Byooviz
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BYOOVIZ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BYOOVIZ. BYOOVIZ™ (ranibizumab-nuna) injection, for intravitreal use Initial U.S. Approval: 2021 BYOOVIZ (ranibizumab-nuna) is biosimilar to LUCENTIS (ranibizumab injection)
e46db299-edd1-4457-89b2-c1e2e505f1b0
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Oct 6, 2023
BIOGEN INC.
DUNS: 121376230
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
ranibizumab-nuna
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
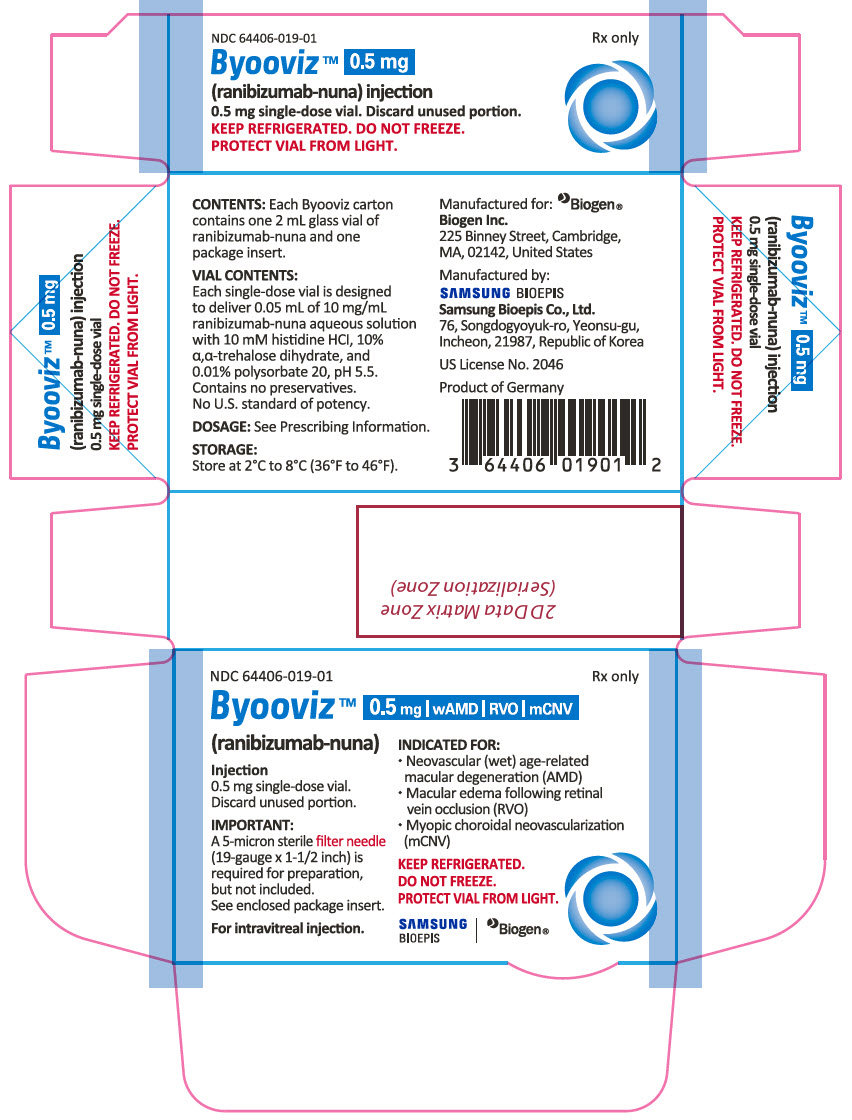
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 0.5 mg Vial Carton
NDC 64406-019-01
Rx only
Byooviz™ 0.5mg wAMD RVO mCNO
(ranibizumab-nuna)
Injection
0.5 mg single-dose vial.
Discard unused portion.
IMPORTANT:
A 5-micron sterilefilter needle (19-gauge x 1-1/2 inch) is required for preparation, but not included.
See enclosed package insert.
For intravitreal injection.
INDICATED FOR:
Neovascular (wet) age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Macular edema following retinal vein occlusion (RVO)
Myopic choroidal neovascularization (mCNV)
KEEP REFRIGERATED.
DO NOT FREEZE.
PROTECT VIAL FROM LIGHT.
SAMSUNG BIOEPIS, Biogen®
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Ocular or Periocular Infections
BYOOVIZ is contraindicated in patients with ocular or periocular infections.
4.2 Hypersensitivity
BYOOVIZ is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to ranibizumab products or any of the excipients in BYOOVIZ. Hypersensitivity reactions may manifest as severe intraocular inflammation.
- Ocular or periocular infections (4.1)
- Hypersensitivity (4.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Endophthalmitis and Retinal Detachments [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Increases in Intraocular Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Thromboembolic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Injection Procedure
Serious adverse reactions related to the injection procedure have occurred in < 0.1% of intravitreal injections, including endophthalmitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)], rhegmatogenous retinal detachment, and iatrogenic traumatic cataract.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of the same or another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data below reflect exposure to 0.5 mg ranibizumab in 440 patients with neovascular AMD in Studies AMD-1, AMD-2, and AMD-3; in 259 patients with macular edema following RVO.
Safety data observed in 224 patients with mCNV, as well as Studies AMD-4 and D-3, were consistent with these results. On average, the rates and types of adverse reactions in patients were not significantly affected by dosing regimen.
Ocular Reactions
Table 1 shows frequently reported ocular adverse reactions in ranibizumab- treated patients compared with the control group.
Table 1 Ocular Reactions in the AMD, and RVO Studies|
Adverse Reaction |
AMD |
AMD |
RVO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ranibizumab |
Control |
Ranibizumab |
Control |
Ranibizumab |
Control | |
|
n=379 |
n=379 |
n=440 |
n=441 |
n=259 |
n=260 | |
|
Conjunctival hemorrhage |
74% |
60% |
64% |
50% |
48% |
37% |
|
Eye pain |
35% |
30% |
26% |
20% |
17% |
12% |
|
Vitreous floaters |
27% |
8% |
19% |
5% |
7% |
2% |
|
Intraocular pressure increased |
24% |
7% |
17% |
5% |
7% |
2% |
|
Vitreous detachment |
21% |
19% |
15% |
15% |
4% |
2% |
|
Intraocular inflammation |
18% |
8% |
13% |
7% |
1% |
3% |
|
Cataract |
17% |
14% |
11% |
9% |
2% |
2% |
|
Foreign body sensation in eyes |
16% |
14% |
13% |
10% |
7% |
5% |
|
Eye irritation |
15% |
15% |
13% |
12% |
7% |
6% |
|
Lacrimation increased |
14% |
12% |
8% |
8% |
2% |
3% |
|
Blepharitis |
12% |
8% |
8% |
5% |
0% |
1% |
|
Dry eye |
12% |
7% |
7% |
7% |
3% |
3% |
|
Visual disturbance or vision blurred |
18% |
15% |
13% |
10% |
5% |
3% |
|
Eye pruritis |
12% |
11% |
9% |
7% |
1% |
2% |
|
Ocular hyperemia |
11% |
8% |
7% |
4% |
5% |
3% |
|
Retinal disorder |
10% |
7% |
8% |
4% |
2% |
1% |
|
Maculopathy |
9% |
9% |
6% |
6% |
11% |
7% |
|
Retinal degeneration |
8% |
6% |
5% |
3% |
1% |
0% |
|
Ocular discomfort |
7% |
4% |
5% |
2% |
2% |
2% |
|
Conjunctival hyperemia |
7% |
6% |
5% |
4% |
0% |
0% |
|
Posterior capsule opacification |
7% |
4% |
2% |
2% |
0% |
1% |
|
Injection site hemorrhage |
5% |
2% |
3% |
1% |
0% |
0% |
Non-Ocular Reactions
Non-ocular adverse reactions with an incidence of ≥ 5% in patients receiving ranibizumab for AMD, and/or RVO and which occurred at a ≥ 1% higher frequency in patients treated with ranibizumab compared to control are shown in Table 2. Though less common, wound healing complications were also observed in some studies.
Table 2 Non-Ocular Reactions in the AMD, and RVO Studies|
Adverse Reaction |
AMD |
AMD |
RVO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ranibizumab |
Control |
Ranibizumab |
Control |
Ranibizumab |
Control | |
|
n=379 |
n=379 |
n=440 |
n=441 |
n=259 |
n=260 | |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
16% |
13% |
8% |
9% |
5% |
4% |
|
Anemia |
8% |
7% |
4% |
3% |
1% |
1% |
|
Nausea |
9% |
6% |
5% |
5% |
1% |
2% |
|
Cough |
9% |
8% |
5% |
4% |
1% |
2% |
|
Constipation |
5% |
7% |
3% |
4% |
0% |
1% |
|
Seasonal allergy |
4% |
4% |
2% |
2% |
0% |
2% |
|
Hypercholesterolemia |
5% |
5% |
3% |
2% |
1% |
1% |
|
Influenza |
7% |
5% |
3% |
2% |
3% |
2% |
|
Renal failure |
1% |
1% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
9% |
8% |
5% |
5% |
2% |
2% |
|
Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
4% |
6% |
3% |
4% |
1% |
0% |
|
Headache |
12% |
9% |
6% |
5% |
3% |
3% |
|
Edema peripheral |
3% |
5% |
2% |
3% |
0% |
1% |
|
Renal failure chronic |
0% |
1% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
|
Neuropathy peripheral |
1% |
1% |
1% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
|
Sinusitis |
8% |
7% |
5% |
5% |
3% |
2% |
|
Bronchitis |
11% |
9% |
6% |
5% |
0% |
2% |
|
Atrial fibrillation |
5% |
4% |
2% |
2% |
1% |
0% |
|
Arthralgia |
11% |
9% |
5% |
5% |
2% |
1% |
|
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
6% |
3% |
3% |
1% |
0% |
0% |
|
Wound healing complications |
1% |
1% |
1% |
0% |
0% |
0% |
6.3 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other ranibizumab products may be misleading.
The pre-treatment incidence of immunoreactivity to ranibizumab was 0%-5% across treatment groups. After monthly dosing with ranibizumab for 6 to 24 months, antibodies to ranibizumab were detected in approximately 1%-9% of patients.
The clinical significance of immunoreactivity to ranibizumab products are unclear at this time. Among neovascular AMD patients with the highest levels of immunoreactivity, some were noted to have iritis or vitritis.
Intraocular inflammation was not observed in patients with RVO patients with the highest levels of immunoreactivity.
6.4 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ranibizumab products. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Ocular: Tear of retinal pigment epithelium among patients with neovascular AMD
- The most common adverse reactions (reported more frequently in ranibizumab treated subjects than control subjects) are conjunctival hemorrhage, eye pain, vitreous floaters, and increased IOP (6.2).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Biogen Inc. at 1-877-422-8360 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 orwww.fda.gov/medwatch.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Animal studies have not been conducted to determine the carcinogenic potential of ranibizumab products. Based on the anti-VEGF mechanism of action of ranibizumab products, treatment with ranibizumab products may pose a risk to reproductive capacity [see Females and Males of Reproductive Potential (8.3)].
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each BYOOVIZ 0.5 mg carton (NDC 64406-019-01) contains a single-dose, 2-mL glass vial designed to deliver 0.05 mL of 10 mg/mL ranibizumab-nuna solution that is clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow.
EACH CARTON IS FOR SINGLE-EYE USE ONLY.
BYOOVIZ should be refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). DO NOT FREEZE. Do not use beyond the date stamped on the label. Protect BYOOVIZ vials from light and store in the original carton until time of use.
Prior to use, the unopened vial can be stored at temperatures up to 86°F (30°C) for up to 72 hours.
