posaconazole
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use POSACONAZOLE ORAL SUSPENSION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for POSACONAZOLE ORAL SUSPENSION. POSACONAZOLE oral suspension Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
282ddea7-47d8-44e4-8806-169d7cafa951
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 7, 2022
Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
DUNS: 080189610
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
posaconazole
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.2 Prophylaxis of Invasive Aspergillus and Candida Infections
Posaconazole is indicated for the prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections in patients who are at high risk of developing these infections due to being severely immunocompromised, such as hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) or those with hematologic malignancies with prolonged neutropenia from chemotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14.2)] as follows:
•
**Posaconazole oral suspension:** adults and pediatric patients 13 years of age and older
1.3 Treatment of Oropharyngeal Candidiasis Including Oropharyngeal
Candidiasis Refractory to Itraconazole and/or Fluconazole
Posaconazole oral suspension is indicated for the treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis, including oropharyngeal candidiasis refractory to itraconazole and/or fluconazole in adults and pediatric patients 13 years of age and older.
Posaconazole is an azole antifungal indicated as follows:
•
**Posaconazole** is indicated for the prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections in patients who are at high risk of developing these infections due to being severely immunocompromised, such as hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients with graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) or those with hematologic malignancies with prolonged neutropenia from chemotherapy as follows: (1.2)
o
**Posaconazole oral suspension:** adults and pediatric patients 13 years of age and older
•
**Posaconazole oral suspension** is indicated for the treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC), including OPC refractory (rOPC) to itraconazole and/or fluconazole in adult and pediatric patients aged 13 years and older. (1.3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Calcineurin-Inhibitor Toxicity
Concomitant administration of posaconazole with cyclosporine or tacrolimus increases the whole blood trough concentrations of these calcineurin- inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Nephrotoxicity and leukoencephalopathy (including deaths) have been reported in clinical efficacy studies in patients with elevated cyclosporine or tacrolimus concentrations. Frequent monitoring of tacrolimus or cyclosporine whole blood trough concentrations should be performed during and at discontinuation of posaconazole treatment and the tacrolimus or cyclosporine dose adjusted accordingly.
5.2 Arrhythmias and QT Prolongation
Some azoles, including posaconazole, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram. In addition, cases of torsades de pointes have been reported in patients taking posaconazole.
Results from a multiple time-matched ECG analysis in healthy volunteers did not show any increase in the mean of the QTc interval. Multiple, time-matched ECGs collected over a 12-hour period were recorded at baseline and steady- state from 173 healthy male and female volunteers (18 to 85 years of age) administered posaconazole oral suspension 400 mg twice daily with a high-fat meal. In this pooled analysis, the mean QTc (Fridericia) interval change from baseline was –5 msec following administration of the recommended clinical dose. A decrease in the QTc(F) interval (–3 msec) was also observed in a small number of subjects (n=16) administered placebo. The placebo-adjusted mean maximum QTc(F) interval change from baseline was <0 msec (–8 msec). No healthy subject administered posaconazole had a QTc(F) interval ≥500 msec or an increase ≥60 msec in their QTc(F) interval from baseline.
Posaconazole should be administered with caution to patients with potentially proarrhythmic conditions. Do not administer with drugs that are known to prolong the QTc interval and are metabolized through CYP3A4 [see Contraindications (4.3) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.3 Electrolyte Disturbances
Electrolyte disturbances, especially those involving potassium, magnesium or calcium levels, should be monitored and corrected as necessary before and during posaconazole therapy.
5.4 Hepatic Toxicity
Hepatic reactions (e.g., mild to moderate elevations in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase, total bilirubin, and/or clinical hepatitis) have been reported in clinical trials. The elevations in liver tests were generally reversible on discontinuation of therapy, and in some instances these tests normalized without drug interruption. Cases of more severe hepatic reactions including cholestasis or hepatic failure including deaths have been reported in patients with serious underlying medical conditions (e.g., hematologic malignancy) during treatment with posaconazole. These severe hepatic reactions were seen primarily in subjects receiving the posaconazole oral suspension 800 mg daily (400 mg twice daily or 200 mg four times a day) in clinical trials.
Liver tests should be evaluated at the start of and during the course of posaconazole therapy. Patients who develop abnormal liver tests during posaconazole therapy should be monitored for the development of more severe hepatic injury. Patient management should include laboratory evaluation of hepatic function (particularly liver tests and bilirubin). Discontinuation of posaconazole must be considered if clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop that may be attributable to posaconazole.
5.5 Renal Impairment
Due to the variability in exposure with posaconazole oral suspension, patients with severe renal impairment should be monitored closely for breakthrough fungal infections [see Dosage and Administration (2.9) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.6 Midazolam Toxicity
Concomitant administration of posaconazole with midazolam increases the midazolam plasma concentrations by approximately 5-fold. Increased plasma midazolam concentrations could potentiate and prolong hypnotic and sedative effects. Patients must be monitored closely for adverse effects associated with high plasma concentrations of midazolam and benzodiazepine receptor antagonists must be available to reverse these effects [see Drug Interactions (7.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.7 Vincristine Toxicity
Concomitant administration of azole antifungals, including posaconazole, with vincristine has been associated with neurotoxicity and other serious adverse reactions, including seizures, peripheral neuropathy, syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion, and paralytic ileus. Reserve azole antifungals, including posaconazole, for patients receiving a vinca alkaloid, including vincristine, who have no alternative antifungal treatment options [see Drug Interactions (7.10)].
5.9 Breakthrough Fungal Infections
Patients who have severe diarrhea or vomiting should be monitored closely for breakthrough fungal infections when receiving posaconazole.
5.10 Venetoclax Toxicity
Concomitant administration of posaconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, with venetoclax may increase venetoclax toxicities, including the risk of tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), neutropenia, and serious infections. In patients with CLL/SLL, administration of posaconazole during initiation and the ramp-up phase of venetoclax is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.6)]. Refer to the venetoclax labeling for safety monitoring and dose reduction in the steady daily dosing phase in CLL/SLL patients.
For patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML), dose reduction and safety monitoring are recommended across all dosing phases when coadministering posaconazole with venetoclax [see Drug Interactions (7.16)]. Refer to the venetoclax prescribing information for dosing instructions.
•
Calcineurin-Inhibitor Toxicity: Posaconazole increases concentrations of cyclosporine or tacrolimus; reduce dose of cyclosporine and tacrolimus and monitor concentrations frequently. (5.1)
•
Arrhythmias and QTc Prolongation: Posaconazole has been shown to prolong the QTc interval and cause cases of TdP. Administer with caution to patients with potentially proarrhythmic conditions. Do not administer with drugs known to prolong QTc interval and metabolized through CYP3A4. (5.2)
•
Electrolyte Disturbances: Monitor and correct, especially those involving potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg++), and calcium (Ca++), before and during posaconazole therapy. (5.3)
•
Hepatic Toxicity: Elevations in liver tests may occur. Discontinuation should be considered in patients who develop abnormal liver tests or monitor liver tests during treatment. (5.4)
•
Concomitant Use with Midazolam: Posaconazole can prolong hypnotic/sedative effects. Monitor patients and benzodiazepine receptor antagonists should be available. (5.6, 7.5)
•
Vincristine Toxicity: Concomitant administration of azole antifungals, including posaconazole, with vincristine has been associated with neurotoxicity and other serious adverse reactions; reserve azole antifungals, including posaconazole, for patients receiving a vinca alkaloid, including vincristine, who have no alternative antifungal treatment options. (5.7, 7.10)
•
Breakthrough Fungal Infections: Monitor patients with severe diarrhea or vomiting when receiving posaconazole oral suspension. (5.9)
•
Venetoclax Toxicity: Concomitant administration of posaconazole with venetoclax may increase venetoclax toxicities, including the risk of tumor lysis syndrome, neutropenia, and serious infections; monitor for toxicity and reduce venetoclax dose. (4.6, 5.10, 7.16)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Posaconazole is an azole antifungal agent available as an injection solution to be diluted before intravenous administration, delayed-release tablet, oral suspension, and powder for delayed-release oral suspension intended for oral administration.
Posaconazole is designated chemically as 4-[4-[4-[4-[[ (3R,5R)-5-(2,4-difluorophenyl)tetrahydro-5-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl)-3-furanyl]methoxy]phenyl]-1-piperazinyl]phenyl]-2-[(1S,2S)-1-ethyl-2-hydroxypropyl]-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one with an empirical formula of C37H42F2N8O4 and a molecular weight of 700.8. The chemical structure is:

Posaconazole is a white to off-white powder that is practically insoluble in water.
Posaconazole oral suspension is a white to off-white, cherry-brandy flavored immediate-release suspension containing 40 mg of posaconazole per mL and the following inactive ingredients: cherry-brandy flavor, citric acid monohydrate, hydroxyethyl cellulose, glycerin, polyoxyl 35 castor oil, simethicone emulsion, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate, sorbitol solution, titanium dioxide, and water.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Posaconazole Oral Suspension
Posaconazole oral suspension is available as a white to off-white, cherry brandy flavored suspension in 4-ounce (120 mL) amber glass bottles with child- resistant closures containing 105 mL of suspension (40 mg of posaconazole per mL).
NDC 0054-0449-49: Bottle of 105 mL
Supplied with each oral suspension bottle is a plastic dosing spoon calibrated for measuring 2.5-mL and 5-mL doses.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
DO NOT FREEZE.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
Non-substitutable:
Posaconazole oral suspension is not substitutable withposaconazole delayed-release tablets orposaconazole powder for delayed-release oral suspension due to the differences in the dosing of each formulation. Therefore, follow the specific dosage recommendations for the formulation [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
Posaconazole oral suspension:
•
Administer with a full meal or with a liquid nutritional supplement or an acidic carbonated beverage (e.g., ginger ale) in patients who cannot eat a full meal [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
•
Co-administration of drugs that can decrease the plasma concentrations of posaconazole should generally be avoided unless the benefit outweighs the risk. If such drugs are necessary, patients should be monitored closely for breakthrough fungal infections [see Drug Interactions (7.6, 7.7, 7.8, 7.9, 7.13)].
2.2 Dosing Regimen in Adult Patients
Table 1: Dosing Regimens in Adult Patients
|
Indication |
Dose and Frequency |
Duration of Therapy |
|
Prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections |
Posaconazole Oral Suspension: 200 mg (5 mL) three times a day. |
Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression. |
|
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis |
Posaconazole Oral Suspension: Loading dose: 100 mg (2.5 mL) twice a day on the first day. Maintenance dose: 100 mg (2.5 mL) once a day thereafter. |
Loading dose: |
|
OPC Refractory (rOPC) to Itraconazole and/or Fluconazole |
Posaconazole Oral Suspension: 400 mg (10 mL) twice a day. |
Duration of therapy is based on the severity of the patient’s underlying disease and clinical response. |
2.3 Dosing Regimen in Pediatric Patients (ages 13 to less than 18 years of
age)
The recommended dosing regimen of posaconazole oral suspension for pediatric patients ages 13 to less than 18 years of age is shown inTable 3[see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 3: Posaconazole Oral Suspension Dosing Regimens for Pediatric Patients (ages 13 to less than 18 years of age)
|
Indication |
Loading Dose (volume) and frequency |
Maintenance Dose (volume) and frequency |
Duration of Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections |
200 mg (5 mL) three times a day |
200 mg (5 mL) three times a day |
Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression. |
|
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis (OPC) |
100 mg (2.5 mL) twice daily on the first day. |
100 mg (2.5 mL) once daily |
13 days |
|
OPC Refractory (rOPC) to Itraconazole and/or Fluconazole |
400 mg (10 mL) twice daily |
400 mg (10 mL) twice daily |
Duration of therapy is based on the severity of the patient’s underlying disease and clinical response. |
2.6 Administration Instructions for Posaconazole Oral Suspension
•
Shake posaconazole oral suspension well before use. Administer with measured dosing spoon (see Figure 1) provided.
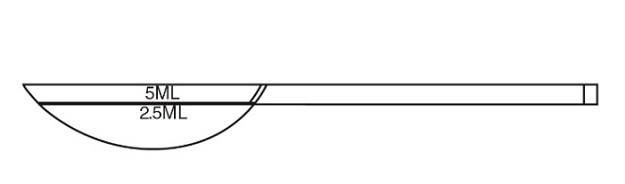
Figure 1: A measured dosing spoon is provided, marked for doses of 2.5 mL and 5 mL.
•
Rinse the spoon with water after each administration and before storage.
•
Administer each dose of posaconazole oral suspension during or immediately (i.e., within 20 minutes) following a full meal [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
•
For patients who cannot eat a full meal, posaconazole delayed-release tablets should be used instead of posaconazole oral suspension for the prophylaxis indication. Posaconzole delayed-release tablets provide higher plasma drug exposures than posaconazole oral suspension under fasted conditions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
•
In patients who cannot eat a full meal and for whom posaconazole delayed-release tablets or posaconazole injection are not options, administer each dose of posaconazole oral suspension with a liquid nutritional supplement or an acidic carbonated beverage (e.g., ginger ale).
•
For patients who cannot eat a full meal or tolerate an oral nutritional supplement or an acidic carbonated beverage and who do not have the option of taking posaconazole delayed-release tablets or posaconazole injection, an alternative antifungal therapy should be considered or patients should be monitored closely for breakthrough fungal infections.
2.7 Non-substitutability between Posaconazole Oral Suspension and Other
Formulations
Posaconazole oral suspension is not substitutable with posaconazole delayed- release tablets or posaconazole powder for delayed-release oral suspension due to the differences in the dosing of each formulation. Therefore, follow the specific dosage recommendations for each of the formulations [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.3)].
2.9 Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of posaconazole oral suspension are not significantly affected by renal impairment. Therefore, no adjustment is necessary for oral dosing in patients with mild to severe renal impairment.
•
**Posaconazole oral suspension** is not substitutable with**posaconazole delayed-release tablets** or**posaconazole powder for delayed-release oral suspension**due to the differences in the dosing of each formulation. Therefore, follow the specific dosage recommendations for the formulation. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)
•
Administer**posaconazole oral suspension** with a full meal (2.1)
|
Table 1: Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients | |
|
Indication |
Dosage Form, Dose, and Duration of Therapy |
|
Prophylaxis of invasive Aspergillus and Candida infections |
Posaconazole Oral Suspension: 200 mg (5 mL) three times a day. Duration of therapy is based on recovery from neutropenia or immunosuppression. (2.2, 2.3) |
|
Oropharyngeal Candidiasis (OPC) |
Posaconazole Oral Suspension: Loading Dose: 100 mg (2.5 mL) twice a day on the first day. Maintenance Dose: 100 mg (2.5 mL) once a day for 13 days. (2.2, 2.3) |
|
OPC Refractory (rOPC) to Itraconazole and/or Fluconazole |
Posaconazole Oral Suspension: 400 mg (10 mL) twice a day. Duration of therapy is based on the severity of the patient’s underlying disease and clinical response. (2.2, 2.3) |
•
For pediatric patients, see the Full Prescribing Information for dosing recommendations for**posaconazole oral suspension** based on the age and indication associated with the dosage form. (1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.3)
