Levemir
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LEVEMIR safely and effectively.See full prescribing information for LEVEMIR. LEVEMIR (insulin detemir) injection, for subcutaneous useInitial U.S. Approval: 2005
9dc15d2d-e707-4014-9834-e202e8fc3089
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
May 3, 2023
A-S Medication Solutions
DUNS: 830016429
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
insulin detemir
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Never Share a LEVEMIR FlexPen, Needle, or Insulin Syringe between
Patients
LEVEMIR FlexPen prefilled pens must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Patients using LEVEMIR vials should never share needles or syringes with another person. Sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
5.2 Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen
Changes in an insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] or hyperglycemia. Repeated insulin injections into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis have been reported to result in hyperglycemia; and a sudden change in the injection site (to an unaffected area) has been reported to result in hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Make any changes to a patient’s insulin regimen under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. Advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to unaffected areas and closely monitor for hypoglycemia. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant antidiabetic products may be needed [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction of insulin, including LEVEMIR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life-threatening or cause death. Hypoglycemia can impair concentration ability and reaction time; this may place the patient and others at risk in situations where these abilities are important (e.g., driving or operating other machinery). LEVEMIR, or any insulin, should not be used during episodes of hypoglycemia [see Contraindications (4)].
Hypoglycemia can happen suddenly and symptoms may differ in each patient and change over time in the same patient. Symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia may be less pronounced in patients with longstanding diabetes, in patients with diabetic neuropathy, using drugs that block the sympathetic nervous system (e.g., beta-blockers) [see Drug Interactions (7)], or who experience recurrent hypoglycemia.
Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
The risk of hypoglycemia generally increases with intensity of glycemic control. The risk of hypoglycemia after an injection is related to the duration of action of the insulin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] and, in general, is highest when the glucose lowering effect of the insulin is maximal. As with all insulins, the glucose lowering effect time course of LEVEMIR may vary among different patients or at different times in the same patient and depends on many conditions, including the area of injection as well as the injection site blood supply and temperature.
Other factors which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia include changes in meal pattern (e.g., macronutrient content or timing of meals), changes in level of physical activity, or changes to concomitant drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)]. When a GLP-1 receptor agonist is used in combination with LEVEMIR, the LEVEMIR dose may need to be lowered or more conservatively titrated to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of hypoglycemia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)].
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Hypoglycemia
Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
5.4 Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors
Accidental mix-ups between insulin products have been reported. To avoid medication errors between LEVEMIR and other insulins, instruct patients to always check the insulin label before each injection.
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulins, including LEVEMIR [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue LEVEMIR; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve. LEVEMIR is contraindicated in patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to insulin detemir or any of the excipients.
5.6 Hypokalemia
All insulins, including LEVEMIR, cause a shift in potassium from the extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia if indicated (e.g., patients using potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum potassium concentrations).
5.7 Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma
Agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention, when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate heart failure. Patients treated with insulin, including LEVEMIR, and a PPAR- gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the PPAR-gamma agonist must be considered.
•
Never Share a LEVEMIR FlexPen, insulin syringe, or needle between patients, even if the needle is changed (5.1).
•
Hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia with changes in insulin regimen: Make changes to a patient’s insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring (5.2).
•
Hypoglycemia: May be life-threatening. Increase frequency of glucose monitoring with changes to: insulin dosage, concomitant drugs, meal pattern, physical activity; and in patients with renal impairment or hepatic impairment or hypoglycemia unawareness (5.3).
•
Hypoglycemia due to medication errors: Accidental mix-ups between insulin products can occur. Instruct patients to check insulin labels before injection (5.4).
•
Hypersensitivity reactions: Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur. Discontinue LEVEMIR, monitor and treat if indicated (5.5).
•
Hypokalemia: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia and treat if indicated (5.6).
•
Fluid retention and heart failure with concomitant use of thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure; consider dosage reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs (5.7).
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Insulin detemir is a long-acting recombinant human insulin analog produced by a process that includes expression of recombinant DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae followed by chemical modification.
Insulin detemir differs from human insulin in that the amino acid threonine in position B30 has been omitted, and a C14 fatty acid chain has been attached to the amino acid B29. Insulin detemir has a molecular formula of C267H402O76N64S6 and a molecular weight of 5.917 kDa. It has the following structure:
Figure 1: Structural Formula of Insulin Detemir
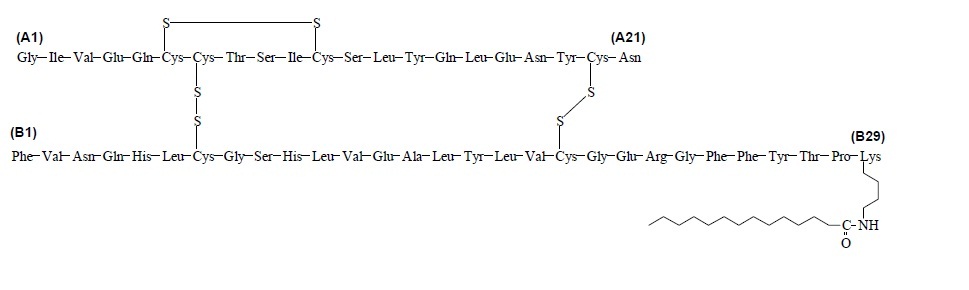
LEVEMIR (insulin detemir) injection is a clear, colorless, aqueous, neutral sterile solution for subcutaneous use. Each milliliter of LEVEMIR contains 100 units insulin detemir, dibasic sodium phosphate (0.71 mg), glycerin (16 mg), metacresol (2.06 mg), phenol (1.8 mg), sodium chloride (1.17 mg), zinc (65.4 mcg), and Water for Injection, USP. Hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide may be added to adjust pH. LEVEMIR has a pH of approximately 7.4.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The primary activity of insulin, including LEVEMIR, is regulation of glucose metabolism. Insulins and its analogs lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake, especially by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulin also inhibits lipolysis and proteolysis, and enhances protein synthesis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Insulin detemir is a soluble, long-acting basal human insulin analog with up to a 24-hour duration of action. The pharmacodynamic profile of LEVEMIR is relatively constant with no pronounced peak.
The duration of action of LEVEMIR is mediated by slowed systemic absorption of insulin detemir molecules from the injection site due to self-association of the drug molecules. In addition, the distribution of insulin detemir to peripheral target tissues is slowed because of binding to albumin.
Figure 2 shows results from a study in patients with type 1 diabetes conducted for a maximum of 24 hours after the subcutaneous injection of LEVEMIR. The mean time between injection and the end of pharmacological effect for insulin detemir ranged from 7.6 hours to >24 hours (24 hours was the end of the observation period).
Figure 2: Glucose Lowering Effect in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes in a 24-hour Glucose Clamp Study
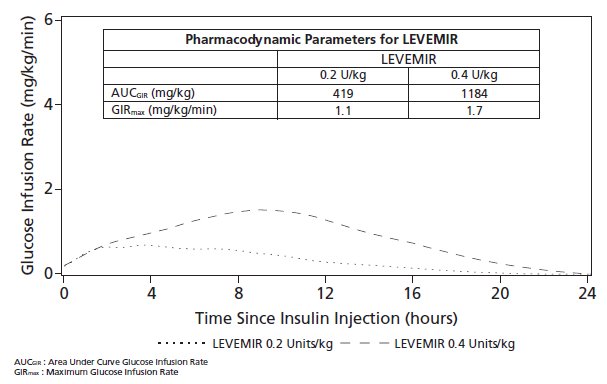
For doses in the interval of 0.2 to 0.4 units/kg, insulin detemir exerts more than 50% of its maximum effect from 3 to 4 hours up to approximately 14 hours after dose administration.
Figure 3 shows glucose infusion rate results from a 16-hour glucose clamp study in patients with type 2 diabetes. The clamp study was terminated at 16 hours according to protocol.
Figure 3: Glucose Lowering Effect in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in a 16-hour Glucose Clamp Study
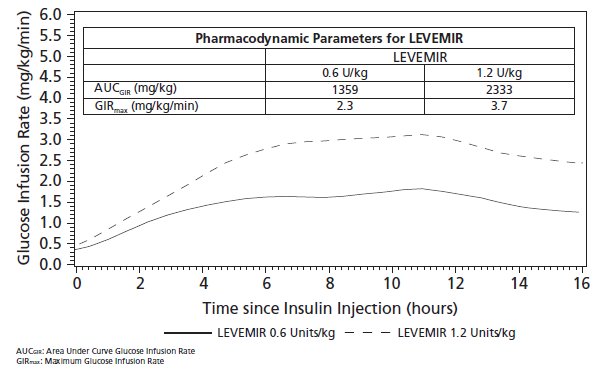
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After subcutaneous injection of LEVEMIR in healthy subjects and in patients with diabetes, insulin detemir serum concentrations had a relatively constant concentration/time profile over 24 hours with the maximum serum concentration (Cmax) reached between 6-8 hours post-dose. Insulin detemir was more slowly absorbed after subcutaneous administration to the thigh where AUC0-5h was 30-40% lower and AUC0-inf was 10% lower than the corresponding AUCs with subcutaneous injections to the deltoid and abdominal regions.
The absolute bioavailability of insulin detemir is approximately 60%.
Distribution
Insulin detemir has an apparent volume of distribution of approximately 0.1 L/kg. More than 98% of insulin detemir in the bloodstream is bound to albumin. The results of in vitro and in vivo protein binding studies demonstrate that there is no clinically relevant interaction between insulin detemir and fatty acids or other protein-bound drugs.
Elimination
After subcutaneous administration in patients with type 1 diabetes, insulin detemir has a terminal half-life of 5 to 7 hours depending on dose.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetic properties of LEVEMIR were studied in pediatric patients 6-12 years, 13-17 years, and adults with type 1 diabetes. In pediatric patients 6-12 years, the insulin detemir plasma area under the curve (AUC) and Cmax were increased by 10% and 24%, respectively, as compared to adults. There was no difference in pharmacokinetics between pediatric patients 13-17 years and adults.
Geriatrics
In a clinical trial studying differences in pharmacokinetics of a single subcutaneous dose of LEVEMIR in young (20 to 35 years) versus elderly (≥68 years) healthy subjects, the insulin detemir AUC was up to 35% higher among the elderly subjects due to reduced clearance [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Gender
No clinically relevant differences in pharmacokinetic parameters of LEVEMIR are observed between males and females.
Race
In two clinical pharmacology studies conducted in healthy Japanese and Caucasian subjects, there were no clinically relevant differences seen in pharmacokinetic parameters. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LEVEMIR were studied in a clamp study comparing patients with type 2 diabetes of Caucasian, African-American, and Latino origin. Dose-response relationships for LEVEMIR were comparable in these three populations.
Renal impairment
A single subcutaneous dose of 0.2 units/kg of LEVEMIR was administered to healthy subjects and those with varying degrees of renal impairment (mild, moderate, severe, and hemodialysis-dependent). In this study, there were no differences in the pharmacokinetics of LEVEMIR between healthy subjects and those with renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic impairment
A single subcutaneous dose of 0.2 units/kg of LEVEMIR was administered to healthy subjects and those with varying degrees of hepatic impairment (mild, moderate and severe). LEVEMIR exposure as estimated by AUC decreased with increasing degrees of hepatic impairment with a corresponding increase in apparent clearance [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Smoking
The effect of smoking on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of LEVEMIR has not been studied.
Liraglutide
No pharmacokinetic interaction was observed between liraglutide and LEVEMIR when separate subcutaneous injections of LEVEMIR 0.5 units/kg (single-dose) and liraglutide 1.8 mg (steady state) were administered in patients with type 2 diabetes.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Standard 2-year carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed. Insulin detemir tested negative for genotoxic potential in the in vitro reverse mutation study in bacteria, human peripheral blood lymphocyte chromosome aberration test, and the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
In a fertility and embryonic development study, insulin detemir was administered to female rats before mating, during mating, and throughout pregnancy at doses up to 300 nmol/kg/day (3 times a human dose of 0.5 units/kg/day, based on plasma AUC ratio). There were no effects on fertility in the rat.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use). There are separate Instructions for Use for the Vials and LEVEMIR FlexPen Prefilled Pen.
Never Share a LEVEMIR FlexPen or Insulin Syringe Between Patients
Advise patients that they must never share a LEVEMIR FlexPen with another person, even if the needle is changed. Advise patients using LEVEMIR vials not to share needles or insulin syringes with another person. Sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia
Inform patients that hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction with insulin. Inform patients of the symptoms of hypoglycemia (e.g., impaired ability to concentrate and react). This may present a risk in situations where these abilities are especially important, such as driving or operating other machinery. Advise patients who have frequent hypoglycemia or reduced or absent warning signs of hypoglycemia to use caution when driving or operating machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise patients that changes in insulin regimen can predispose to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and that changes in insulin regimen should be made under close medical supervision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with LEVEMIR. Inform patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors
Instruct patients to always check the insulin label before each injection to avoid mix-ups between insulin products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Novo Nordisk®, Levemir®, NovoLog®, FlexPen®, and NovoFine® are registered trademarks of Novo Nordisk A/S.
Patent Information: https://www.novonordisk-us.com/products/product- patents.html
© 2005-2022 Novo Nordisk
Manufactured by:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, NJ 08536
U.S. License Number 1261
For information about LEVEMIR contact:
Novo Nordisk Inc.
800 Scudders Mill Road
Plainsboro, New Jersey 08536
1-800-727-6500
www.novonordisk-us.com
