxone, 8.6 mg buprenorphine with 2.1 mg naloxone and 11.4 mg buprenorphine with 2.9 mg naloxone. Each sublingual tablet also contains mannitol, citric acid, sodium citrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, sucralose, menthol, silicon dioxide and sodium stearyl fumarate and menthol flavor.
Chemically, buprenorphine HCl is (2S)-2-[17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4,5α-epoxy-3-hydroxy-6-methoxy-6α,14-ethano-14α-morphinan-7α-yl]-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol hydrochloride. It has the following chemical structure:
![ It has the following chemical structure:Chemically, buprenorphine HCl is (2S)-2-[17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4,5α-epoxy-3-hydroxy-6-methoxy-6α,14-ethano-14α-morphinan-7α-yl]-3,3-dimethylbutan-2-ol hydrochloride.](/dailymed/image.cfm?name=zubsolv-sublingual- tablets-01.jpg&id=876680)
Buprenorphine HCl has the molecular formula C29 H41 NO4 • HCl and the molecular weight is 504.10. It is a white or off-white crystalline powder, sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in cyclohexane.
Chemically, naloxone HCl dihydrate is 17-Allyl-4,5α-epoxy-3,14-dihydroxymorphinan-6-one hydrochloride dihydrate. It has the following chemical structure:
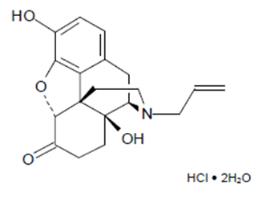
Naloxone HCl dihydrate has the molecular formula C19H21NO4 • HCl • 2H20 and the molecular weight is 399.87. It is a white to slightly off-white powder and is freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, and practically insoluble in toluene and ether.
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
Highlight: ZUBSOLV contains buprenorphine, a partial opioid agonist, and naloxone, an opioid antagonist, and is indicated for treatment of opioid dependence. (1)
ZUBSOLV should be used as part of a complete treatment plan that includes counseling and psychosocial support. (1)
1****INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ZUBSOLV is indicated for treatment of opioid dependence. ZUBSOLV should be used as part of a complete treatment plan that includes counseling and psychosocial support.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
Highlight: * Following induction, ZUBSOLV is administered sublingually as a single daily dose. (2.1)
- Strongly consider prescribing naloxone at the time ZUBSOLV is initiated or renewed because patients being treated for opioid use disorder have the potential for relapse, putting them at risk for opioid overdose. (2.2)
- To avoid precipitating withdrawal, induction with ZUBSOLV should be undertaken when objective and clear signs of withdrawal are evident and Zubsolv should be administered in divided doses when used as initial treatment. (2.3)
- For patients dependent on short-acting opioid products who are in opioid withdrawal; on Day 1, administer up to 5.7 mg/1.4 mg of Zubsolv (in divided doses). On Day 2, administer up to a total dose of 11.4 mg/2.9 mg of Zubsolv as a single dose. (2.3)
- For patients dependent on methadone or long-acting opioid products, induction onto sublingual buprenorphine monotherapy is recommended on Days 1 and 2 of treatment. (2.3)
- The maintenance dose of ZUBSOLV is generally in the range of 2.9 mg/0.71 mg to 17.2 mg/4.2 mg per day and should be based on clinical response. (2.4)
- Administer Zubsolv as directed in the Full Prescribing Information. (2.5)
- When discontinuing treatment, gradually taper to avoid signs and symptoms of withdrawal. (2.8)
2****DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
The difference in bioavailability of ZUBSOLV compared to Suboxone® sublingual tablet requires a different tablet strength to be given to the patient. One ZUBSOLV 5.7 mg/1.4 mg sublingual tablet provides equivalent buprenorphine exposure to one Suboxone 8 mg/2 mg sublingual tablet.
Medication should be prescribed in consideration of the frequency of visits. Provision of multiple refills is not advised early in treatment or without appropriate patient follow-up visits.
2.2 Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid
Overdose
Discuss the availability of naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose with the patient and caregiver. Because patients being treated for opioid use disorder have the potential for relapse, putting them at risk for opioid overdose, strongly consider prescribing naloxone for the emergency treatment of opioid overdose, both when initiating and renewing treatment with ZUBSOLV. Also consider prescribing naloxone if the patient has household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or opioid overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Advise patients and caregivers that naloxone may also be administered for a known or suspected overdose with ZUBSOLV itself. Higher than normal doses and repeated administration of naloxone may be necessary due to the long duration of action of ZUBSOLV and its affinity for the mu receptor [see Overdosage (10)].
Inform patients and caregivers of their options for obtaining naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program) [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
2.3 Induction
Prior to induction, consideration should be given to the type of opioid dependence i.e., long- or short-acting opioid products, the time since last opioid use, and the degree or level of opioid dependence.
Patients dependent on heroin or other short-acting opioid products
Patients dependent on heroin or other short-acting opioid products may be induced with either ZUBSOLV or with sublingual buprenorphine monotherapy. At treatment initiation, the first dose of ZUBSOLV should be administered when objective signs of moderate opioid withdrawal appear, not less than six hours after the patient last used opioids, to avoid precipitating an opioid withdrawal syndrome.
It is recommended that an adequate treatment dose, titrated to clinical effectiveness, be achieved as rapidly as possible. In some studies, a too- gradual induction over several days led to a high rate of drop-out of buprenorphine patients during the induction period.
On Day 1, an induction dosage of up to 5.7 mg/1.4 mg ZUBSOLV is recommended. Clinicians should start with an initial dose of 1.4 mg/0.36 mg ZUBSOLV. The remainder of the Day 1 dose of up to 4.2 mg/1.08 mg should be divided into doses of 1 to 2 tablets of 1.4 mg/0.36 mg at 1.5 to 2 hour intervals. Some patients (e.g., those with recent exposure to buprenorphine) may tolerate up to 3 x 1.4 mg/0.36 mg ZUBSOLV as a single, second dose.
On Day 2, a single daily dose of up to 11.4 mg/2.9 mg ZUBSOLV is recommended.
Patients dependent on methadone or long-acting opioid products
Patients dependent on methadone or long-acting opioid products may be more susceptible to precipitated and prolonged withdrawal during induction than those on short-acting opioid products.
Buprenorphine/naloxone combination products have not been evaluated in adequate and well-controlled studies for induction in patients who are physically dependent on long-acting opioid products, and the naloxone in these combination products is absorbed in small amounts by the sublingual route and could cause worse precipitated and prolonged withdrawal. For this reason, buprenorphine monotherapy is recommended in patients taking long-acting opioids when used according to approved administration instructions**.** Following induction, the patient may then be transitioned to once-daily ZUBSOLV.
2.4 Maintenance
- The dosage of ZUBSOLV from Day 3 onwards should be progressively adjusted in increments/decrements of 2.9 mg/0.71 mg or lower of buprenorphine/naloxone to a level that holds the patient in treatment and suppresses opioid withdrawal signs and symptoms.
- After treatment induction to the recommended dose of 11.4 mg/2.9 mg buprenorphine/naloxone per day, dosing should be further adjusted based on the individual patient and clinical response. The maintenance dose of ZUBSOLV is generally in the range of 2.9 mg/0.71 mg buprenorphine/naloxone to 17.2 mg/4.2 mg buprenorphine/naloxone per day. Dosages higher than 17.2 mg/4.2 mg buprenorphine/naloxone daily have not been investigated in randomized clinical trials but may be appropriate for some patients.
- When determining the prescription quantity for unsupervised administration, consider the patient’s level of stability, the security of his or her home situation, and other factors likely to affect the ability to manage supplies of take-home medication.
- There is no maximum recommended duration of maintenance treatment. Patients may require treatment indefinitely and should continue for as long as patients are benefiting and the use of ZUBSOLV contributes to the intended treatment goals.
2.5 Method of Administration
ZUBSOLV must be administered whole. Do not cut, chew, or swallow ZUBSOLV. Advise patients not to eat or drink anything until the tablet is completely dissolved. ZUBSOLV should be placed under the tongue until dissolved. The dissolve time for ZUBSOLV varies between individuals, and the median dissolve time observed was 5 minutes. For dosages requiring more than one sublingual tablet, place all tablets in different places under the tongue at the same time. Patients should keep the tablets under the tongue until dissolved; swallowing the tablets reduces the bioavailability of the drug. To ensure consistency in bioavailability, patients should follow the same manner of dosing with continued use of the product.
If a sequential mode of administration is preferred, patients should follow the same manner of dosing to ensure consistency in bioavailability.
Proper administration technique should be demonstrated to the patient.
Advise patients to do the following after the product has completely dissolved in the oral mucosa: take a sip of water, swish gently around the teeth and gums, and swallow. Advise patients to wait for at least one hour after taking Zubsolv before brushing teeth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13.), Postmarketing Experience (6.2), Information for Patients (17), and the Medication Guide].
2.6 Clinical Supervision
Treatment should be initiated with supervised administration, progressing to unsupervised administration as the patient’s clinical stability permits. ZUBSOLV is subject to diversion and abuse. When determining the prescription quantity for unsupervised administration, consider the patient’s level of stability, the security of his or her home situation, and other factors likely to affect the ability to manage supplies of take-home medication.
Ideally patients should be seen at reasonable intervals (e.g., at least weekly during the first month of treatment) based upon the individual circumstances of the patient. Medication should be prescribed in consideration of the frequency of visits. Provision of multiple refills is not advised early in treatment or without appropriate patient follow-up visits. Periodic assessment is necessary to determine compliance with the dosing regimen, effectiveness of the treatment plan, and overall patient progress.
Once a stable dosage has been achieved and patient assessment (e.g., urine drug screening) does not indicate illicit drug use, less frequent follow-up visits may be appropriate. A once-monthly visit schedule may be reasonable for patients on a stable dosage of medication who are making progress toward their treatment objectives. Continuation or modification of pharmacotherapy should be based on the healthcare provider’s evaluation of treatment outcomes and objectives such as:
- Absence of medication toxicity
- Absence of medical or behavioral adverse effects
- Responsible handling of medications by the patient
- Patient’s compliance with all elements of the treatment plan (including recovery-oriented activities, psychotherapy, and/or other psychosocial modalities)
- Abstinence from illicit drug use (including problematic alcohol and/or benzodiazepine use)
If treatment goals are not being achieved, the healthcare provider should re- evaluate the appropriateness of continuing the current treatment.
2.7 Unstable Patients
Healthcare providers will need to decide when they cannot appropriately provide further management for particular patients. For example, some patients may be abusing or dependent on various drugs, or unresponsive to psychosocial intervention such that the healthcare provider does not feel that he/she has the expertise to manage the patient. In such cases, the healthcare provider may want to assess whether to refer the patient to a specialist or more intensive behavioral treatment environment. Decisions should be based on a treatment plan established and agreed upon with the patient at the beginning of treatment.
Patients who continue to misuse, abuse, or divert buprenorphine products or other opioids should be provided with, or referred to, more intensive and structured treatment.
2.8 Discontinuing Treatment
The decision to discontinue therapy with ZUBSOLV after a period of maintenance should be made as part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Advise patients of the potential to relapse to illicit drug use following discontinuation of opioid agonist/partial agonist medication-assisted treatment. Taper patients to avoid the occurrence of withdrawal signs and symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
2.9 Switching between ZUBSOLV Sublingual Tablets and Other
Buprenorphine/Naloxone Combination Products
For patients being switched between ZUBSOLV and other buprenorphine/naloxone products dosage adjustments may be necessary. Patients should be monitored for over-medication as well as withdrawal or other signs of under-dosing.
The differences in bioavailability of ZUBSOLV compared to Suboxone tablet require that different tablet strengths be given to the patient. One ZUBSOLV 5.7 mg/1.4 mg sublingual tablet provides equivalent buprenorphine exposure to one Suboxone 8 mg/2 mg sublingual tablet.
When switching between Suboxone dosage strengths and ZUBSOLV dosage strengths the corresponding dosage strengths are:
|
Suboxone sublingual tablets, including generic equivalents |
Corresponding dosage strength of ZUBSOLV sublingual tablets |
|
One 2 mg/0.5 mg sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablet |
One 1.4 mg/0.36 mg ZUBSOLV sublingual tablet |
|
4 mg/1 mg buprenorphine/naloxone taken as: |
One 2.9 mg/0.71 mg ZUBSOLV sublingual tablet |
|
One 8 mg/2 mg sublingual buprenorphine/naloxone tablet |
One 5.7 mg/1.4 mg ZUBSOLV |
|
12 mg/3 mg buprenorphine/naloxone, taken as: |
One 8.6 mg/2.1 mg ZUBSOLV |
|
16 mg/4 mg buprenorphine/naloxone, taken as: |
One 11.4 mg/2.9 mg ZUBSOLV |
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
Highlight: * Lactation: Buprenorphine passes into mother’s milk. (8.2)
-
Geriatric Patients: Monitor for sedation and Respiratory Depression. (8.5)
-
Moderate and Severe Hepatic Impairment: Buprenorphine/naloxone products are not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment and may not be appropriate for patients with moderate hepatic impairment. (8.6)
8****USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The data on use of buprenorphine, one of the active ingredients in ZUBSOLV, in pregnancy, are limited; however, these data do not indicate an increased risk of major malformations specifically due to buprenorphine exposure. There are limited data from randomized clinical trials in women maintained on buprenorphine that were not designed appropriately to assess the risk of major malformations [see Data]. Observational studies have reported on congenital malformations among buprenorphine-exposed pregnancies, but were also not designed appropriately to assess the risk of congenital malformations specifically due to buprenorphine exposure [see Data]. The extremely limited data on sublingual naloxone exposure in pregnancy are not sufficient to evaluate a drug-associated risk.
Reproductive and developmental studies in rats and rabbits identified adverse events at clinically relevant and higher doses. Embryofetal death was observed in both rats and rabbits administered buprenorphine during the period of organogenesis at doses approximately 6 and 0.3 times, respectively, the human sublingual dose of 16 mg/day of buprenorphine. Pre- and post-natal development studies in rats demonstrated increased neonatal deaths at 0.3 times and above and dystocia at approximately 3 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg/day of buprenorphine. No clear teratogenic effects were seen when buprenorphine was administered during organogenesis with a range of doses equivalent to or greater than the human sublingual dose of 16 mg/day of buprenorphine. However, increases in skeletal abnormalities were noted in rats and rabbits administered buprenorphine daily during organogenesis at doses approximately 0.6 and approximately equal to the human sublingual dose of 16 mg/day of buprenorphine, respectively. In a few studies, some events such as acephalus and omphalocele were also observed but these findings were not clearly treatment-related [see Data]. Based on animal data, advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and Embryo-fetal Risk
Untreated opioid addiction in pregnancy is associated with adverse obstetrical outcomes such as low birth weight, preterm birth, and fetal death. In addition, untreated opioid addiction often results in continued or relapsing illicit opioid use.
Dose Adjustment during Pregnancy and the Postpartum Period
Dosage adjustments of buprenorphine, such as using higher doses, may be required during pregnancy, even if the patient was maintained on a stable dose prior to pregnancy. Dosing should be based on individual response, and withdrawal signs and symptoms should be monitored closely and the dose adjusted as necessary.
Fetal/neonatal Adverse Reactions
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome may occur in newborn infants of mothers who are receiving treatment with ZUBSOLV.
Neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome presents as irritability, hyperactivity and abnormal sleep pattern, high pitched cry, tremor, vomiting, diarrhea, and/or failure to gain weight. Signs of neonatal withdrawal usually occur in the first days after birth. The duration and severity of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome may vary. Observe newborns for signs of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome and manage accordingly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Labor or Delivery
Opioid-dependent women on buprenorphine maintenance therapy may require additional analgesia during labor.
Data
Human Data
Studies have been conducted to evaluate neonatal outcomes in women exposed to buprenorphine during pregnancy. Limited data from trials, observational studies, case series, and case reports on buprenorphine use in pregnancy do not indicate an increased risk of major malformations specifically due to buprenorphine. Several factors may complicate the interpretation of investigations of the children of women who take buprenorphine during pregnancy, including maternal use of illicit drugs, late presentation for prenatal care, infection, poor compliance, poor nutrition, and psychosocial circumstances. Interpretation of data is complicated further by the lack of information on untreated opioid-dependent pregnant women, who would be the most appropriate group for comparison. Rather, women on another form of opioid medication-assisted treatment, or women in the general population are generally used as the comparison group. However, women in these comparison groups may be different from women prescribed buprenorphine-containing products with respect to maternal factors that may lead to poor pregnancy outcomes.
In a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, controlled trial [Maternal Opioid Treatment: Human Experimental Research (MOTHER)] designed primarily to assess neonatal opioid withdrawal effects, opioid-dependent pregnant women were randomized to buprenorphine (n=86) or methadone (n=89) treatment, with enrollment at an average gestational age of 18.7 weeks in both groups. A total of 28 of the 86 women in the buprenorphine group (33%) and 16 of the 89 women in the methadone group (18%) discontinued treatment before the end of pregnancy.
Among women who remained in treatment until delivery, there was no difference between buprenorphine-treated and methadone-treated groups in the number of neonates requiring NOWS treatment or in the peak severity of NOWS. Buprenorphine-exposed neonates required less morphine (mean total dose, 1.1 mg vs. 10.4 mg), had shorter hospital stays (10.0 days vs. 17.5 days), and shorter duration of treatment for NOWS (4.1 days vs. 9.9 days) compared to the methadone-exposed group. There were no differences between groups in other primary outcomes (neonatal head circumference,) or secondary outcomes (weight and length at birth, preterm birth, gestational age at delivery, and 1-minute and 5-minute Apgar scores), or in the rates of maternal or neonatal adverse events. The outcomes among mothers who discontinued treatment before delivery and may have relapsed to illicit opioid use are not known. Because of the imbalance in discontinuation rates between the buprenorphine and methadone groups, the study findings are difficult to interpret.
Animal Data
ZUBSOLV has been shown to have differences in bioavailability compared to other buprenorphine/naloxone-containing sublingual products. The exposure margins listed below are based on body surface area comparisons (mg/m2) to the human sublingual dose of 16 mg buprenorphine via Suboxone, which is equivalent to a human sublingual dose of 11.4 mg buprenorphine via ZUBSOLV.
Effects on embryo-fetal development were studied in Sprague-Dawley rats and Russian white rabbits following oral (1:1) and intramuscular (IM) (3:2) administration of mixtures of buprenorphine and naloxone during the period of organogenesis. Following oral administration to rats, no teratogenic effects were observed at buprenorphine doses up to 250 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 150 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg) in the presence of maternal toxicity (mortality). Following oral administration to rabbits, no teratogenic effects were observed at buprenorphine doses up to 40 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 50 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg) in the absence of clear maternal toxicity. No definitive drug-related teratogenic effects were observed in rats and rabbits at IM doses up to 30 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure approximately 20 times and 35 times, respectively, the human sublingual dose of 16 mg). Maternal toxicity resulting in mortality was noted in these studies in both rats and rabbits. Acephalus was observed in one rabbit fetus from the low-dose group and omphalocele was observed in two rabbit fetuses from the same litter in the mid-dose group; no findings were observed in fetuses from the high-dose group. Maternal toxicity was seen in the high-dose group but not at the lower doses where the findings were observed. Following oral administration of buprenorphine to rats, dose- related post-implantation losses, evidenced by increases in the numbers of early resorptions with consequent reductions in the numbers of fetuses, were observed at doses of 10 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure approximately 6 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg). In the rabbit, increased post- implantation losses occurred at an oral dose of 40 mg/kg/day. Following IM administration in the rat and the rabbit, post-implantation losses, as evidenced by decreases in live fetuses and increases in resorptions, occurred at 30 mg/kg/day.
Buprenorphine was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits after IM or subcutaneous (SC) doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 3 and 6 times, respectively, the human sublingual dose of 16 mg), after IV doses up to 0.8 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 0.5 times and equal to, respectively, the human sublingual dose of 16 mg), or after oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day in rats (estimated exposure was approximately 95 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg) and 25 mg/kg/day in rabbits (estimated exposure was approximately 30 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg). Significant increases in skeletal abnormalities (e.g., extra thoracic vertebra or thoraco- lumbar ribs) were noted in rats after SC administration of 1 mg/kg/day and up (estimated exposure was approximately 0.6 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg), but were not observed at oral doses up to 160 mg/kg/day. Increases in skeletal abnormalities in rabbits after IM administration of 5 mg/kg/day (estimated exposure was approximately 6 times the human daily sublingual dose of 16 mg) in the absence of maternal toxicity or oral administration of 1 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure was approximately equal to the human sublingual dose of 16 mg) were not statistically significant.
In rabbits, buprenorphine produced statistically significant pre-implantation losses at oral doses of 1 mg/kg/day or greater and post-implantation losses that were statistically significant at IV doses of 0.2 mg/kg/day or greater (estimated exposure approximately 0.3 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg). No maternal toxicity was noted at doses causing post-implantation loss in this study.
Dystocia was noted in pregnant rats treated intramuscularly with buprenorphine from Gestation Day 14 through Lactation Day 21 at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg). Fertility, pre-, and post-natal development studies with buprenorphine in rats indicated increases in neonatal mortality after oral doses of 0.8 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.5 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg), after IM doses of 0.5 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.3 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg), and after SC doses of 0.1 mg/kg/day and up (approximately 0.06 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg). An apparent lack of milk production during these studies likely contributed to the decreased pup viability and lactation indices. Delays in the occurrence of righting reflex and startle response were noted in rat pups at an oral dose of 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 50 times the human sublingual dose of 16 mg).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on two studies in 13 lactating women, maintained on buprenorphine treatment, buprenorphine and its metabolite norbuprenorphine were present in low levels in human milk and available data have not shown adverse reactions in breastfed infants. There are no data on the combination product buprenorphine/naloxone in breastfeeding, however oral absorption of naloxone is limited. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ZUBSOLV and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from the drug or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Advise the breastfeeding women taking buprenorphine products to monitor the infant for increased drowsiness and breathing difficulties.
Data
Data were consistent from two studies (N=13) of breastfeeding infants whose mothers were maintained on sublingual doses of buprenorphine ranging from 2.4 to 24 mg/day, showing that the infants were exposed to less than 1% of the maternal daily dose.
In a study of six lactating women who were taking a median sublingual buprenorphine dose of 0.29 mg/kg/day 5 to 8 days after delivery, breast milk provided a median infant dose of 0.42 mcg/kg/day of buprenorphine and 0.33 mcg/kg/day of norbuprenorphine, equal to 0.2% and 0.12%, respectively, of the maternal weight-adjusted dose (relative dose/kg (%) of norbuprenorphine was calculated from the assumption that buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine are equipotent).
Data from a study of seven lactating women who were taking a median sublingual buprenorphine dose of 7 mg/day an average of 1.12 months after delivery indicated that the mean milk concentrations (Cavg) of buprenorphine and norbuprenorphine were 3.65 mcg/L and 1.94 mcg/L respectively. Based on the study data, and assuming milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day, an exclusively breastfed infant would receive an estimated mean absolute infant dose (AID) of 0.55 mcg/kg/day of buprenorphine and 0.29 mcg/kg/day of norbuprenorphine, or a mean relative infant dose (RID) of 0.38% and 0.18%, respectively, of the maternal weight-adjusted dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Chronic use of opioids may cause reduced fertility in females and males of reproductive potential. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ZUBSOLV have not been established in pediatric patients. This product is not appropriate for the treatment of neonatal opioid withdrawal syndrome in neonates, because it contains naloxone, an opioid antagonist.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of buprenorphine/naloxone sublingual tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they responded differently than younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience have not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. Due to possible decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy in geriatric patients, the decision to prescribe ZUBSOLV should be made cautiously in individuals 65 years of age or older and these patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of toxicity or overdose.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of buprenorphine and naloxone has been evaluated in a pharmacokinetic study. Both drugs are extensively metabolized in the liver. While no clinically significant changes have been observed in subjects with mild hepatic impairment; the plasma levels have been shown to be higher and half-life values have been shown to be longer for both buprenorphine and naloxone in subjects with moderate and severe hepatic impairment. The magnitude of the effects on naloxone is greater than that on buprenorphine in both moderately and severely impaired subjects. The difference in magnitude of the effects on naloxone and buprenorphine are greater in subjects with severe hepatic impairment than in subjects with moderate hepatic impairment, and therefore the clinical impact of these effects is likely to be greater in patients with severe hepatic impairment than in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Buprenorphine/naloxone products should be avoided in patients with severe hepatic impairment and may not be appropriate for patients with moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
No differences in buprenorphine pharmacokinetics were observed between 9 dialysis-dependent and 6 normal patients following IV administration of 0.3 mg buprenorphine. The effects of renal failure on naloxone pharmacokinetics are unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17****PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Storage and Disposal
Because of the risks associated with accidental ingestion, misuse, and abuse, advise patients to store ZUBSOLV securely, out of sight and reach of children, and in a location not accessible by others, including visitors to the home [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.11), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2)]. Inform patients that leaving ZUBSOLV unsecured can pose a deadly risk to others in the home.
Advise patients and caregivers that when medicines are no longer needed, they should be disposed of promptly. Expired, unwanted, or unused ZUBSOLV should be disposed of by flushing the unused medication down the toilet if a drug take- back option is not readily available. Inform patients that they can visit www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for a complete list of medicines recommended for disposal by flushing, as well as additional information on disposal of unused medicines.
Advise patients to read the FDA-approved patient labeling. (Medication Guide)
Safe Use
Before initiating treatment with ZUBSOLV, explain the points listed below to caregivers and patients. Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide each time ZUBSOLV is dispensed because new information may be available.
- ZUBSOLV must be administered whole. Advise patients not to cut, chew, or swallow ZUBSOLV.
- Inform patients and caregivers that potentially fatal additive effects may occur if ZUBSOLV is used with benzodiazepines or other CNS depressants, including alcohol. Counsel patients that such medications should not be used concomitantly unless supervised by a health care provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3), Drug Interactions (7)].
- Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize respiratory depression and emphasize the importance of calling 911 or getting emergency medical help right away in the event of a known or suspected overdose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Patient Access to Naloxone for the Emergency Treatment of Opioid Overdose
Because patients being treated for opioid use disorder are at risk for relapse, discuss the importance of having access to naloxone with the patient and caregiver. Also discuss the importance of having access to naloxone if there are household members (including children) or other close contacts at risk for accidental ingestion or opioid overdose.
Inform patients and caregivers of the options for obtaining naloxone as permitted by individual state naloxone dispensing and prescribing requirements or guidelines (e.g., by prescription, directly from a pharmacist, or as part of a community-based program).
Educate patients and caregivers on how to recognize the signs and symptoms of an opioid overdose.
Explain to patients and caregivers that naloxone’s effects are temporary, and that they must call 911 or get emergency medical help right away in all cases of known or suspected opioid overdose, even if naloxone is administered. Repeat administration may be necessary, particularly for overdose involving ZUBSOLV, because naloxone is often not effective at the doses available for patient access [Dosage and Administration ( 2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Overdosage (10)].
If naloxone is prescribed, also advise patients and caregivers:
• How to treat with naloxone in the event of an opioid overdose
• To tell family and friends about their naloxone and to keep it in a place where family and friends can easily access it in an emergency
• To read the Patient Information (or other educational material) that will come with their naloxone. Emphasize the importance of doing this before an opioid emergency happens, so the patient and caregiver will know what to do.
- Advise patients that ZUBSOLV contain an opioid that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medications or street drugs, to keep their tablets in a safe place, and to protect them from theft.
- Instruct patients to keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place, out of the sight and reach of children. Accidental or deliberate ingestion by a child may cause respiratory depression that can result in death. Advise patients to seek medical attention immediately if a child is exposed to ZUBSOLV.
- Inform patients that opioids could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition resulting from concomitant administration of serotonergic drugs. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare providers if they are taking, or plan to take serotonergic medications [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Inform patients that opioids could cause adrenal insufficiency, a potentially life-threatening condition. Adrenal insufficiency may present with non-specific symptoms and signs such as nausea, vomiting, anorexia, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, and low blood pressure. Advise patients to seek medical attention if they experience a constellation of these symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Advise patients to never give ZUBSOLV to anyone else, even if he or she has the same signs and symptoms. It may cause harm or death.
- Advise patients that selling or giving away this medication is against the law.
- Advise patients that, after ZUBSOLV has completely dissolved in the oral mucosa, to take a sip of water, swish it gently around their teeth and gums, and swallow. Advise patients to wait for at least one hour after taking ZUBSOLV before brushing teeth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
- Refer patients to dental care services and encourage them to have regular dental checkups while taking ZUBSOLV. Instruct patients to inform their dentist that they have started therapy on ZUBSOLV [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
- Caution patients that ZUBSOLV may impair the mental or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially dangerous tasks such as driving or operating machinery. Caution should be taken especially during drug induction and dose adjustment and until individuals are reasonably certain that buprenorphine therapy does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
- Advise patients not to change the dosage of ZUBSOLV without consulting their healthcare provider.
- Advise patients to take ZUBSOLV once a day, after induction.
- Advise patients that if they miss a dose of ZUBSOLV they should take it as soon as they remember. If it is almost time for the next dose, they should skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time.
- Inform patients that ZUBSOLV can cause drug dependence and that withdrawal signs and symptoms may occur when the medication is discontinued.
- Advise patients seeking to discontinue treatment with buprenorphine for opioid dependence should be advised to work closely with their healthcare provider on a tapering schedule and inform them of the potential to relapse to illicit drug use associated with discontinuation of opioid agonist/partial agonist medication-assisted treatment.
- Advise patients that, like other opioids, ZUBSOLV may produce orthostatic hypotension in ambulatory individuals [see Warnings and Precautions. (5.16)].
- Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider if any other prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or herbal preparations are prescribed or currently being used [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Advise women that if they are pregnant while being treated with ZUBSOLV, the baby may have signs of withdrawal at birth and that withdrawal is treatable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise women who are breastfeeding to monitor the infant for drowsiness and difficulty breathing [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- Inform patients that chronic use of opioids may cause reduced fertility. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Advise patients to inform their family members that, in the event of emergency, the treating healthcare provider or emergency room staff should be informed that the patient is physically dependent on an opioid and that the patient is being treated with ZUBSOLV.
Manufactured for and distributed by Orexo US, Inc.
Morristown, NJ 07960 USA
For patent information: https://orexo.com/operations/us-pharma
ZUBSOLV is a licensed trademark of Orexo US, Inc.
© 2025 Orexo US, Inc. All rights reserved.
Suboxone® is a registered trademark of Indivior UK Limited
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
ZUBSOLV**®****(Zub-solve) (buprenorphine and naloxone) Sublingual Tablet, CIII**
This “Instructions for Use” contains information on how to correctly take ZUBSOLV sublingual tablets.
Important Information You Need to Know Before TakingZUBSOLV sublingual tablets:
- Your healthcare provider should show you how to takeZUBSOLV sublingual tablets the right way.
Preparing to take ZUBSOLV sublingual tablets:
- Follow the same instructions every time you take a dose of ZUBSOLV.
- ZUBSOLV comes in a blister pack with 10 blister units. Each blister unit contains a ZUBSOLV tablet.
- Take the dose prescribed by your doctor as follows:
◦ Pull apart 1 of the blister units from the blister pack by tearing along the dotted lines (perforations) until it is fully separated (See Figure A).

◦ When the blister unit is fully separated, fold the single unit down at dotted line toward the blister (See Figure B).

◦ Slowly tear down at notch to open the blister unit (See Figure C).

◦ Do not push ZUBSOLV tablets through the foil. This could cause the tablet to break.
◦ As soon as you remove your prescribed dose of ZUBSOLV from the blister pack place the tablet under your tongue (See Figures D, E, and F). If more than 1 tablet is required, place the tablets in different places under your tongue at the same time.
◦ Let the tablet dissolve completely. ZUBSOLV usually dissolves in your mouth within 5 minutes. If your mouth is dry, take a sip of water to moisten it. Spit out or swallow the water and dry your hands if they are wet before you place the ZUBSOLV tablet under your tongue.
- While ZUBSOLV is dissolving, do not chew or swallow the tablet because the medicine will not work as well.
- Do not eat or drink anything until the ZUBSOLV tablet has completely dissolved.
- Talking while the tablet is dissolving can affect how well the medicine in ZUBSOLV is absorbed.
- After ZUBSOLV is completely dissolved, rinse your mouth with water and swallow. Wait for at least one hour before brushing teeth.
- If you miss a dose of ZUBSOLV, take your medicine when you remember. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at your regular time. Do not take 2 doses at the same time unless your doctor tells you to. If you are not sure about your dosing, call your doctor.
- Do not stop taking ZUBSOLV suddenly. You could become sick and have withdrawal symptoms because your body has become used to the medicine. Physical dependence is not the same as drug addiction. Your doctor can tell you more about the differences between physical dependence and drug addiction. To have fewer withdrawal symptoms, ask your doctor how to stop using ZUBSOLV the right way.
If you take too much ZUBSOLV go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
Storing ZUBSOLV sublingual tablets?
- Store ZUBSOLV at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep ZUBSOLV in a safe place, out of the**sight*and reach of children.
Disposing of ZUBSOLV sublingual tablets?
- Dispose of expired, unwanted, or unused ZUBSOLV by promptly flushing down the toilet, if a drug take-back option is not readily available. Visit www.fda.gov/drugdisposal for additional information on disposal of unused medicines.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 06/2022
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
Medication Guide |
|
IMPORTANT: Keep ZUBSOLV in a secure place away from children. Accidental use by a child is a medical emergency and can result in death. If a child accidentally uses ZUBSOLV, get emergency help or call 911 right away. Tell your healthcare provider if you are living in a household where there are small children. |
|
What is the most important information I should know about ZUBSOLV?
*Do not take ZUBSOLV with certain medicines. Taking ZUBSOLV with other opioid medicines, benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other central nervous system depressants (including street drugs) can cause severe drowsiness, decreased awareness, breathing problems, coma, and death. *Do not inject (“shoot-up”) ZUBSOLV. Injecting ZUBSOLV may cause life-threatening infections and other serious health problems, Injecting ZUBSOLV may cause sudden serious withdrawal symptoms such as pain, cramps, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, sleep problems, and cravings.
|
|
What is ZUBSOLV?
|
|
Who should not take ZUBSOLV? |
|
What should I tell my doctor before taking ZUBSOLV?
Tell your healthcare provider if you are: ***pregnant or plan to become pregnant.**If you take ZUBSOLV while pregnant, your baby may have symptoms of opioid withdrawal at birth that could be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. ***breastfeeding.**ZUBSOLV can pass into your breast milk and harm your baby. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take ZUBSOLV. Monitor your baby for increased drowsiness and breathing problems if you breastfeed during treatment with ZUBSOLV. Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, or herbal supplements. |
|
How should I take ZUBSOLV?
|
|
What should I avoid while taking ZUBSOLV? ***Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or perform any other dangerous activities until you know how ZUBSOLV affects you.**Buprenorphine can cause drowsiness and slow reaction times. ZUBSOLV can make you sleepy, dizzy, or lightheaded. *You should not drink alcoholor use prescription or over-the-counter medicines that contain alcohol while taking ZUBSOLV, because this can lead to loss of consciousness or even death. |
|
What are the possible side effects of ZUBSOLV? *Trouble breathing. Taking ZUBSOLV with other opioid medicines, benzodiazepines, alcohol, or other central nervous system depressants can cause breathing problems that can lead to coma and death. *Sleepiness, dizziness, and problems with coordination. *Physical dependence or abuse. *Liver problems. Call your healthcare provider right away if you notice any of these symptoms:
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of ZUBSOLV. |
|
Manufactured for and distributed by Orexo US, Inc. Morristown, NJ 07960 USA |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 06/2022
