Perforomist
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PERFOROMIST INHALATION SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PERFOROMIST INHALATION SOLUTION. PERFOROMIST (formoterol fumarate) Inhalation Solution Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
fb2fe258-fe2e-47f6-8adf-ca75bf6f90af
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
May 1, 2019
Mylan Specialty L.P.
DUNS: 194775557
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
formoterol fumarate dihydrate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
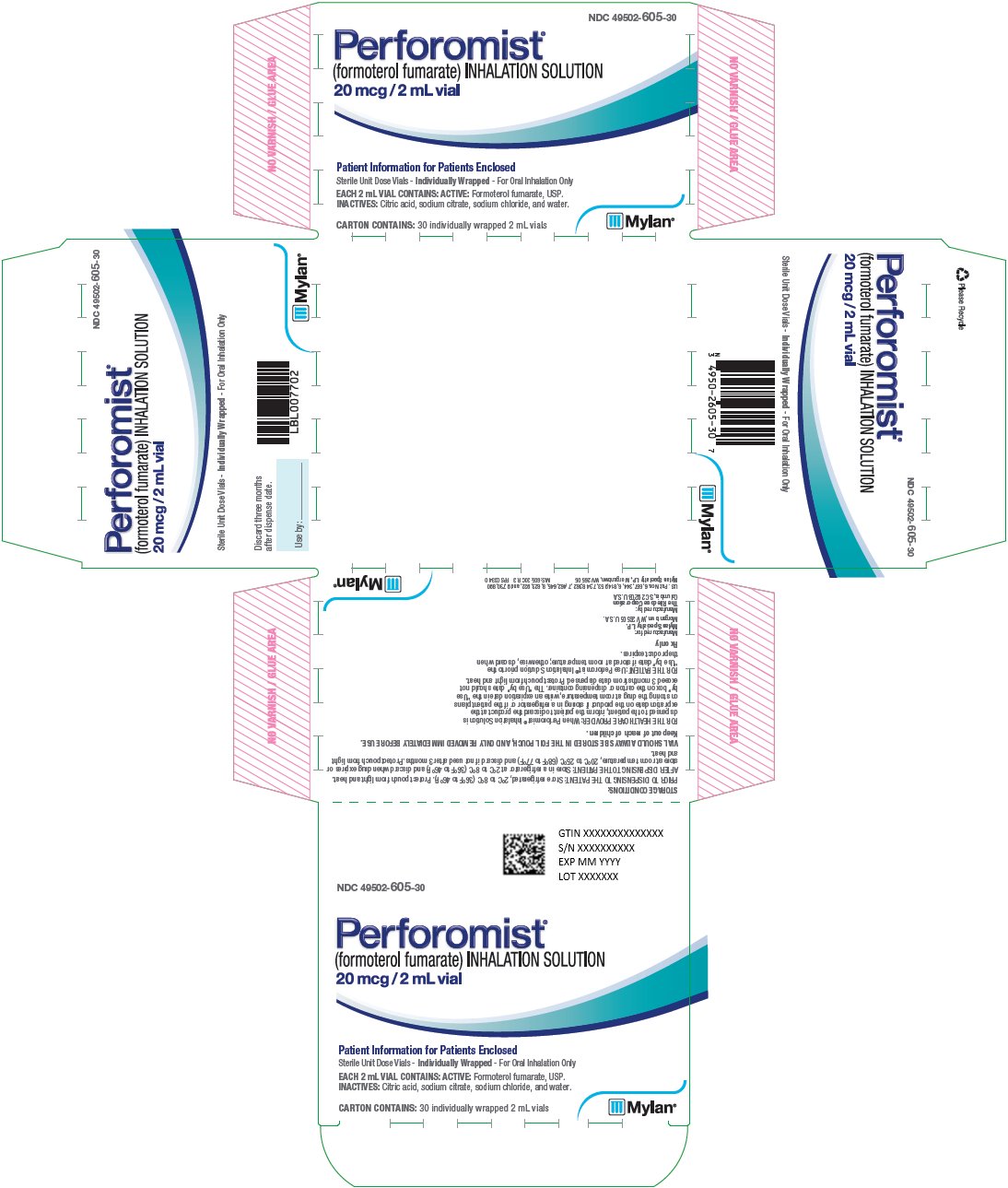
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 20 mcg/2 mL
NDC 49502-605-30
Perforomist**®**
(formoterol fumarate) INHALATION SOLUTION
20 mcg/2 mL vial
Patient Information for Patients Enclosed
Sterile Unit Dose Vials -Individually Wrapped - For Oral Inhalation Only
EACH 2 mL VIAL CONTAINS: ACTIVE: Formoterol fumarate, USP.
INACTIVES: Citric acid, sodium citrate, sodium chloride, and water.
CARTON CONTAINS: 30 individually wrapped 2 mL vials
Discard three months
after dispense date.
Use by: ________
STORAGE CONDITIONS:
PRIOR TO DISPENSING TO THE PATIENT: Store refrigerated, 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect pouch from light and heat.
AFTER DISPENSING TO THE PATIENT: Store in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and discard when drug expires or store at room temperature, 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) and discard if not used after 3 months. Protect pouch from light and heat.
VIAL SHOULD ALWAYS BE STORED IN THE FOIL POUCH, AND ONLY REMOVED IMMEDIATELY BEFORE USE.
Keep out of reach of children.
FOR THE HEALTHCARE PROVIDER: When Perforomist® Inhalation Solution is
dispensed to the patient, inform the patient to discard the product at the
expiration date on the product if storing in a refrigerator or if the patient
plans
on storing the drug at room temperature, write an expiration date in the “Use
by” box on the carton or dispensing container. The “Use by” date should not
exceed 3 months from date dispensed. Protect pouch from light and heat.
FOR THE PATIENT: Use Perforomist® Inhalation Solution prior to the
“Use by” date if stored at room temperature; otherwise, discard when
the product expires.
Rx only
Manufactured for:
Mylan Specialty L.P.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
Manufactured by:
The Ritedose Corporation
Columbia, SC 29203 U.S.A.
U.S. Pat. Nos. 6,667,344, 6,814,953, 7,348,362, 7,462,645, 8,623,922, and 9,730,890
Mylan Specialty L.P., Morgantown, WV 26505
MS:605:30C:R3 RPSC0340
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonists, such as PERFOROMIST, as monotherapy (without an inhaled corticosteroid) for asthma increase the risk of asthma- related events. PERFOROMIST is not indicated for the treatment of asthma** **[see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.1)].
6.1 Beta2-Agonist Adverse Reaction Profile
Adverse reactions to PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution are expected to be similar in nature to other beta2-adrenergic receptor agonists including: angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, dry mouth, muscle cramps, palpitations, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, insomnia, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, and metabolic acidosis.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults with COPD
The data described below reflect exposure to PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution 20 mcg twice daily by oral inhalation in 586 patients, including 232 exposed for 6 months and 155 exposed for at least 1 year. PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution was studied in a 12-week, placebo- and active-controlled trial (123 subjects treated with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution) and a 52-week, active- controlled trial (463 subjects treated with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution). Patients were mostly Caucasians (88%) between 40-90 years old (mean, 64 years old) and had COPD, with a mean FEV1 of 1.33 L. Patients with significant concurrent cardiac and other medical diseases were excluded from the trials.
Table 1 shows adverse reactions from the 12-week, double-blind, placebo- controlled trial where the frequency was greater than or equal to 2% in the PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution group and where the rate in the PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution group exceeded the rate in the placebo group. In this trial, the frequency of patients experiencing cardiovascular adverse events was 4.1% for PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution and 4.4% for placebo. There were no frequently occurring specific cardiovascular adverse events for PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution (frequency greater than or equal to 1% and greater than placebo). The rate of COPD exacerbations was 4.1% for PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution and 7.9% for placebo.
TABLE 1|
Number of patients with adverse reactions in the 12-week multiple-dose controlled clinical trial | ||||
|
Adverse Reaction |
PERFOROMIST |
Placebo | ||
|
n |
(%) |
n |
(%) | |
|
Total Patients |
123 |
(100) |
114 |
(100) |
|
Diarrhea |
6 |
(4.9) |
4 |
(3.5) |
|
Nausea |
6 |
(4.9) |
3 |
(2.6) |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
4 |
(3.3) |
2 |
(1.8) |
|
Dry Mouth |
4 |
(3.3) |
2 |
(1.8) |
|
Vomiting |
3 |
(2.4) |
2 |
(1.8) |
|
Dizziness |
3 |
(2.4) |
1 |
(0.9) |
|
Insomnia |
3 |
(2.4) |
0 |
0 |
Patients treated with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution 20 mcg twice daily in the 52-week open-label trial did not experience an increase in specific clinically significant adverse events above the number expected based on the medical condition and age of the patients.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Anaphylactic reactions, urticaria, angioedema (presenting as face, lip, tongue, eye, pharyngeal, or mouth edema), rash, and bronchospasm
Most common adverse reactions (>2% and more common than placebo) are diarrhea, nausea, nasopharyngitis, dry mouth, vomiting, dizziness, and insomnia (6.2)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Mylan at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Adrenergic Drugs
If additional adrenergic drugs are to be administered by any route, they should be used with caution because the sympathetic effects of formoterol may be potentiated [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.3, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7)].
7.2 Xanthine Derivatives, Steroids, or Diuretics
Concomitant treatment with xanthine derivatives, steroids, or diuretics may potentiate any hypokalemic effect of adrenergic agonists [see WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS (5.7)].
7.3 Non-potassium Sparing Diuretics
The ECG changes and/or hypokalemia that may result from the administration of non-potassium sparing diuretics (such as loop or thiazide diuretics) can be acutely worsened by beta-agonists, especially when the recommended dose of the beta-agonist is exceeded. Although the clinical significance of these effects is not known, caution is advised in the co-administration of beta-agonists with non-potassium sparing diuretics.
7.4 MAO Inhibitors, Tricyclic Antidepressants, QTc Prolonging Drugs
Formoterol, as with other beta2-agonists, should be administered with extreme caution to patients being treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, or drugs known to prolong the QTc interval because the effect of adrenergic agonists on the cardiovascular system may be potentiated by these agents. Drugs that are known to prolong the QTc interval have an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias.
7.5 Beta-blockers
Beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists (beta-blockers) and formoterol may inhibit the effect of each other when administered concurrently. Beta-blockers not only block the therapeutic effects of beta-agonists, but may produce severe bronchospasm in COPD patients. Therefore, patients with COPD should not normally be treated with beta-blockers. However, under certain circumstances, e.g., as prophylaxis after myocardial infarction, there may be no acceptable alternatives to the use of beta-blockers in patients with COPD. In this setting, cardioselective beta-blockers could be considered, although they should be administered with caution.
•
Other adrenergic drugs may potentiate effect. Use with caution. (5.3, 7.1)
•
Xanthine derivatives, steroids, diuretics, or non-potassium sparing diuretics may potentiate hypokalemia or ECG changes. Use with caution. (5.7, 7.2, 7.3)
•
MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants and drugs that prolong QTc interval may potentiate effect on the cardiovascular system. Use with extreme caution. (7.4)
•
Beta-blockers may decrease effectiveness. Use with caution and only when medically necessary. (7.5)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
PERFOROMIST (formoterol fumarate) Inhalation Solution is supplied as 2 mL of formoterol fumarate inhalation solution packaged in a 2.5 mL single-use low- density polyethylene vial and overwrapped in a foil pouch. Each vial contains 2 mL of a clear, colorless solution composed of formoterol fumarate dihydrate, USP equivalent to 20 mcg of formoterol fumarate in an isotonic, sterile aqueous solution containing sodium chloride, pH adjusted to 5.0 with citric acid and sodium citrate.
The active component of PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution is formoterol fumarate dihydrate, USP, a racemate. Formoterol fumarate dihydrate is a beta2-adrenergic bronchodilator. Its chemical name is (±)-2-hydroxy-5-[(1RS)-1-hydroxy-2-[[(1RS)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]-amino]ethyl]formanilide fumarate dihydrate; its structural formula is:
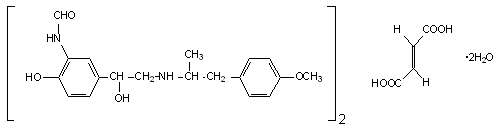
Formoterol fumarate dihydrate, USP has a molecular weight of 840.92 and its empirical formula is (C19H24N2O4)2•C4H4O4•2H2O. Formoterol fumarate dihydrate, USP is a white to yellowish crystalline powder, which is freely soluble in glacial acetic acid, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol and isopropanol, slightly soluble in water, and practically insoluble in acetone, ethyl acetate, and diethyl ether.
PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution does not require dilution prior to administration by nebulization. Like all other nebulized treatments, the amount delivered to the lungs will depend on patient factors and the nebulization system used and its performance.
Using the PARI-LC Plus® nebulizer (with a facemask or mouthpiece) connected to a PRONEB® Ultra compressor under in vitro conditions, the mean delivered dose from the mouthpiece was approximately 7.3 mcg (37% of label claim). The mean nebulizer flow rate was 4 LPM and the nebulization time was 9 minutes. PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution should be administered from a standard jet nebulizer at adequate flow rates via a facemask or mouthpiece.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult COPD Trial
PERFOROMIST (formoterol fumarate) Inhalation Solution was evaluated in a 12-week, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, randomized, parallel- group, multicenter trial conducted in the United States. Of a total enrollment of 351 adults (age range: 40 to 86 years; mean age: 63 years) with COPD who had a mean pre-bronchodilator FEV1 of 1.34 liters (44% of predicted), 237 patients were randomized to PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution 20 mcg or placebo, administered twice daily via a PARI-LC Plus® nebulizer with a PRONEB® Ultra compressor. The diagnosis of COPD was based upon a prior clinical diagnosis of COPD, a smoking history (at least 10 pack-years), age (at least 40 years), and spirometry results (pre-bronchodilator baseline FEV1 at least 30% and less than 70% of the predicted value, and the FEV1/FVC less than 70%). About 58% of patients had bronchodilator reversibility, defined as a 10% or greater increase in FEV1 after inhalation of 2 actuations (180 mcg) of albuterol from a metered dose inhaler. About 86% (106) of patients treated with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution and 74% (84) of placebo patients completed the trial.
PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution 20 mcg twice daily resulted in significantly greater post-dose bronchodilation (as measured by serial FEV1 for 12 hours post-dose; the primary efficacy analysis) compared to placebo when evaluated at endpoint (week 12 for completers and last observation for dropouts). Similar results were seen on Day 1 and at subsequent timepoints during the trial.
Mean FEV1 measurements at Day 1 (Figure 1) and at endpoint (Figure 2) are shown below.
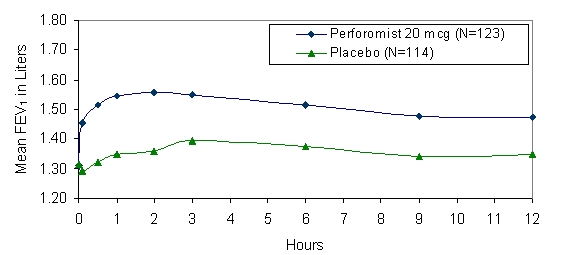
Figure 1 Mean* FEV1 at Day 1
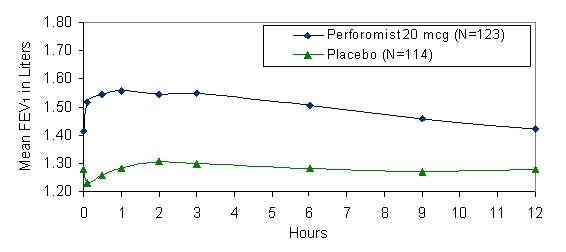
Figure 2 Mean* FEV1 at Endpoint after 12 Weeks of Treatment
* Figures show least-squares means adjusted for baseline FEV1
Patients treated with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution used less rescue albuterol during the trial compared to patients treated with placebo.
Examination of age (≥ 65 or younger) and gender subgroups did not identify differences in response to PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution. There were too few non-Caucasian subjects to assess differences in populations defined by race adequately.
In the 12-week study, 78% of subjects achieved a 15% increase from baseline FEV1 following the first dose of PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution 20 mcg. In these subjects, the median time to onset of bronchodilation, defined as 15% increase in FEV1, was 11.7 minutes. When defined as an increase in FEV1 of 12% and 200 mL, the time to onset of bronchodilation was 13.1 minutes after dosing. The median time to peak bronchodilator effect was 2 hours after dosing.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Serious Asthma-Related Events
Inform patients that long-acting beta agonist, such as PERFOROMIST, when used as monotherapy [without an inhaled corticosteroid], increase the risk of serious asthma-related events, including asthma-related death. PERFOROMIST is not indicated for the treatment of asthma.
Acute Exacerbations or Deteriorations
PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution is not indicated for relief of acute symptoms, and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Acute symptoms should be treated with an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist (the healthcare provider should provide the patient with such medication and instruct the patient in how it should be used). Patients should be instructed to seek medical attention if their symptoms worsen despite recommended doses of PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution, if PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution treatment becomes less effective, or if they need more inhalations of a short-acting beta2-agonist than usual.
Appropriate Dosing
Patients should not stop using PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution unless told to do so by a healthcare provider because symptoms may get worse. Patients should not inhale more than the prescribed number of vials at any one time. The daily dosage of PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution should not exceed one vial twice daily (40 mcg total daily dose). Excessive use of sympathomimetics may cause significant cardiovascular effects and may be fatal.
Concomitant Therapy
Patients who have been taking inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists (e.g., albuterol) on a regular basis should be instructed to discontinue the regular use of these products and use them only for symptomatic relief of acute symptoms. PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution should not be used in conjunction with other inhaled medications containing long-acting beta2-agonists. Patients should be warned not to stop or change the dose of other concomitant COPD therapy without medical advice, even if symptoms improve after initiating treatment with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution.
Common Adverse Reactions with Beta2-agonists
Patients should be informed that treatment with beta2-agonists may lead to adverse reactions that include palpitations, chest pain, rapid heart rate, increased or decreased blood pressure, headache, tremor, nervousness, dry mouth, muscle cramps, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, low blood potassium, high blood sugar, high blood acid, or trouble sleeping [see ADVERSE REACTIONS (6.1)].
Instructions for Administration
It is important that patients understand how to use PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution with a nebulizer appropriately [see the accompanying Patient Information]. Patients should be instructed not to mix other medications with PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution or ingest PERFOROMIST Inhalation Solution. Patients should throw the plastic dispensing container away immediately after use. Due to their small size, the container and top pose a danger of choking to young children.
Manufactured for:
Mylan Specialty L.P.
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.
Manufactured by:
The Ritedose Corporation
Columbia, SC 29203 U.S.A.
U.S. Pat. No. 6,667,344
U.S. Pat. No. 6,814,953
U.S. Pat. No. 7,348,362
U.S. Pat. No. 7,462,645
U.S. Pat. No. 8,623,922
U.S. Pat. No. 9,730,890
FORMIS:R3
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
