DOPTELET
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOPTELET safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOPTELET. DOPTELET (avatrombopag ) tablets, for oral useDOPTELET® SPRINKLE (avatrombopag) oral granules Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
e2d5960d-6c18-46cc-86bd-089222b09852
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 13, 2025
AkaRx, Inc.
DUNS: 080307190
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
avatrombopag
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
avatrombopag maleate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
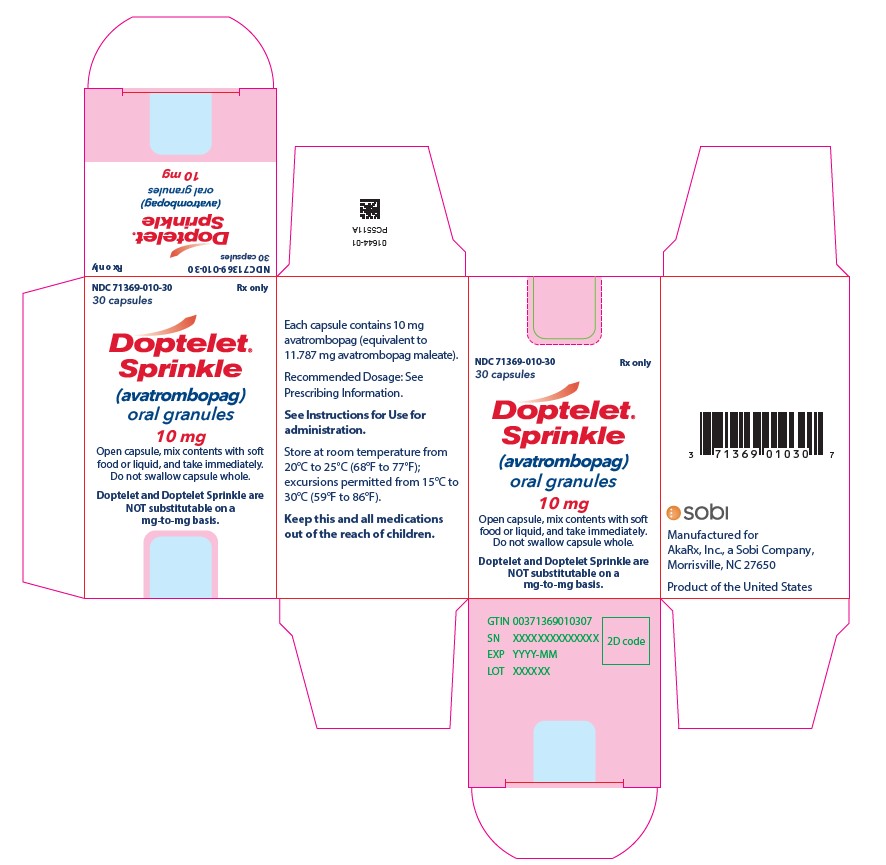
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71369-010-30
10 mg per capsule
Rx Only
Doptelet Sprinkle
one bottle with 30 capsules
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1****INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Thrombocytopenia in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
(CLD)
DOPTELET is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure.
1.2 Treatment of Thrombocytopenia in Adult Patients with Chronic Immune
Thrombocytopenia (ITP)
DOPTELET is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment.
1.3 Treatment of Thrombocytopenia in Pediatric Patients 1 Year and Older
with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP)
DOPTELET is indicated for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in pediatric patients 1 year and older with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment.
DOPTELET is a thrombopoietin receptor agonist indicated for the treatment of:
- Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure. (1.1)
- Thrombocytopenia in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment. (1.2)
- Thrombocytopenia in pediatric patients 1 year and older with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia who have had an insufficient response to a previous treatment (1.3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4****CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5****WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
DOPTELET is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist and TPO receptor agonists have been associated with thrombotic and thromboembolic complications in patients with chronic liver disease or immune thrombocytopenia. In patients with chronic liver disease, thromboembolic events (portal vein thrombosis) occurred in 0.4% (1/274) of patients receiving DOPTELET. In adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, thromboembolic events (arterial or venous) occurred in 7% (9/128) of patients receiving DOPTELET.
Consider the potential increased thrombotic risk when administering DOPTELET to patients with known risk factors for thromboembolism, including genetic prothrombotic conditions (e.g., Factor V Leiden, Prothrombin 20210A, Antithrombin deficiency or Protein C or S deficiency) and acquired risk factors (e.g., antiphospholipid syndrome).
DOPTELET should not be administered to patients with chronic liver disease or immune thrombocytopenia in an attempt to normalize platelet counts. Monitor platelet counts and follow the dosing guidelines to achieve target platelet counts [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 and 2.5)]. Monitor patients receiving DOPTELET for signs and symptoms of thromboembolic events and institute treatment promptly.
Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications: DOPTELET is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist and TPO receptor agonists have been associated with thrombotic and thromboembolic complications in patients with chronic liver disease or immune thrombocytopenia.
Monitor platelet counts. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thromboembolic events and institute treatment promptly. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trial Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
The safety of DOPTELET was evaluated in two international, identically designed, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials, ADAPT-1 and ADAPT-2, in which 430 patients with chronic liver disease and thrombocytopenia received either DOPTELET (n=274) or placebo (n=156) daily for 5 days prior to a scheduled procedure, and had 1 post-dose safety assessment. Patients were divided into two groups based on their mean platelet count at baseline:
- Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (less than 40×109/L) who received DOPTELET 60 mg once daily for 5 days
- High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (40 to less than 50×109/L) who received DOPTELET 40 mg once daily for 5 days
The majority of patients were males (65%) and median subject age was 58 years (ranging from 19-86 years of age). The racial and ethnic distribution was White (60%), Asian (33%), Black (3%) and Other (3%).
The most common adverse reactions (those occurring in ≥3% of patients) in the DOPTELET-treated groups (60 mg or 40 mg) across the pooled data from the two trials are summarized in Table 8.
Table 8**:Adverse Reactions with a Frequency ≥3% in Patientswith ChronicLiverDiseaseTreatedwith DOPTELET – Pooled Data ADAPT-1 and ADAPT-2**
|
Adverse Reactions |
Low Baseline |
High Baseline |
Combined** Baseline** | |||
|
DOPTELET |
Placebo |
DOPTELET |
Placebo |
Total |
Total | |
|
Pyrexia |
11 |
9 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
9 |
|
Abdominal Pain |
6 |
7 |
7 |
6 |
7 |
6 |
|
Nausea |
6 |
8 |
7 |
6 |
7 |
7 |
|
Headache |
4 |
8 |
7 |
5 |
6 |
6 |
|
Fatigue |
4 |
4 |
3 |
2 |
4 |
3 |
|
Edema Peripheral |
3 |
2 |
4 |
2 |
3 |
2 |
For the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the incidence of serious adverse reactions was 7% (11/159) in the 60 mg DOPTELET treatment group. For the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the incidence of serious adverse reactions was 8% (9/115) in the 40 mg DOPTELET treatment group. The most common serious adverse reaction reported with DOPTELET was hyponatremia. Two DOPTELET-treated patients (0.7%) developed hyponatremia.
Adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation of DOPTELET were anemia, pyrexia, and myalgia; each was reported in a single (0.4%) patient in the DOPTELET (60 mg) treatment group.
Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
The safety of DOPTELET was evaluated in four clinical trials in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia: two Phase 3 trials (one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, and one randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trial) and two Phase 2 trials (one randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging, trial, and one open-label extension trial) in 161 patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia in both the double-blind and open-label extension phases.
The pooled safety data from these four clinical trials includes 128 patients who received 2.5 to 40 mg of DOPTELET once daily for a median duration of exposure of 29.1 weeks and had 1 post-dose safety assessment. The majority of patients were female (63%) and median subject age was 50.5 years (ranging from 18-88 years of age). The racial and ethnic distribution was White (84%), Black (6%), Asian (6%) and Other (6%).
The most common adverse reactions (those occurring in ≥10% of patients) in the DOPTELET-treated patients across the pooled safety data from the four trials are summarized in Table 9.
Table 9**: Adverse Reactions with a Frequency ≥10% in Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia Treated with DOPTELET – Pooled Data from Clinical Trials**
|
Adverse Reactions |
DOPTELET (N=128) % |
Placebo (N= 22) % |
|
Headache |
31 |
14 |
|
Fatigue |
28 |
9 |
|
Contusion |
26 |
18 |
|
Epistaxis |
19 |
18 |
|
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection |
15 |
5 |
|
Arthralgia |
13 |
0 |
|
Gingival Bleeding |
13 |
0 |
|
Petechiae |
11 |
9 |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
10 |
0 |
The incidence of serious adverse reactions was 9% (12/128) in the DOPTELET treatment group. Serious adverse reactions reported in more than 1 individual DOPTELET-treated patient included headache, occurring in 1.6% (2/128).
Adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation of DOPTELET that were reported in more than 1 patient included headache, occurring in 1.6% (2/128).
Pediatric Patients with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
The data described below reflect median exposure to DOPTELET of 12 weeks for 54 pediatric patients (≥1 to <18 years of age) with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia across the core phase of one double-blind, placebo- controlled trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Table 10 presents the most common adverse reactions (experienced by greater than or equal to 10% of pediatric patients 1 year and older receiving DOPTELET) with a higher incidence for DOPTELET versus placebo.
Table 10: Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia Treated with DOPTELET****a
|
Adverse Reactions |
DOPTELET(N=54) |
Placebo(N=21) |
|
Viral Infectionb |
20 |
5 |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
20 |
10 |
|
Cough |
17 |
0 |
|
Pyrexia |
17 |
0 |
|
Oropharyngeal Pain |
13 |
0 |
a Adverse reactions that occurred in ≥10% of DOPTELET-treated patients and ≥2% more than placebo-treated patients.
b Viral infection includes viral upper respiratory infection, viral infection, COVID-19, parainfluenza virus infection, and rhinovirus infection.
Two patients experienced serious adverse reactions: thrombocytosis and headache. Two patients experienced adverse reactions resulting in discontinuation of DOPTELET: vomiting and headache (in one patient) and leukocytosis (in one patient).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of DOPTELET. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions including pruritus, rash, choking sensation, erythema, pharyngeal edema, pruritus generalized, rash macular, swelling face, and swollen tongue.
In adult patients with chronic liver disease, the most common adverse reactions (≥3%) were pyrexia, abdominal pain, nausea, headache, fatigue, and edema peripheral. (6.1)
In adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia, the most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were headache, fatigue, contusion, epistaxis, upper respiratory tract infection, arthralgia, gingival bleeding, petechiae and nasopharyngitis. (6.1)
In pediatric patients with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia, the most common adverse reactions (≥10%) were viral infection, nasopharyngitis, cough, pyrexia, and oropharyngeal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sobi, Inc. at 1-866-773-5274 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 orwww.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7****DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Other Drugs on DOPTELET in Patients with Persistent or
Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
Moderate or Strong Dual Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4
Concomitant use with a moderate or strong dual inhibitor of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 increases avatrombopag AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of DOPTELET toxicities. Reduce the starting dosage of DOPTELET when used concomitantly with a moderate or strong dual inhibitor of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 (see Table 4 and Table 7) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 and 2.6)].
In patients starting moderate or strong dual inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 while receiving DOPTELET, monitor platelet counts and adjust DOPTELET dose as necessary (see Table 2 and Table 3; and Table 5 and Table 6) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 and 2.5)].
Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4
Concomitant use with a moderate or strong dual inducer of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 decreases avatrombopag AUC [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce DOPTELET efficacy. Increase the recommended starting dosage of DOPTELET when used concomitantly with a moderate or strong dual inducer of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 (see Table 4 and Table 7) [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 and 2.6)].
In patients starting moderate or strong dual inducers of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 while receiving DOPTELET, monitor platelet counts and adjust DOPTELET dose as necessary (see Table 2 and Table 3; and Table 5 and Table 6) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3 and 2.5)].
Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
No dosage adjustments are required for patients with chronic liver disease.
Moderate or Strong Dual CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 Inducers or Inhibitors: Dose adjustments are recommended for patients with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia. (7.1)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8****USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal reproduction studies, DOPTELET may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman (see Data). The available data on DOPTELET in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of avatrombopag resulted in adverse developmental outcomes when administered during organogenesis in rabbits and during organogenesis and the lactation period in rats. However, these findings were observed at exposures based on an AUC substantially higher than the AUC observed in patients at the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg once daily. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and of miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies, avatrombopag was administered during organogenesis at doses of 100, 300, and 1000 mg/kg/day in rats and doses of 100, 300, and 600 mg/kg/day in rabbits. Minimal decreases in fetal weights were observed in rats at the maternally toxic dose of 1000 mg/kg/day with exposures 190 times the human exposure based on AUC. Spontaneous abortions were observed at all doses tested in rabbits and were associated with decreased body weights and food consumption at 300 and 600 mg/kg/day; exposures at the lowest dose of 100 mg/kg/day were 10 times the AUC in patients at the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg once daily. There were no embryo-fetal effects in rats administered avatrombopag at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (53 times the human exposure based on AUC) or rabbits administered avatrombopag at doses up to 600 mg/kg (35 times the human exposure based on AUC).
In pre- and postnatal development studies in rats, avatrombopag was administered during both the organogenesis and lactation periods at doses ranging from 5 to 600 mg/kg/day. Doses of 100, 300, and 600 mg/kg/day caused maternal toxicity leading to total litter losses, decreased body weight in pups, and increased pup mortality, with the majority of the pup mortality occurring from postnatal days 14 to 21. At a dose of 50 mg/kg/day that did not produce clear maternal toxicity, avatrombopag caused increased pup mortality from postnatal days 4 to 21, and mortality continued through postnatal day 25. The 50 mg/kg/day dose also decreased body weight gain in the pups, resulting in a delay in sexual maturation. There were no effects on behavioral or reproductive functions in the offspring. The 50 mg/kg/day dose resulted in maternal exposures 43 times and pup exposures approximately 3 times the AUC observed in patients at the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg once daily.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of avatrombopag in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Avatrombopag was present in the milk of lactating rats. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely the drug will be present in human milk. Due to the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child from DOPTELET, breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with DOPTELET and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose (see Clinical Considerations).
Clinical Considerations
MinimizingExposure
A lactating woman receiving DOPTELET for brief periods, such as prior to an invasive procedure, should interrupt breastfeeding and pump and discard breastmilk during treatment and for two weeks after the last dose of DOPTELET in order to minimize exposure to a breastfed child. Advise lactating women receiving chronic DOPTELET therapy not to breastfeed during treatment with DOPTELET and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of DOPTELET tablet for the treatment of persistent or chronic ITP have been established in pediatric patients aged 6 years and older. The safety and effectiveness of DOPTELET SPRINKLE for the treatment of persistent or chronic ITP have been established in pediatric patients aged 1 to <6 years. Use of DOPTELET tablet and DOPTELET SPRINKLE for their respective populations is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled study in pediatric patients aged 1 year and older [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
In a 10-week juvenile toxicology study in rats, avatrombopag was administered at doses ranging from 20 to 300 mg/kg/day. There was no test article-related mortality and there were no clinical signs at doses up to 300 mg/kg/day. In the stomach, dose-dependent degeneration, regenerative hyperplasia, and atrophy of the glandular epithelium occurred at 100 and 300 mg/kg/day; exposures at 100 mg/kg/day in male rats were 14 times the AUC in patients at the highest recommended dose of 60 mg once daily. An increased incidence of background focal mineralization was also observed in the kidneys of females at 300 mg/kg/day (female rat exposure was 50 times the human exposure based on AUC at the 60 mg daily dose).
8.5 Geriatric Use
There were 112 patients 65 years of age and older in the clinical studies for Chronic Liver Disease and Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia [see Clinical Studies (14.1 and 14.2)]. Of the total number of DOPTELET-treated patients in these studies, 71 (23%) were 65 years of age and older, while 12 (4%) were 75 years of age and older. Clinical studies of DOPTELET did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
- Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm (8.1)
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Indications and Usage (1.3) 07/2025
Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8) 07/2025
Warnings and Precautions (5.1) 07/2024
Indications and Usage (1.3) 07/2025
Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, 2.8) 07/2025
Warnings and Precautions (5.1) 07/2024
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10****OVERDOSAGE
In the event of overdose, platelet count may increase excessively and result in thrombotic or thromboembolic complications. Closely monitor the patient and platelet count. Treat thrombotic complications in accordance with standard of care.
No antidote for DOPTELET overdose is known.
Hemodialysis is not expected to enhance the elimination of DOPTELET because avatrombopag is only approximately 6% renally excreted and is highly bound to plasma proteins.
Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdose management recommendations.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Use and Administration Instructions
- Select the recommended product (DOPTELET tablets or DOPTELET SPRINKLE) based on the indication and patient’s age.
- Administer DOPTELET tablets and DOPTELET SPRINKLE with food.
- DOPTELET tablets and DOPTELET SPRINKLE are not substitutable on a mg-to-mg basis.
- The mixture prepared from the granules in DOPTELET SPRINKLE capsules is more bioavailable than DOPTELET tablets [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. There is no experience from clinical trials in switching between dosing with the granules and the tablet. If the formulation is switched, monitor platelet counts weekly until stable platelet counts are obtained and adjust dosing as needed before resuming monthly monitoring.
2.2 Recommended Dosage of DOPTELET Tablets for Patients with Chronic Liver
Disease
Begin DOPTELET tablets dosing 10 days to 13 days prior to the scheduled procedure. The recommended daily dose of DOPTELET is based on the patient’s platelet count prior to the scheduled procedure (see Table 1). Patients should undergo their procedure 5 days to 8 days after the last dose of DOPTELET.
DOPTELET tablets should be taken orally once daily for 5 consecutive days with food. All 5 days of dosing should be completed.
Table****1:** Recommended DOPTELET Tablets Dosage and Duration in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease Scheduled to Undergo a Procedure**
|
Platelet Count |
Recommended DOPTELET Dosage |
Duration |
|
Less than 40×109/L |
60 mg (3 tablets) orally once daily |
5 days |
|
40×109/L to less than 50×109/L |
40 mg (2 tablets) orally once daily |
5 days |
DOPTELET tablets have been investigated only as a single 5-day once daily dosing regimen in clinical trials in patients with chronic liver disease [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. DOPTELET should not be administered to patients with chronic liver disease in an attempt to normalize platelet counts.
Monitoring**:** Obtain a platelet count prior to administration of DOPTELET therapy and on the day of a procedure to ensure an adequate increase in platelet count.
2.3 Recommended Dosage of DOPTELET Tablets for Adult Patients with Chronic
Immune Thrombocytopenia and Pediatric Patients 6 Years and Older with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
Use the lowest dose of DOPTELET needed to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50×109/L as necessary to reduce the risk for bleeding. Dose adjustments are based on platelet count response. Do not use DOPTELET to normalize platelet counts.
Initial Dosage**:**
- Begin DOPTELET tablets at an initial dosage of 20 mg (1 tablet) orally once daily with food (see Table 3).
- The recommended initial dosages of DOPTELET tablets are different for patients receiving certain concomitant medications (see Table 4).
Monitoring**:** After initiating therapy with DOPTELET, assess platelet counts weekly until a stable platelet count greater than or equal to 50×109/L has been achieved, and then obtain platelet counts monthly thereafter. Obtain platelet counts weekly for at least 4 weeks following discontinuation of DOPTELET.
Dose Adjustments**:**
DOPTELET tablet dose adjustments (see Table 2 and Table 3) are based on the platelet count response. Do not exceed a DOPTELET daily dose of 40 mg (2 tablets).
Table2: DOPTELET Tablets Recommended Dose Adjustments for Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia and Pediatric Patients 6 Years and Older with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Platelet Count |
Dose Adjustment or Action |
|
Less than 50×109/L after at least 2 weeks of DOPTELET tablets |
|
|
Between 200×109/L and 400×109/L |
|
|
Greater than 400×109/L |
|
|
Less than 50×109/L after 4 weeks of DOPTELET 40 mg (2 tablets) once daily |
|
|
Greater than 400×109/L after 2 weeks of DOPTELET 20 mg (1 tablet) weekly |
|
Table3: DOPTELET Tablet Dose Levels for Titration in Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia and Pediatric Patients 6 Years and Older with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Dosage |
Dose Level |
|
40 mg (2 tablets) orally Once Daily |
6 |
|
40 mg (2 tablets) orallyThree Times a Week AND 20 mg (1 tablet) orally on the Four Remaining Days of Each Week |
5 |
|
20 mg (1 tablet) orally Once Daily* |
4 |
|
20 mg (1 tablet) orally Three Times a Week |
3 |
|
20 mg (1 tablet) orally Twice a Week OR 40 mg Once Weekly |
2 |
|
20 mg (1 tablet) orally Once Weekly |
1 |
*Initial dosage regimen for all patients except those taking Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers or Moderate or Strong Dual Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4.
Discontinuation:
- Discontinue DOPTELET tablets if the platelet count does not increase to greater than or equal to 50×109/L after 4 weeks of dosing at the maximum dose of 40 mg (2 tablets) once daily.
- Discontinue DOPTELET tablets if the platelet count is greater than 400×109/L after 2 weeks of dosing at 20 mg (1 tablet) once weekly.
2.4 Recommended Initial Dosage of DOPTELET Tablets with Concomitant
Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers or Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4
The recommended initial dosages of DOPTELET tablets with concomitant moderate or strong dual inducers or inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia and pediatric patients 6 years and older with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: DOPTELET Tablets Recommended Initial Dosage with Concomitant Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers or Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 for Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia and Pediatric Patients 6 Years and Older with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Concomitant Medications |
Recommended Initial Dosage |
|
Moderate or strong dual inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 |
20 mg (1 tablet) orally three times a week |
|
Moderate or strong dual inducers of |
40 mg (2 tablets) orally once daily |
2.5 Recommended Dosage of DOPTELET SPRINKLE for Patients 1 Year to Less
than 6 Years with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
Use the lowest dose of DOPTELET SPRINKLE needed to achieve and maintain a platelet count greater than or equal to 50×109/L as necessary to reduce the risk for bleeding. Dose adjustments are based on platelet count response. Do not use DOPTELET SPRINKLE to normalize platelet counts.
Initial Dosage**:**
- Begin DOPTELET SPRINKLE at an initial dosage of 10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally once daily with food (see Table 6).
- The recommended initial dosages of DOPTELET SPRINKLE are different for patients receiving certain concomitant medications (see Table 7).
Monitoring**:**
After initiating therapy with DOPTELET SPRINKLE, assess platelet counts weekly until a stable platelet count greater than or equal to 50×109/L has been achieved, and then obtain platelet counts monthly thereafter. Obtain platelet counts weekly for at least 4 weeks following discontinuation of DOPTELET SPRINKLE.
Dose Adjustments**:**
DOPTELET SPRINKLE dose adjustments (see Table 5 and Table 6) are based on the platelet count response. Do not exceed a DOPTELET SPRINKLE daily dose of 20 mg (content of 2 capsules).
Table 5: DOPTELET SPRINKLE Dose Adjustments for Patients 1 Year to Less than 6 Years with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Platelet Count |
Dose Adjustment or Action |
|
Less than 50×109/L after at least 2 weeks of DOPTELET SPRINKLE |
|
|
Between 200×109/L and 400×109/L |
|
|
Greater than 400×109/L |
|
|
Less than 50×109/L after 4 weeks of DOPTELET SPRINKLE 20 mg (content of 2 capsules) once daily |
|
|
Greater than 400×109/L after 2 weeks of DOPTELET SPRINKLE 10 mg (content of 1 capsule) weekly |
|
**Table 6: DOPTELET SPRINKLE Dose Levels for Titration in Pediatric Patients 1 Year to Less than 6 Years with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia **
|
Dosage |
Dose Level |
|
20 mg (content of 2 capsules) orally Once Daily |
6 |
|
20 mg (content of 2 capsules) orally Three Times a Week AND 10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally on the Four Remaining Days of Each Week |
5 |
|
10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally Once Daily* |
4 |
|
10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally Three Times a Week |
3 |
|
10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally Twice a Week OR 20 mg (content of 2 capsules) orally Once Weekly |
2 |
|
10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally Once Weekly |
1 |
*Initial dose regimen for all patients except those taking Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers or Moderate or Strong Dual Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4.
Discontinuation**:**
- Discontinue DOPTELET SPRINKLE if the platelet count does not increase to greater than or equal to 50×109/L after 4 weeks of dosing at the maximum dose of 20 mg (content of 2 capsules) once daily.
- Discontinue DOPTELET SPRINKLE if the platelet count is greater than 400×109/L after 2 weeks of dosing at 10 mg (content of 1 capsule) once weekly.
2.6 Recommended Initial Dosage of DOPTELET SPRINKLE with Concomitant
Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers or Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4
The recommended initial dosages of DOPTELET SPRINKLE with concomitant moderate or strong dual inducers or inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 in pediatric patients 1 year to less than 6 years with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia are summarized in Table 7.
Table 7: DOPTELET SPRINKLE Recommended Initial Dosage with Concomitant Moderate or Strong Dual Inducers or Inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 for Pediatric Patients 1 Year to Less than 6 Years with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Concomitant Medications |
Recommended Initial Dosage |
|
Moderate or strong dual inhibitors of CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 |
10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally three times a week |
|
Moderate or strong dual inducers of |
20 mg (content of 2 capsules) orally once daily |
2.7 Important Preparation and Administration Instructions for DOPTELET
SPRINKLE
- Open the capsules and sprinkle the granules onto a small amount of a soft food or liquid in a spoon or cup.
- Donot swallow the capsules whole. Do not chew or crush the granules.
- Use the entire contents of the capsules to achieve the dose.
- The following soft foods and liquids are suitable:
- Soft foods: applesauce; strawberry jelly; yogurt (plain)
- Liquids: milk (whole or skim); orange juice; pediatric electrolyte solution (unflavored); water
- The following soft foods and liquids are suitable:
- Mix the granules into the soft food or liquid; the granules will not dissolve.
- Consume the mixture immediately after preparation; it should not be saved for future use.
- Rinse the spoon or cup with the soft food or liquid to ensure that the full dose is administered.
2.8 Missed Dose
In the case of a missed dose of DOPTELET tablets or DOPTELET SPRINKLE, patients should take the missed dose as soon as they remember. Patients should not take two doses at one time to make up for a missed dose and should take the next dose at the usual time the next day.
- DOPTELET tablets and DOPTELET SPRINKLE are not substitutable on a mg-to-mg basis.
- DOPTELET SPRINKLE capsules should be opened, and the contents (oral granules) mixed with a soft food or liquid. Administer immediately after mixing. Do not swallow the capsules whole.
- Administer DOPTELET tablets and DOPTELET SPRINKLE with food. (2.1, 2.3, 2.5)
- Chronic Liver Disease: Dose DOPTELET tablets based upon platelet count prior to procedure, orally for 5 days beginning 10 days to 13 days before procedure. For platelet count less than 40×109/L, the dose is 60 mg (3 tablets) orally once daily; for platelet count 40 to less than 50×109/L the dose is 40 mg (2 tablets) orally once daily. (2.2)
- Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia and Pediatric Patients 6 Years and Older with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia: Initiate DOPTELET tablets at 20 mg (1 tablet) orally once daily. Adjust the dose or frequency of dosing to maintain platelet count greater than or equal to 50×109/L. Do not exceed 40 mg (2 tablets) per day.
- Pediatric Patients 1 Year to Less than 6 Years with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia: Initiate DOPTELET SPRINKLE oral granules at 10 mg (content of 1 capsule) orally once daily. Adjust the dose or frequency of dosing to maintain platelet count greater than or equal to 50×109/L. Do not exceed 20 mg (content of 2 capsules) per day.
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets
DOPTELET Tablets: 20 mg as round, biconvex, yellow, film-coated tablets debossed with “AVA” on one side and “20” on the other side.
Oral Granules
DOPTELET SPRINKLE: 10 mg as Size 0 capsules containing white to off-white granules. The capsules have a white opaque body and light blue opaque cap with a black arrow symbol imprinted on the body and cap.
Tablet: 20 mg (3)
Oral Granules: 10 mg (3)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
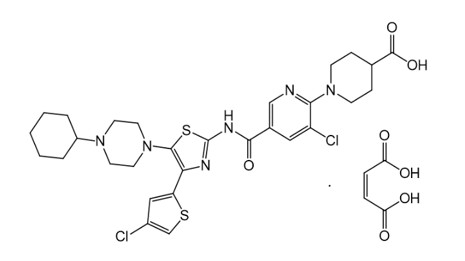
The active ingredient in DOPTELET is avatrombopag maleate, a thrombopoietin receptor agonist. The chemical name of avatrombopag maleate is 4-piperidinecarboxylic acid, 1-[3-chloro-5-[[[4-(4-chloro-2-thienyl)-5-(4-cyclohexyl-1-piperazinyl)-2-thiazolyl]amino]carbonyl]-2-pyridinyl]-, (2Z)-2-butenedioate (1:1). It has the molecular formula C29H34Cl2N6O3S2 · C4H4O4. The molecular weight is 765.73.
The structural formula is:
The aqueous solubility of avatrombopag maleate at various pH levels indicates that the drug substance is practically insoluble at pH 1 to 11.
DOPTELET is provided as an immediate-release tablet and as a sprinkle capsule that contains oral granules.
Each DOPTELET tablet contains 20 mg avatrombopag (equivalent to 23.6 mg of avatrombopag maleate) and the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. Coating film: ferric oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Each DOPTELET SPRINKLE capsule contains 10 mg avatrombopag (equivalent to 11.8 mg of avatrombopag maleate) and the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone Type A, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. Capsule shells: Hypromellose.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12****CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Avatrombopag is an orally bioavailable, small molecule TPO receptor agonist that stimulates proliferation and differentiation of megakaryocytes from bone marrow progenitor cells, resulting in an increased production of platelets. Avatrombopag does not compete with TPO for binding to the TPO receptor and has an additive effect with TPO on platelet production.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Platelet Response
DOPTELET tablet administered to adult patients resulted in dose- and exposure- dependent elevations in platelet counts. The onset of the platelet count increase was observed within 3 to 5 days of the start of treatment, with peak effect after 10 to 13 days. Post treatment, platelet counts decreased gradually, returning to near baseline values.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At exposures similar to that achieved at the 40 mg and 60 mg tablet dose, DOPTELET did not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent. Mean QTc prolongation effects >20 ms are not anticipated with the highest recommended therapeutic dosing regimen based on analysis of data from the pooled clinical trials in patients with chronic liver disease.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of avatrombopag were determined following administration of DOPTELET tablets, and pharmacokinetic parameters are presented as geometric mean (CV%) unless otherwise specified. Avatrombopag demonstrated dose- proportional pharmacokinetics after single doses from 10 mg (0.5 times the lowest approved dosage) to 80 mg (1.3 times the highest recommended dosage). Healthy subjects administered 40 mg of avatrombopag had a geometric mean (%CV) maximal concentration (Cmax) of 166 (84%) ng/mL and area under the time- concentration curve extrapolated to infinity (AUC0-inf) of 4198 (83%) ng.hr/mL. The pharmacokinetics of avatrombopag were similar in both healthy subjects and the chronic liver disease population.
The relative bioavailability of DOPTELET SPRINKLE compared to DOPTELET tablet has not been studied. However, a prototype of DOPTELET SPRINKLE demonstrated a 22% higher geometric mean Cmax and a 38% higher geometric mean AUC for avatrombopag compared to DOPTELET tablet, both administered to healthy adult subjects under the fed condition.
Table 11 summarizes avatrombopag exposure in a virtual adult population and in pediatric patients with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia.
Table 11: Summary of Avatrombopag Exposure in a Virtual Adult Population and Pediatric****Patients with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Cohort |
Adults 20 mg dailyDOPTELETtablet |
≥12 to <18 years N=21 20 mg dailyDOPTELETtablet |
≥6 to <12 years N=20 20 mg dailyDOPTELETtablet |
≥1 to <6 years N=12 10 mg daily****DOPTELET SPRINKLE |
|
Cmax,ss (ng/mL) | ||||
|
Geometric mean (CV) |
165 (61.3) |
168 (36.7) |
267 (25.7) |
221 (35.6) |
|
AUCss (ng × h/mL) | ||||
|
Geometric mean (CV) |
3277 (62.2) |
3372 (41.5) |
4942 (28.7) |
4030 (38.6) |
AUCss = area under the concentration time curve at steady-state; Cmax,ss =
maximal concentration at steady-state;
CV = coefficient of variation expressed as a percent; N = number of
individuals.
Absorption
The median time to maximal concentration (Tmax) occurred at 5 to 6 hours post- dose.
Effect of Food
Avatrombopag AUC0-inf and Cmax were not affected when DOPTELET tablets were co-administered with a low-fat meal (500 calories, 3 g fat, 15 g protein, and 108 g carbohydrates) or a high-fat meal (918 calories, 59 g fat, 39 g protein, and 59 g carbohydrates). The variability of avatrombopag exposure was reduced by 40% to 60% with food. The Tmax of avatrombopag was delayed by 0 to 2 hours when DOPTELET tablets were administered with a low-fat or high-fat meal (median Tmax range 5 to 8 hours) compared to the fasted state.
Geometric mean exposure increased by approximately 19% and 32% for Cmax and AUC, respectively, when a prototype of DOPTELET SPRINKLE was administered in the fed state compared to the fasted state, and between-subject variability estimates for AUC and Cmax were decreased after administration in the fed state.
Distribution
Avatrombopag has an estimated mean apparent volume of distribution (%CV) of 180 L (25%). Avatrombopag is greater than 96% bound to human plasma proteins.
Elimination
The mean plasma elimination half-life (%CV) of avatrombopag is approximately 19 hours (19%). The mean (%CV) of the apparent clearance of avatrombopag is estimated to be 6.9 L/hr (29%).
Metabolism
Avatrombopag is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 and CYP3A4.
Excretion
Fecal excretion accounted for 88% of the administered dose, with 34% of the dose excreted as unchanged avatrombopag. Only 6% of the administered dose was found in urine.
Specific Populations
Age (1-86 years), sex, race [Whites, African-Americans, and East Asians (i.e., Japanese, Chinese and Koreans)], and any hepatic impairment (Child-Turcotte- Pugh (CTP) grade A, B, and C, or Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score 4-23) and mild to moderate renal impairment (CLcr ≥30 mL/min) did not have clinically meaningful effects on the pharmacokinetics of avatrombopag.
Lower body weight was associated with higher avatrombopag Cmax and AUC following the proposed starting dose in patients aged 6 years and older weighing 16.3 to 175 kg. Pediatric patients aged 1 to less than 6 years had 34% higher Cmax and 23% higher AUC following administration of 10 mg daily DOPTELET SPRINKLE compared to adults who received 20 mg daily DOPTELET tablets.
The effect of severe renal impairment (CLcr <30 mL/min, Cockcroft-Gault), including patients requiring hemodialysis, on avatrombopag pharmacokinetics is unknown.
Drug Interactions
Clinical Studies
Table 12 summarizes the effect of other drugs on the pharmacokinetics of avatrombopag.
Table 12: Drug Interactions: Changes in Pharmacokinetics of Avatrombopag in the Presence of****Co-Administered Drug
|
Co-administered Drug* |
Geometric Mean Ratio (90% CI) of Avatrombopag PK with/without Co- administered Drug [No Effect=1.00] | |
|
AUC****0-inf |
C****max | |
|
Strong CYP3A Inhibitor | ||
|
Itraconazole |
1.37 |
1.07 |
|
Moderate CYP3A and CYP2C9 Inhibitor | ||
|
Fluconazole |
2.16 |
1.17 |
|
Moderate CYP2C9 and Strong CYP3A Inducer | ||
|
Rifampin |
0.57 |
1.04 |
|
P-gp Inhibitor | ||
|
Cyclosporine |
0.83 |
0.66 |
|
P-gp and Moderate CYP3A Inhibitor | ||
|
Verapamil |
1.61 |
1.26 |
*at steady state, except for cyclosporine which was administered as a single dose.
In Vitro Studies Where Drug Interaction Potential Was Not Further Evaluated Clinically
CYP enzymes: Avatrombopag does not inhibit CYP1A, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 or CYP3A, does not induce CYP1A, CYP2B6, CYP2C or CYP3A, and weakly induces CYP2C8 and CYP2C9.
Transporter systems: Avatrombopag inhibits organic anion transporter (OAT) 3 and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), but not organic anion transporter polypeptide (OATP) 1B1 or 1B3, organic cation transporter (OCT) 2 or OAT1.
Avatrombopag is not a substrate for OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT2, OAT1 or OAT3.
12.5 Pharmacogenomics
The CYP2C92 and CYP2C93 loss-of-function polymorphisms result in reduced CYP2C9 enzymatic activity. In a pooled pharmacogenomic analysis of avatrombopag studies, subjects heterozygous for CYP2C9 loss-of-function polymorphisms (intermediate metabolizers [n=24]) had approximately 1.4-fold higher exposure and subjects homozygous for CYP2C9 loss-of-function polymorphisms (poor metabolizers [n=2]) had approximately 2-fold higher exposure compared to subjects wild-type for CYP2C9 (normal metabolizers [n=94]).
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13****NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In two-year carcinogenicity studies, avatrombopag was administered orally at doses of 20, 60, and 160 mg/kg/day in mice and doses of 20, 50, and 160 mg/kg/day in rats. Avatrombopag induced a statistically significant increase in neuroendocrine cell (enterochromaffin-like cell, ECL cell) gastric tumors (carcinoids) in the stomach at 160 mg/kg in female rats. The 160 mg/kg/day dose resulted in exposures 117 times the AUC observed in patients at the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg once daily. The gastric carcinoids were considered likely due to prolonged hypergastrinemia observed in toxicity studies. Hypergastrinemia-related gastric carcinoids in rodents are generally considered to be of low risk or relevance to humans.
Avatrombopag was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay or clastogenic in an in vitro human lymphocyte chromosomal aberrations assay or in an in vivo rat bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Avatrombopag did not affect fertility or early embryonic development in male rats at exposures 22 times, or in female rats at exposures 114 times, the AUC observed in patients at the maximum recommended dose of 60 mg once daily.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Patients with Chronic Liver Disease
The efficacy of DOPTELET for the treatment of thrombocytopenia in patients with chronic liver disease who are scheduled to undergo a procedure was established in 2 identically-designed multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials (ADAPT-1 [NCT01972529] and ADAPT-2 [NCT01976104]). In each trial, patients were assigned to the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (<40×10] and ADAPT-2 [NCT01976104]). In each trial, patients were assigned to the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (<40×109/L) or the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (≥40 to <50×109/L) based on their platelet count at baseline. Patients were then randomized in a 2:1 ratio to either DOPTELET or placebo. Patients were stratified according to hepatocellular cancer (HCC) status and risk of bleeding associated with the elective procedure (low, moderate, or high). Patients undergoing neurosurgical interventions, thoracotomy, laparotomy or organ resection were not eligible for enrollment.
Patients in the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort received 60 mg DOPTELET or matching placebo once daily for 5 days, and patients in the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort received 40 mg DOPTELET or matching placebo once daily for 5 days. Eligible patients were scheduled to undergo their procedure (low, moderate, or high bleeding risk) 5 to 8 days after their last dose of treatment. Patient populations were similar between the pooled Low and High Baseline Platelet Count Cohorts and consisted of 66% male and 35% female; median age 58 years and 61% White, 34% Asian, and 3% Black.
In ADAPT-1, a total of 231 patients were randomized, 149 patients were treated with DOPTELET and 82 patients were treated with placebo. In the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET- treated group was 31.1×109/L and for the placebo-treated patients was 30.7×109/L. In the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated patients was 44.3×109/L and for placebo-treated patients was 44.9×109/L.
In ADAPT-2, a total of 204 patients were randomized, 128 patients were treated with DOPTELET and 76 patients were treated with placebo. In the Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET- treated group was 32.7×109/L and for the placebo-treated patients was 32.5×109/L. In the High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort, the mean baseline platelet count for the DOPTELET-treated patients was 44.3×109/L and for the placebo-treated patients was 44.5×109/L.
Across both baseline platelet count cohorts and the avatrombopag and placebo treatment groups, patients underwent a broad spectrum of types of scheduled procedures that ranged from low to high bleeding risk. Overall, the majority of patients (60.8% [248/430] subjects) in all treatment groups underwent low bleeding risk procedures, 17.2% (70/430) of patients underwent procedures associated with moderate bleeding risk, and 22.1% (90/430) of subjects underwent procedures associated with high bleeding risk. The proportions of patients undergoing low, moderate, and high-risk procedures were similar between the avatrombopag and placebo treatment groups.
The major efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients who did not require a platelet transfusion or any rescue procedure for bleeding after randomization and up to 7 days following an elective procedure. Additional secondary efficacy outcomes were the proportion of patients who achieved platelet counts of >50×109/L on the day of procedure, and the change in platelet count from baseline to procedure day.
Responders were defined as patients who did not require a platelet transfusion or any rescue procedure for bleeding after randomization and up to 7 days following a scheduled procedure. The following were considered rescue therapies to manage the risk of bleeding associated with a procedure: whole blood transfusion, packed red blood cell (RBC) transfusion, platelet transfusion, fresh frozen plasma (FFP) or cryoprecipitate administration, Vitamin K, desmopressin, recombinant activated factor VII, aminocaproic acid, tranexamic acid, or surgical or interventional radiology procedures performed to achieve hemostasis and control blood loss. In both baseline platelet count cohorts, patients in the DOPTELET treatment groups had a greater proportion of responders than the corresponding placebo treatment groups that was both clinically meaningful and statistically significant as detailed in Table 13.
Table 13**:**** Proportion ofPatientsNot Requiring a Platelet Transfusion**** or Any Rescue Procedure forBleeding by Baseline Platelet Count Cohort and Treatment Group – ADAPT-1and****ADAPT-2**
|
Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort (<40**×109****/L)** | ||||
|
Category |
ADAPT-1 |
ADAPT-2 | ||
|
DOPTELET |
Placebo (n=48) |
DOPTELET |
Placebo (n=43) | |
|
Responders |
66% |
23% |
69% |
35% |
|
Difference of Proportion vs. Placebo****b |
43% |
34% | ||
|
p-value****d |
**˂**0.0001 |
0.0006 | ||
|
High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort**(≥40 to <50****×109****/L)** | ||||
|
Category |
ADAPT-1 |
ADAPT-2 | ||
|
DOPTELET |
Placebo |
DOPTELET |
Placebo | |
|
Responders |
88% |
38% |
88% |
33% |
|
Difference of Proportion vs. Placebo****b |
50% |
55% | ||
|
p-value****d |
˂0.0001 |
˂0.0001 |
- Two-sided 95% confidence interval based on normal approximation.
- Difference of Proportion vs. placebo = Proportion of Responders for DOPTELET – Proportion of Responders for placebo.
- 95% confidence interval calculated based on normal approximation.
- By Cohhran-Mantel-Haenszel Testing stratified by bleeding risk for the procedure.
In addition, both trials demonstrated a higher proportion of patients who achieved the target platelet count of ≥50×109/L on the day of procedure, a secondary efficacy endpoint, in both DOPTELET-treated groups versus the placebo-treated groups for both cohorts (Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort – ADAPT-1: 69% vs 4%, respectively; p˂0.0001, ADAPT-2: 67% vs 7%, respectively; p <0.0001; High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort – ADAPT-1: 88% vs 21%, respectively; p <0.0001: ADAPT-2: 93% vs 39%, respectively; p <0.0001). Further, both trials demonstrated a greater mean change in platelet counts from baseline to the day of the procedure, a secondary efficacy endpoint, in both DOPTELET-treated groups versus the placebo-treated groups for both cohorts (Low Baseline Platelet Count Cohort – ADAPT-1: 32×109/L vs 0.8×109/L, respectively; p<0.0001; ADAPT-2: 31.3×109/L vs 3.0×109/L, respectively; p <0.0001; High Baseline Platelet Count Cohort – ADAPT-1: 37.1×109/L vs 1.0×109/L, respectively; p <0.0001; ADAPT-2: 44.9×109/L vs 5.9×109/L, respectively; p <0.0001).
A measured increase in platelet counts was observed in both DOPTELET treatment groups over time beginning on Day 4 post-dose, that peaked on Day 10-13, decreased 7 days post-procedure, and then returned to near baseline values by Day 35.
14.2 Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
Randomized Phase 3 Clinical Trial
The efficacy of DOPTELET in adult patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenia was evaluated in a Phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT01438840). Patients had previously received one or more prior chronic immune thrombocytopenia therapies and had an average of screening and baseline platelet counts <30×109/L. Patients were centrally stratified by splenectomy status, baseline platelet count (≤15×109/L or >15×109/L to <30×109/L), and use of concomitant chronic immune thrombocytopenia medication, and then randomized (2:1) to receive either DOPTELET or placebo for 6 months. Patients received a starting dose of 20 mg once daily, with doses subsequently titrated based on platelet response.
Forty-nine patients were randomized, 32 to DOPTELET and 17 to placebo, with similar mean [SD] baseline platelet counts in the 2 treatment groups (14.1 [8.6]×109/L and 12.7 [7.8]×109/L, respectively). The median age was 44 years, 63% were female, and 94% were Caucasian, 4% Asian and 2% Black. The median duration of exposure was 26 weeks for DOPTELET-treated patients and 6 weeks for placebo-treated patients. The major efficacy outcome in this trial was the cumulative number of weeks in which the platelet count was ≥50×109/L during the 6-month treatment period in the absence of rescue therapy. DOPTELET- treated patients had a longer duration of platelet counts ≥50×109/L in the absence of rescue therapy than those who received placebo (median 12.4 [0, 25] vs 0 [0, 2] weeks, respectively, p<0.0001) (see Table 14).
Table 14**:Cumulative Number of Weeks of Platelet Response–**Phase 3 Trial in Adult Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
|
Primary Efficacy Analysis |
DOPTELET (n=32) |
Placebo (n=17) |
|
Cumulative Number of Weeks with a Platelet Response* | ||
|
Mean (SD) |
12.0 (8.75) |
0.1 (0.49) |
|
Median |
12.4 |
0.0 |
|
Min, Max |
0, 25 |
0, 2 |
|
p-value of Wilcoxon rank sum test |
<0.0001 |
Max=maximum, Min=minimum, SD=Standard deviation.
*Cumulative number of weeks of platelet response is defined as the total numbers of weeks in which the platelet count was ≥50×109/L during 6 months of treatment in the absence of rescue therapy.
In addition, a larger proportion of patients in the DOPTELET treatment group had platelet counts ≥50×109/L at Day 8 compared to placebo (21/32; 66% vs 0/17; 0.0%, respectively; p<0.0001).
14.3 Pediatric Patients with Persistent or Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia
The efficacy and safety of DOPTELET was evaluated in pediatric patients ≥1 to <18 years of age with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial (NCT 04516967), which included a 12-week randomized treatment phase (Core Phase).
Patients were required to have had a diagnosis of primary ITP for ≥6 months and had an insufficient response to at least one previous treatment, with an average of 2 baseline platelet counts less than 30×109/L. Patients (n=75) were randomized (3:1) to receive DOPTELET (n=54) or placebo (n=21). The starting dose for patients 6 years and older was 20 mg (tablet), while the starting dose for the youngest cohort was 10 mg (oral granules mixed with a soft food or liquid). Doses could be subsequently titrated based on platelet response.
Enrollment was 52% male and 48% female. The median age of patients receiving DOPTELET was 8.5 years (range 1 to 17) while the median age of patients receiving placebo was 10.0 years (range 3 to 17). Patients identified their race as White (84%), Asian (5.3%), and Other (5.3%); 5.3% did not report race. Patients identified their ethnicity as Not Hispanic or Latino (86.7%) and Hispanic or Latino (6.7%); 2.7% did not report ethnicity and 4% had unknown ethnicity.
The median baseline platelet counts were 10.4×109/L in the DOPTELET group and 11.5×109/L in the placebo group. The percentage of patients who had received 3 or more prior ITP therapies was 68.5% in the avatrombopag group and 66.7% in the placebo group. Most patients in the trial received at least one other TPO receptor agonist as a prior therapy (74.1% in the DOPTELET group and 71.4% in the placebo group).
The efficacy of DOPTELET in this trial was evaluated by durable platelet response, defined as the proportion of patients achieving at least 6 out of 8 weekly platelet counts ≥50×109/L during the last 8 weeks of the 12-week Treatment Period in the Core Phase in the absence of rescue medication (Table 15).
Efficacy was also evaluated by platelet response, defined as the proportion of subjects achieving at least 2 consecutive platelet assessments ≥50×109/L in the Core Phase in the absence of rescue medication.
Table 15: Durable Platelet Response and Platelet Response - Phase 3 Trial in Pediatric Patients with Persistent or Chronic ITP - Full Analysis Set
|
Endpoint |
DOPTELET |
Placebo | |
|
Durable platelet response, n% | |||
|
Yes |
15 (27.8) |
0 | |
|
No |
39 (72.2) |
21 (100.0) | |
|
Difference of proportion (avatrombopag – placebo) (95% CI) |
27.8 (15.8, 39.7) | ||
|
CMH (avatrombopag vs. placebo) p-value |
p=0.0077a | ||
|
Platelet response, n% | |||
|
Yes |
44 (81.5) |
0 | |
|
No |
10 (18.5) |
21 (100.0) | |
|
Difference of proportion (avatrombopag – placebo) (95% CI) |
81.5 (71.1, 91.8) | ||
|
CMH (avatrombopag vs. placebo) p-value |
p <0.0001a | ||
CI, Confidence interval; CMH, Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel; N, Total number of subjects; n, Number of subjects; Full Analysis Set includes all randomized subjects.
a Denotes p-value from Fisher’s Exact Test, which was used in place of CMH test due to sparse number of responders in the strata.
Note: The CMH test is adjusted for age cohort and baseline platelet counts.
DOPTELET was superior to placebo in other major efficacy outcomes that evaluated platelet counts. At Day 8, 55.6% (95% CI: 41.4%, 69.1%) of DOPTELET versus no placebo patients (95% CI: 0.0%, 16.1%) had a platelet count ≥50×109/L in the absence of rescue therapy (p <0.0001). The mean percentage of weeks that subjects had a platelet count ≥50×109/L during the Core Phase in the absence of rescue therapy was significantly higher for DOPTELET versus placebo, 48.9% (SD: 25.22%) versus 1.2% (SD: 3.92%) (p <0.0001).
The proportion of subjects who required rescue therapy during the Core Phase was significantly lower (p=0.0008) in the DOPTELET group (7.4% [95% CI: 2.1%, 17.9%]) than in the placebo group (42.9% [95% CI: 21.8%, 66.0%]).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16****HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 DOPTELET Tablets
DOPTELET 20 mg tablets are supplied as round, biconvex, yellow, film-coated tablets, and debossed with “AVA” on one side and “20” on the other side.
|
How Supplied |
Carton NDC |
Blister Card NDC |
|
Carton of one blister card with 10 tablets |
NDC 71369-020-10 |
NDC 71369-020-11 |
|
Carton of one blister card with 15 tablets |
NDC 71369-020-15 |
NDC 71369-020-16 |
|
Carton of two blister cards, each with 15 tablets |
NDC 71369-020-30 |
NDC 71369-020-16 |
Store DOPTELET tablets at room temperature from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Store tablets in the original package.
16.2 DOPTELET SPRINKLE
DOPTELET SPRINKLE is supplied as 10 mg capsules with a white opaque body and light blue opaque cap with a black arrow symbol imprinted on the body and cap. The capsule is filled with white to off-white granules.
|
How Supplied |
** Carton and Bottle NDC** |
|
Carton with one bottle of 30 capsules (containing oral granules) |
NDC 71369-010-30 |
Store DOPTELET SPRINKLE capsules at room temperature from 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17****PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling: Patient Information and, for DOPTELET SPRINKLE, Instructions for Use.
Prior to treatment, patients should fully understand and be informed of the following risks and considerations for DOPTELET:
Risks
Thrombotic/Thromboembolic Complications
DOPTELET is a thrombopoietin (TPO) receptor agonist and TPO receptor agonists have been associated with thrombotic and thromboembolic complications in patients with chronic liver disease or immune thrombocytopenia. Portal vein thrombosis has been reported in patients with chronic liver disease treated with TPO receptor agonists. Various thromboembolic complications (arterial and venous) have been reported in patients treated with DOPTELET [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Drug Interactions
DOPTELET may be affected by other drugs and may require a dose adjustment when co-administered with other drugs; therefore, advise patients to report their use of any other prescription or nonprescription medications or dietary supplements [see Dosage and Administration (2.4 and 2.6), Drug Interactions (7)].
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their prescriber of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with DOPTELET and for at least 2 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Administration Instructions for DOPTELET SPRINKLE
- Inform patients and caregivers to open the capsules and mix the contents with the recommended soft foods or liquids. Administer immediately after mixing. Do not swallow the capsules whole. Do not chew or crush the granules.
- Advise patients and caregivers to read and follow the Instructions for Use for DOPTELET SPRINKLE.
DOPTELET and DOPTELET SPRINKLE are not substitutable on a milligram-to- milligram basis
- Advise patients and caregivers that DOPTELET and DOPTELET SPRINKLE are not substitutable on a milligram-to-milligram basis.
- To avoid a dosing error from using the wrong dosage form, strongly advise patients and caregivers to visually inspect the product to verify the correct dosage form each time the prescription is filled.
DOPTELET is a registered trademark of AkaRx, Inc.
Manufactured for AkaRx, Inc., Morrisville, North Carolina 27560
©2025
For more information, go to www.DOPTELET.com or call 1-855-454-3887.
PI0002 R8
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
PATIENT INFORMATION DOPTELET® (dop-TEL-et) (avatrombopag) tablets, for oral use DOPTELET® SPRINKLE (dop-TEL-et SPRINK-el) (avatrombopag) oral granules |
|
What are DOPTELET and DOPTELET SPRINKLE?
DOPTELET tablets and DOPTELET SPRINKLE are different dosage forms of DOPTELET. DOPTELET SPRINKLE is a capsule that contains granules that are mixed with a soft food or liquid for dosing. DOPTELET tablets and DOPTELET SPRINKLE are not used to make platelet counts normal. It is not known if DOPTELET tablets or DOPTELET SPRINKLE are safe and effective in children younger than 1 year of age. |
|
Before you take DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect the way DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE works. |
|
How should I take DOPTELET?
How should I give DOPTELET SPRINKLE?
|
|
What are the possible side effects of DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE? DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE may cause serious side effects, including: Blood clots. People with chronic liver disease or persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia and people with certain blood clotting conditions may have an increased risk of developing blood clots. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get signs and symptoms of a blood clot, including: • swelling, pain, or tenderness in your legs • fast heartbeat • shortness of breath • stomach (abdominal) pain or tenderness • chest pain The most common side effects of DOPTELET when used to treat low blood platelet counts in adults with chronic liver disease (CLD) who are scheduled to have a medical or dental procedure are: • fever • headache • stomach (abdominal) pain • tiredness • nausea • swelling of hands or feet The most common side effects of DOPTELET****when used to treat low blood platelet counts in adults with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) are: • headache • joint pain • tiredness • bleeding gums • bruising • purple or red spots on your skin • nosebleed • runny nose • upper respiratory infection The most common side effects of DOPTELETor DOPTELET SPRINKLEwhen used to treat low blood platelet counts in children 1 year and older with persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) are: • viral infection • fever • runny nose • pain in the mouth or throat • cough These are not all of the possible side effects of DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store DOPTELET tablets or DOPTELET SPRINKLE?
**Keep DOPTELET tablets,**DOPTELET SPRINKLE and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give DOPTELET tablets or DOPTELET SPRINKLE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about DOPTELET or DOPTELET SPRINKLE that is written for health professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in DOPTELET tablets or DOPTELET SPRINKLE? **Active ingredient:**avatrombopag **Inactive ingredients in DOPTELET tablets:**colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and microcrystalline cellulose. Tablet coating film: ferric oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. Inactive ingredients in DOPTELET SPRINKLE: crospovidone Type A, magnesium stearate, mannitol, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. Capsule shells: Hypromellose. DOPTELET is a registered trademark of AkaRx, Inc. Manufactured for AkaRx, Inc., Morrisville, North Carolina 27560 For more information, go to www.DOPTELET.com or call 1-855-454-3887. |
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 07/2025 PI0001 R8
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DOPTELET**®**** SPRINKLE (dop-TEL-et SPRINK-el)** (avatrombopag) oral granules | |
|
Read these Instructions for Use to prepare and give a dose of DOPTELET SPRINKLE correctly**.** *Important information that you need to know before giving DOPTELET SPRINKLE: ** The contents of DOPTELET SPRINKLE should be sprinkled onto a soft food or liquid, as described below.**
| |
|
Steps to prepare and give a dose of DOPTELET SPRINKLE:
| |
|
Soft foods
|
Liquids
|
|
3. Carefully open the capsule (or 2 capsules if prescribed) by pulling it apart.
4. Mix or stir the granules into the soft food or liquid. The granules will**
notdissolve. | |
|
How should I store DOPTELET SPRINKLE?
Keep DOPTELET SPRINKLE and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
|
DOPTELET is a registered trademark of AkaRx, Inc. Manufactured for AkaRx, Inc., Morrisville, North Carolina 27560 For more information, go to www.DOPTELET.com or call 1-855-454-3887. |
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 07/2025 PI0003 R1
