SulfaMed
0cee76fc-8e0b-4c6f-ab38-5cabdc5ca4ce
PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG LABEL
Aug 20, 2025
VetOne
DUNS: 019926120
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
sulfadimethoxine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
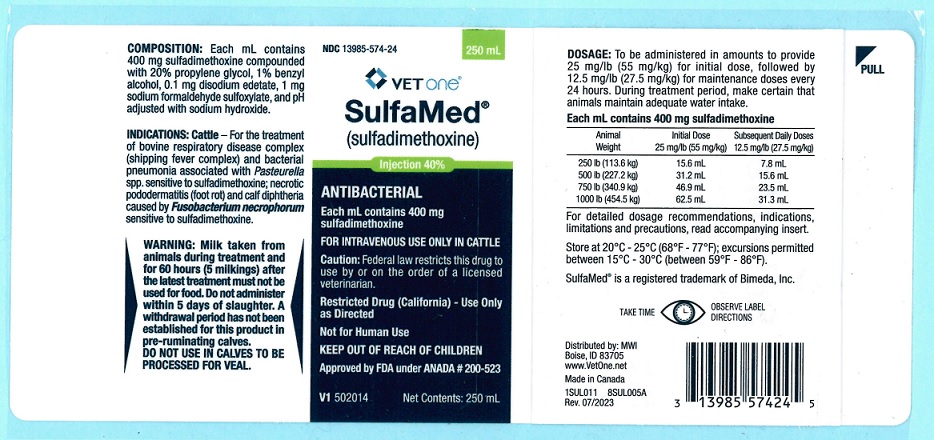
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
INDICATIONS: SulfaMed Injection 40% is indicated for the treatment of bovine respiratory disease complex (shipping fever complex) and bacterial pneumonia associated with Pasteurella spp. sensitive to sulfadimethoxine; necrotic pododermatitis (foot rot) and calf diphtheria caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum sensitive to sulfadimethoxine.
LIMITATIONS: Sulfadimethoxine is not effective in viral or rickettsial infections, and as with any antibacterial agent, occasional failures in therapy may occur due to resistant microorganisms. The usual precautions in sulfonamide therapy should be observed.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION: SulfaMed (sulfadimethoxine) Injection 40% is a low-dosage,
rapidly absorbed, long-acting sulfonamide, effective for the treatment of
shipping fever complex, bacterial pneumonia, calf diphtheria, and foot rot in
cattle.
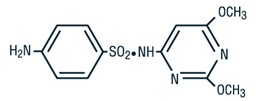
Sulfadimethoxine is a white, almost tasteless and odorless compound.
Chemically, it is N1-(2,6-dimethoxy-4-pyrimidinyl) sulfanilamide. The
structural formula is:
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS SECTION
Restricted Drug (California) - Use Only as Directed
Not for Human Use
MECHANISM OF ACTION SECTION
ACTIONS: Sulfadimethoxine has been demonstrated clinically or in the laboratory to be effective against a variety of organisms, such as streptococci, klebsiella, proteus, shigella, staphylococci, escherichia, and salmonella. 1,2
The systemic sulfonamides which include sulfadimethoxine are bacteriostatic agents. Sulfonamides competitively inhibit bacterial synthesis of folic acid (pteroylglutamic acid) from para-aminobenzoic acid. Mammalian cells are capable of utilizing folic acid in the presence of sulfonamides.
The tissue distribution of sulfadimethoxine, as with all sulfonamides, is a function of plasma levels, degree of plasma protein binding, and subsequent passive distribution in the tissues of the lipid-soluble unionized form. The relative amounts are determined by both its pKa and by the pH of each tissue. Therefore, levels tend to be higher in less acid tissue and body fluids or those diseased tissues having high concentrations of leucocytes.2
Slow renal excretion results from a high degree of tubular reabsorption,3 and plasma protein binding is very high, providing a blood reservoir of the drug. Thus, sulfadimethoxine maintains higher blood levels than most other long- acting sulfonamides. Single, comparatively low doses of sulfadimethoxine give rapid and sustained therapeutic blood levels.1
To assure successful sulfonamide therapy (1) the drug must be given early in the course of the disease, and it must produce a high sulfonamide level in the body rapidly after administration, (2) therapeutically effective sulfonamide levels must be maintained in the body throughout the treatment period, (3) treatment should continue for a short period of time after the clinical signs have disappeared, and (4) the causative organisms must be sensitive to this class of drugs.
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & OR TOXICOLOGY SECTION
TOXICITY AND SAFETY: Data regarding acute (LD50) and chronic toxicities of sulfadimethoxine indicate the drug is very safe. The LD50 in mice is greater than 2 g/kg of body weight when administered intraperitoneally and greater than 16 g/kg when administered orally. In dogs receiving massive single oral doses of 3.2 g/kg of body weight, diarrhea was the only adverse effect observed. Dogs given 160 mg/kg of body weight orally daily for 13 weeks showed no signs of toxicity.
In cattle sulfadimethoxine has been shown to be safe through extensive clinical use with other dosage forms. In addition, studies with intravenous administration of sulfadimethoxine injection 40% have demonstrated that hemolysis of erythrocytes does not occur by this route of administration. Sulfadimethoxine has a relatively high solubility at the pH normally occurring in the kidney, precluding the possibility of precipitation and crystalluria.
WARNINGS SECTION
WARNING:: Milk taken from animals during treatment and for 60 hours (5 milkings) after the latest treatment must not be used for food. Do not administer within 5 days of slaughter.
A withdrawal period has not been established for this product in preruminating calves.
DO NOT USE IN CALVES TO BE PROCESSED FOR VEAL.
PRECAUTIONS SECTION
PRECAUTIONS: During treatment period, make certain that animals maintain adequate water intake.
If animals show no improvement within 2 or 3 days, consult your veterinarian.
Tissue damage may result from perivascular infiltration.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: SulfaMed Injection 40% must be administered only by the intravenous route in cattle. Cattle should receive 1 mL of SulfaMed Injection 40% per 16 lb of body weight (55 mg/kg) as an initial dose, followed by 0.5 mL per 16 lb of body weight (27.5 mg/kg) every 24 hours thereafter. Sulfadimethoxine Boluses may be utilized for maintenance therapy in cattle. Representative weights and doses are indicated in the following table:
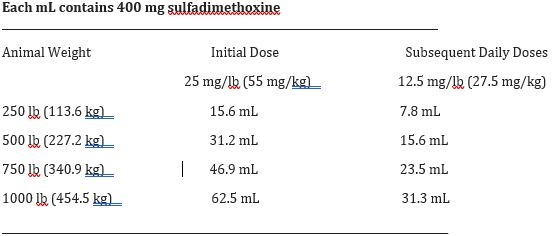
Length of treatment depends on the clinical response. In most cases treatment for 3 - 5 days is adequate. Treatment should be continued until the animal is asymptomatic for 48 hours.
DIRECTIONS FOR INTRAVENOUS INJECTION:
1. A nose lead and/or halter sufficiently strong enough to effectively restrain or hold the animal's head steady so that the intravenous injection can be made with ease.
2. Hypodermic needles, 16 or 18 gauge and 2 inches long. Only new, sharp and sterile hypodermic needles should be used. Dull needles should be discarded. Extra needles should always be available in case the needle being used should become clogged.
3. Hypodermic syringes, 40- or 50-mL sterile, disposable or reusable glass syringes should be available.
4. Alcohol (70%) or equally effective antiseptic for disinfecting the skin.
Preparation of equipment: Glass syringes and regular hypodermic needles
should be thoroughly cleaned and washed. Following this, the needles and
syringes should be immersed in boiling water for 30 minutes prior to each
injection. Regular hypodermic needles should not be used more than 3-4 times
as repeated skin puncturing and boiling of the needles causes them to become
quite dull. Disposable hypodermic needles and syringes should not be used more
than once.
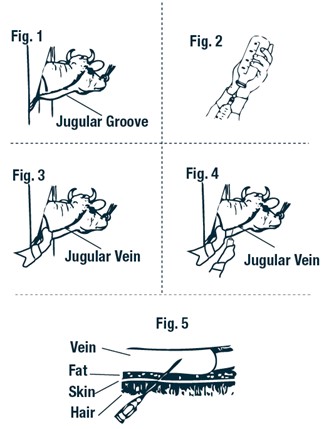
Restraint of animal: The cow should preferably be in a stanchion for
maximum restraint. If this is not possible, the animal should be restrained in
a manner to prevent excessive movement. A nose lead should be applied and the
animal's head turned sidewise to stretch the skin and tense the muscles of the
neck region (See Figure 1).
Locating the jugular vein: Once the animal has been restrained (as above),
you will notice a long depression of the skin from below the angle of the jaw
to just above the shoulder. This is known as the jugular furrow or jugular
groove. The jugular vein is located just under the jugular groove (See Figure
1).
Preparation of SulfaMed Injection 40% for injection: The rubber cap of the
bottle should be thoroughly cleaned with 70% alcohol or other satisfactory
antiseptic. The correct amount of SulfaMed Injection 40% for treatment should
be calculated (see dosage directions) and that amount withdrawn into a syringe
(See Figure 2). One or two syringefuls of air should be injected into the
bottle first to make withdrawing the drug easier. SulfaMed Injection 40%
should preferably be at room temperature when filling syringes and when
injecting intravenously.
Entering the vein: The skin of the injection area should be clean and free
of dirt. Cotton saturated with 70% alcohol (or suitable antiseptic) should be
used to wipe the injection site. Apply pressure over the jugular vein close to
the shoulder. This will reduce the flow of blood to the heart and cause
jugular vein to bulge or enlarge (See Figure 3). When the jugular vein has
been "raised", insert the hypodermic needle at a 45° angle through the skin
just underneath the jugular vein. The beveled edge of the hypodermic needle
should be up (See Figure 4).
After the skin has been punctured, the point of the needle should be directed
toward the side of the vein and pushed into the center of the vein (See Figure
5). When the needle is in the center of the vein, there will be free flow of
blood back through the needle. Release external pressure when you are sure the
needle is within the vein.
Injecting the SulfaMed Injection 40%: After the needle has been accurately
inserted into the jugular vein, firmly attach the syringe containing SulfaMed
Injection 40% to the inserted hypodermic needle. Caution; be sure syringe is
free of air. Exert firm pressure on the plunger of the syringe to inject the
SulfaMed Injection 40% while the barrel is held firmly. The injection should
be made moderately slow - never rapidly. If the animal moves, causing
resistance in pushing the plunger of the syringe, or if a bubble of the drug
is noted under the skin, the needles is no longer within the vein. The needle
should be repositioned.
When the injection is completed, quickly withdraw the syringe and needle with
a quick pull and apply light pressure over the injection site with alcohol and
cotton to minimize bleeding from the puncture site.
To report adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Bimeda, Inc. at 1-888-524-6322. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
STORAGE: Store at 20°C - 25°C (68°F - 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C - 30°C (between 59°F - 86°F).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
HOW SUPPLIED: : SulfaMed Injection 40% is available in the following dosage form for cattle: SulfaMed Injection 40% - Each mL contains 400 mg sulfadimethoxine compounded with 20% propylene glycol, 1% benzyl alcohol, 0.1 mg disodium edetate, 1 mg sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate, and pH adjusted with sodium hydroxide, 250 mL bottles.
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-523
REFERENCES SECTION
REFERENCES
1. Data on file from Hoffman-La Roche Inc., Nutley, New Jersey.
2. Stowe CM: The sulfonamides. In Jones LM (ed). Veterinary Pharmacologyand Therapeutics, Ames, Iowa, Iowa State University Press, chapter 33, 1965.
3. Baggot, JD: Some aspects of drug persistence in domestic animals. Res Vet Sci 11:(2) 130, 1970.
