Atropine Sulfate
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ATROPINE SULFATE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ATROPINE SULFATE INJECTION. ATROPINE SULFATE injection, for intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intraosseous or endotracheal use. Initial U.S. Approval: 1960
38404931-980b-0019-e063-6394a90a933f
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 23, 2025
ProPharma Distribution
DUNS: 883394285
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Atropine Sulfate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Atropine Sulfate 20 mL Vial Label
NDC 84549-580-20

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Atropine is indicated for temporary blockade of severe or life threatening muscarinic effects, e.g., as an antisialagogue, an antivagal agent, an antidote for organophosphorus, carbamate, or muscarinic mushroom poisoning, and to treat symptomatic bradycardia.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Atropine may cause anaphylaxis.
5.2 Worsening of Ischemic Heart Disease
In patients with ischemic heart disease, the total dose should be restricted to 2 to 3 mg (maximum 0.03 to 0.04 mg/kg) to avoid atropine-induced tachycardia, increased myocardial oxygen demand and the potential for worsening cardiac ischemia or increasing infarction size.
5.3 Acute Glaucoma
Atropine may precipitate acute glaucoma.
5.4 Pyloric Obstruction
Atropine may convert partial organic pyloric stenosis into complete obstruction.
5.5 Complete Urinary Retention
Atropine may lead to complete urinary retention in patients with prostatic hypertrophy.
5.6 Viscid Plugs
Atropine may cause thickening of bronchial secretions and formation of viscid plugs in patients with chronic lung disease.
5.7 Benzyl Alcohol
The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse
events and death in neonates. The "gasping syndrome"(characterized by central
nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, gasping respirations, and high
levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites found in the blood and urine) has
been associated with benzyl alcohol dosages >99 mg/kg/day in neonates and low-
birth weight infants. Additional symptoms may include gradual neurological
deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities,
skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and
cardiovascular collapse.
Although normal therapeutic doses of this product deliver amounts of benzyl
alcohol that are substantially lower than those reported in association with
the "gasping syndrome", the minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which toxicity
may occur is not known. Premature and low-birth weight infants may be more
likely to develop toxicity. Practitioners administering this and other
medications containing benzyl alcohol should consider the combined daily
metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources.
Hypersensitivity ( 5.1)
Worsening of Ischemic Heart Disease ( 5.2)
Acute Glaucoma ( 5.3)
Pyloric obstruction ( 5.4)
Complete urinary retention ( 5.5)
Viscid plugs ( 5.6)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in labeling:
-
Hypersensitivity (5.1)
-
Worsening of Ischemic Heart Disease (5.2)
-
Acute Glaucoma (5.3)
-
Pyloric Obstruction (5.4)
-
Complete Urinary Retention (5.5)
-
Viscid Plugs (5.6)
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use
of atropine sulfate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a
population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate
their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Most of the side effects of atropine are directly related to its
antimuscarinic action. Dryness of the mouth, blurred vision, photophobia and
tachycardia commonly occur. Anhidrosis can produce heat intolerance.
Constipation and difficulty in micturition may occur. Occasional
hypersensitivity reactions have been observed, including serious skin rashes.
Paralytic ileus may occur. Exacerbation of reflux has been reported. Larger or
toxic doses may produce such central effects as restlessness, tremor, fatigue,
locomotor difficulties, delirium, followed by hallucinations, depression, and
ultimately, medullary paralysis and death. Large doses can also lead to
circulatory collapse. In such cases, blood pressure declines and death due to
respiratory failure may ensue following paralysis and coma.
Most adverse reactions are directly related to atropine’s antimuscarinic action. Dryness of the mouth, blurred vision, photophobia and tachycardia commonly occur with chronic administration of therapeutic doses. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Mexiletine
Atropine Sulfate Injection decreased the rate of mexiletine absorption without altering the relative oral bioavailability; this delay in mexiletine absorption was reversed by the combination of atropine and intravenous metoclopramide during pretreatment for anesthesia.
Mexiletine: Decreases rate of mexiletine absorption. ( 7.1)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic or mutagenic potential of atropine or its potential to affect fertility adversely.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Administration
Inspect parenteral drug products for particulate matter and discoloration
prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not
administer unless solution is clear and seal is intact. After initial use,
discard unused portion within 24 hours.
Intravenous administration is usually preferred, but subcutaneous,
intramuscular, endotracheal, and intraosseous administration are possible.
2.2 Adult Dosage
Table 1: Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients
|
Use |
Initial Dose |
Continued Treatment |
|
Antisialagogue or other antivagal (preanesthesia and during surgery) |
0.5 to 1 mg IV/IM/SC 30-60 minutes preoperatively |
Repeat as needed every 4-6 hours. |
|
Organophosphorus, carbamate or muscarinic mushroom poisoning |
1 to 6 mg IV/IM/ET depending on severity of symptoms |
Repeat as needed every |
|
Symptomatic bradycardia* |
0.5 mg IV/IM or 1 to 2 mg ET by diluting in no more than 10 mL sterile water for injection or 0.9% sodium chloride |
As needed every 3 to 5 minutes |
|
IV=intravenous; IM=intramuscular; SC=subcutaneous; ET=endotracheal |
2.3 Pediatric Dosage
Table 2: Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients
|
Use |
Initial Dose |
Continued Treatment |
|
Antisialagogue or other antivagal (preanesthesia and during surgery)* |
0.02 mg/kg IV/IM/SC 30-60 minutes preoperatively |
Repeat as needed every 4-6 hours. Maximum Single Dose Maximum Total Dose |
|
Organophosphorus, carbamate, or muscarinic mushroom poisoning |
0.02 to 0.06 mg/kg IV/IM/IO/ET |
Repeat as needed every 5 minutes Dose may be doubled with each administration until response (reduced
bronchospasm, improved oxygenation and drying of pulmonary secretions). Maximum Total Dose: |
|
Symptomatic bradycardia due to increased vagal tone or primary AV conduction block (not secondary to hypoxia) * * |
0.02 mg/kg IV/IO or |
Repeat as needed every 5 minutes |
|
IV=intravenous; IM=intramuscular; SC=subcutaneous; IO=intraosseous;
ET=endotracheal; |
2.4 Dosing in Patients with Ischemic Heart Disease
Limit the total dose of atropine sulfate to 0.03 to 0.04 mg/kg [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP, 8 mg per 20 mL (0.4 mg per mL), is a non- pyrogenic, isotonic, clear solution and is supplied in a multiple dose glass vial.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited available data with Atropine Sulfate Injection use in pregnant women
are insufficient to inform a drug associated risk of adverse developmental
outcomes (see Data). There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with
untreated severe or life-threatening muscarinic events (see Clinical
Considerations). Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with
Atropine Sulfate Injection.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the
indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of
birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population,
the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in
clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Severe or life-threatening muscarinic events such as acute organophosphate
poisoning and symptomatic bradycardia are medical emergencies in pregnancy
which can be fatal if left untreated. Life-sustaining therapy for the pregnant
woman should not be withheld due to potential concerns regarding the effects
of atropine on the fetus.
Data
Human Data
No adequate and well-controlled studies are available regarding use of
atropine in pregnant women. In a cohort study of 401 pregnancies in the first
trimester and 797 pregnancies in the second or third trimester, atropine use
was not associated with an increased risk of congenital malformation. In a
surveillance study, 381 newborns were exposed to atropine during the first
trimester; 18 major birth defects were observed when 16 were expected. No
specific pattern of major birth defects was identified. In another
surveillance study of 50 pregnancies in the first trimester, atropine use was
not associated with an increased risk of malformations. Methodological
limitations of these observational studies including the inability to control
for the dosage and timing of atropine exposure, underlying maternal disease,
or concomitant maternal drug use, cannot definitively establish or exclude any
drug-associated risk during pregnancy.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Trace amounts of atropine have been reported in human milk after oral intake.
There are no available data on atropine levels in human milk after intravenous
injection, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk
production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear
determination of the risk of atropine to an infant during lactation.
Clinical Considerations
Minimizing exposure
The elimination half-life of atropine is more than doubled in children less
than 2 years of age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].To minimize potential
infant exposure to Atropine Sulfate Injection, a woman may pump and discard
her milk for 24 hours after use before resuming to breastfeed her infant.
8.5 Geriatric Use
An evaluation of current literature revealed no clinical experience identifying differences in response between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Excessive dosing may cause palpitation, dilated pupils, difficulty in
swallowing, hot dry skin, thirst, dizziness, restlessness, tremor, fatigue and
ataxia. Toxic doses lead to restlessness and excitement, hallucinations,
delirium and coma. Depression and circulatory collapse occur only with severe
intoxication. In such cases, blood pressure declines and death due to
respiratory failure may ensue following paralysis and coma.
The fatal adult dose of atropine is not known. In pediatric populations, 10 mg
or less may be fatal.
In the event of toxic overdosage, a short acting barbiturate or diazepam may
be given as needed to control marked excitement and convulsions. Large doses
for sedation should be avoided because central depressant action may coincide
with the depression occurring late in atropine poisoning. Central stimulants
are not recommended.
Physostigmine, given as an atropine antidote by slow intravenous injection of
1 to 4 mg (0.5 to 1 mg in pediatric populations), rapidly abolishes delirium
and coma caused by large doses of atropine. Since physostigmine is rapidly
destroyed, the patient may again lapse into coma after one to two hours, and
repeated doses may be required.
Artificial respiration with oxygen may be necessary. Ice bags and alcohol
sponges help to reduce fever, especially in pediatric populations.
Atropine is not removed by dialysis.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP is a sterile, nonpyrogenic, isotonic, clear solution of atropine sulfate in water for injection with sodium chloride sufficient to render the solution isotonic. It is administered parenterally by subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous injection.
Each mL contains atropine sulfate, 0.4 mg; benzyl alcohol, 9 mg; sodium chloride 9 mg. May contain sulfuric acid for pH adjustment. pH 3.5 (3.0 to 3.8).
Sodium chloride added to render the solution isotonic for injection of the active ingredient is present in amounts insufficient to affect serum electrolyte balance of sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) ions.
Atropine Sulfate, USP is chemically designated lα H, 5α H-Tropan-3-α-ol (±)-tropate (ester), sulfate (2:1) (salt) monohydrate, (C 17H 23NO 3) 2· H 2SO 4· H 2O, colorless crystals or white crystalline powder very soluble in water. It has the following structural formula:
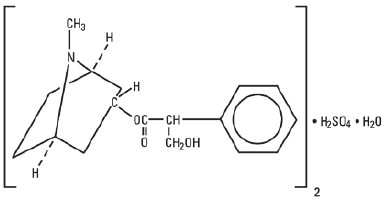
Atropine, a naturally occurring belladonna alkaloid, is a racemic mixture of equal parts of d- and 1-hyocyamine, whose activity is due almost entirely to the levo isomer of the drug.
Sodium Chloride, USP is chemically designated NaCl, a white crystalline powder freely soluble in water.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Atropine is an antimuscarinic agent since it antagonizes the muscarine-like actions of acetylcholine and other choline esters.
Atropine inhibits the muscarinic actions of acetylcholine on structures innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves, and on smooth muscles which respond to endogenous acetylcholine but are not so innervated. As with other antimuscarinic agents, the major action of atropine is a competitive or surmountable antagonism which can be overcome by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine at receptor sites of the effector organ (e.g., by using anticholinesterase agents which inhibit the enzymatic destruction of acetylcholine). The receptors antagonized by atropine are the peripheral structures that are stimulated or inhibited by muscarine (i.e., exocrine glands and smooth and cardiac muscle). Responses to postganglionic cholinergic nerve stimulation also may be inhibited by atropine but this occurs less readily than with responses to injected (exogenous) choline esters.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Atropine-induced parasympathetic
inhibition may be preceded by a transient phase of stimulation, especially on the heart where small doses first slow the rate before characteristic tachycardia develops due to paralysis of vagal control. Atropine exerts a more potent and prolonged effect on heart, intestine and bronchial muscle than scopolamine, but its action on the iris, ciliary body and certain secretory glands is weaker than that of scopolamine. Unlike the latter, atropine in clinical doses does not depress the central nervous system but may stimulate the medulla and higher cerebral centers. Although mild vagal excitation occurs, the increased respiratory rate and (sometimes) increased depth of respiration produced by atropine are more probably the result of bronchiolar dilatation. Accordingly, atropine is an unreliable respiratory stimulant and large or repeated doses may depress respiration.
Adequate doses of atropine abolish various types of reflex vagal cardiac slowing or asystole. The drug also prevents or abolishes bradycardia or asystole produced by injection of choline esters, anticholinesterase agents or other parasympathomimetic drugs, and cardiac arrest produced by stimulation of the vagus. Atropine also may lessen the degree of partial heart block when vagal activity is an etiologic factor. In some patients with complete heart block, the idioventricular rate may be accelerated by atropine; in others, the rate is stabilized. Occasionally a large dose may cause atrioventricular (A-V) block and nodal rhythm.
Atropine in clinical doses counteracts the peripheral dilatation and abrupt decrease in blood pressure produced by choline esters. However, when given by itself, atropine does not exert a striking or uniform effect on blood vessels or blood pressure. Systemic doses slightly raise systolic and lower diastolic pressures and can produce significant postural hypotension. Such doses also slightly increase cardiac output and decrease central venous pressure. Occasionally, therapeutic doses dilate cutaneous blood vessels, particularly in the "blush" area (atropine flush), and may cause atropine "fever" due to suppression of sweat gland activity in infants and small children.
The effects of intravenous atropine on heart rate (maximum heart rate) and saliva flow (minimum flow) after I.V. administration (rapid, constant infusion over 3 min.) are delayed by 7 to 8 minutes after drug administration and both effects are non-linearly related to the amount of drug in the peripheral compartment. Changes in plasma atropine levels following intramuscular administration (0.5 to 4 mg doses) and heart rate are closely overlapped but the time course of the changes in atropine levels and behavioral impairment indicates that pharmacokinetics is not the primary rate-limiting mechanism for the central nervous system effect of atropine.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
****After intramuscular administration, atropine is absorbed with peak
concentration occurring at 30 min following injection.
Effects of exercise:
Exercise following intramuscular administration of atropine significantly
increases the absorption of atropine due to increased perfusion in the muscle,
with an increase in AUC by approximately 20% and Cmax by approximately 80%.
Distribution
Atropine is distributed throughout the body. Atropine’s plasma protein binding
is about 44% and saturable in the 2 to 20 mcg/mL concentration range.
Elimination
****The pharmacokinetics of atropine is nonlinear after intravenous
administration of 0.5 to 4 mg. Atropine disappears from the blood following
injection with a plasma half-life of about 2-4 hours. Much of the drug is
destroyed by enzymatic hydrolysis, particularly in the liver, with 13 to 50%
is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Metabolism
****The major metabolites of atropine are noratropine, atropin-n-oxide,
tropine, and tropic acid. The metabolism of atropine is inhibited by
organophosphate pesticides.
Specific Populations
Pregnant Women
Atropine readily crosses the placental barrier and enters the fetal
circulation, but is not found in amniotic fluid.
Nursing Mother
Traces are found in various secretions, including milk.
Pediatric and Geriatric Patients
The elimination half-life of atropine is more than doubled in children under
two years, and the elderly (> 65 years old) compared to other age groups.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Atropine Sulfate Injection, USP is a non-pyrogenic, isotonic, clear solution and is supplied as follows:
Single Vial
NDC# 84549-580-20
Description
8 mg per 20 mL
(0.4 mg per mL)
Multiple-dose vial
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. After initial use, store between 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) and discard within 24 hours.

www.fresenius-kabi.com/us
451539
Issued: March 2018
