Cystadane
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Cystadane safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Cystadane. Cystadane (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) powder Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
31a684d0-cd98-4e46-b43a-ccbd17c41559
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 11, 2023
Recordati Rare Diseases
DUNS: 767598352
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
betaine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from a limited number of published case reports and postmarketing experience with CYSTADANE use in pregnancy have not identified any drug associated risks for major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with betaine.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of betaine in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CYSTADANE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CYSTADANE or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CYSTADANE have been established in pediatric patients. The majority of case studies of homocystinuria patients treated with CYSTADANE have been pediatric patients, including patients ranging in age from 24 days to 17 years [see Clinical Studies ( 14)]. Children younger than 3 years of age may benefit from dose titration [see Dosage and Administration ( 2.1)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
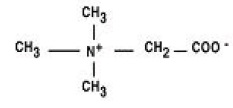
CYSTADANE (betaine anhydrous for oral solution) is an agent for the treatment of homocystinuria. It contains no ingredients other than anhydrous betaine. CYSTADANE is a white, granular, hygroscopic powder, which is diluted in water and administered orally. The chemical name of betaine anhydrous powder is trimethylglycine. It has a molecular weight of 117.15. The structural formula is:
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CYSTADANE acts as a methyl group donor in the remethylation of homocysteine to methionine in patients with homocystinuria. Betaine occurs naturally in the body. It is a metabolite of choline and is present in small amounts in foods such as beets, spinach, cereals, and seafood.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
CYSTADANE was observed to lower plasma homocysteine concentrations in three types of homocystinuria, including CBS deficiency; MTHFR deficiency; and cbl defect. Patients have taken CYSTADANE for many years without evidence of tolerance. There has been no demonstrated correlation between Betaine concentrations and homocysteine concentrations.
In CBS-deficient patients, large increases in methionine concentrations over baseline have been observed. CYSTADANE has also been demonstrated to increase low plasma methionine and S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) concentrations in patients with MTHFR deficiency and cbl defect.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies of CYSTADANE are not available. Plasma betaine concentrations following adminstration of CYSTADANE have not been measured in patients and have not been correlated to homocysteine concentrations.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Preparation and Administration Instructions
Instruct patients and caregivers to administer CYSTADANE as follows:
- Shake bottle lightly before removing cap.
- Measure the number of scoops for the patient’s dose with the scoop provided. One level scoop (1.7 mL) is equivalent to 1 gram of betaine anhydrous powder.
- Mix powder with 4 to 6 ounces (120 to 180 mL) of water, juice, milk, or formula until completely dissolved, or mix with food, then ingest mixture immediately.
- Always replace the cap tightly after using and protect bottle from moisture.
Supplied by:
Recordati Rare Diseases
Puteaux, France
Licensed to and Distributed by:
Recordati Rare Diseases Inc.
Lebanon, NJ 08833 U.S.A.

For drug or ordering information please call AnovoRx Group, LLC, Customer service at 1-888-487-4703.

CYSTADANE ® is a licensed trademark of Recordati Rare Diseases Inc.
This product label may have been updated. For the most recent prescribing information, please visit www.recordatirarediseases.com.
Part No.: Recordati Rare Diseases, OEP1000 V2
