GLEOLAN
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GLEOLAN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GLEOLAN. GLEOLAN® (aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride) for oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: [1999]
4873911e-a5d7-47e3-9679-fa5c95999323
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 10, 2024
Medexus Pharma, Inc.
DUNS: 078811131
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
AMINOLEVULINIC ACID HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 1,500 mg Vial Carton
NDC 59137-231-01
Rx only
Gleolan ®
(aminolevulinic
acid hydrochloride)
for oral solution
1,500 mg
Reconstitute Prior To Use.
For Oral Use Only
SINGLE-DOSE VIAL.
Discard Unused Portion
One Vial
MEDEXUS
PHARMA
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gleolan is indicated in patients with glioma [suspected World Health Organization (WHO) Grades III or IV on preoperative imaging] as an adjunct for the visualization of malignant tissue during surgery.
Gleolan is an optical imaging agent indicated in patients with glioma (suspected World Health Organization Grades III or IV on preoperative imaging) as an adjunct for the visualization of malignant tissue during surgery. ( 1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Phototoxic Reaction
Due to the risk of phototoxic reactions, do not administer phototoxic drugs (St. John's wort, griseofulvin, thiazide diuretics, sulfonylureas, phenothiazines, sulphonamides, quinolones and tetracyclines), and topical preparations containing ALA for 24 hours during the perioperative period [see Drug Interactions (7)] . Reduce exposure to sunlight or room lights for 48 hours after administration of Gleolan.
5.2 Risk of Misinterpretation
Errors may occur with the use of Gleolan for intraoperative visualization of malignant glioma, including false negatives and false positives. Non- fluorescing tissue in the surgical field does not rule out the presence of tumor in patients with glioma [see Clinical Studies (14)] . Fluorescence may be seen in areas of inflammation or metastases from other tumor types.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including serious hypersensitivity reactions have occurred; these reactions include anaphylactic shock, swelling, and urticaria [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.2)] . Always have cardiopulmonary resuscitation personnel and equipment readily available and monitor all patients for hypersensitivity reactions.
- Phototoxic reactions: Do not administer phototoxic drugs (St. John's wort, griseofulvin, thiazide diuretics, sulfonylureas, phenothiazines, sulphonamides, quinolones and tetracyclines), and topical preparations containing ALA for 24 hours during the perioperative period. Reduce exposure to sunlight or room lights for 48 hours after oral administration of Gleolan. ( 5.1, 7)
- Risk of misinterpretation: Non-fluorescing tissue in the surgical field does not rule out the presence of tumor. ( 5.2, 14)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Phototoxic Drugs
Patients exposed to a photosensitizing agent may experience a phototoxic skin reaction (severe sunburn). Due to the risk of possible phototoxic reactions, avoid administering phototoxic drugs such as St. John's wort, griseofulvin, thiazide diuretics, sulfonylureas, phenothiazines, sulphonamides, quinolones and tetracyclines, and topical preparations containing ALA for 24 hours before and after administration of Gleolan.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Chemical Properties
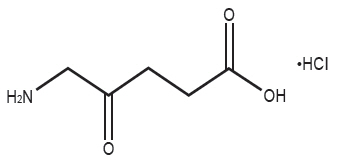
Gleolan (aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride) is an optical imaging agent for oral solution. The 50-mL, clear vial contains 1,500 mg of lyophilized aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride powder (equivalent to 1,170 mg aminolevulinic acid). After reconstitution, the product has a concentration of 30 mg aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride per mL (equivalent to 23.4 mg aminolevulinic acid per mL). The chemical name is 5-amino-4-oxo-pentanoic acid hydrochloride. The chemical formula for aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride is C 5H 10ClNO 3. Its molecular weight is 167.59 g/mol with the following structural formula:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ALA occurs endogenously as a metabolite that is formed in the mitochondria from succinyl-CoA and glycine. Exogenous administration of ALA leads to accumulation of the ALA metabolite PpIX in tumor cells. The reason for the accumulation of PpIX in neoplastic brain tissue is not known.
During glioma surgery, Gleolan is used with an operating microscope adapted with a blue emitting light source (power density 40-80 mW/cm 2) and filters for excitation light of wavelength 375 to 440 nm, and observation at wavelengths of 620 to 710 nm. This allows tumor tissue to be visualized as red fluorescence. Tissue lacking sufficient PpIX concentrations appears blue.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The effect of the timing of the Gleolan dosing on fluorescence intensity in brain tissue is unknown. The relationship between systemic ALA plasma concentrations at the time of visualization and fluorescence intensity in brain is also unknown. The dose of 20 mg / kg provided stronger ALA-induced fluorescence in glioma tissue by both visual and spectrophotometric assessment compared to lower doses tested.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Administration of the approved recommended dose of Gleolan did not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In 12 healthy subjects, the mean half-life of ALA following the recommended dose of Gleolan solution was 0.9 ± 1.2 hours (mean ± std dev) with a range of 0.8 to 1.3 hours. Maximum concentrations of the PpIX metabolite (T maxfor PpIX) occurred with a median of 4 hours and a range of 1.2 to 7.8 hours. The elimination half-life of PpIX was 3.6 ± 1.8 hours (mean ± std dev) with a range of 1.2 to 7.8 hours.
Absorption
In 12 healthy subjects, the absolute bioavailability of ALA following the recommended dose of Gleolan solution was 100.0% ± 1.1 with a range of 78.5% to 131.2%. Maximum ALA plasma concentrations were reached with a median of 0.8 hour (range 0.5 – 1.0 hour).
Distribution
In in vitro experiments using ALA concentrations up to approximately 25% of the maximal concentration that occurs in plasma following the recommended dose of Gleolan solution, the mean protein binding of ALA was 12%.
Elimination
Metabolism
Exogenous ALA is metabolized to PpIX, but the fraction of administered ALA that is metabolized to PpIX is unknown. The average plasma AUC of PpIX is less than 6% of that of ALA.
Excretion
In 12 healthy subjects, excretion of parent ALA in urine in the 12 hours following administration of the recommended dose of Gleolan solution was 34 ± 8% (mean ± std dev) with a range of 27% to 57%.
Specific Populations
The effect of renal or hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of ALA following Gleolan administration is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
In vitro studies suggest that phenytoin and other anti-convulsants may decrease cellular PpIX accumulation following Gleolan dosing.
ALA is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of 20 mg / kg ALA HCl was evaluated in 3 clinical studies (Study 1-3) involving patients, ages 18 to 75 years old, who had a preoperative MRI compatible with high-grade glioma (WHO Grade III or IV) and were undergoing surgical resection.
Study 1 was an open-label study of 33 patients with newly diagnosed high-grade glioma and Study 2 was an open-label study of 36 patients with recurrent high- grade glioma. In Studies 1 and 2, after initial debulking was carried out under white light, biopsies were obtained under fluorescent light from fluorescent and nonfluorescent sites. Presence of fluorescence (positive/negative) was compared to tumor status (true/false) using histopathology as the reference standard. True positives and false positives among fluorescent biopsies and true negatives and false negatives among nonfluorescent biopsies are provided in Table 1.
Study 3 was a randomized, multicenter study in 415 patients with a preoperative diagnosis of high-grade glioma by MRI. Patients were randomized in 1:1 ratio to ALA fluorescence arm or to white light control arm. Biopsies were obtained from tumor-core, tumor-margin and regions just distant to the tumor margins. In 349 patients high grade glioma was confirmed by a blinded central read and histopathology. The remaining patients were diagnosed with metastatic disease, abscess, low-grade glioma or other conditions.
In patients with confirmed high-grade glioma randomized to the ALA fluorescence arm, presence of fluorescence at a biopsy level was compared to tumor status using histopathology as the reference standard (Table 1). In 4 patients with low-grade glioma (WHO Grade I or II) who received ALA HCl, 9 out of 10 biopsies were false negative.
The extent of resection among patients with confirmed high-grade glioma in the ALA fluorescence arm was compared to that among patient in the control arm, with the "completeness" of resection being determined by a central blinded read of early post-surgical MRI. Percentage of patients who had "completeness" of resection was 64% in the ALA arm and 38% in the control arm, with the difference of 26% [95% CI: (16%, 36%)].
Table 1. Presence of Fluorescence Compared to Histopathology (biopsy level)|
Study 1 |
Study 2 |
Study 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Number of Fluorescent Biopsies |
185 |
354 |
319 |
|
True Positive |
178 |
342 |
312 |
|
False Positive |
7 |
12 |
7 |
|
Number of Nonfluorescent Biopsies |
112 |
16 |
160 |
|
True Negative |
27 |
3 |
30 |
|
False Negative |
85 |
13 |
130 |
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Gleolan (NDC 59137-231-01) is supplied as 1,500 mg of lyophilized aminolevulinic acid hydrochloride powder (equivalent to 1,170 mg aminolevulinic acid), for oral solution in a 50-mL clear, colorless, glass vial with a rubber stopper and an aluminum crimp seal.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 25 °C (77 °F); excursions permitted to 15-30 °C (59-86 °F).
