INLYTA
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INLYTA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INLYTA. INLYTA (axitinib) tablets, for oral administration Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
84137882-e000-47da-bd5b-fa76ab3c76f9
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 11, 2024
Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc
DUNS: 134489525
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
axitinib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
axitinib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg Tablet Bottle Label
Pfizer
NDC 0069-0151-11
Inlyta**®**
(axitinib) tablets
5 mg
60 Tablets
Rx only
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 First-Line Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
INLYTA in combination with avelumab is indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab is indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced RCC.
1.2 Second-Line Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma
INLYTA as a single agent is indicated for the treatment of advanced RCC after failure of one prior systemic therapy.
INLYTA is a kinase inhibitor indicated:
•
in combination with avelumab, for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC). (1.1)
•
in combination with pembrolizumab, for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced RCC. (1.1)
•
as a single agent, for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) after failure of one prior systemic therapy. (1.2)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]:
•
Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Arterial thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Venous thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Cardiac failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Gastrointestinal perforation and fistula formation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Thyroid dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
•
Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
•
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
•
Hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of INLYTA has been evaluated in combination with avelumab in JAVELIN Renal 101 and pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-426 for the first-line treatment of patients with advanced RCC [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The data described [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] reflect exposure to INLYTA in combination with avelumab in 434 patients and pembrolizumab in 429 patients [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The safety of INLYTA has been evaluated in 715 patients in second-line monotherapy studies, which included 537 patients with advanced RCC. The data described [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] reflect exposure to INLYTA in 359 patients with advanced RCC who participated in a randomized clinical study versus sorafenib [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
First-Line Advanced RCC
INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab
The safety of INLYTA in combination with avelumab was evaluated in JAVELIN Renal 101. Patients with autoimmune disease other than type I diabetes mellitus, vitiligo, psoriasis, or thyroid disorders not requiring immunosuppressive treatment were excluded. Patients received INLYTA 5 mg twice daily (N=434) in combination with avelumab 10 mg/kg every 2 weeks administered or sunitinib 50 mg once daily for 4 weeks followed by 2 weeks off (N=439).
In the INLYTA plus avelumab arm, 70% were exposed to avelumab for ≥6 months and 29% were exposed for ≥1 year in JAVELIN Renal 101 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The median age of patients treated with INLYTA in combination with avelumab was 62 years (range: 29 to 83), 38% of patients were 65 years or older, 71% were male, 75% were White, and the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance score was 0 (64%) or 1 (36%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.8% of patients receiving INLYTA in combination with avelumab. These included sudden cardiac death (1.2%), stroke (0.2%), myocarditis (0.2%), and necrotizing pancreatitis (0.2%).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 35% of patients receiving INLYTA in combination with avelumab. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1% of patients included diarrhea (2.5%), dyspnea (1.8%), hepatotoxicity (1.8%), venous thromboembolic disease (1.6%), acute kidney injury (1.4%), and pneumonia (1.2%).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction of either INLYTA or avelumab occurred in 22% of patients: 19% avelumab only, 13% INLYTA only, and 8% both drugs. The most common adverse reactions (>1%) resulting in permanent discontinuation of avelumab or the combination were hepatotoxicity (6%) and infusion-related reaction (1.8%).
Dose interruptions or reductions due to an adverse reaction, excluding temporary interruptions of avelumab infusions due to infusion-related reactions, occurred in 76% of patients receiving INLYTA in combination with avelumab. This includes interruption of avelumab in 50% of patients. INLYTA was interrupted in 66% and dose reduced in 19% of patients. The most common adverse reaction (>10%) resulting in interruption of avelumab was diarrhea (10%). The most common adverse reactions resulting in either interruption or dose reduction of INLYTA were diarrhea (19%), hypertension (18%), palmar- plantar erythrodysesthesia (18%), and hepatotoxicity (10%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients receiving INLYTA in combination with avelumab were diarrhea, fatigue, hypertension, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, mucositis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, dysphonia, decreased appetite, hypothyroidism, rash, hepatotoxicity, cough, dyspnea, abdominal pain, and headache.
Forty-eight (11%) of patients treated with INLYTA in combination with avelumab received an oral prednisone dose equivalent to ≥40 mg daily for an immune- mediated adverse reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Table 4 summarizes adverse reactions that occurred in ≥20% of INLYTA in combination with avelumab-treated patients.
Table 4: Adverse Reactions (≥20%) of Patients Receiving INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab (JAVELIN Renal 101 Trial)*|
Adverse Reactions |
INLYTA plus Avelumab (N=434) |
Sunitinib (N=439) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades |
Grade 3–4 |
All Grades |
Grade 3–4 | |
|
Toxicity was graded per National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Version 4.03 (NCI CTCAE v4). | ||||
Þ ß à è | ||||
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
|
Diarrhea† |
62 |
8 |
48 |
2.7 |
|
Nausea |
34 |
1.4 |
39 |
1.6 |
|
Mucositis‡ |
34 |
2.8 |
35 |
2.1 |
|
Hepatotoxicity§ |
24 |
9 |
18 |
3.6 |
|
Abdominal pain¶ |
22 |
1.4 |
19 |
2.1 |
|
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions | ||||
|
Fatigue# |
53 |
6 |
54 |
6 |
|
Vascular Disorders | ||||
|
HypertensionÞ |
50 |
26 |
36 |
17 |
|
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders | ||||
|
Musculoskeletal painß |
40 |
3.2 |
33 |
2.7 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders | ||||
|
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia |
33 |
6 |
34 |
4 |
|
Rashà |
25 |
0.9 |
16 |
0.5 |
|
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders | ||||
|
Dysphonia |
31 |
0.5 |
3.2 |
0 |
|
Dyspneaè |
23 |
3.0 |
16 |
1.8 |
|
Cough |
23 |
0.2 |
19 |
0 |
|
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders | ||||
|
Decreased appetite |
26 |
2.1 |
29 |
0.9 |
|
Endocrine Disorders | ||||
|
Hypothyroidism |
25 |
0.2 |
14 |
0.2 |
|
Nervous System Disorders | ||||
|
Headache |
21 |
0.2 |
16 |
0.2 |
Other clinically important adverse reactions that occurred in less than 20% of patients in JAVELIN Renal 101 included arthralgia, weight decreased, and chills.
Patients received pre-medication with an anti-histamine and acetaminophen prior to each infusion. Infusion-related reactions occurred in 12% (Grade 3: 1.6%; no Grade 4) of patients treated with INLYTA in combination with avelumab.
Table 5 summarizes selected laboratory abnormalities that occurred in ≥20% of INLYTA in combination with avelumab-treated patients.
Table 5: Selected Laboratory Abnormalities Worsening from Baseline Occurring in ≥20% of Patients Receiving INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab (JAVELIN Renal 101 Trial)*|
Laboratory Abnormality |
INLYTA plus Avelumab |
Sunitinib† | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Any Grade |
Grade 3–4 |
Any Grade |
Grade 3–4 | |
| ||||
|
Chemistry | ||||
|
Blood triglycerides increased |
71 |
13 |
48 |
5 |
|
Blood creatinine increased |
62 |
2.3 |
68 |
1.4 |
|
Blood cholesterol increased |
57 |
1.9 |
22 |
0.7 |
|
Alanine aminotransferase increased (ALT) |
50 |
9 |
46 |
3.2 |
|
Aspartate aminotransferase increased (AST) |
47 |
7 |
57 |
3.2 |
|
Blood sodium decreased |
38 |
9 |
37 |
10 |
|
Lipase increased |
37 |
14 |
25 |
7 |
|
Blood potassium increased |
35 |
3.0 |
28 |
3.9 |
|
Blood bilirubin increased |
21 |
1.4 |
23 |
1.4 |
|
Hematology | ||||
|
Platelet count decreased |
27 |
0.7 |
80 |
1.5 |
|
Hemoglobin decreased |
21 |
2.1 |
65 |
8 |
INLYTA in Combination with Pembrolizumab
The safety of INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab was investigated in KEYNOTE-426 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Patients with medical conditions that required systemic corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications or had a history of severe autoimmune disease other than type 1 diabetes, vitiligo, Sjogren's syndrome, and hypothyroidism stable on hormone replacement were ineligible. Patients received INLYTA 5 mg orally twice daily and pembrolizumab 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks, or sunitinib 50 mg once daily for 4 weeks and then off treatment for 2 weeks. The median duration of exposure to the combination therapy of INLYTA and pembrolizumab was 10.4 months (range: 1 day to 21.2 months).
The study population characteristics were: median age of 62 years (range: 30 to 89), 40% age 65 or older; 71% male; 80% White; and 80% Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS) of 90–100 and 20% KPS of 70–80.
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3.3% of patients receiving INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab. These included 3 cases of cardiac arrest, 2 cases of pulmonary embolism and 1 case each of cardiac failure, death due to unknown cause, myasthenia gravis, myocarditis, Fournier's gangrene, plasma cell myeloma, pleural effusion, pneumonitis, and respiratory failure.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 40% of patients receiving INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab. Serious adverse reactions in ≥1% of patients receiving INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab included hepatotoxicity (7%), diarrhea (4.2%), acute kidney injury (2.3%), dehydration (1%), and pneumonitis (1%).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction of either INLYTA or pembrolizumab occurred in 31% of patients; 13% pembrolizumab only, 13% INLYTA only, and 8% both drugs. The most common adverse reaction (>1%) resulting in permanent discontinuation of INLYTA, pembrolizumab, or the combination was hepatotoxicity (13%), diarrhea/colitis (1.9%), acute kidney injury (1.6%), and cerebrovascular accident (1.2%).
Dose interruptions or reductions due to an adverse reaction, excluding temporary interruptions of pembrolizumab infusions due to infusion-related reactions, occurred in 76% of patients receiving pembrolizumab in combination with INLYTA. This includes interruption of pembrolizumab in 50% of patients. INLYTA was interrupted in 64% of patients and dose reduced in 22% of patients. The most common adverse reactions (>10%) resulting in either interruption or reduction of INLYTA were hepatotoxicity (21%), diarrhea (19%), and hypertension (18%) and the most common adverse reactions (>10%) resulting in interruption of pembrolizumab were hepatotoxicity (14%) and diarrhea (11%).
The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients receiving INLYTA and pembrolizumab were diarrhea, fatigue/asthenia, hypertension, hepatotoxicity, hypothyroidism, decreased appetite, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, nausea, stomatitis/mucosal inflammation, dysphonia, rash, cough, and constipation.
Twenty-seven percent (27%) of patients treated with INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab received an oral prednisone dose equivalent to ≥40 mg daily for an immune-mediated adverse reaction.
Tables 6 and 7 summarize the adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, that occurred in at least 20% of patients treated with INLYTA and pembrolizumab in KEYNOTE-426.
Table 6: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥20% of Patients Treated with INLYTA and Pembrolizumab (KEYNOTE-426 Trial)|
Adverse Reactions |
INLYTA plus Pembrolizumab N=429 |
Sunitinib N=425 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades* |
Grades 3–4 |
All Grades |
Grades 3–4 | |
| ||||
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders | ||||
|
Diarrhea† |
56 |
11 |
45 |
5 |
|
Nausea |
28 |
0.9 |
32 |
0.9 |
|
Constipation |
21 |
0 |
15 |
0.2 |
|
General | ||||
|
Fatigue/Asthenia |
52 |
5 |
51 |
10 |
|
Vascular | ||||
|
Hypertension‡ |
48 |
24 |
48 |
20 |
|
Hepatobiliary | ||||
|
Hepatotoxicity§ |
39 |
20 |
25 |
4.9 |
|
Endocrine | ||||
|
Hypothyroidism |
35 |
0.2 |
32 |
0.2 |
|
Metabolism and Nutrition | ||||
|
Decreased appetite |
30 |
2.8 |
29 |
0.7 |
|
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue | ||||
|
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome |
28 |
5 |
40 |
3.8 |
|
Stomatitis/Mucosal inflammation |
27 |
1.6 |
41 |
4 |
|
Rash¶ |
25 |
1.4 |
21 |
0.7 |
|
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal | ||||
|
Dysphonia |
25 |
0.2 |
3.3 |
0 |
|
Cough |
21 |
0.2 |
14 |
0.5 |
|
Laboratory Test* |
INLYTA plus Pembrolizumab |
Sunitinib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades† |
Grade 3–4 |
All Grades |
Grade 3–4 | |
| ||||
|
Chemistry | ||||
|
Hyperglycemia |
62 |
9 |
54 |
3.2 |
|
Increased ALT |
60 |
20 |
44 |
5 |
|
Increased AST |
57 |
13 |
56 |
5 |
|
Increased creatinine |
43 |
4.3 |
40 |
2.4 |
|
Hyponatremia |
35 |
8 |
29 |
8 |
|
Hyperkalemia |
34 |
6 |
22 |
1.7 |
|
Hypoalbuminemia |
32 |
0.5 |
34 |
1.7 |
|
Hypercalcemia |
27 |
0.7 |
15 |
1.9 |
|
Hypophosphatemia |
26 |
6 |
49 |
17 |
|
Increased alkaline phosphatase |
26 |
1.7 |
30 |
2.7 |
|
Hypocalcemia‡ |
22 |
0.2 |
29 |
0.7 |
|
Blood bilirubin increased |
22 |
2.1 |
21 |
1.9 |
|
Activated partial thromboplastin time prolonged§ |
22 |
1.2 |
14 |
0 |
|
Hematology | ||||
|
Lymphopenia |
33 |
11 |
46 |
8 |
|
Anemia |
29 |
2.1 |
65 |
8 |
|
Thrombocytopenia |
27 |
1.4 |
78 |
14 |
Second-Line Advanced RCC
The median duration of treatment was 6.4 months (range 0.03 to 22.0) for patients who received INLYTA and 5.0 months (range 0.03 to 20.1) for patients who received sorafenib. Dose modifications or temporary delay of treatment due to an adverse reaction occurred in 199/359 patients (55%) receiving INLYTA and 220/355 patients (62%) receiving sorafenib. Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction occurred in 34/359 patients (9%) receiving INLYTA and 46/355 patients (13%) receiving sorafenib.
The most common (≥20%) adverse reactions observed following treatment with INLYTA were diarrhea, hypertension, fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, dysphonia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (hand-foot) syndrome, weight decreased, vomiting, asthenia, and constipation. Table 8 presents adverse reactions reported in ≥10% patients who received INLYTA or sorafenib.
Table 8: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥10% of Patients Who Received INLYTA or Sorafenib|
Adverse Reaction* |
INLYTA |
Sorafenib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
(N=359) |
(N=355) | |||
|
All Grades† |
Grade 3/4 |
All Grades† |
Grade 3/4 | |
|
% |
% |
% |
% | |
| ||||
|
Diarrhea |
55 |
11 |
53 |
7 |
|
Hypertension |
40 |
16 |
29 |
11 |
|
Fatigue |
39 |
11 |
32 |
5 |
|
Decreased appetite |
34 |
5 |
29 |
4 |
|
Nausea |
32 |
3 |
22 |
1 |
|
Dysphonia |
31 |
0 |
14 |
0 |
|
Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome |
27 |
5 |
51 |
16 |
|
Weight decreased |
25 |
2 |
21 |
1 |
|
Vomiting |
24 |
3 |
17 |
1 |
|
Asthenia |
21 |
5 |
14 |
3 |
|
Constipation |
20 |
1 |
20 |
1 |
|
Hypothyroidism |
19 |
<1 |
8 |
0 |
|
Cough |
15 |
1 |
17 |
1 |
|
Mucosal inflammation |
15 |
1 |
12 |
1 |
|
Arthralgia |
15 |
2 |
11 |
1 |
|
Stomatitis |
15 |
1 |
12 |
<1 |
|
Dyspnea |
15 |
3 |
12 |
3 |
|
Abdominal pain |
14 |
2 |
11 |
1 |
|
Headache |
14 |
1 |
11 |
0 |
|
Pain in extremity |
13 |
1 |
14 |
1 |
|
Rash |
13 |
<1 |
32 |
4 |
|
Proteinuria |
11 |
3 |
7 |
2 |
|
Dysgeusia |
11 |
0 |
8 |
0 |
|
Dry skin |
10 |
0 |
11 |
0 |
|
Dyspepsia |
10 |
0 |
2 |
0 |
|
Pruritus |
7 |
0 |
12 |
0 |
|
Alopecia |
4 |
0 |
32 |
0 |
|
Erythema |
2 |
0 |
10 |
<1 |
Selected adverse reactions (all grades) that were reported in <10% of patients treated with INLYTA included dizziness (9%), upper abdominal pain (8%), myalgia (7%), dehydration (6%), epistaxis (6%), anemia (4%), hemorrhoids (4%), hematuria (3%), tinnitus (3%), lipase increased (3%), glossodynia (3%), pulmonary embolism (2%), rectal hemorrhage (2%), hemoptysis (2%), deep vein thrombosis (1%), retinal-vein occlusion/thrombosis (1%), polycythemia (1%), and transient ischemic attack (1%).
Table 9 presents the most common laboratory abnormalities reported in ≥10% patients who received INLYTA or sorafenib.
Table 9: Laboratory Abnormalities Occurring in ≥10% of Patients Who Received INLYTA or Sorafenib|
Laboratory Abnormality |
N |
INLYTA |
N |
Sorafenib | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All Grades* |
Grade 3/4 |
All Grades* |
Grade 3/4 | |||
|
% |
% |
% |
% | |||
|
ALP: alkaline phosphatase; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST: aspartate aminotransferase | ||||||
| ||||||
|
Hematology | ||||||
|
Hemoglobin decreased |
320 |
35 |
<1 |
316 |
52 |
4 |
|
Lymphocytes (absolute) decreased |
317 |
33 |
3 |
309 |
36 |
4 |
|
Platelets decreased |
312 |
15 |
<1 |
310 |
14 |
0 |
|
White blood cells decreased |
320 |
11 |
0 |
315 |
16 |
<1 |
|
Chemistry | ||||||
|
Creatinine increased |
336 |
55 |
0 |
318 |
41 |
<1 |
|
Bicarbonate decreased |
314 |
44 |
<1 |
291 |
43 |
0 |
|
Hypocalcemia |
336 |
39 |
1 |
319 |
59 |
2 |
|
ALP increased |
336 |
30 |
1 |
319 |
34 |
1 |
|
Hyperglycemia |
336 |
28 |
2 |
319 |
23 |
2 |
|
Lipase increased |
338 |
27 |
5 |
319 |
46 |
15 |
|
Amylase increased |
338 |
25 |
2 |
319 |
33 |
2 |
|
ALT increased |
331 |
22 |
<1 |
313 |
22 |
2 |
|
AST increased |
331 |
20 |
<1 |
311 |
25 |
1 |
|
Hypernatremia |
338 |
17 |
1 |
319 |
13 |
1 |
|
Hypoalbuminemia |
337 |
15 |
<1 |
319 |
18 |
1 |
|
Hyperkalemia |
333 |
15 |
3 |
314 |
10 |
3 |
|
Hypoglycemia |
336 |
11 |
<1 |
319 |
8 |
<1 |
|
Hyponatremia |
338 |
13 |
4 |
319 |
11 |
2 |
|
Hypophosphatemia |
336 |
13 |
2 |
318 |
49 |
16 |
Selected laboratory abnormalities (all grades) that were reported in <10% of patients treated with INLYTA included hemoglobin increased (above the upper limit of normal) (9% for INLYTA versus 1% for sorafenib) and hypercalcemia (6% for INLYTA versus 2% for sorafenib).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of INLYTA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Vascular disorders: arterial (including aortic), aneurysms, dissections, and rupture.
Most common adverse reactions (≥20%) are:
INLYTA in combination with avelumab: diarrhea, fatigue, hypertension, musculoskeletal pain, nausea, mucositis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia, dysphonia, decreased appetite, hypothyroidism, rash, hepatotoxicity, cough, dyspnea, abdominal pain, and headache. (6.1)
INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab: diarrhea, fatigue/asthenia, hypertension, hepatotoxicity, hypothyroidism, decreased appetite, palmar- plantar erythrodysesthesia, nausea, stomatitis/mucosal inflammation, dysphonia, rash, cough, and constipation. (6.1)
INLYTA as a single agent: diarrhea, hypertension, fatigue, decreased appetite, nausea, dysphonia, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia (hand-foot) syndrome, weight decreased, vomiting, asthenia, and constipation. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pfizer Inc. at 1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors
Co-administration of ketoconazole, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4/5, increased the plasma exposure of axitinib in healthy volunteers. Co-administration of INLYTA with strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors should be avoided. Grapefruit or grapefruit juice may also increase axitinib plasma concentrations and should be avoided. Selection of concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A4/5 inhibition potential is recommended. If a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor must be co-administered, the INLYTA dose should be reduced [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 CYP3A4/5 Inducers
Co-administration of rifampin, a strong inducer of CYP3A4/5, reduced the plasma exposure of axitinib in healthy volunteers. Co-administration of INLYTA with strong CYP3A4/5 inducers (e.g., rifampin, dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifabutin, rifapentine, phenobarbital, and St. John's wort) should be avoided. Selection of concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A4/5 induction potential is recommended [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Moderate CYP3A4/5 inducers (e.g., bosentan, efavirenz, etravirine, modafinil, and nafcillin) may also reduce the plasma exposure of axitinib and should be avoided if possible.
•
Avoid strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors. If unavoidable, reduce the INLYTA dose. (2.2, 7.1)
•
Avoid strong CYP3A4/5 inducers. (7.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Dosage and Administration, Recommended Dosing (2.1) |
9/2022 |
|
Dosage and Administration, Dose Modification Guidelines (2.2) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Hypertension (5.1) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Arterial Thromboembolic Events (5.2) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Venous Thromboembolic Events (5.3) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Hemorrhage (5.4) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Cardiac Failure (5.5) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Impaired Wound Healing (5.8) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (5.9) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Proteinuria (5.10) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Hepatotoxicity (5.11) |
9/2022 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (5.13) |
9/2022 |
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
•
1 mg tablets of INLYTA: red, film-coated, oval tablets, debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "1 XNB" on the other side.
•
5 mg tablets of INLYTA: red, film-coated, triangular tablets, debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "5 XNB" on the other side.
1 mg and 5 mg tablets (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action, INLYTA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available human data to inform the drug-associated risk. In developmental toxicity studies, axitinib was teratogenic, embryotoxic and fetotoxic in mice at exposures lower than human exposures at the recommended starting dose (see Data). Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. However, the background risk in the United States (U.S.) general population of major birth defects is 2%–4% and of miscarriage is 15%–20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
When INLYTA is used in combination with avelumab or pembrolizumab, refer to the full prescribing information of avelumab or pembrolizumab for pregnancy information.
Data
Animal Data
Oral axitinib administered twice daily to female mice prior to mating and through the first week of pregnancy caused an increase in post-implantation loss at all doses tested (≥15 mg/kg/dose, approximately 10 times the systemic exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended starting dose). In an embryo- fetal developmental toxicity study, pregnant mice received oral doses of 0.15, 0.5 and 1.5 mg/kg/dose axitinib twice daily during the period of organogenesis. Embryo-fetal toxicities observed in the absence of maternal toxicity included malformation (cleft palate) at 1.5 mg/kg/dose (approximately 0.5 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose) and variation in skeletal ossification at ≥0.5 mg/kg/dose (approximately 0.15 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of axitinib in human milk, or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child from INLYTA, advise lactating women not to breastfeed during treatment and for 2 weeks after the last dose.
When INLYTA is used in combination with avelumab or pembrolizumab, refer to the full prescribing information of avelumab or pembrolizumab for lactation information.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on findings in animal studies, INLYTA can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. When INLYTA is used in combination with avelumab or pembrolizumab, refer to the full prescribing information of avelumab or pembrolizumab for contraception information.
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with INLYTA.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with INLYTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
Males
Based on findings in animal studies, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 1 week after the last dose.
Infertility
Females and Males
Based on findings in animals, INLYTA may impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and efficacy of INLYTA in pediatric patients have not been studied.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
Toxicities in bone and teeth were observed in immature mice and dogs administered oral axitinib twice daily for 1 month or longer. Effects in bone consisted of thickened growth plates in mice and dogs at ≥15 mg/kg/dose (approximately 6 and 15 times, respectively, the systemic exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended starting dose). Abnormalities in growing incisor teeth (including dental caries, malocclusions and broken and/or missing teeth) were observed in mice administered oral axitinib twice daily at ≥5 mg/kg/dose (approximately 1.5 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose). Other toxicities of potential concern to pediatric patients have not been evaluated in juvenile animals.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, 123/359 patients (34%) treated with INLYTA were ≥65 years of age. Although greater sensitivity in some older individuals cannot be ruled out, no overall differences were observed in the safety and effectiveness of INLYTA between patients who were ≥65 years of age and younger.
Of the 434 patients randomized to INLYTA 5 mg twice daily administered in combination with avelumab 10 mg/kg in the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial, 38% were 65 years or older and 8% were 75 years or older. No overall difference in safety or efficacy was reported between patients who were ≥65 years of age and younger.
Of the 432 patients randomized to INLYTA 5 mg twice daily administered in combination with pembrolizumab 200 mg in the KEYNOTE-426 trial, 40% were 65 years or older. No overall difference in safety or efficacy was reported between patients who were ≥65 years of age and younger.
No dosage adjustment is required in elderly patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
In a dedicated hepatic impairment trial, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, systemic exposure following a single dose of INLYTA was similar in subjects with baseline mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A) and higher in subjects with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B).
No starting dose adjustment is required when administering INLYTA to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A). A starting dose decrease is recommended when administering INLYTA to patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
INLYTA has not been studied in subjects with severe hepatic impairment (Child- Pugh class C).
8.7 Renal Impairment
No dedicated renal impairment trial for axitinib has been conducted. Based on the population pharmacokinetic analyses, no significant difference in axitinib clearance was observed in patients with pre-existing mild to severe renal impairment (15 mL/min ≤creatinine clearance [CLcr] <89 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No starting dose adjustment is needed for patients with pre-existing mild to severe renal impairment. Caution should be used in patients with end-stage renal disease (CLcr <15 mL/min).
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no specific treatment for INLYTA overdose.
In a controlled clinical study with INLYTA for the treatment of patients with RCC, 1 patient inadvertently received a dose of 20 mg twice daily for 4 days and experienced dizziness (Grade 1).
In a clinical dose finding study with INLYTA, subjects who received starting doses of 10 mg twice daily or 20 mg twice daily experienced adverse reactions which included hypertension, seizures associated with hypertension, and fatal hemoptysis.
In cases of suspected overdose, INLYTA should be withheld and supportive care instituted.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Axitinib has been shown to inhibit receptor tyrosine kinases including vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFR)-1, VEGFR-2, and VEGFR-3 at therapeutic plasma concentrations. These receptors are implicated in pathologic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression. VEGF-mediated endothelial cell proliferation and survival were inhibited by axitinib in vitro and in mouse models. Axitinib was shown to inhibit tumor growth and phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 in tumor xenograft mouse models.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The effect of a single oral dose of INLYTA (5 mg) in the absence and presence of 400 mg ketoconazole on the QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized, single-blinded, two-way crossover study in 35 healthy subjects. No large changes in mean QTc interval (i.e., >20 ms) from placebo were detected up to 3 hours post-dose. However, small increases in mean QTc interval (i.e., <10 ms) cannot be ruled out.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The population pharmacokinetic analysis pooled data from 17 trials in healthy subjects and patients with cancer. A two-compartment disposition model with first-order absorption and lag-time adequately describes the axitinib concentration-time profile.
Absorption and Distribution
Following single oral 5-mg dose administration, the median Tmax ranged from 2.5 to 4.1 hours. Based on the plasma half-life, steady state is expected within 2 to 3 days of dosing. Dosing of axitinib at 5 mg twice daily resulted in approximately 1.4-fold accumulation compared to administration of a single dose. At steady state, axitinib exhibits approximately linear pharmacokinetics within the 1-mg to 20-mg dose range. The mean absolute bioavailability of axitinib after an oral 5 mg dose is 58%.
Compared to overnight fasting, administration of INLYTA with a moderate fat meal resulted in 10% lower AUC and a high fat, high-calorie meal resulted in 19% higher AUC. INLYTA can be administered with or without food [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Axitinib is highly bound (>99%) to human plasma proteins with preferential binding to albumin and moderate binding to α1-acid glycoprotein. In patients with advanced RCC (n=20), at the 5 mg twice daily dose in the fed state, the geometric mean (CV%) Cmax and AUC0–24 were 27.8 (79%) ng/mL and 265 (77%) ng.h/mL, respectively. The geometric mean (CV%) clearance and apparent volume of distribution were 38 (80%) L/h and 160 (105%) L, respectively.
Metabolism and Elimination
The plasma half-life of INLYTA ranges from 2.5 to 6.1 hours. Axitinib is metabolized primarily in the liver by CYP3A4/5 and to a lesser extent by CYP1A2, CYP2C19, and UGT1A1. Following oral administration of a 5-mg radioactive dose of axitinib, approximately 41% of the radioactivity was recovered in feces and approximately 23% was recovered in urine. Unchanged axitinib, accounting for 12% of the dose, was the major component identified in feces. Unchanged axitinib was not detected in urine; the carboxylic acid and sulfoxide metabolites accounted for the majority of radioactivity in urine. In plasma, the N-glucuronide metabolite represented the predominant radioactive component (50% of circulating radioactivity) and unchanged axitinib and the sulfoxide metabolite each accounted for approximately 20% of the circulating radioactivity.
The sulfoxide and N-glucuronide metabolites show approximately ≥400-fold less in vitro potency against VEGFR-2 compared to axitinib.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Effects of Other Drugs on INLYTA
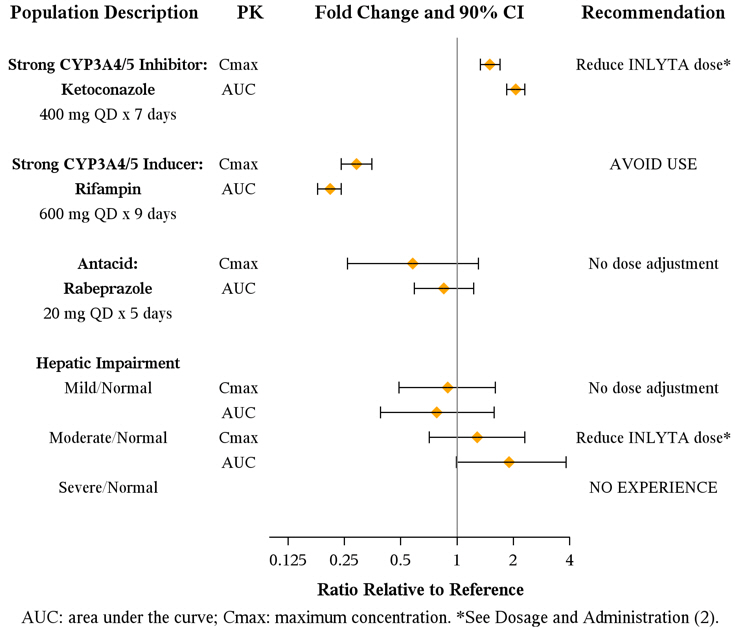
Axitinib is metabolized primarily in the liver by CYP3A4/5. Additionally, the aqueous solubility of axitinib is pH dependent, with higher pH resulting in lower solubility. The effects of a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor, a strong CYP3A4/5 inducer, and an antacid on the pharmacokinetics of axitinib are presented in Figure 1 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Figure 1. Impact of Co-administered Drugs and Hepatic Impairment on Axitinib Pharmacokinetics
Effects of INLYTA on Other Drugs
In vitro studies demonstrated that axitinib has the potential to inhibit CYP1A2 and CYP2C8. However, co-administration of axitinib with paclitaxel, a CYP2C8 substrate, did not increase plasma concentrations of paclitaxel in patients.
In vitro studies indicated that axitinib does not inhibit CYP2A6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, CYP3A4/5, or UGT1A1 at therapeutic plasma concentrations. In vitro studies in human hepatocytes indicated that axitinib does not induce CYP1A1, CYP1A2, or CYP3A4/5.
Axitinib is an inhibitor of the efflux transporter P-glycoprotein (P-gp) in vitro. However, INLYTA is not expected to inhibit P-gp at therapeutic plasma concentrations.
Specific Populations
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The effects of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of axitinib are presented in Figure 1 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
Population pharmacokinetic analysis (based on pre-existing renal function) was carried out in 590 healthy volunteers and patients, including five with severe renal impairment (15 mL/min ≤CLcr <29 mL/min), 64 with moderate renal impairment (30 mL/min ≤CLcr <59 mL/min), and 139 with mild renal impairment (60 mL/min ≤CLcr <89 mL/min). Mild to severe renal impairment did not have meaningful effects on the pharmacokinetics of axitinib. Data from only one patient with end-stage renal disease are available [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Other Intrinsic Factors
Population pharmacokinetic analyses indicate that there are no clinically relevant effects of age, gender, race, body weight, body surface area, UGT1A1 genotype, or CYP2C19 genotype on the clearance of axitinib.
INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab
When INLYTA 5 mg was administered in combination with avelumab 10 mg/kg, the respective exposures of INLYTA and avelumab were comparable to the single agents. There was no evidence to suggest a clinically relevant change of avelumab clearance over time in patients with advanced RCC.
INLYTA in Combination with Pembrolizumab
When INLYTA 5 mg was administered in combination with pembrolizumab 200 mg, the respective exposures of INLYTA and pembrolizumab were comparable to the single agents.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
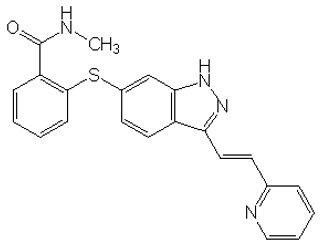
11 DESCRIPTION
INLYTA (axitinib) is a kinase inhibitor. Axitinib has the chemical name N-methyl-2-[3-((E)-2-pyridin-2-yl-vinyl)-1H-indazol-6-ylsulfanyl]-benzamide. The molecular formula is C22H18N4OS and the molecular weight is 386.47 Daltons. The chemical structure is:
Axitinib is a white to light-yellow powder with a pKa of 4.8. The solubility of axitinib in aqueous media over the range pH 1.1 to pH 7.8 is in excess of 0.2 µg/mL. The partition coefficient (n-octanol/water) is 3.5.
INLYTA is supplied as red, film-coated tablets containing either 1 mg or 5 mg of axitinib together with microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, and Opadry® II red 32K15441 as inactive ingredients. The Opadry II red 32K15441 film coating contains lactose monohydrate, HPMC 2910/Hypromellose 15cP, titanium dioxide, triacetin (glycerol triacetate), and red iron oxide.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 First-Line Advanced RCC
INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab
The efficacy and safety of INLYTA in combination with avelumab was demonstrated in the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial (NCT02684006), a randomized, multicenter, open-label, study of INLYTA in combination with avelumab in 886 patients with untreated advanced RCC regardless of tumor PD-L1 expression [intent-to-treat (ITT) population]. Patients with autoimmune disease or conditions requiring systemic immunosuppression were excluded.
Randomization was stratified according to Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) Performance Status (PS) (0 vs. 1) and region (United States vs. Canada/Western Europe vs. the rest of the world). Patients were randomized (1:1) to one of the following treatment arms:
•
INLYTA 5 mg twice daily orally was given in combination with avelumab 10 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 2 weeks (N=442). Patients who tolerated INLYTA 5 mg twice daily without Grade 2 or greater INLYTA-related adverse events for 2 consecutive weeks could increase to 7 mg and then subsequently to 10 mg twice daily. INLYTA could be interrupted or reduced to 3 mg twice daily and subsequently to 2 mg twice daily to manage toxicity.
•
Sunitinib 50 mg once daily orally for 4 weeks followed by 2 weeks off (N=444) until radiographic or clinical progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Treatment with INLYTA and avelumab continued until RECIST v1.1-defined progression of disease by Blinded Independent Central Review (BICR) assessment or unacceptable toxicity. Administration of INLYTA and avelumab was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression if the patient was clinically stable and considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Assessment of tumor status was performed at baseline, after randomization at 6 weeks, then every 6 weeks thereafter up to 18 months after randomization, and every 12 weeks thereafter until documented confirmed disease progression by BICR.
Baseline characteristics were a median age of 61 years (range: 27 to 88), 38% of patients were 65 years or older, 75% were male, 75% were White, and the ECOG PS was 0 (63%) or 1 (37%), respectively. Patient distribution by International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database (IMDC) risk groups was 21% favorable, 62% intermediate, and 16% poor.
The major efficacy outcome measures were progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by an BICR using RECIST v1.1 and overall survival (OS) in patients with PD-L1-positive tumors using a clinical trial assay (PD-L1 expression level ≥1%). Since PFS was statistically significant in patients with PD-L1-positive tumors [HR 0.61 (95% CI: 0.48, 0.79)], it was then tested in the ITT population and a statistically significant improvement in PFS in the ITT population was also demonstrated.
With a median overall survival follow-up of 19 months, overall survival data were immature with 27% deaths in the ITT population.
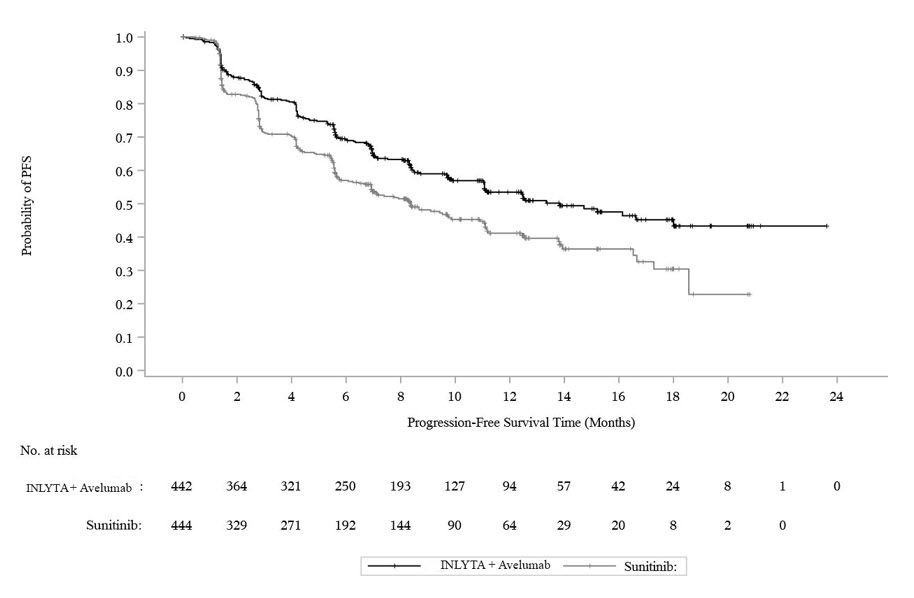
Efficacy results are presented in Table 10 and Figure 2.
Table 10: Efficacy Results from JAVELIN Renal 101 Trial-ITT|
Efficacy Endpoints (Based on BICR Assessment) |
INLYTA plus avelumab |
Sunitinib |
|---|---|---|
|
BICR: Blinded Independent Central Review; CI: Confidence interval; NE: Not estimable. | ||
| ||
|
Progression-Free Survival (PFS) | ||
|
Events (%) |
180 (41) |
216 (49) |
|
Median in Months (95% CI) |
13.8 (11.1, NE) |
8.4 (6.9, 11.1) |
|
Hazard ratio (95% CI) |
0.69 (0.56, 0.84) | |
|
2-sided p-value* |
0.0002 | |
|
Confirmed Objective Response Rate (ORR) | ||
|
Objective Response Rate n (%) |
227 (51.4) |
114 (25.7) |
|
(95% CI) |
(46.6, 56.1) |
(21.7, 30.0) |
|
Complete Response (CR) n (%) |
15 (3.4) |
8 (1.8) |
|
Partial Response (PR) n (%) |
212 (48) |
106 (24) |
Figure 2. K-M Estimates for PFS Based on BICR Assessment - ITT
INLYTA in Combination with Pembrolizumab
The efficacy of INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab was investigated in KEYNOTE-426 (NCT02853331), a randomized, multicenter, open-label trial conducted in 861 patients who had not received systemic therapy for advanced RCC. Patients were enrolled regardless of PD-L1 tumor expression status. Patients with active autoimmune disease requiring systemic immunosuppression within the last 2 years were ineligible. Randomization was stratified by International Metastatic RCC Database Consortium (IMDC) risk categories (favorable versus intermediate versus poor) and geographic region (North America versus Western Europe versus "Rest of the World").
Patients were randomized (1:1) to one of the following treatment arms:
•
INLYTA 5 mg orally, twice daily in combination with pembrolizumab 200 mg intravenously every 3 weeks up to 24 months. Patients who tolerated INLYTA 5 mg twice daily for 2 consecutive cycles (6 weeks) could increase to 7 mg and then subsequently to 10 mg twice daily. INLYTA could be interrupted or reduced to 3 mg twice daily and subsequently to 2 mg twice daily to manage toxicity.
•
Sunitinib 50 mg orally, once daily for 4 weeks and then off treatment for 2 weeks.
Treatment with INLYTA and pembrolizumab continued until RECIST v1.1-defined progression of disease or unacceptable toxicity. Administration of INLYTA and pembrolizumab was permitted beyond RECIST-defined disease progression if the patient was clinically stable and considered to be deriving clinical benefit by the investigator. Assessment of tumor status was performed at baseline, after randomization at Week 12, then every 6 weeks thereafter until Week 54, and then every 12 weeks thereafter.
The study population characteristics were: median age of 62 years (range: 26 to 90); 38% age 65 or older; 73% male; 79% White and 16% Asian; 20% and 80% of patients had a baseline KPS of 70 to 80 and 90 to 100, respectively; and patient distribution by IMDC risk categories was 31% favorable, 56% intermediate and 13% poor.
The main efficacy outcome measures were OS and PFS as assessed by BICR according to RECIST v1.1, modified to follow a maximum of 10 target lesions and a maximum of 5 target lesions per organ. Additional efficacy outcome measures included ORR, as assessed by BICR. A statistically significant improvement in OS was demonstrated at the first pre-specified interim analysis in patients randomized to INLYTA in combination with pembrolizumab compared with sunitinib. The trial also demonstrated statistically significant improvements in PFS and ORR.
An updated OS analysis was conducted when 418 deaths were observed based on the planned number of deaths for the pre-specified final analysis. Table 11 and Figure 3 summarize the efficacy results for KEYNOTE-426.
Table 11: Efficacy Results in KEYNOTE-426|
Endpoint |
INLYTA and Pembrolizumab |
Sunitinib |
|---|---|---|
|
CI: confidence interval; NR: not reached; ORR: objective response rate; OS: overall survival; PFS: progression-free survival. | ||
| ||
|
OS | ||
|
Number of patients with event (%) |
59 (14%) |
97 (23%) |
|
Median in months (95% CI) |
NR (NR, NR) |
NR (NR, NR) |
|
Hazard ratio* (95% CI) |
0.53 (0.38, 0.74) | |
|
p-Value † |
<0.0001 ‡ | |
|
12-month OS rate |
90% (86, 92) |
78% (74, 82) |
|
Updated OS | ||
|
Number of patients with event (%) |
193 (45%) |
225 (52%) |
|
Median in months (95% CI) |
45.7 (43.6, NR) |
40.1 (34.3, 44.2) |
|
Hazard ratio* (95% CI) |
0.73 (0.60, 0.88) | |
|
PFS | ||
|
Number of patients with event (%) |
183 (42%) |
213 (50%) |
|
Median in months (95% CI) |
15.1 (12.6, 17.7) |
11.0 (8.7, 12.5) |
|
Hazard ratio* (95% CI) |
0.69 (0.56, 0.84) | |
|
p-Value † |
0.0001§ | |
|
ORR | ||
|
Overall confirmed response rate (95% CI) |
59% (54, 64) |
36% (31, 40) |
|
Complete response rate |
6% |
2% |
|
Partial response rate |
53% |
34% |
|
p-Value¶ |
<0.0001 |
Figure 3. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Overall Survival in KEYNOTE-426
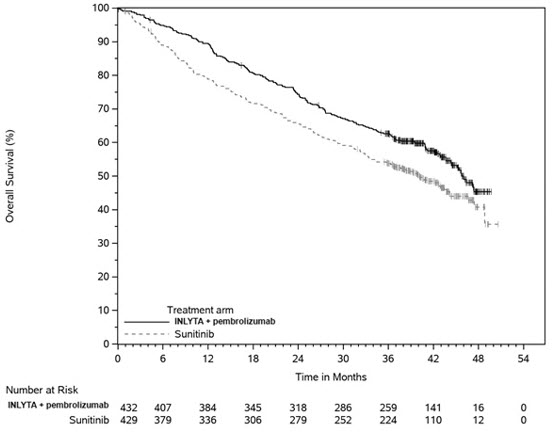
In an exploratory analysis, the updated analysis of OS in patients with IMDC favorable, intermediate, intermediate/poor, and poor risk demonstrated a HR of 1.17 (95% CI: 0.76, 1.80), 0.67 (95% CI: 0.52, 0.86), 0.64 (95% CI: 0.52, 0.80), and 0.51 (95% CI: 0.32, 0.81), respectively.
14.2 Second-Line Advanced RCC
The safety and efficacy of INLYTA were evaluated in a randomized, open-label, multicenter Phase 3 study. Patients (N=723) with advanced RCC whose disease had progressed on or after treatment with 1 prior systemic therapy, including sunitinib-, bevacizumab-, temsirolimus-, or cytokine-containing regimens were randomized (1:1) to receive INLYTA (N=361) or sorafenib (N=362). Progression- free survival (PFS) was assessed by a blinded independent central review committee. Other endpoints included objective response rate (ORR) and overall survival (OS).
Of the patients enrolled in this study, 389 patients (54%) had received 1 prior sunitinib-based therapy, 251 patients (35%) had received 1 prior cytokine-based therapy (interleukin-2 or interferon-alfa), 59 patients (8%) had received 1 prior bevacizumab-based therapy, and 24 patients (3%) had received 1 prior temsirolimus-based therapy. The baseline demographic and disease characteristics were similar between the INLYTA and sorafenib groups with regard to age (median 61 years), gender (72% male), race (75% white, 21% Asian), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (55% 0, 45% 1), and histology (99% clear cell).
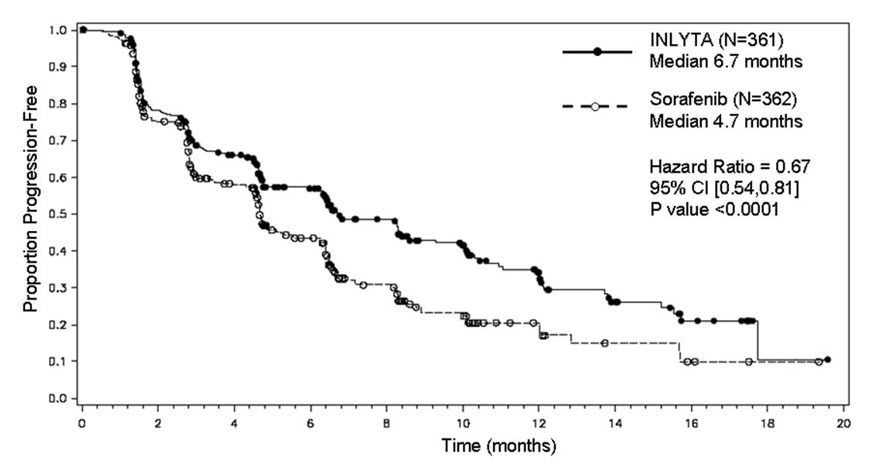
There was a statistically significant advantage for INLYTA over sorafenib for the endpoint of PFS (see Table 12 and Figure 4). There was no statistically significant difference between the arms in OS.
Table 12: Efficacy Results|
Endpoint/Study Population |
INLYTA |
Sorafenib |
HR (95% CI) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CI: Confidence interval; HR: Hazard ratio (INLYTA/sorafenib); ITT: Intent-to- treat; ORR: Objective response rate; NS: Not significant; OS: Overall survival; PFS: Progression-free survival | ||||
| ||||
|
Overall ITT |
N= 361 |
N = 362 | ||
|
Median PFS*,† in months (95% CI) |
6.7 (6.3, 8.6) |
4.7 (4.6, 5.6) |
0.67 (0.54, 0.81) |
<0.0001‡ |
|
Median OS in months |
20.1 (16.7, 23.4) |
19.2 (17.5, 22.3) |
0.97 (0.80, 1.17) |
NS |
|
ORR % (95% CI) |
19.4 (15.4, 23.9) |
9.4 (6.6, 12.9) |
2.06§ (1.41, 3.00) |
-¶ |
|
PFS by prior treatment | ||||
|
Sunitinib-refractory subgroup |
N=194 |
N=195 | ||
|
Median, months (95% CI) |
4.8 (4.5, 6.4) |
3.4 (2.8, 4.7) |
0.74 (0.57, 0.96) |
-¶ |
|
Cytokine-refractory subgroup |
N=126 |
N=125 | ||
|
Median, months (95% CI) |
12.1 (10.1, 13.9) |
6.5 (6.3, 8.3) |
0.46 (0.32, 0.68) |
-¶ |
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier Curve for Progression-Free Survival by Independent Assessment (Intent-to-Treat Population)
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
INLYTA tablets are supplied as follows:
•
1 mg tablets are red film-coated, oval tablets debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "1 XNB" on the other; available in bottles of 180: NDC 0069-0145-01.
•
5 mg tablets are red film-coated, triangular tablets debossed with "Pfizer" on one side and "5 XNB" on the other; available in bottles of 60: NDC 0069-0151-11.
•
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
PATIENT INFORMATION | |||
|
Important information: If your healthcare provider prescribes INLYTA for you to be taken with avelumab or pembrolizumab, also read the Medication Guide for avelumab or pembrolizumab. | |||
|
What is INLYTA? • • It is not known if INLYTA is safe and effective in children. | |||
|
Before taking INLYTA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: • • • • • • • • For females, tell your healthcare provider if you: • • • For males with female partners who are able to become pregnant: • • Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
INLYTA and certain other medicines can affect each other causing serious side
effects. | |||
|
How should I take INLYTA? • • • • • • • • | |||
|
What should I avoid while taking INLYTA? • | |||
|
What are the possible side effects of INLYTA? • • | |||
|
o o o |
o o o o | ||
|
• o | |||
|
• • • • |
• • • • | ||
|
o o | |||
|
• | |||
|
o o |
o o | ||
|
• o o o | |||
|
• | |||
|
o o o |
o o o | ||
|
• o o | |||
|
• | |||
|
o o o |
o o o o | ||
|
• • Tell your healthcare provider right way if you have any of the following symptoms: | |||
|
o o o |
o o | ||
|
• | |||
|
o o o o |
o o o o | ||
|
The most common side effects of INLYTA with avelumab include: | |||
|
o o o o o o o o o |
o o o o o o o | ||
|
The most common side effects of INLYTA with pembrolizumab include: | |||
|
o o o o o o o |
o o o o o o | ||
|
The most common side effects of INLYTA when used alone include: | |||
|
o o o o o o |
o o o o | ||
|
INLYTA may cause fertility problems in males and females, which may affect
your ability to have a child. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a
concern for you. | |||
|
How should I store INLYTA? Store INLYTA at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep INLYTA and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of INLYTA. | |||
|
What are the ingredients in INLYTA? | |||
|
|
LAB-0439-7.0 | ||
|
For more information, go to www.inlyta.com or call
877-0744-5675 |
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: September 2022
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
This product's labeling may have been updated. For the most recent prescribing information, please visit www.pfizer.com.

LAB-0561-7.0
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
First-Line Advanced RCC
INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab
The recommended starting dosage of INLYTA is 5 mg orally taken twice daily (12 hours apart) with or without food in combination with avelumab 800 mg administered as an intravenous infusion over 60 minutes every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. When INLYTA is used in combination with avelumab, dose escalation of INLYTA above the initial 5 mg dose may be considered at intervals of two weeks or longer. Review the Full Prescribing Information for recommended avelumab dosing information.
INLYTA in Combination with Pembrolizumab
The recommended starting dosage of INLYTA is 5 mg orally twice daily (12 hours apart) with or without food in combination with pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks or 400 mg every 6 weeks administered as an intravenous infusion over 30 minutes until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. When INLYTA is used in combination with pembrolizumab, dose escalation of INLYTA above the initial 5 mg dose may be considered at intervals of six weeks or longer. Review the Full Prescribing Information for recommended pembrolizumab dosing information.
Second-Line Advanced RCC
When INLYTA is used as a single agent, the recommended starting oral dose is 5 mg twice daily. Administer INLYTA doses approximately 12 hours apart with or without food.
Important Administration Instructions
Advise patients to swallow INLYTA whole with a full glass of water. If the patient vomits or misses a dose, an additional dose should not be taken. Advise the patient to take the next prescribed dose at the usual time.
2.2 Dose Modification Guidelines
Dose increase or reduction is recommended based on individual safety and tolerability.
Recommended INLYTA dosage increases and reductions are provided in Table 1.
Over the course of treatment, patients who tolerate INLYTA for at least two consecutive weeks with no adverse reactions Grade >2 (according to the Common Toxicity Criteria for Adverse Events [CTCAE]), are normotensive, and are not receiving anti-hypertension medication, may have their dose increased.
Table 1:Recommended Dosage Increases and Reductions for INLYTA|
Dose Modification |
Dose Regimen |
|---|---|
| |
|
Recommended starting dosage |
5 mg twice daily |
|
Dosage increase | |
|
First dose increase |
7 mg twice daily |
|
Second dose increase |
10 mg twice daily |
|
Dosage reduction* | |
|
First dose reduction† |
3 mg twice daily |
|
Second dose reduction |
2 mg twice daily |
Recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions for INLYTA are provided in Table 2.
Table 2:Recommended Dosage Modification for INLYTA for Adverse Reactions|
Adverse Reaction |
Severity |
Dosage Modifications for INLYTA |
|---|---|---|
|
Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] |
SBP > 150 mmHg or DBP > 100 mmHg despite antihypertensive treatment |
• |
|
SBP > 160 mmHg or DBP > 105 mmHg |
• • | |
|
Grade 4 or hypertensive crisis |
• | |
|
Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] |
Grade 3 or 4 |
• • |
|
Cardiac failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] |
Asymptomatic cardiomyopathy (left ventricular ejection fraction greater than 20% but less than 50% below baseline or below the lower limit of normal if baseline was not obtained) |
• • |
|
Clinically manifested congestive heart failure |
• | |
|
Impaired wound healing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)] |
Any Grade |
• • |
|
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)] |
Any Grade |
• |
|
Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)] |
2 or more grams proteinuria per 24 hours |
• • |
|
Other Adverse Reactions |
Grade 3 |
• |
|
Grade 4 |
• • |
Table 3 represents additional recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions when INLYTA is administered in combination with avelumab or pembrolizumab.
See the Full Prescribing Information for additional dosage information for avelumab or pembrolizumab including dose modifications for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Table 3: Recommended Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions for INLYTA in Combination with Avelumab or Pembrolizumab|
Treatment |
Adverse Reaction |
Severity* |
Dosage Modifications for INLYTA |
|---|---|---|---|
|
ALT = alanine aminotransferase, AST = aspartate aminotransferase, ULN = upper limit normal | |||
| |||
|
INLYTA in combination with avelumab OR pembrolizumab |
Liver enzyme elevations† |
ALT or AST at least 3 times ULN but less than 10 times ULN without concurrent total bilirubin at least 2 times ULN |
• • |
|
ALT or AST increases to more than 3 times ULN with concurrent total bilirubin at least 2 times ULN or ALT or AST at least 10 times ULN |
• | ||
|
Diarrhea |
Grade 1–2 |
• | |
|
Grade 3 |
• | ||
|
Grade 4 |
• | ||
|
INLYTA in combination with avelumab |
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events (MACE) |
Grade 3 or 4 |
• |
2.3 Dosage Modification for Drug Interactions
Strong CYP3A4/5 Inhibitors
The concomitant use of strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors should be avoided (e.g., ketoconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, atazanavir, indinavir, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, and voriconazole). Selection of an alternate concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A4/5 inhibition potential is recommended. Although INLYTA dose adjustment has not been studied in patients receiving strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitors, if a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor must be co-administered, a dose decrease of INLYTA by approximately half is recommended, as this dose reduction is predicted to adjust the axitinib area under the plasma concentration vs time curve (AUC) to the range observed without inhibitors. The subsequent doses can be increased or decreased based on individual safety and tolerability. If co-administration of the strong inhibitor is discontinued, the INLYTA dose should be returned (after 3 – 5 half-lives of the inhibitor) to that used prior to initiation of the strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Dosage Modification for Hepatic Impairment
No starting dose adjustment is required when administering INLYTA to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A). Based on the pharmacokinetic data, the INLYTA starting dose should be reduced by approximately half in patients with baseline moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class B). The subsequent doses can be increased or decreased based on individual safety and tolerability. INLYTA has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
•
INLYTA 5 mg orally twice daily with avelumab 800 mg every 2 weeks. (2.1)
•
INLYTA 5 mg orally twice daily with pembrolizumab 200 mg every 3 weeks or 400 mg every 6 weeks. (2.1)
•
INLYTA as a single agent the starting dose is 5 mg orally twice daily. (2.1)
•
Dose adjustments can be made based on individual safety and tolerability. (2.2)
•
Administer INLYTA dose approximately 12 hours apart with or without food. (2.1)
•
INLYTA should be swallowed whole with a glass of water. (2.1)
•
See Full Prescribing Information for dosage modifications for adverse reactions. (2.2)
•
If a strong CYP3A4/5 inhibitor is required, decrease the INLYTA dose by approximately half. (2.2)
•
For patients with moderate hepatic impairment, decrease the starting dose by approximately half. (2.2)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with axitinib.
Axitinib was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in the in vitro human lymphocyte chromosome aberration assay. Axitinib was genotoxic in the in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
INLYTA has the potential to impair reproductive function and fertility in humans. In repeat-dose toxicology studies, findings in the male reproductive tract were observed in the testes/epididymis (decreased organ weight, atrophy or degeneration, decreased numbers of germinal cells, hypospermia or abnormal sperm forms, reduced sperm density and count) at ≥15 mg/kg/dose administered orally twice daily in mice (approximately 7 times the systemic exposure (AUC) in patients at the recommended starting dose) and ≥1.5 mg/kg/dose administered orally twice daily in dogs (approximately 0.1 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose). Findings in the female reproductive tract in mice and dogs included signs of delayed sexual maturity, reduced or absent corpora lutea, decreased uterine weights and uterine atrophy at ≥5 mg/kg/dose (approximately 1.5 or 0.3 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose compared to mice and dogs, respectively).
In a fertility study in mice, axitinib did not affect mating or fertility rate when administered orally twice daily to males at any dose tested up to 50 mg/kg/dose following at least 70 days of administration (approximately 57 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose). In female mice, reduced fertility and embryonic viability were observed at all doses tested (≥15 mg/kg/dose administered orally twice daily) following at least 15 days of treatment with axitinib (approximately 10 times the AUC in patients at the recommended starting dose).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypertension
Advise patients that hypertension may develop during INLYTA treatment and that blood pressure should be monitored regularly during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Arterial/Venous Thromboembolic Events
Advise patients that arterial and venous thromboembolic events have been observed during INLYTA treatment and to inform their doctor if they experience symptoms suggestive of thromboembolic events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
Hemorrhage
Advise patients that INLYTA may increase the risk of bleeding and to promptly inform their doctor of any bleeding episodes [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Cardiac Failure
Advise patients that cardiac failure may develop during INLYTA treatment and that signs or symptoms of cardiac failure should be regularly monitored for during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Advise patients that gastrointestinal disorders such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and constipation may develop during INLYTA treatment and to seek immediate medical attention if they experience persistent or severe abdominal pain because cases of gastrointestinal perforation and fistula have been reported in patients taking INLYTA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Abnormal Thyroid Function
Advise patients that abnormal thyroid function may develop during INLYTA treatment and to inform their doctor if symptoms of abnormal thyroid function occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Impaired Wound Healing
Advise patients that INLYTA may impair wound healing. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of any planned surgical procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome
Advise patients to inform their doctor if they have worsening of neurological function consistent with RPLS (headache, seizure, lethargy, confusion, blindness and other visual and neurologic disturbances) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
Advise patients receiving INLYTA in combination with avelumab to contact their healthcare provider immediately for signs or symptoms of cardiovascular events including but not limited to new or worsening chest discomfort, dyspnea, or peripheral edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant. Inform female patients of the risk to a fetus and potential loss of the pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with INLYTA and for 1 week after the last dose.
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 1 week following the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
When INLYTA is used in combination with avelumab or pembrolizumab, refer to the full prescribing information of avelumab or pembrolizumab for pregnancy and contraception information.
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed while taking INLYTA and for 2 weeks after receiving the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
When INLYTA is used in combination with avelumab or pembrolizumab, refer to the full prescribing information of avelumab or pembrolizumab for lactation information.
Infertility
Advise males and females of reproductive potential that INLYTA may impair fertility [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to inform their doctor of all concomitant medications, vitamins, or dietary and herbal supplements.

