Mifepristone
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Mifepristone tablets, 200mg safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Mifepristone tablets, 200mg. Mifepristone tablets, 200mg for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
b63fad9b-7f12-4400-9019-b0586054e534
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 30, 2023
GenBioPro, Inc.
DUNS: 078364058
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
MIFEPRISTONE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL
NDC 43393-001-01
Mifepristone Tablet
200 mg
1 Tablet

NDC 43393-001-01
Mifepristone Tablet
200 mg
Rx Only
1 Tablet
NDC 43393-001-06
Mifepristone Tablet
200 mg
Rx Only
Contains 6 Cartons
Each Carton Contains 1 Tablet
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infection and Sepsis
As with other types of abortion, cases of serious bacterial infection, including very rare cases of fatal septic shock, have been reported following the use of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg [see Boxed Warning]. Healthcare providers evaluating a patient who is undergoing a medical abortion should be alert to the possibility of this rare event. A sustained (>4 hours) fever of 100.4°F or higher, severe abdominal pain, or pelvic tenderness in the days after a medical abortion may be an indication of infection.
A high index of suspicion is needed to rule out sepsis (e.g., from Clostridium sordellii) if a patient reports abdominal pain or discomfort or general malaise (including weakness, nausea, vomiting or diarrhea) more than 24 hours after taking misoprostol. Very rarely, deaths have been reported in patients who presented without fever, with or without abdominal pain, but with leukocytosis with a marked left shift, tachycardia, hemoconcentration, and general malaise. No causal relationship between Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol use and an increased risk of infection or death has been established. Clostridium sordellii infections have also been reported very rarely following childbirth (vaginal delivery and caesarian section), and in other gynecologic and non-gynecologic conditions.
5.2 Uterine Bleeding
Uterine bleeding occurs in almost all patients during a medical abortion. Prolonged heavy bleeding (soaking through two thick full-size sanitary pads per hour for two consecutive hours) may be a sign of incomplete abortion or other complications and prompt medical or surgical intervention may be needed to prevent the development of hypovolemic shock. Counsel patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience prolonged heavy vaginal bleeding following a medical abortion [see Boxed Warning].
Women should expect to experience vaginal bleeding or spotting for an average of 9 to 16 days. Women report experiencing heavy bleeding for a median duration of 2 days.
Up to 8% of all subjects may experience some type of bleeding for 30 days or more. In general, the duration of bleeding and spotting increased as the duration of the pregnancy increased.
Decreases in hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit, and red blood cell count may occur in patients who bleed heavily.
Excessive uterine bleeding usually requires treatment by uterotonics, vasoconstrictor drugs, surgical uterine evacuation, administration of saline infusions, and/or blood transfusions. Based on data from several large clinical trials, vasoconstrictor drugs were used in 4.3% of all subjects, there was a decrease in hemoglobin of more than 2 g/dL in 5.5% of subjects, and blood transfusions were administered to ≤0.1% of subjects. Because heavy bleeding requiring surgical uterine evacuation occurs in about 1% of patients, special care should be given to patients with hemostatic disorders, hypocoagulability, or severe anemia.
5.3 Mifepristone REMS Program
Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called the Mifepristone REMS Program, because of the risks of serious complications [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1, 5.2)]
Notable requirements of the Mifepristone REMS Program include the following:
- Prescribers must be certified with the program by completing the Prescriber Agreement Form
- Patients must sign a Patient Agreement Form
- Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg must be dispensed to patients by or under the supervision of a certified prescriber, or by certified pharmacies on prescriptions issued by certified prescribers
Further information is available at 1-855-MIFEINFO (1-855-643-3463).
5.4 Ectopic Pregnancy
Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg is contraindicated in patients with a confirmed or suspected ectopic pregnancy because mifepristone is not effective for terminating ectopic pregnancies [see Contraindications ( 4)]. Healthcare providers should remain alert to the possibility that a patient who is undergoing a medical abortion could have an undiagnosed ectopic pregnancy because some of the expected symptoms experienced with a medical abortion (abdominal pain, uterine bleeding) may be similar to those of a ruptured ectopic pregnancy. The presence of an ectopic pregnancy may have been missed even if the patient underwent ultrasonography prior to being prescribed Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg.
Patients who became pregnant with an IUD in place should be assessed for ectopic pregnancy.
5.5 Rhesus Immunization
The use of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg is assumed to require the same preventive measures as those taken prior to and during surgical abortion to prevent rhesus immunization.
- Ectopic pregnancy: Exclude before treatment. ( 5.4)
- Rhesus immunization: Prevention needed as for surgical abortion. ( 5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections:
- Infection and sepsis [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]
- Uterine bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Information presented on common adverse reactions relies solely on data from US studies, because rates reported in non-US studies were markedly lower and are not likely generalizable to the US population. In three US clinical studies totaling 1,248 women through 70 days gestation who used mifepristone 200 mg orally followed 24-48 hours later by misoprostol 800mcg buccally, women reported adverse reactions in diaries and in interviews at the follow-up visit. These studies enrolled generally healthy women of reproductive age without contraindications to mifepristone or misoprostol use according to the Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg product label.Gestational age was assessed prior to study enrollment using the date of the woman's last menstrual period, clinical evaluation, and/or ultrasound examination.
About 85% of patients report at least one adverse reaction following administration of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol, and many can be expected to report more than one such reaction. The most commonly reported adverse reactions (>15%) were nausea, weakness, fever/chills, vomiting, headache, diarrhea, and dizziness (see Table 1). The frequency of adverse reactions varies between studies and may be dependent on many factors including the patient population and gestational age.
Abdominal pain/cramping is expected in all medical abortion patients and its incidence is not reported in clinical studies. Treatment with Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol is designed to induce uterine bleeding and cramping to cause termination of an intrauterine pregnancy. Uterine bleeding and cramping are expected consequences of the action of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol as used in the treatment procedure. Most patients can expect bleeding more heavily than they do during a heavy menstrual period [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2) ].
Table 1 lists the adverse reactions reported in US clinical studies with incidence >15% of women.
Table 1 Adverse Reactions Reported in Women Following Administration of Mifepristone (oral) and Misoprostol (buccal) in US Clinical Studies
|
Adverse Reaction |
# US ** studies** |
Number of Evaluable ** Women** |
Range of ** frequency (%)** |
Upper Gestational Age of Studies ** Reporting Outcome** |
|
Nausea |
3 |
1,248 |
51-75% |
70 days |
|
Weakness |
2 |
630 |
55-58% |
63 days |
|
Fever/chills |
1 |
414 |
48% |
63 days |
|
Vomiting |
3 |
1,248 |
37-48% |
70 days |
|
Headache |
2 |
630 |
41-44% |
63 days |
|
Diarrhea |
3 |
1,248 |
18-43% |
70 days |
|
Dizziness |
2 |
630 |
39-41% |
63 days |
One study provided gestational-age stratified adverse reaction rates for women who were 57-63 and 64-70 days; there was little difference in frequency of the reported common adverse reactions by gestational age.
Information on serious adverse reactions was reported in six US and four non- US clinical studies, totaling 30,966 women through 70 days gestation who used mifepristone 200mg orally followed 24-48 hours later by misoprostol 800mcg buccally. Serious adverse reaction rates were similar between US and non-US studies, so rates from both US and non-US studies are presented. In the US studies, one studied women through 56 days gestation, four through 63 days gestation, and one through 70 days gestation, while in the non-US studies, two studied women through 63 days gestation, and two through 70 days gestation. Serious adverse reactions were reported in <0.5% of women. Information from the US and non-US studies is presented in Table 2.
Table 2 Serious Adverse Reactions Reported in Women Following Administration of Mifepristone (oral) and Misoprostol (buccal) in US and Non-US Clinical Studies
|
NR= Not reported *This outcome represents a single patient who experienced death related to sepsis. | ||||||
|
Adverse ** Reaction** |
US |
Non-US | ||||
|
# of studies |
Number of Evaluable Women |
Range of ** frequency (%)** |
# of ** studies** |
Number of ** Evaluable** ** Women** |
Range of ** frequency** ** (%)** | |
|
Transfusion |
4 |
17,774 |
0.03-0.5% |
3 |
12,134 |
0-0.1% |
|
Sepsis |
1 |
629 |
0.2% |
1 |
11,155 |
<0.01% * |
|
ER visit |
2 |
1,043 |
2.9-4.6% |
1 |
95 |
0 |
|
Hospitalization ** Related to** ** Medical Abortion** |
3 |
14,339 |
0.04-0.6% |
3 |
1,286 |
0-0.7% |
|
Infection without ** sepsis** |
1 |
216 |
0 |
1 |
11,155 |
0.2% |
|
Hemorrhage |
NR |
NR |
NR |
1 |
11,155 |
0.1% |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infections and infestations: post-abortal infection (including endometritis, endomyometritis, parametritis, pelvic infection, pelvic inflammatory disease, salpingitis)
Blood and the lymphatic system disorders: anemia
Immune system disorders: allergic reaction (including anaphylaxis, angioedema, hives, rash, itching)
Psychiatric disorders: anxiety
Cardiac disorders: tachycardia (including racing pulse, heart palpitations, heart pounding)
Vascular disorders: syncope, fainting, loss of consciousness, hypotension (including orthostatic), light-headedness
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: shortness of breath
Gastrointestinal disorders: dyspepsia
Musculoskeletal, connective tissue and bone disorders: back pain, leg pain
Reproductive system and breast disorders: uterine rupture, ruptured ectopic pregnancy, hematometra, leukorrhea
General disorders and administration site conditions: pain
Most common adverse reactions (>15%) are nausea, weakness, fever/chills, vomiting, headache, diarrhea, and dizziness. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GenBioPro, Inc. at 1-855-643-3463 or medical@genbiopro.comor www.MIFEINFO.comor FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs that May Reduce Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg Exposure (Effect of
CYP 3A4 Inducers on Mifepristone tablets, 200mg)
CYP450 3A4 is primarily responsible for the metabolism of mifepristone. CYP3A4 inducers such as rifampin, dexamethasone, St. John's Wort, and certain anticonvulsants (such as phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine) may induce mifepristone metabolism (lowering serum concentrations of mifepristone). Whether this action has an impact on the efficacy of the dose regimen is unknown. Refer to the follow-up assessment [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.3)] to verify that treatment has been successful.
7.2 Drugs that May Increase Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg Exposure (Effect
of CYP 3A4 Inhibitors on Mifepristone tablets, 200mg)
Although specific drug or food interactions with mifepristone have not been studied, on the basis of this drug's metabolism by CYP 3A4, it is possible that ketoconazole, itraconazole erythromycin, and grapefruit juice may inhibit its metabolism (increasing serum concentrations of mifepristone). Mifepristone tablets, 200mg should be used with caution in patients currently or recently treated with CYP 3A4 inhibitors.
7.3 Effects of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg on Other Drugs (Effect of
Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg on CYP 3A4Substrates)
Based on in vitro inhibition information, coadministration of mifepristone may lead to an increase in serum concentrations of drugs that are CYP 3A4 substrates. Due to the slow elimination of mifepristone from the body, such interaction may be observed for a prolonged period after its administration. Therefore, caution should be exercised when mifepristone is administered with drugs that are CYP 3A4 substrates and have a narrow therapeutic range.
- CYP3A4 inducers can lower mifepristone concentrations. ( 7.1)
- CYP3A4 inhibitors can increase mifepristone concentrations. Use with caution. ( 7.2)
- CYP3A4 substrate concentrations can be increased. Caution with coadministration of substrates with narrow therapeutic margin. ( 7.3)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Regimen
For purposes of this treatment, pregnancy is dated from the first day of the last menstrual period. The duration of pregnancy may be determined from menstrual history and clinical examination. Assess the pregnancy by ultrasonographic scan if the duration of pregnancy is uncertain or if ectopic pregnancy is suspected.
Remove any intrauterine device (“IUD”) before treatment with Mifepristone tablets, 200mg begins [see Contraindications ( 4)].
The dosing regimen for Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol is:
Mifepristone 200 mg orally + misoprostol 800 mcg buccally
• Day One: Mifepristone 200 mg Administration
One 200 mg tablet of Mifepristone is taken in a single oral dose.
• Day Two or Three: Misoprostol Administration (minimum 24-hour interval between, Mifepristone and misoprostol)
Four 200 mcg tablets (total dose 800 mcg) of misoprostol are taken by the buccal route.
Tell the patient to place two 200 mcg misoprostol tablets in each cheek pouch (the area between the cheek and gums) for 30 minutes and then swallow any remnants with water or another liquid (see Figure 1).
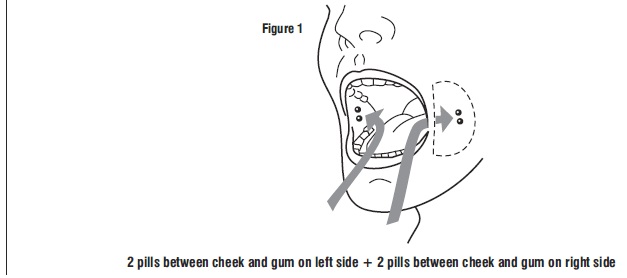
Patients taking Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg must take misoprostol within 24 to 48 hours after taking Mifepristone. The effectiveness of the regimen may be lower if misoprostol is administered less than 24 hours or more than 48 hours after mifepristone administration.
Because most women will expel the pregnancy within 2 to 24 hours of taking misoprostol [see Clinical Studies ( 14)] , discuss with the patient an appropriate location for them to be when taking the misoprostol, taking into account that expulsion could begin within 2 hours of administration.
2.2 Patient Management Following Misoprostol Administration
During the period immediately following the administration of misoprostol, the patient may need medication for cramps or gastrointestinal symptoms [see Adverse Reactions ( 6)] .
Give the patient:
- Instructions on what to do if significant discomfort, excessive vaginal bleeding or other adverse reactions occur
- A phone number to call if the patient has questions following the administration of the misoprostol
- The name and phone number of the healthcare provider who will behandling emergencies.
2.3 Post-treatment Assessment: Day 7 to 14
Patients should follow-up with their healthcare provider approximately 7 to 14 days after the administration of Mifepristone. This assessment is very important to confirm that complete termination of pregnancy has occurred and to evaluate the degree of bleeding. Termination can be confirmed by medical history, clinical examination, human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) testing, or ultrasonographic scan. Lack of bleeding following treatment usually indicates failure; however, prolonged or heavy bleeding is not proof of a complete abortion.
The existence of debris in the uterus (e.g., if seen on ultrasonography) following the treatment procedure will not necessarily require surgery for its removal.
Patients should expect to experience vaginal bleeding or spotting for an average of 9 to 16 days. Women report experiencing heavy bleeding for a median duration of 2 days. Up to 8% of women may experience some type of bleeding for more than 30 days. Persistence of heavy or moderate vaginal bleeding at the time of follow-up, however, could indicate an incomplete abortion.
If complete expulsion has not occurred, but the pregnancy is not ongoing, patients may be treated with another dose of misoprostol 800mcg buccally. There have been rare reports of uterine rupture in women who took mifepristone tablets, 200 mg and misoprostol, including women with prior uterine rupture or uterine scar and patients who received multiple doses of misoprostol within 24 hours. Patients who choose to use a repeat dose of misoprostol should have a follow-up visit with their healthcare provider in approximately 7 days to assess for complete termination.
Surgical evacuation is recommended to manage ongoing pregnancies after medical abortion [see Use in Specific Populations ( 8.1)] . Advise the patient whether you will provide such care or will refer her to another provider as part of counseling prior to prescribing Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg.
2.4 Contact for Consultation
For consultation 24 hours a day, 7 days a week with an expert in mifepristone, call GenBioPro, Inc. at 1-855-MIFEINFO (1-855-643-3463).
- 200 mg Mifepristone on Day 1, followed 24-48 hours after Mifepristone dosing by 800 mcg buccal misoprostol. ( 2.1)
- Instruct the patient what to do if significant adverse reactions occur. ( 2.2)
- Follow-up is needed to confirm complete termination of pregnancy. ( 2.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Mifepristone is indicated, in a regimen with misoprostol, for the medical termination of intrauterine pregnancy through 70 days gestation. Risks to pregnant patients are discussed throughout the labeling.
Refer to misoprostol labeling for risks to pregnant patients with the use of misoprostol.
The risk of adverse developmental outcomes with a continued pregnancy after a failed pregnancy termination with Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg in a regimen with misoprostol is unknown; however, the process of a failed pregnancy termination could disrupt normal embryo-fetal development and result in adverse developmental effects. Birth defects have been reported with a continued pregnancy after a failed pregnancy termination with Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg in a regimen with misoprostol. In animal reproduction studies, increased fetal losses were observed in mice, rats, and rabbits and skull deformities were observed in rabbits with administration of mifepristone at doses lower than the human exposure level based on body surface area.
Data
Animal Data
In teratology studies in mice, rats and rabbits at doses of 0.25 to 4.0mg/kg (less than 1/100 to approximately 1/3 the human exposure based on body surface area), because of the antiprogestational activity of mifepristone, fetal losses were much higher than in control animals. Skull deformities were detected in rabbit studies at approximately 1/6 the human exposure, although no teratogenic effects of mifepristone have been observed to date in rats or mice.
These deformities were most likely due to the mechanical effects of uterine contractions resulting from inhibition of progesterone action.
8.2 Lactation
Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg is present in human milk. Limited data demonstrate undetectable to low levels of the drug in human milk with the relative (weight-adjusted) infant dose 0.5% or less as compared to maternal dosing. There is no information on the effects of Mifepristone tablets, 200 use of misoprostol. The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with any potential adverse effects on the breast- fed child from Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg in a regimen with misoprostol.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg have been established in pregnant females. Data from a clinical study of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg that included a subset of 322 females under age 17 demonstrated a safety and efficacy profile similar to that observed in adults.
- Pregnancy: Risk of fetal malformations in ongoing pregnancy if not terminated is unknown. ( 8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION, Medication Guide
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The anti-progestational activity of mifepristone results from competitive interaction with progesterone at progesterone-receptor sites. Based on studies with various oral doses in several animal species (mouse, rat, rabbit, and monkey), the compound inhibits the activity of endogenous or exogenous progesterone, resulting in effects on the uterus and cervix that, when combined with misoprostol, result in termination of an intrauterine pregnancy.
During pregnancy, the compound sensitizes the myometrium to the contraction- inducing activity of prostaglandins.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Use of Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg in a regimen with misoprostol disrupts pregnancy by causing decidual necrosis, myometrial contractions, and cervical softening, leading to the expulsion of the products of conception.
Doses of 1mg/kg or greater of mifepristone have been shown to antagonize the endometrial and myometrial effects of progesterone in women.
Antiglucocorticoid and antiandrogenic activity: Mifepristone also exhibits antiglucocorticoid and weak antiandrogenic activity. The activity of the glucocorticoid dexamethasone in rats was inhibited following doses of 10 to 25 mg/kg of mifepristone. Doses of 4.5mg/kg or greater in human beings resulted in a compensatory elevation of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and cortisol. Antiandrogenic activity was observed in rats following repeated administration of doses from 10 to 100 mg/kg.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Mifepristone is rapidly absorbed after oral ingestion with non-linear pharmacokinetics for C max after single oral doses of 200 mg and 600 mg in healthy subjects.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of a 20 mg mifepristone oral dose in females of childbearing age is 69%. Following oral administration of a single dose of 600mg, mifepristone is rapidly absorbed, with a peak plasma concentration of 1.98 ± 1.0mg/L occurring approximately 90 minutes after ingestion.
Following oral administration of a single dose of 200 mg in healthy men (n=8), mean C max was1.77 ± 0.7 mg/L occurring approximately 45 minutes after ingestion. Mean AUC0-∞ was 25.8± 6.2 mg*hr/L.
Distribution
Mifepristone is 98% bound to plasma proteins, albumin, and 1-acid glycoprotein. Binding to the latter protein is saturable, and the drug displays nonlinear kinetics with respect to plasma concentration and clearance.
Elimination
Following a distribution phase, elimination of mifepristone is slow at first (50% eliminated between 12 and 72 hours) and then becomes more rapid with a terminal elimination half-life of 18 hours.
Metabolism
Metabolism of mifepristone is primarily via pathways involving N-demethylation and terminal hydroxylation of the 17-propynyl chain. In vitro studies have shown that CYP450 3A4 is primarily responsible for the metabolism. The three major metabolites identified in humans are: (1) RU 42 633, the most widely found in plasma, is the N-monodemethylated metabolite; (2) RU 42 848, which results from the loss of two methyl groups from the 4-dimethylaminophenyl in position 11ß; and (3) RU 42 698, which results from terminal hydroxylation of the 17-propynyl chain.
Excretion
By 11 days after a 600mg dose of tritiated compound, 83% of the drug has been accounted for by the feces and 9% by the urine. Serum concentrations are undetectable by 11 days.
Specific Populations
The effects of age, hepatic disease and renal disease on the safety, efficacy and pharmacokinetics of mifepristone have not been investigated.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No long-term studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of mifepristone have been performed.
Mutagenesis
Results from studies conducted in vitro and in animals have revealed no genotoxic potential for mifepristone. Among the tests carried out were: Ames test with and without metabolic activation; gene conversion test in Saccharomyces cerevisiae D4 cells; forward mutation in Schizosaccharomyces pompe P1 cells; induction of unscheduled DNA synthesis in cultured HeLa cells; induction of chromosome aberrations in CHO cells; in vitro test for gene mutation in V79 Chinese hamster lung cells; and micronucleus test in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
In rats, administration of 0.3mg/kg mifepristone per day caused severe disruption of the estrus cycles for the three weeks of the treatment period. Following resumption of the estrus cycle, animals were mated and no effects on reproductive performance were observed.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Safety and efficacy data from clinical studies of mifepristone 200 mg orally followed 24-48 hours later by misoprostol 800 mcg buccally through 70 days gestation are reported below. Success was defined as the complete expulsion of the products of conception without the need for surgical intervention. The overall rates of success and failure, shown by reason for failure based on 22 worldwide clinical studies (including 7 US studies) appear in Table 3.
The demographics of women who participated in the US clinical studies varied depending on study location and represent the racial and ethnic variety of American females. Females of all reproductive ages were represented, including females less than 18 and more than 40 years of age; most were 27 years or younger.
Table 3 Outcome Following Treatment with Mifepristone (oral) and Misoprostol (buccal) Through 70 Days Gestation
|
US Trials |
Non-US Trials | |
|
N |
16,794 |
18,425 |
|
Complete Medical Abortion |
97.4% |
96.2% |
|
Surgical Intervention***** |
2.6% |
3.8% |
|
Ongoing Pregnancy****** |
0.7% |
0.9% |
** Ongoing pregnancy is a subcategory of surgical intervention, indicating the percent of women who have surgical intervention due to an ongoing pregnancy. |
The results for clinical studies that reported outcomes, including failure rates for ongoing pregnancy, by gestational age are presented in Table 4.
Table 4 Outcome by Gestational Age Following Treatment with Mifepristone and Misoprostol (buccal) for US and Non-US Clinical Studies
|
<49 days |
50-56 days |
57-63 days |
64-70 days | |||||||||
|
N |
% |
Number of ** Evaluable** ** Studies** |
N |
% |
Number of ** Evaluable** ** Studies** |
N |
% |
Number of ** Evaluable** ** Studies** |
N |
% |
Number of ** Evaluable** ** Studies** | |
|
Complete ** medical** ** abortion** |
12,046 |
98.1 |
10 |
3,941 |
96.8 |
7 |
2,294 |
94.7 |
9 |
479 |
92.7 |
4 |
|
Surgical ** intervention** ** for ongoing** ** pregnancy** |
10,272 |
0.3 |
6 |
3,788 |
0.8 |
6 |
2,211 |
2 |
8 |
453 |
3.1 |
3 |
One clinical study asked subjects through 70 days gestation to estimate when they expelled the pregnancy, with 70% providing data. Of these, 23-38% reported expulsion within 3 hours and over 90% within 24 hours of using misoprostol.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg is only available through a restricted program called the Mifepristone REMS Program [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)]
Mifepristone tablets, 200 mg is supplied as light yellow, circular, bi-convex, uncoated tablets debossed with “S” on one side and plain on other side. Each tablet contains 200 mg of mifepristone. One tablet is individually blistered on one blister card that is packaged in an individual package (National Drug Code 43393-001-01).
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15 to 30°C (59 to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
