Vesanoid
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VESANOID safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VESANOID.VESANOID (tretinoin) capsules, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 1995
7fed0b42-2098-4418-9977-c373c3ffd24a
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Nov 22, 2023
H2-Pharma, LLC
DUNS: 028473634
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Tretinoin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 61269-750-10
VESANOID
(tretinoin) Capsules
10 mg
Rx only
100 capsules

BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY and DIFFERENTIATION SYNDROME
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VESANOID is indicated for the induction of remission in adults and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) characterized by the presence of the t(15;17) translocation or PML/RARα gene expression, and who are refractory to or who have relapsed from anthracycline chemotherapy or for whom anthracycline-based chemotherapy is contraindicated.
VESANOID is a retinoid indicated for induction of remission in adults and pediatric patients 1 year of age and older with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL), characterized by presence of t(15;17) translocation or presence of PML/RARα gene expression, and who are refractory to or who have relapsed from anthracycline chemotherapy or for whom anthracycline-based chemotherapy is contraindicated. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
VESANOID is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to VESANOID, any of its components, or other retinoids. Reactions have included rash, pruritus, face edema, and dyspnea. [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Hypersensitivity to VESANOID, any of its components, or other retinoids (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Differentiation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Leukocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Intracranial hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Lipid abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia
The safety of VESANOID was evaluated in patients with APL who received VESANOID at a dose of 22.5 mg/m2 orally twice daily [see Clinical Studies (14)].
The most common adverse reactions (≥30%) were headache, fever, skin/mucous membrane dryness, bone pain, malaise, shivering, upper respiratory tract disorders, dyspnea, hemorrhage, infections, nausea/vomiting, rash, peripheral edema, leukocytosis, pain, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, chest discomfort, abdominal pain.
Table 1 summarizes the adverse reactions for patients with APL.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) Occurring in Patients with APL Who Received VESANOID
|
Adverse Reaction |
VESANOID |
|
All Grades (%) | |
|
Nervous system disorders | |
|
Headache |
86 |
|
Dizziness |
20 |
|
Paresthesias |
17 |
|
Anxiety |
17 |
|
Insomnia |
14 |
|
Depression |
14 |
|
Confusion |
11 |
|
General disorders | |
|
Fever |
83 |
|
Skin/mucous membrane dryness |
77 |
|
Malaise |
66 |
|
Shivering |
63 |
|
Peripheral edema |
52 |
|
Pain |
37 |
|
Chest discomfort |
32 |
|
Edema |
29 |
|
Mucositis |
26 |
|
Weight increase |
23 |
|
Anorexia |
17 |
|
Weight decrease |
17 |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | |
|
Bone pain |
77 |
|
Myalgia |
14 |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders | |
|
Upper respiratory tract disorders |
63 |
|
Dyspnea |
60 |
|
Respiratory insufficiency |
26 |
|
Pleural effusion |
20 |
|
Rales |
14 |
|
Expiratory wheezing |
14 |
|
Pneumonia |
14 |
|
Vascular disorders | |
|
Hemorrhage |
60 |
|
Gastrointestinal hemorrhage |
34 |
|
Flushing |
23 |
|
Hypotension |
14 |
|
Hypertension |
11 |
|
Phlebitis |
11 |
|
Infections and infestations | |
|
Infections |
58 |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders | |
|
Nausea/vomiting |
57 |
|
Abdominal pain |
31 |
|
Other gastrointestinal disorders |
26 |
|
Diarrhea |
23 |
|
Constipation |
17 |
|
Dyspepsia |
14 |
|
Abdominal distention |
11 |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | |
|
Rash |
54 |
|
Pruritus |
20 |
|
Increased sweating |
20 |
|
Alopecia |
14 |
|
Skin changes |
14 |
|
Blood and lymphatic system disorders | |
|
Leukocytosis |
49 |
|
Differentiation syndrome1 |
26 |
|
Disseminated intravascular coagulation |
26 |
|
Ear and labyrinth disorders | |
|
Earache or feeling of fullness in the ears |
23 |
|
Cardiac disorders | |
|
Arrhythmias |
23 |
|
Eye disorders | |
|
Visual disturbances |
17 |
|
Ocular disorders |
17 |
|
Renal and urinary disorders | |
|
Renal insufficiency |
11 |
1Differentiation syndrome can be associated with other commonly reported events such as fever, leukocytosis, dyspnea, pneumonia, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, hypotension, edema, weight gain, and renal failure.
Adverse reactions that occurred in <10% of patients who received VESANOID include:
- Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatosplenomegaly (9%), hepatitis (3%), unspecified liver disorder (3%).
- Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Flank pain (9%), bone inflammation (3%).
- Nervous system disorders: Agitation (9%), cerebral hemorrhage (9%), intracranial hypertension (9%), hallucination (6%), abnormal gait, agnosia, aphasia, asterixis, cerebellar edema, cerebellar disorders, convulsions, coma, CNS depression, dysarthria, encephalopathy, facial paralysis, hemiplegia, hyporeflexia, hypotaxia, no light reflex, neurologic reaction, spinal cord disorder, stroke, tremor, leg weakness, unconsciousness, dementia, forgetfulness, somnolence, and slow speech (3% each).
- Renal and urinary disorders: Dysuria (9%), acute renal failure, micturition frequency, renal tubular necrosis, and enlarged prostate (3% each).
- Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Lower respiratory tract disorders (9%), pulmonary infiltration (6%), bronchial asthma, pulmonary edema, larynx edema, and unspecified pulmonary disease (3% each).
- Infections and infestations: Cellulitis (8%).
- Blood and lymphatic system disorders: Lymph disorders (6%).
- Cardiovascular disorders: Cardiac failure (6%), cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, enlarged heart, heart murmur, myocarditis, pericarditis, and secondary cardiomyopathy (3% each).
- Ear and labyrinth disorders: Hearing loss and other unspecified auricular disorders (6%), irreversible hearing loss (<1%).
- General disorders: Face edema (6%), pallor (6%), hypothermia (3%).
- Metabolism and nutrition disorders: Fluid imbalance (6%), acidosis (3%).
- Eye disorders: Changed visual acuity (6%), visual field defects (3%).
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Ascites, ulcer (3% each).
- Vascular disorders: Ischemia and pulmonary hypertension (3% each).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Erythema nodosum, basophilia and hyperhistaminemia, Sweet’s Syndrome, organomegaly, hypercalcemia, pancreatitis, myositis, thrombosis (both venous and arterial), thrombocytosis, genital ulceration and vasculitis, predominantly involving the skin.
The most common adverse reactions (≥30%) are headache, fever, skin/mucous membrane dryness, bone pain, malaise, shivering, upper respiratory tract disorders, dyspnea, hemorrhage, infections, nausea/vomiting, rash, peripheral edema, leukocytosis, pain, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, chest discomfort, abdominal pain (6.1).
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Integrated Therapeutic Solutions at 1-800-978-4082 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. **
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on VESANOID
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
The coadministration of VESANOID with ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, increased tretinoin plasma concentration, which may increase the risk of adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of VESANOID with strong CYP3A inhibitors if possible. Monitor patients taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor with VESANOID more frequently for adverse reactions.
Strong CYP3A Inducers
The coadministration of VESANOID with strong CYP3A4 inducers may decrease tretinoin plasma concentrations, which may reduce its efficacy. Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A inducers if possible.
7.2 Concomitant Use of Products Known to Cause Intracranial Hypertension
Intracranial hypertension has been reported in patients who received VESANOID and concomitant use of other products that can cause intracranial hypertension, such as tetracyclines, may increase the risk. Avoid concomitant use of VESANOID with other products agents that can cause intracranial hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
7.3 Vitamin A
The concomitant use of vitamin A with VESANOID may lead to vitamin A related adverse reactions. Avoid concomitant use of VESANOID with vitamin A.
7.4 Anti-fibrinolytic Agents
Fatal thrombotic complications have been reported in patients who have received VESANOID and concomitant use of anti-fibrinolytic agents may increase the risk. Avoid concomitant use of VESANOID with anti-fibrinolytic agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors and Inducers: Avoid coadministration with strong CYP3A inhibitors and inducers. (7.1)
- Concomitant Use of Products Known to Cause Intracranial Hypertension: Avoid concomitant use with other products that can cause intracranial hypertension. (7.2)
- Vitamin A: Avoid concomitant use with vitamin A. (7.3)
- Anti-fibrinolytic Agents: Avoid concomitant use with anti-fibrinolytic agents. (7.4)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 10 mg, two-tone (lengthwise) with orange-yellow and reddish-brown, imprinted with “10 mg” in black ink
Capsules: 10 mg (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], VESANOID can cause embryo-fetal loss and malformations when administered to a pregnant woman. VESANOID is a retinoid and there is an increased risk of major congenital malformations, spontaneous abortions and premature births following exposure to retinoids during pregnancy in humans. Tretinoin was teratogenic and embryotoxic in mice, rats, hamsters, rabbits and pigtail monkeys at doses less than the human dose on a mg/m2 basis (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
VESANOID is a retinoid and increased spontaneous abortions and major fetal abnormalities related to the use of retinoids have been documented in humans. Reported malformations include abnormalities of the central nervous system, musculoskeletal system, external ear, eye, thymus and great vessels; and facial dysmorphia, cleft palate, and parathyroid hormone deficiency. Some of these abnormalities were fatal.
IQ scores less than 85, with or without obvious CNS abnormalities, have been reported in pediatrics exposed to retinoids in utero.
Animal Data
Tretinoin causes fetal resorptions and a decrease in live fetuses in all animals studied. Gross external, soft tissue and skeletal alterations occurred at doses higher than 0.7 mg/kg/day in mice, 2 mg/kg/day in rats, 7 mg/kg/day in hamsters, and at a dose of 10 mg/kg/day, the only dose tested, in pigtail monkeys (about 1/20, 1/4, and 1/2 and 4 times the human dose, respectively, on a mg/m2 basis).
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of tretinoin in human milk, the effects on the breastfeed child or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from VESANOID in breastfed infants, advise women not to breastfed during treatment with VESANOID and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Use in Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
VESANOID can cause embryo-fetal loss and malformations when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating VESANOID. Females of reproductive potential must have a negative pregnancy test within 1 week prior to initiating VESANOID with a sensitivity of at least 50 mIU/mL.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to abstain continuously from sexual intercourse or to use two effective methods of contraception. Counsel patients to use two effective methods of contraception during treatment with VESANOID and for 1 month after the last dose. Two methods of effective contraception is indicated even where there has been a history of infertility, unless due to hysterectomy. Refer females of reproductive potential to a qualified provider of contraceptive methods, if needed.
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and after treatment with VESANOID and for 1 week after the last dose.
Infertility
Males
Based on testicular toxicities observed in dogs, VESANOID may impair male fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. The reversibility of effect on fertility is unknown.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of VESANOID has been established in pediatric patients 1 year of age and older and the information on this use is discussed throughout the labeling. The maximum tolerated dose is lower in pediatric patients compared to adults. Some pediatric patients experience severe headache and intracranial hypertension, which required management with an analgesic and a lumbar puncture. Dose reduction may be considered for pediatric patients experiencing serious and/or intolerable adverse reactions.
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 1 year of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Across clinical studies of VESANOID, 21% were 60 years and older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients.
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
In case of overdose with VESANOID, reversible signs of hypervitaminosis A (headache, nausea, vomiting, mucocutaneous symptoms) can appear. Overdosage with other retinoids has been associated with transient headache, facial flushing, cheilosis, abdominal pain, dizziness and ataxia. These symptoms have quickly resolved without apparent residual effects.
There is no specific treatment in the case of an overdose; however, it is important that the patient be treated in a special hematological unit.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Tretinoin is a retinoid. The chemical name is all-trans retinoic acid. The molecular formula is C20H28O2 and the molecular weight is 300.44 g/mol. The structural formula is:
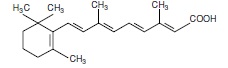
It is a yellow to light orange, crystalline powder with melting point at about 182°C (with decomposition). Tretinoin is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in methylene chloride, and slightly soluble in ethanol (96%).
VESANOID (tretinoin) is available as capsules containing 10 mg tretinoin for oral use. Each capsule also contains yellow beeswax, hydrogenated soya-bean oil, partially hydrogenated soya-bean oil and refined soya-bean oil. The capsule shell contains gelatin, glycerol (85%), dry substance of Karion 83, titanium dioxide, yellow iron oxide, red iron oxide and traces of monogramming ink.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tretinoin induces cytodifferentiation and decreased proliferation of APL cells in culture and in vivo. In APL patients, tretinoin treatment produces an initial maturation of the primitive promyelocytes derived from the leukemic clone, followed by a repopulation of the bone marrow and peripheral blood by normal, polyclonal hematopoietic cells in patients achieving complete remission (CR). The exact mechanism of action of tretinoin in APL is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of VESANOID have not been characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following the administration of VESANOID 22.5 mg/m2 orally twice daily, the mean ± SD peak tretinoin concentrations after the first dose was 394 ± 89 and after 1 week of continuous treatment was 138 ± 139 ng/mL, while area under the curve (AUC) after the first dose was 537 ± 191 ng·h/mL and after 1 week of continuous treatment was 249 ± 185 ng·h/mL.
Absorption
Time to reach peak concentration was between 1 and 2 hours. The absolute bioavailability of VESANOID was approximately 50%.
Effect of Food
The effect of food on the absorption of VESANOID has not been characterized. Food increases the absorption of retinoids, as a class.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of tretinoin has not been determined.
Protein binding is greater than 95%, predominately to albumin. Plasma protein binding remains constant over the concentration range of 10 to 500 ng/mL.
Elimination
The terminal elimination half-life of tretinoin following initial dosing is 0.5 to 2 hours in patients with APL.
Metabolism
Tretinoin induced its own metabolism with plasma concentrations after 1 week of continuous therapy decreased to one-third of their day 1 values. Tretinoin is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, CYP3A4, 2C8, and 2E and undergoes glucuronidation by UGT2B7. Metabolites include 9-cis retinoic acid, 13-cis retinoic acid, 4-oxo trans retinoic acid, 4-oxo cis retinoic acid, and 4-oxo trans retinoic acid glucuronide. The metabolites 4-oxo retinoic acid and 4-oxo trans retinoic acid glucuronide have one-third of the pharmacological activity of the parent compound.
Excretion
Following administration of radiolabeled tretinoin 2.75 mg and 50 mg (0.53 to 9.6 times the approved recommended dosage based on 1.7 m2), approximately 63% of radioactivity was recovered in the urine within 72 hours and 31% appeared in the feces within 6 days.
Specific Populations
The effect of age, sex, race, renal impairment, and hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of tretinoin is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Coadministration of ketoconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased tretinoin AUC by 72%.
In Vitro Studies
Effect of Tretinoin on Transporters: Tretinoin does not inhibit P-gp and BCRP in vitro.
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
VESANOID is supplied as 10 mg, two-tone (lengthwise) orange-yellow and reddish-brown capsules with black print “10 mg” available in:
- 100 count bottles with child-resistant closure NDC# 61269-750-10
Store at 20ºC to 25ºC (68ºF to 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Keep bottle tightly closed. Protect from light.
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise female patients of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use 2 methods of effective contraception during treatment with VESANOID and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with VESANOID and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Differentiation Syndrome
Advise patients that VESANOID can cause differentiation syndrome. Ask patients to immediately report any symptoms suggestive of differentiation syndrome, such as fever, cough or difficulty breathing, decreased urinary output, low blood pressure, rapid weight gain, or swelling of their arms or legs, to their healthcare provider for further evaluation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Patients Without t(15;17) Translocation or PML/RARα Fusion
Advise patients that VESANOID is not recommended for use in patients without t(15;17) translocation or PML/RARα fusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Leukocytosis
Inform patients that rapidly evolving leukocytosis, which can be life- threatening, can occur during treatment with VESANOID [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Intracranial Hypertension
Advise patients that VESANOID can cause intracranial hypertension, especially in pediatric patients. Ask patients to immediately report any symptoms suggestive of intracranial hypertension, such as headache, nausea, vomiting, and visual disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Lipid Abnormalities
Inform patients that hypercholesterolemia and/or hypertriglyceridemia can occur during treatment with VESANOID. Advise patients on the need for monitoring fasting triglycerides and cholesterol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients that VESANOID can cause elevated liver function tests. Advise patients on the need for monitoring of liver function tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Thromboembolic Events
Inform patients that venous and arterial thromboembolic events, including cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction and renal infarct can occur during treatment with VESANOID [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with VESANOID and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Administration Instructions
Advise patients to swallow VESANOID capsules whole with water. Advise patients not to chew, dissolve, or open capsules. Advise patients not to take a missed dose of VESANOID unless it is more than 10 hours until the next scheduled dose. Advise patients that if vomiting occurs after VESANOID administration, that they should not take an additional dose, but continue with the next scheduled dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines
Advise patients that the ability to drive or operate machinery might be impaired when treated with VESANOID, particularly if patients are experiencing dizziness or severe headache.
VESANOID® is a registered trademark of CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH.
Licensed by:
CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH
Ziegelhof 24
17489 Greifswald, Germany
Distributed by:
H2-Pharma, LLC
611 Industrial Park Blvd
Montgomery, AL 36117, USA
© 2019 CHEPLAPHARM Arzneimittel GmbH. All rights reserved.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Information
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating VESANOID. Females of reproductive potential must have a negative pregnancy test before initiating VESANOID [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of VESANOID is 22.5 mg/m2 orally twice daily until complete remission is documented. Discontinue VESANOID 30 days after achievement of complete remission or after 90 days of treatment, whichever occurs first.
Discontinue VESANOID if the t(15;17) translocation or PML/RARα fusion has not been identified [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Take VESANOID with a meal.
Swallow VESANOID capsules whole with water. Do not chew, dissolve, or open capsule.
Do not take a missed dose of VESANOID unless it is more than 10 hours until the next scheduled dose.
If vomiting occurs after VESANOID administration, do not take an additional dose, but continue with the next scheduled dose.
- The recommended dosage of VESANOID is 22.5 mg/m2 orally twice daily until complete remission. (2.2)
- Discontinue 30 days after achievement of complete remission or after 90 days of treatment, whichever occurs first. (2.2)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No 2-year carcinogenicity studies in rodents have been conducted with tretinoin. In a carcinogenicity study, female B5D2F1 mice pretreated with a carcinogen diethylnitrosamine (DEN, intraperitoneal 50 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg) received dietary supplement of all-trans-retinoic acid (tretinoin) for 12 months. Tretinoin at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day in the diet (about 2 times the human dose on a mg/m2 basis) was shown to increase the rate of DEN-induced mouse hepatocellular carcinomas. Tretinoin in combination with 50 mg/kg of DEN also increased the incidence of hemangiomas and hemangiosarcomas.
Tretinoin was negative when tested in the Ames and Chinese hamster V79 cell HGPRT assays for mutagenicity. A 2-fold increase in the sister chromatid exchange (SCE) has been demonstrated in human diploid fibroblasts, but other chromosome aberration assays, including an in vitro assay in human peripheral lymphocytes and an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay, did not show a clastogenic or aneuploidogenic effect.
Adverse effects on fertility and reproductive performance were not observed in studies conducted in rats at doses up to 5 mg/kg/day (about 2/3 the human dose on a mg/m2 basis). In a 6-week toxicology study in dogs, testicular degeneration, with increased numbers of immature spermatozoa, were observed at 10 mg/kg/day (about 4 times the equivalent human dose in mg/m2).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of VESANOID has been evaluated in 114 previously treated patients and in 67 previously untreated (“de novo”) patients with APL in one open- label, uncontrolled single investigator clinical study (Memorial Sloan- Kettering Cancer Center [MSKCC]) and in two cohorts of compassionate cases treated by multiple investigators under the auspices of the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Patients received VESANOID 22.5 mg/m2 orally twice daily for up to 90 days following the first dose or 30 days following achievement of complete remission. Efficacy results are shown Table 2.
Table 2. Efficacy Results in a Controlled Clinical Trial (MSKCC) and Compassionate Use
|
MSKCC |
NCI Cohort 1 |
NCI Cohort 2 | ||||
|
Relapsed N = 20 |
De Novo n = 15 |
Relapsed* N = 48 |
De Novo n = 14 |
Relapsed n = 46 |
De Novo † n = 38 | |
|
Complete Remission |
16 (80%) |
11 (73%) |
24 (50%) |
5 (36%) |
24 (52%) |
26 (68%) |
|
Median Survival (months) |
10.8 |
NR |
5.8 |
0.5 |
8.8 |
NR |
|
Median Follow-up (months) |
9.9 |
42.9 |
5.6 |
1.2 |
8.0 |
13.1 |
NR = Not Reached
NA = Not Available
*Including 9 chemorefractory patients
†Including 8 patients who received chemotherapy but failed to enter remission
The median time to complete remission was between 40 and 50 days (range: 2 to 120 days). Most patients received cytotoxic chemotherapy during the remission phase.
Ten of 15 pediatric cases achieved complete remission (8 of 10 males and 2 of 5 females).
