Docetaxel
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOCETAXEL INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOCETAXEL INJECTION. DOCETAXEL injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
2c806400-5fdc-4398-8475-37f700b3191f
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 31, 2022
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
DUNS: 119723554
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Docetaxel
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Docetaxel
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
Drug Labeling Information
BOXED WARNING SECTION
**WARNING: TOXIC DEATHS, HEPATOTOXICITY, NEUTROPENIA, HYPERSENSITIVITY
REACTIONS, and FLUID RETENTION**
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies and its mechanism of action, Docetaxel Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. Available data from case reports in the literature and pharmacovigilance with docetaxel use in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform the drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Docetaxel Injection contains alcohol which can interfere with neurobehavioral development [see Clinical Considerations]. In animal reproductive studies, administration of docetaxel to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis caused an increased incidence of embryo-fetal toxicities, including intrauterine mortality, at doses as low as 0.02 and 0.003 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area, respectively [see Data]. Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, miscarriage, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Docetaxel Injection contains alcohol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. Published studies have demonstrated that alcohol is associated with fetal harm including central nervous system abnormalities, behavioral disorders, and impaired intellectual development.
Data
Animal data
Intravenous administration of ≥0.3 and 0.03 mg/kg/day docetaxel to pregnant rats and rabbits, respectively, during the period of organogenesis caused an increased incidence of intrauterine mortality, resorptions, reduced fetal weights, and fetal ossification delays. Maternal toxicity was also observed at these doses, which were approximately 0.02 and 0.003 times the daily maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of docetaxel in human milk, or on its effects on milk production or the breastfed child. No lactation studies in animals have been conducted. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Docetaxel Injection and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating Docetaxel Injection.
Contraception
Females
Docetaxel Injection can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 6 months after the last dose of Docetaxel Injection.
Males
Based on genetic toxicity findings, advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of Docetaxel Injection.
Infertility
Based on findings in animal studies, Docetaxel Injection may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The alcohol content of Docetaxel Injection should be taken into account when given to pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
The efficacy of docetaxel in pediatric patients as monotherapy or in combination has not been established. The overall safety profile of docetaxel in pediatric patients receiving monotherapy or TCF was consistent with the known safety profile in adults.
Docetaxel has been studied in a total of 289 pediatric patients: 239 in 2 trials with monotherapy and 50 in combination treatment with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (TCF).
Docetaxel Monotherapy
Docetaxel monotherapy was evaluated in a dose-finding phase 1 trial in 61 pediatric patients (median age 12.5 years, range 1 to 22 years) with a variety of refractory solid tumors. The recommended dose was 125 mg/m2 as a 1-hour intravenous infusion every 21 days. The primary dose limiting toxicity was neutropenia.
The recommended dose for docetaxel monotherapy was evaluated in a phase 2 single-arm trial in 178 pediatric patients (median age 12 years, range 1 to 26 years) with a variety of recurrent/refractory solid tumors. Efficacy was not established with tumor response rates ranging from one complete response (CR) (0.6%) in a patient with undifferentiated sarcoma to four partial responses (2.2%) seen in one patient each with Ewing Sarcoma, neuroblastoma, osteosarcoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Docetaxel in Combination
Docetaxel was studied in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (TCF) versus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (CF) for the induction treatment of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) in pediatric patients prior to chemoradiation consolidation. Seventy-five patients (median age 16 years, range 9 to 21 years) were randomized (2:1) to docetaxel (75 mg/m2) in combination with cisplatin (75 mg/m2) and 5-fluorouracil (750 mg/m2) (TCF) or to cisplatin (80 mg/m2) and 5-fluorouracil (1000 mg/m2/day) (CF). The primary endpoint was the CR rate following induction treatment of NPC. One patient out of 50 in the TCF group (2%) had a complete response while none of the 25 patients in the CF group had a complete response.
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic parameters for docetaxel were determined in 2 pediatric solid tumor trials. Following docetaxel administration at 55 mg/m2 to 235 mg/m2 in a 1-hour intravenous infusion every 3 weeks in 25 patients aged 1 to 20 years (median 11 years), docetaxel clearance was 17.3±10.9 L/h/m2.
Docetaxel was administered in combination with cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (TCF), at dose levels of 75 mg/m2 in a 1-hour intravenous infusion day 1 in 28 patients aged 10 to 21 years (median 16 years, 17 patients were older than 16). Docetaxel clearance was 17.9±8.75 L/h/m2, corresponding to an AUC of 4.20±2.57 mcg•h/mL.
In summary, the body surface area adjusted clearance of docetaxel monotherapy and TCF combination in children were comparable to those in adults [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy in elderly patients.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
In a study conducted in chemotherapy-naive patients with NSCLC (TAX326), 148 patients (36%) in the Docetaxel Injection+cisplatin group were 65 years of age or greater. There were 128 patients (32%) in the vinorelbine+cisplatin group 65 years of age or greater. In the Docetaxel Injection+cisplatin group, patients less than 65 years of age had a median survival of 10.3 months (95% CI: 9.1 months, 11.8 months) and patients 65 years or older had a median survival of 12.1 months (95% CI: 9.3 months, 14 months). In patients 65 years of age or greater treated with Docetaxel Injection+cisplatin, diarrhea (55%), peripheral edema (39%) and stomatitis (28%) were observed more frequently than in the vinorelbine+cisplatin group (diarrhea 24%, peripheral edema 20%, stomatitis 20%). Patients treated with Docetaxel Injection+cisplatin who were 65 years of age or greater were more likely to experience diarrhea (55%), infections (42%), peripheral edema (39%) and stomatitis (28%) compared to patients less than the age of 65 administered the same treatment (43%, 31%, 31% and 21%, respectively).
When Docetaxel Injection was combined with carboplatin for the treatment of chemotherapy-naive, advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma, patients 65 years of age or greater (28%) experienced higher frequency of infection compared to similar patients treated with Docetaxel Injection+cisplatin, and a higher frequency of diarrhea, infection and peripheral edema than elderly patients treated with vinorelbine+cisplatin.
Prostate Cancer
Of the 333 patients treated with Docetaxel Injection every three weeks plus prednisone in the prostate cancer study (TAX327), 209 patients were 65 years of age or greater and 68 patients were older than 75 years. In patients treated with Docetaxel Injection every three weeks, the following treatment emergent adverse reactions occurred at rates ≥10% higher in patients 65 years of age or greater compared to younger patients: anemia (71% vs. 59%), infection (37% vs. 24%), nail changes (34% vs. 23%), anorexia (21% vs. 10%), weight loss (15% vs. 5%) respectively.
Breast Cancer
In the adjuvant breast cancer trial (TAX316), Docetaxel Injection in combination with doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide was administered to 744 patients of whom 48 (6%) were 65 years of age or greater. The number of elderly patients who received this regimen was not sufficient to determine whether there were differences in safety and efficacy between elderly and younger patients.
Gastric Cancer
Among the 221 patients treated with Docetaxel Injection in combination with cisplatin and fluorouracil in the gastric cancer study, 54 were 65 years of age or older and 2 patients were older than 75 years. In this study, the number of patients who were 65 years of age or older was insufficient to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. However, the incidence of serious adverse reactions was higher in the elderly patients compared to younger patients. The incidence of the following adverse reactions (all grades, regardless of relationship): lethargy, stomatitis, diarrhea, dizziness, edema, febrile neutropenia/neutropenic infection occurred at rates ≥10% higher in patients who were 65 years of age or older compared to younger patients. Elderly patients treated with TCF should be closely monitored.
Head and Neck Cancer
Among the 174 and 251 patients who received the induction treatment with Docetaxel Injection in combination with cisplatin and fluorouracil (TPF) for SCCHN in the TAX323 and TAX324 studies, 18 (10%) and 32 (13%) of the patients were 65 years of age or older, respectively.
These clinical studies of Docetaxel Injection in combination with cisplatin and fluorouracil in patients with SCCHN did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience with this treatment regimen has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Avoid Docetaxel Injection in patients with bilirubin >ULN and patients with AST and/or ALT >1.5 x ULN concomitant with alkaline phosphatase >2.5 x ULN [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The alcohol content of Docetaxel Injection should be taken into account when given to patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
- Lactation: Advise women not to breastfeed. (8.2)
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Verify pregnancy status of females prior to initiation of Docetaxel Injection. (8.3)
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
PATIENT INFORMATION
|
Docetaxel (doe-se-tax-el) Injection | |
|
What is the most important information I should know about Docetaxel Injection? Docetaxel Injection can cause serious side effects, including death. *The chance of death in people who receive Docetaxel Injection is higher if you: * have liver problems * receive high doses of Docetaxel Injection * have non-small cell lung cancer and have been treated with chemotherapy medicines that contain platinum *Docetaxel Injection can affect your blood cells. Your healthcare provider should do routine blood tests during treatment with Docetaxel Injection. This will include regular checks of your white blood cell counts. If your white blood cells are too low, your healthcare provider may not treat you with Docetaxel Injection until you have enough white blood cells. People with low white blood cell counts can develop life-threatening infections. The earliest sign of infection may be fever. Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for how often to take your temperature during treatment with Docetaxel Injection. Call your healthcare provider right away if you have a fever. ***Swelling (inflammation) of the small intestine and colon.**This can happen at any time during treatment and could lead to death as early as the first day you get symptoms. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop new or worse symptoms of intestinal problems, including stomach (abdominal) pain or tenderness or diarrhea, with or without fever. *Severe allergic reactions are medical emergencies that can happen in people who receive Docetaxel Injection and can lead to death. You may be at higher risk of developing a severe allergic reaction to Docetaxel Injection if you are allergic to paclitaxel. Your healthcare provider will monitor you closely for allergic reactions during your Docetaxel Injection infusion. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these signs of a severe allergic reaction:
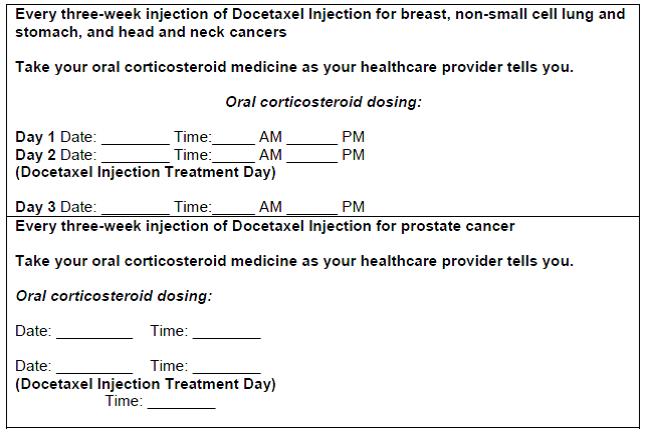
*Your body may hold too much fluid (severe fluid retention) during treatment with Docetaxel Injection. This can be life threatening. To decrease the chance of this happening, you must take another medicine, a corticosteroid, before each Docetaxel Injection treatment. You must take the corticosteroid exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Tell your healthcare provider or nurse before your Docetaxel Injection treatment if you forgot to take your corticosteroid dose or do not take it as your healthcare provider tells you. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have swelling in your legs or feet, weight gain or shortness of breath. ***Risk of new cancers.**An increase in new (second) cancers has happened in people treated with Docetaxel Injection together with certain other anticancer treatments. This includes certain blood cancers, such as acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (NHL), and kidney cancer. * Changes in blood counts due to leukemia and other blood disorders may occur years after treatment with Docetaxel Injection. Your healthcare provider will check you for new cancers during and after your treatment with Docetaxel Injection. *Severe skin problems. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these signs of a severe skin reaction: | |
|
What is Docetaxel Injection? Docetaxel Injection is a prescription anticancer medicine used to treat certain people with:
It is not known if Docetaxel Injection is effective in children. | |
|
Do not receive Docetaxel Injection if you:
See “What is the most important information I should know about Docetaxel Injection?” for the signs and symptoms of a severe allergic reaction. See the end of this Patient Information for a complete list of the ingredients in Docetaxel Injection. | |
|
Before you receive Docetaxel Injection, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Females who are able to become pregnant:
Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant should use effective birth control during treatment with Docetaxel Injection and for 3 months after the last dose. Talk to your healthcare provider if you have questions about birth control options that are right for you.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Docetaxel Injection may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect the way Docetaxel Injection works. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | |
|
How will I receive Docetaxel Injection?
| |
|
What are the possible side effects of Docetaxel Injection? Docetaxel Injection may cause serious side effects including death.
*Neurologic problems. Neurologic symptoms are common in people who receive Docetaxel Injection but can be severe. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have numbness, tingling, or burning in your hands or feet (peripheral neuropathy) or weakness of your legs, feet, arms, or hands (motor weakness). *Vision problems including blurred vision or loss of vision. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any vision changes. ***Docetaxel Injection contains alcohol.**The alcohol content in Docetaxel Injection may impair your ability to drive or use machinery right after receiving Docetaxel Injection. Consider whether you should drive, operate machinery or do other dangerous activities right after you receive Docetaxel Injection treatment. *Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is caused by the fast breakdown of cancer cells. TLS can cause kidney failure, the need for dialysis treatment, or heart problems, and may lead to death. Your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check for TLS when you first start treatment and during treatment with Docetaxel Injection. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any symptoms of TLS during treatment with Docetaxel Injection, including: | |
|
|
| |
|
The most common side effects of Docetaxel Injection include: | |
|
|
|
Tell your healthcare provider if you have a fast or irregular heartbeat, severe shortness of breath, dizziness or fainting during your infusion. If any of these events occurs after your infusion, get medical help right away. Docetaxel Injection may affect fertility in males. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you. These are not all the possible side effects of Docetaxel Injection. For more information ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of Docetaxel
Injection. | |
|
What are the ingredients in Docetaxel Injection? Manufactured In Romania By:**Sindan Pharma SRL,**Bucharest 1, Romania 011171 | |
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: I 7/2022 |