Differin
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DIFFERIN Lotion safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DIFFERIN Lotion. DIFFERIN (adapalene) lotion, for topical use Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
78b3c1f9-0fc2-4075-6cf0-454a492e6ae3
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Apr 19, 2023
Galderma Laboratories, L.P.
DUNS: 047350186
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
adapalene
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Drug Labeling Information
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from clinical trials with DIFFERIN Lotion use in pregnant women
are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects,
miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal
reproduction studies, oral administration of adapalene to pregnant rats and
rabbits during organogenesis at dose exposures 122 and 243 times,
respectively, the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD)
of 2 g resulted in fetal skeletal and visceral malformations (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No malformations were observed in rats treated with oral adapalene doses of
0.15 to 5.0 mg/kg/day, up to 24 times the MRHD based on a mg/m2 comparison.
However, malformations were observed in rats and rabbits when treated with
oral doses of ≥ 25 mg/kg/day adapalene (122 and 243 times the MRHD,
respectively, based on a mg/m2 comparison). Findings included cleft palate,
microphthalmia, encephalocele, and skeletal abnormalities in rats and
umbilical hernia, exophthalmos, and kidney and skeletal abnormalities in
rabbits.
Dermal adapalene embryofetal development studies in rats and rabbits at doses up to 6.0 mg/kg/day (29 and 58 times the MRHD, respectively, based on a mg/m2 comparison) exhibited no fetotoxicity and only minimal increases in skeletal variations (supernumerary ribs in both species and delayed ossification in rabbits).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of topical adapalene lotion or its
metabolite in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects
on milk production. In animal studies, adapalene is present in rat milk with
oral administration of the drug. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is
likely that the drug will be present in human milk. It is possible that
topical administration of large amounts of adapalene could result in
sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk
(see Clinical Considerations). The developmental and health benefits of
breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for
DIFFERIN Lotion and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from
DIFFERIN Lotion or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
To minimize potential exposure to the breastfed infant via breastmilk, use
DIFFERIN Lotion on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration
possible while breastfeeding. Avoid application of DIFFERIN Lotion to areas
with increased risk for potential ingestion by or ocular exposure to the
breastfeeding child.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of DIFFERIN Lotion in pediatric patients under the age of 12 have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of DIFFERIN Lotion did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
DIFFERIN (adapalene) Lotion, for topical use, contains adapalene in a white to off-white oil-in-water emulsion.
Adapalene is a naphthoic acid derivative with retinoid-like properties. The chemical name for adapalene is (6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4methoxyphenyl]- 2-naphthoic acid). Adapalene has the following structural formula:
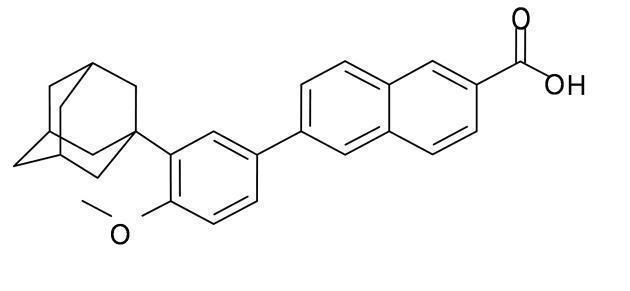
Adapalene:
Molecular formula: C28H28O3 Molecular weight: 412.5
Each gram of DIFFERIN Lotion contains 1 mg of adapalene. The lotion also
contains the following inactive ingredients: carbomer 941, disodium edetate,
medium chain triglycerides, methylparaben, phenoxyethanol, poloxamer 124,
polyoxyl-6-polyoxyl-32 palmitostearate, PPG12/SMDI copolymer, propylene
glycol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium hydroxide, and stearyl alcohol.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Adapalene binds to specific retinoic acid nuclear receptors but does not bind to cytosolic receptor protein. Biochemical and pharmacological profile studies have demonstrated that adapalene is a modulator of cellular differentiation, keratinization and inflammatory processes. However, the significance of these findings with regard to the mechanism of action of adapalene for the treatment of acne is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Pharmacodynamics of DIFFERIN Lotion is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic exposure of adapalene following a topical application of DIFFERIN Lotion was studied in two pharmacokinetic (PK) clinical trials. The first trial was conducted in 14 adult subjects 18 to 29 years of age with severe acne and the second trial was conducted in 13 adolescent subjects 12 to 17 years of age with moderate to severe acne.
In each trial, subjects were treated with 2 g of DIFFERIN Lotion applied once daily to approximately 1000 cm² of acne involved skin for 28 days (adolescent subjects) or 30 days (adult subjects). Serial plasma samples were collected at 24 or 72 hours following application on days 1, 15 and 28/30.
Daily topical application of DIFFERIN Lotion resulted in low systemic exposure to adapalene in the two populations (adult and adolescent subjects). In the adult population, all plasma concentrations in 12 out of 14 subjects were below the limit of quantification (LOQ=0.1 ng/mL). One subject had one sample above LOQ at day 30 and the other subject had four plasma samples above LOQ on both days 1 and 15, which ranged from 0.102 and 0.131 ng/mL.
In the adolescent population, plasma concentrations were quantifiable (>0.1 ng/mL) in five subjects. On Day 28, the mean Cmax was 0.128 ± 0.049 ng/mL (range: <0.100 to 0.244 ng/mL) and the mean of AUC0-24hr was 3.07 ± 1.21 ng.hr/mL (range: 1.86 to 4.93 ng.hr/mL). Adapalene plasma concentrations in all subjects were below the limit of quantification (<0.1 ng/mL) 48 hours after the last application on Day 28.
