Firazyr
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FIRAZYR (icatibant) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FIRAZYR. FIRAZYR (icatibant) Injection, for subcutaneous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2011
ed6657ca-ab68-477a-9968-e12dc928b540
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 19, 2024
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
DUNS: 039997266
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
icatibant acetate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 3 mL Syringe Carton - 54092-702-01
Takeda
Prefilled Syringe
Rx ONLY
NDC 54092-702-01
Sample - Not For Sale
Carton contains:
One single-dose,
prefilled syringe and one 25G
hypodermic needle.
Full prescribing information with
patient injection instructions.
The syringe is closed with a protective cap.
firazyr®
(icatibant injection)
30 mg/3 mL
(10 mg/mL)
FOR SUBCUTANEOUS USE ONLY

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FIRAZYR® (icatibant) is indicated for the treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults 18 years of age and older.
FIRAZYR is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist indicated for treatment of acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults 18 years of age and older. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Laryngeal Attacks
Given the potential for airway obstruction during acute laryngeal HAE attacks, patients should be advised to seek medical attention in an appropriate healthcare facility immediately in addition to treatment with FIRAZYR.
Laryngeal attacks: Following treatment of laryngeal attacks with FIRAZYR, advise patients to seek immediate medical attention. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The safety of icatibant was evaluated in three controlled trials that included 223 patients who received FIRAZYR 30 mg (n=113), placebo (n=75), or comparator (n=38). The mean age at study entry was 38 years (range 18 to 83 years), 64% were female, and 95% were white. The data described below represent adverse reactions observed from the two placebo-controlled trials, consisting of 77 patients who received FIRAZYR at a dose of 30 mg SC, and 75 who received placebo.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions (occurring in greater than 1% of patients and at a higher rate with FIRAZYR versus placebo) are shown in Table 1.
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Table 1 Adverse reactions observed in >1% of patients with acute attacks of HAE and at a higher rate with FIRAZYR versus placebo in the placebo-controlled trials*|
FIRAZYR |
Placebo | |
|---|---|---|
|
System Organ Class |
Subjects (%) |
Subjects (%) |
| ||
|
General disorders and administration site conditions | ||
|
Injection site reaction † |
75 (97) |
25 (33) |
|
Pyrexia |
3 (4) |
0 |
|
Investigations | ||
|
Transaminase increased |
3 (4) |
0 |
|
Nervous system disorders | ||
|
Dizziness |
2 (3) |
1 (1) |
The third trial was active-controlled and was comprised of 35 patients who received FIRAZYR 30 mg and 38 patients who received the comparator. Adverse reactions for FIRAZYR were similar in nature and frequency to those reported in Table 1.
In all three controlled trials, patients were eligible for treatment of subsequent attacks in an open-label extension. Patients were treated with FIRAZYR 30 mg and could receive up to 3 doses of FIRAZYR 30 mg administered at least 6 hours apart for each attack. A total of 225 patients were treated with 1,076 doses of 30 mg FIRAZYR for 987 attacks of acute HAE. Adverse reactions similar in nature and frequency were observed to those seen in the controlled phase of the trials. Other adverse reactions reported included rash, nausea, and headache in patients exposed to FIRAZYR.
The safety of self-administration was evaluated in a separate, open-label trial in 56 patients with HAE. In this trial, the safety profile of FIRAZYR in patients who self-administered FIRAZYR was similar in nature and frequency to that of patients whose therapy was administered by healthcare professionals.
6.2 Immunogenicity
Across repeated treatment in the controlled trials, 4 patients tested positive for anti-icatibant antibodies. Three of these patients had subsequent tests which were negative. No hypersensitivity or anaphylactic reactions were reported with FIRAZYR. No association between anti-icatibant antibodies and efficacy was observed.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of FIRAZYR: urticaria. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions were injection site reactions, which occurred in almost all patients (97%) in clinical trials. Other common adverse reactions occurring in greater than 1% of patients included pyrexia, transaminase increase, dizziness, and rash. (6.1)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. at 1-800-828-2088 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 ACE Inhibitors
FIRAZYR is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist and thereby has the potential to have a pharmacodynamic interaction with ACE inhibitors where FIRAZYR may attenuate the antihypertensive effect of ACE inhibitors. Clinical trials to date have excluded subjects taking ACE inhibitors.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
The recommended dose of FIRAZYR is 30 mg administered by subcutaneous (SC) injection in the abdominal area. Additional doses may be administered at intervals of at least 6 hours if response is inadequate or if symptoms recur. No more than 3 doses may be administered in any 24 hour period.
2.2 Administration Instructions
FIRAZYR should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. The drug solution should be clear and colorless. Do not administer if the product contains particulates or is discolored.
Attach the provided 25 gauge needle to the syringe hub and screw on securely. Do not use a different needle. Disinfect the injection site and administer FIRAZYR by subcutaneous injection over at least 30 seconds.
Patients may self-administer FIRAZYR upon recognition of symptoms of an HAE attack after training under the guidance of a healthcare professional [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- 30 mg injected subcutaneously in the abdominal area. (2.1)
- If response is inadequate or symptoms recur, additional injections of 30 mg may be administered at intervals of at least 6 hours. (2.1)
- Do not administer more than 3 injections in 24 hours. (2.1)
- Patients may self-administer upon recognition of an HAE attack. (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
FIRAZYR injection is supplied in a prefilled syringe delivering 30 mg icatibant. Each syringe delivers 3 mL solution with a concentration of 10 mg per mL.
Injection: 10 mg per mL (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from published literature and the pharmacovigilance database with Firazyr (icatibant) use in pregnant women have not identified a drug- associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, icatibant, administered by the subcutaneous route during the period of organogenesis, did not cause structural abnormalities in rats or rabbits; however, premature birth and abortion were observed in rabbits at doses approximately 0.025 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) and higher. Decreased embryofetal survival was observed in rabbits at a subcutaneous dose that was 13 times the MRHD. In a pre- and post-natal development study in rats, delayed parturition was observed at subcutaneous doses 0.5 times the MRHD and higher, which resulted in deaths of dams at doses 2 times the MRHD and higher. Fetal death and early pup deaths were observed with doses 2 times the MRHD (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study with rats that received icatibant from gestation days 7 to 18, there was no evidence of any treatment-related structural abnormalities or effects on embryo-fetal survival with maternal doses up to 2.7 times the MRHD (on a mg/m2 basis with maternal subcutaneous doses up to 25 mg/kg/day). In a fertility and early embryonic development study with rats, icatibant increased pre-implantation loss at a dose that was 7 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis at a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg/day).
In an embryo-fetal development study with rabbits that received icatibant from gestation days 7 to 18, premature birth and abortion rates increased at doses approximately 0.025 times the MRHD and higher (on a mg/m2 basis at maternal subcutaneous doses of 0.1 mg/kg and higher). Icatibant treatment resulted in dose-related decreases of total implantations and total number of live fetuses as well as dose-related increases of percent pre-implantation loss at a dose that was 13 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis with a maternal subcutaneous dose of 10 mg/kg/day). There was no evidence of any treatment-related structural abnormalities with maternal doses up to 13 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis with maternal subcutaneous doses up to 10 mg/kg/day).
In a pre- and post-natal development study in the rat, dams received icatibant by the subcutaneous route at doses of 1, 3, and 10 mg/kg/day from gestation day 6 to post-partum (PPD) day 20. Delayed parturition was observed at doses 0.5 times the MRHD and higher (on an AUC basis with maternal subcutaneous doses of 1 mg/kg/day and higher), which resulted in deaths of dams at doses 2 times the MRHD and higher (on an AUC basis with maternal subcutaneous doses of 3 mg/kg/day and higher). Fetal death and increased pup deaths through PPD 4 were observed with doses 2 times the MRHD (on an AUC with a maternal subcutaneous dose of 3 mg/kg/day and higher). Impairment of pup righting reflex and decreased pup hair growth were also observed at 7 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis with a maternal dose of 10 mg/kg). Icatibant and the M2 metabolite were found in maternal milk following subcutaneous administration of icatibant. The no effect dose for F1 pups was identified at a dose 0.5 times the MRHD (on an AUC basis with a maternal subcutaneous dose of 1 mg/kg/day). A no effect dose was not identified for F0 maternal toxicity.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of icatibant in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Icatibant and the M2 metabolite were found in rat milk following subcutaneous administration of icatibant (see Data). When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. However, systemic absorption of icatibant in infants is not expected after oral exposure through breast milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for FIRAZYR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from FIRAZYR or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data
Icatibant is excreted into the milk of lactating rats at concentrations that sometimes slightly exceeded those measured in the maternal plasma.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 18 years have not been established.
Juvenile Toxicity Data
Subcutaneous daily administration of icatibant to young rats during the juvenile period of development (postnatal days 22-70) delayed the sexual maturation of male reproductive tissues (atrophy of testes and epididymides) at exposures approximating one-third or greater the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. Impaired fertility and reproductive performance were also observed in male rats at the end of the postnatal treatment period at exposures approximating the MRHD or greater on a mg/m2 basis. No effects were observed in females at exposures approximating 3-fold the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis. The observed tissue findings in males were consistent with those seen in sexually mature rats and dogs and are attributed to antagonism of the bradykinin B2 receptor and subsequent effects on gonadotropins. The observed effects may be a consequence of daily icatibant administration. Toxicity to the testis did not occur in dogs treated twice a week for 9 months [see Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility (13.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of FIRAZYR did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Elderly patients are likely to have increased systemic exposure to FIRAZYR compared to younger (18-45 years) patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Since other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in efficacy and safety between elderly and younger patients, no dose adjustment is recommended.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
FIRAZYR was studied in patients with mild to moderate (Child Pugh scores of 5 to 8) hepatic impairment. No change in systemic exposure is noted in these patient populations. No dose adjustment is required in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Although a formal renal impairment study has not been conducted, 10 of 37 patients treated with FIRAZYR had hepatorenal syndrome with glomerular filtration rate (GFR) below 60 mL/min. FIRAZYR is cleared non-renally and hence it is not expected to show any change in systemic exposure in patients with impaired renal function. No dose adjustment is required in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Elderly patients demonstrate increased systemic exposure to icatibant. Differences in efficacy and safety between elderly and younger patients have not been identified. (8.5)
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
FIRAZYR® and the FIRAZYR Logo® are registered trademarks of Shire Orphan Therapies GmbH. TAKEDA® and the TAKEDA Logo® are registered trademarks of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
© 2024 Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. All rights reserved.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
In a clinical study evaluating a 90 mg dose (30 mg in each of 3 subcutaneous sites), the adverse event profile was similar to that seen with 30 mg administered in a single subcutaneous site.
In another clinical study, a dose of 3.2 mg/kg administered intravenously (approximately 8 times the therapeutic dose for HAE) caused erythema, itching and hypotension in healthy subjects. No therapeutic intervention was necessary.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of FIRAZYR for the treatment of acute attacks of HAE in adults were studied in three controlled clinical trials. Among the 223 patients in these studies, the mean age was 38 years, 64% were female, and 95% were white. Approximately 57% of patients reported use of attenuated androgens, antifibrinolytic agents, or C1 inhibitors. Response to therapy was primarily assessed using visual analog scores on a 100 mm scale and patient- and physician-reported symptom scores for abdominal and cutaneous pain and swelling.
Trial 1 was a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study of 98 adult patients with a median age of 36 years. Patients who had developed moderate to severe cutaneous or abdominal or mild to moderate laryngeal attacks of HAE were randomized to receive either FIRAZYR 30 mg or placebo by subcutaneous injection. Patients with severe laryngeal attacks of HAE received open-label FIRAZYR 30 mg. The primary endpoint was assessed using a 3-item composite visual analog score (VAS), comprised of averaged assessments of skin swelling, skin pain, and abdominal pain. Response was defined as at least a 50% reduction from the pretreatment composite 3-item VAS score (Figure 2). The median time to 50% reduction in symptoms for patients with cutaneous or abdominal attacks treated with FIRAZYR (n=43) compared to placebo (n=45) was 2.0 hours [95% CI 1.5, 3.0] versus 19.8 hours [95% CI 6.1, 26.3], respectively (p<0.001).
Figure 2 Time to 50% reduction from baseline in 3-item VAS score.
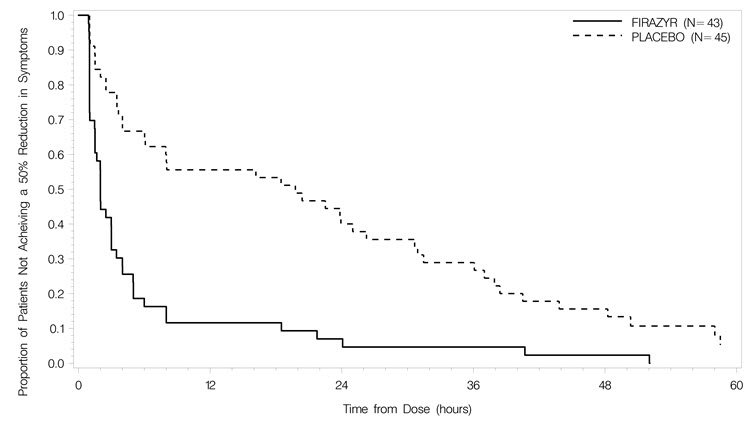
Other evaluated endpoints included time to almost complete symptom relief (VAS<10 mm) and rescue medication use. In Trial 1, the median times to almost complete symptom relief were 8.0 versus 36.0 hours for FIRAZYR and placebo, respectively. In terms of rescue medication use, 3/43 (7%) patients treated with FIRAZYR used additional rescue medication in comparison to 18/45 (40%) patients treated with placebo.
In a second placebo-controlled trial and an active-controlled trial, a total of 26 and 35 patients, respectively, received FIRAZYR 30 mg for the treatment of an acute HAE attack. Across the three trials, FIRAZYR had a median time to 50% reduction from baseline symptoms ranging from 2.0 to 2.3 hours.
Recurrent attacks
In all three controlled trials, patients were eligible for treatment of subsequent attacks in an open-label extension. Patients were treated with FIRAZYR 30 mg and could receive up to 3 doses of FIRAZYR 30 mg administered at least 6 hours apart for each attack. A total of 225 patients were treated with 1,076 doses of 30 mg FIRAZYR for 987 attacks of acute HAE in these trials. In an assessment of the first 5 FIRAZYR-treated attacks (621 doses for 582 attacks), the median times to a 50% reduction from the pretreatment composite 3-itemVAS score were similar across attacks (2.0, 2.0, 2.4, 2.0, 1.5 hours). The majority (93%) of these attacks of HAE were treated with a single dose of FIRAZYR.
Laryngeal attacks
A total of 60 patients with laryngeal attacks were treated with FIRAZYR in the controlled trials. Efficacy results were similar to those observed for non- laryngeal (cutaneous and abdominal) sites of attack.
Self-administration
Self-administration of FIRAZYR by 56 patients was assessed in an open label trial. Patients who administered FIRAZYR during an acute attack of HAE had a median time to 50% reduction from the pretreatment composite 3-itemVAS score of 2.6 hours.
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
PATIENT INFORMATION |
Please read this Patient Information before you use FIRAZYR and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is FIRAZYR?
- FIRAZYR is a medicine used to treat acute attacks of hereditary angioedema (HAE) in adults 18 years and older.
- It is not known if FIRAZYR is safe or effective for children under 18 years of age.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using FIRAZYR?
Before you use FIRAZYR, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions including if you:
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if FIRAZYR will harm your unborn baby. You and your healthcare provider will decide if FIRAZYR is right for you.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if FIRAZYR passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you use FIRAZYR.
**Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take,**including prescription and over the counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I use FIRAZYR?
- Read the Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information leaflet for detailed instructions about the right way to use FIRAZYR.
- Use FIRAZYR exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Your healthcare provider will prescribe the right dose of FIRAZYR for you and tell you when to use it.
- Your healthcare provider will teach you or a caregiver how to give FIRAZYR injections.
- If your symptoms continue or come back, you may repeat your FIRAZYR injection at least six hours apart.
- Do not use more than 3 doses in 24 hours. *If you have a laryngeal attack, inject FIRAZYR and then go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while using FIRAZYR?
Tiredness, drowsiness, and dizziness can happen in people who take FIRAZYR. If this happens, do not drive a car, use machinery, or do anything that needs you to be alert.
What are the possible side effects of FIRAZYR?
The most common side effects of FIRAZYR include:
- redness, bruising, swelling, warmth, burning, itching, irritation, hives, numbness, pressure, or pain at the injection site
- fever
- too much of an enzyme called transaminase in your blood
- dizziness
- nausea
- headache
- rash
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all of the possible side effects of FIRAZYR. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store FIRAZYR?
- Store FIRAZYR between 36°F to 77°F (2°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze.
- Store FIRAZYR in the original carton until you are ready to use it.
Keep FIRAZYR and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of FIRAZYR
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use FIRAZYR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FIRAZYR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about FIRAZYR. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about FIRAZYR that is written for health professionals.
For more information, go to www.FIRAZYR.com or call 1-800-828-2088.
What are the ingredients in FIRAZYR?
Active ingredient: icatibant acetate
**Inactive Ingredients:**sodium chloride (isotonicity reagent), glacial acetic acid (pH adjuster), sodium hydroxide (pH adjuster), and water
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FIRAZYR (FIR-a-zeer) |
Step 1. Preparing your dose of FIRAZYR
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- You will need the following supplies:
- Your FIRAZYR carton that includes 1 single-dose FIRAZYR prefilled syringe and 1 needle.
- 1 alcohol wipe
- The medicine inside your FIRAZYR prefilled syringe should be clear and colorless. Do not use your FIRAZYR prefilled syringe if the solution contains particles, is cloudy, or has an unusual color.
Figure A
Step 2. Remove the prefilled syringe and needle from the carton. See Figure B.

** Figure B**
Step 3. Twist the needle cap lid to break the seal (the needle should remain inside the protective needle cap until ready to use).SeeFigure C.
** Figure C**
Step 4. Remove the protective cap from the end of the pre-filled syringe by unscrewing the cap. Hold the syringe firmly. Carefully attach the needle to the prefilled syringe containing the colorless FIRAZYR solution.See Figure D.
** Figure D**
Step 5. Firmly screw the needle on the prefilled syringe. Be careful not to remove the needle from the needle cap. SeeFigure E.
** Figure E**
Preparing the Injection Site
**Step 6. Choose the injection site.**The injection site should be a fold of skin on your stomach, about 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 cm) below your belly button on either side.SeeFigure F.
The area you choose for injection should be at least 2 inches (5 cm) away from any scars. Do not choose an area that is bruised, swollen, or painful.
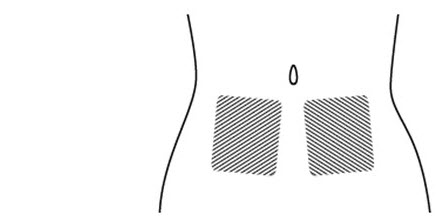
** Figure F**
Step 7. Clean your FIRAZYR injection site with an alcohol wipe and allow it to dry. See****Figure G.
** Figure G**
Injecting your FIRAZYR
Step 8. Remove the needle from the needle cap by holding the needle cap and carefully pulling the syringe.Do not pull up on the plunger. See Figure H.
** Figure H**
Step 9. Hold the FIRAZYR prefilled syringe in 1 hand, between your fingers and thumb. SeeFigure I.
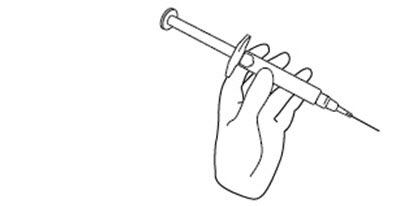
** Figure I**
Step 10. Use your other hand to gently pinch the fold of skin you cleaned with the alcohol wipe between your thumb and fingers for your injection. See Figure J.
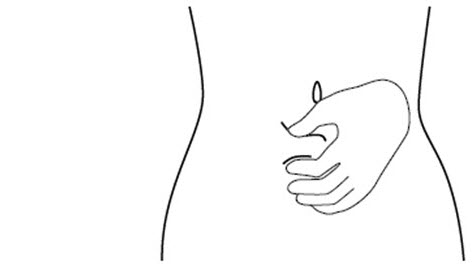
** Figure J**
Step 11. Hold the syringe between a 45-to-90 degree angle to your skin with the needle facing the fold of skin you are holding. SeeFigure K.
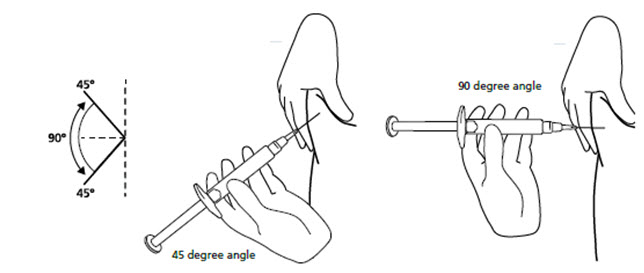
** Figure K**
Step 12. Hold the fold of skin. Bring the syringe to the skin and quickly insert the needle into the skin fold. SeeFigure L.
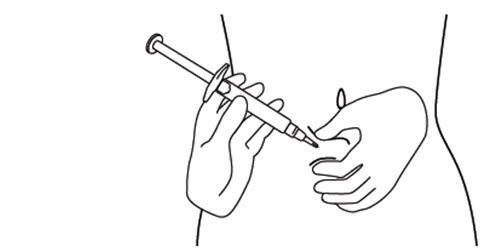
** Figure L**
Step 13. Push the plunger, at the top of the syringe, for at least 30 seconds until no FIRAZYR is in the syringe. SeeFigure M.
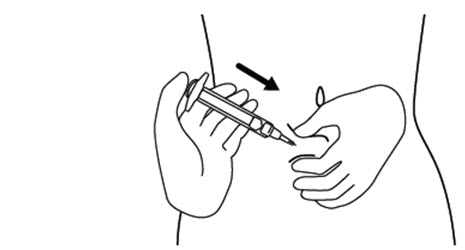
** Figure M**
Step 14. Release the skin fold and gently pull the needle out. See Figure N.
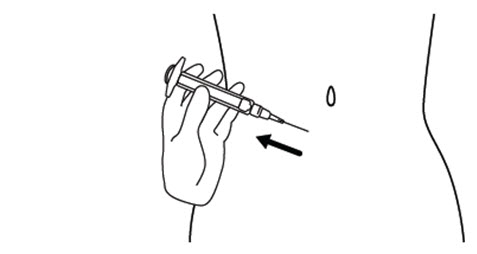
** Figure N**
Disposal of your used FIRAZYR prefilled syringe
Step 15. Place your used FIRAZYR syringe, with the needle attached, in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles and syringes in your household trash.
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA’s website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal.
Do not dispose of your sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this.Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
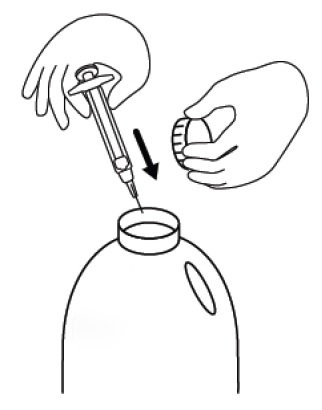
** Figure O**
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
FIRAZYR® and the FIRAZYR Logo® are registered trademarks of Shire Orphan Therapies GmbH. TAKEDA® and the TAKEDA Logo® are registered trademarks of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
© 2024 Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited. All rights reserved.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: January 2024
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
FIRAZYR (icatibant) is a synthetic decapeptide with five non-proteinogenic amino acids. The chemical structure of icatibant acetate is presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Chemical Structure
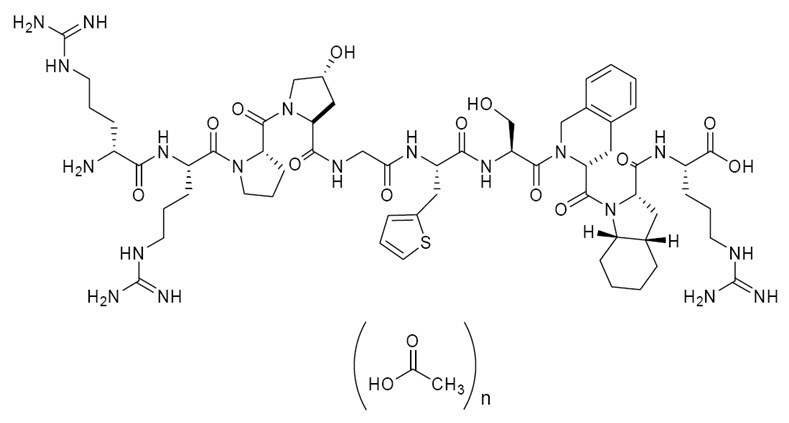
Chemical name: D-Arginyl-L-arginyl-L- prolyl-L[(4R)-4-hydroxyprolyl]-glycyl-L[3-(2-thienyl)alanyl]-L-seryl-D-(1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-3-ylcarbonyl)-L[(3aS,7aS)-octahydroindol-2-ylcarbonyl]-L-arginine, acetate salt
FIRAZYR is provided as a sterile, isotonic, and buffered solution of icatibant acetate in a single-dose, prefilled syringe for subcutaneous administration. Each mL of the solution contains 10 mg of icatibant (free base) which is equivalent to 11.38 mg of icatibant acetate. Each prefilled syringe delivers 3 mL of solution equivalent to a 30 mg icatibant dose. The solution is clear and colorless.
The solution also contains sodium chloride (isotonicity reagent), glacial acetic acid (pH adjuster), sodium hydroxide (pH adjuster) and water for injection with a pH of approximately 5.5. The solution does not contain preservatives.
Pharmacological class: Icatibant is a bradykinin B2 receptor antagonist.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Icatibant is a competitive antagonist selective for the bradykinin B2 receptor, with an affinity similar to bradykinin. Hereditary angioedema is caused by an absence or dysfunction of C1-esterase-inhibitor, a key regulator of the Factor XII/kallikrein proteolytic cascade that leads to bradykinin production. Bradykinin is a vasodilator which is thought to be responsible for the characteristic HAE symptoms of localized swelling, inflammation, and pain. Icatibant inhibits bradykinin from binding the B2 receptor and thereby treats the clinical symptoms of an acute, episodic attack of HAE.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Following bradykinin challenge, intravenous administration of FIRAZYR caused dose and time-dependent inhibition of development of bradykinin-induced hypotension, vasodilation, and reflex tachycardia in healthy young subjects. FIRAZYR intravenous doses of 0.4 and 0.8 mg/kg infused over 4 hours inhibited response to bradykinin challenge for 6 to 8 hours following completion of the infusion. Based on exposure-response analysis, a subcutaneous dose of 30 mg FIRAZYR is predicted to be effective against bradykinin challenge for at least 6 hours. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
The effect of FIRAZYR 30 and 90 mg following a single subcutaneous injection on QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, placebo-, and active-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) four-period crossover thorough QT study in 72 healthy subjects. In a study with demonstrated ability to detect small effects, the upper bound of the one-sided 95% confidence interval for the largest placebo adjusted, baseline-corrected QTc based on individual correction method (QTcI) was below 10 ms, the threshold for regulatory concern. The dose of 90 mg is adequate to represent the high exposure clinical scenario.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of FIRAZYR has been characterized in studies using both intravenous and subcutaneous administration to healthy subjects and patients. The pharmacokinetic profile of FIRAZYR in patients with HAE is similar to that in healthy subjects.
The absolute bioavailability of FIRAZYR following a 30 mg subcutaneous dose is approximately 97%. Following subcutaneous administration of a single 30 mg dose of FIRAZYR to healthy subjects (N=96), a mean (± standard deviation) maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of 974 ± 280 ng/mL was observed after approximately 0.75 hours. The mean area under the concentration-time curve (AUC0-∞) after a single 30 mg dose was 2165 ± 568 ng∙hr/mL, with no evidence of accumulation of icatibant following three 30 mg doses administered 6 hours apart. Following subcutaneous administration, plasma clearance was 245 ± 58 mL/min with a mean elimination half-life of 1.4 ± 0.4 hours and volume of distribution at steady state (Vss) of 29.0 ± 8.7 L.
Icatibant is extensively metabolized by proteolytic enzymes to inactive metabolites that are primarily excreted in the urine, with less than 10% of the dose eliminated as unchanged drug. Icatibant is not degraded by oxidative metabolic pathways, is not an inhibitor of major cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzymes (CYP 1A2, 2A6, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, 2E1, and 3A4) and is not an inducer of CYP 1A2 and 3A4.
Special populations
Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetic parameters of FIRAZYR were found to be generally comparable between healthy subjects (n=8) and mild to moderate (Child Pugh scores of 5 to 8) hepatic impaired patients (n=8) following a dose of 0.15 mg/kg/day as continuous intravenous infusion over 3 days. In a separate study, FIRAZYR clearance in subjects with a wide range of hepatic impairment (Child- Pugh scores of 7 to 15) was similar to that in healthy subjects. No dose adjustment is necessary for patients with impairment of hepatic function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Renal Impairment
Since renal clearance of icatibant is a minor eliminating pathway, renal impairment is not expected to affect the pharmacokinetics of FIRAZYR and hence a formal renal impairment study was not conducted for FIRAZYR. In 10 patients with hepatorenal syndrome (GFR 30-60 mL/min), clearance of FIRAZYR was not dependent on renal function and therefore, did not show any observable differences in the plasma levels of icatibant or its metabolites compared to subjects with normal renal function. No dose adjustment is necessary for patients with impairment of renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Age and Gender
Three 30 mg subcutaneous doses of FIRAZYR administered every 6 hours were studied in young (18 to 45 years of age) and elderly (over 65 years of age) healthy male and female subjects. Following single-dose administration of 30 mg subcutaneous FIRAZYR, elderly males and females showed approximately 2-fold higher AUC compared to young males and females, respectively. However, only minor differences (~12-14%) between Cmax of gender–matched elderly and young subjects were observed. Older subjects tend to exhibit lower clearance compared to younger subjects and therefore higher systemic exposure. Gender effect on FIRAZYR pharmacokinetics was also observed in addition to age effect. Clearance of FIRAZYR is significantly correlated with bodyweight with lower clearance values noted for lower bodyweights. Hence, females with typically lower body weights compared to males exhibit lower clearance values, resulting in approximately 2-fold higher systemic exposure (both AUC and Cmax) compared to males. Differences in efficacy and safety between elderly and younger patients and male and female patients have not been identified. Dose adjustment based on age and gender is not warranted.
Drug Interactions
Formal drug-drug interaction studies were not conducted with FIRAZYR. Icatibant metabolism is not mediated by CYP450 enzymes. In vitro study did not show any significant inhibition and/or induction of drug metabolizing CYP450 enzymes; therefore, metabolic drug interactions between FIRAZYR and CYP450 substrates, inhibitors and inducers are not expected.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Two-year studies were conducted in CD1 mice and Wistar rats to assess the carcinogenic potential of FIRAZYR. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in mice and rats at icatibant subcutaneous doses up to 15 mg/kg/day (twice per week) and 6 mg/kg/day (daily), respectively (approximately 10-fold and 6-fold greater than the MRHD on an AUC basis, respectively).
Icatibant tested negative for genotoxicity in the in vitro Ames bacterial reverse mutation test, in vitro Chinese hamster bone marrow chromosome aberration assay, and in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Daily subcutaneous administration of icatibant to rats and dogs caused ovarian, uterine, and testicular atrophy/degeneration and adverse effects on the mammary and prostate glands. In rats, testicular atrophy, reduced prostate gland secretion, decreased testosterone levels and degenerate corpora lutea occurred at doses greater than or equal to 3 mg/kg (approximately 5-fold greater than the MRHD in males and 2-fold greater than the MRHD in females on an AUC basis) and a decrease in developing ovarian follicles, mammary gland masculinization, and uterine atrophy occurred at doses greater than or equal to 10 mg/kg (approximately 6-fold greater than MRHD in females on an AUC basis). In dogs, reduced sperm counts and uterine atrophy occurred at doses greater than or equal to 1 mg/kg (approximately 2-fold greater than the MRHD on an AUC basis). Atrophy of the testes and prostate with decreased testosterone levels, decreased ovary size and decreased number of developing follicles occurred at a dose of 10 mg/kg (approximately 30-fold greater than the MRHD in males and 15-fold greater than at the MRHD in females on an AUC basis).
In contrast to the effects of daily icatibant administration, toxicity to the ovary, uterus, testis, mammary gland, and prostate did not occur in dogs treated twice a week for 9 months. AUC exposures from a dose of 3 mg/kg in these dogs were 5- and 3-fold the MRHD exposures in men and women, respectively. Sperm counts and testosterone remained unaffected over the course of the study in male dogs dosed twice a week.
Reproduction studies in male mice and rats with daily administration of icatibant found no effects on fertility or reproductive performance with intravenous doses up to 81 mg/kg (approximately 5-fold greater than the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) or subcutaneous doses up to 10 mg/kg (approximately 11-fold greater than the MRHD on an AUC basis), respectively.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
The B2 receptor has been implicated in the cardioprotective effects of bradykinin and antagonism of this receptor could potentially have negative cardiovascular effects during reperfusion after acute ischemia. Icatibant decreased coronary blood flow in the isolated guinea pig heart and aggravated the duration of post-ischemic reperfusion arrhythmias in the isolated rat heart. Intracoronary infusion of icatibant in an anesthetized myocardial infarction dog model increased mortality rate 2-fold over saline ischemia. There is limited human experience in acute ischemia. FIRAZYR should be used during acute coronary ischemia, unstable angina pectoris, or in the weeks following a stroke only if the benefit exceeds the theoretical risk to the patient.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
FIRAZYR is supplied as a single-dose, prefilled syringe for subcutaneous administration. Each syringe delivers 3 mL of a sterile solution of icatibant 30 mg (as icatibant acetate). Each glass syringe has a bromobutyl plunger stopper, which is not made of latex natural rubber.
FIRAZYR is available in cartons containing one single-dose, prefilled syringe and one 25 G Luer lock needle. NDC 54092-702-02.
FIRAZYR is also available in a pack containing 3 cartons; each carton contains one single-dose, prefilled syringe and one 25 G Luer lock needle. NDC 54092-702-03.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Keep out of the reach of children.
Store between 2 - 25° C (36 - 77° F).
Do not freeze.
Store in carton until time of administration.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
17.1 Information for Patients
Patients may self-administer FIRAZYR upon recognition of an HAE attack after training under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Patients with laryngeal symptoms should seek medical attention immediately in an appropriate healthcare facility after administration of FIRAZYR [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Injection site reactions are reported in most patients after administration of FIRAZYR. Other adverse reactions reported after administration of FIRAZYR include pyrexia, increase in transaminases, dizziness, and rash [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Tiredness, drowsiness, and dizziness have been reported following the use of FIRAZYR. Patients should be advised not to drive or use machinery if they feel tired or dizzy.
