SODIUM POLYSTYRENE SULFONATE
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension. Sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension, for oral or rectal use Initial U.S. Approval: 1958
9a50c6d4-e619-438d-8af9-bb758ea7ba7e
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 13, 2023
Bryant Ranch Prepack
DUNS: 171714327
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
sodium polystyrene sulfonate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate Powder
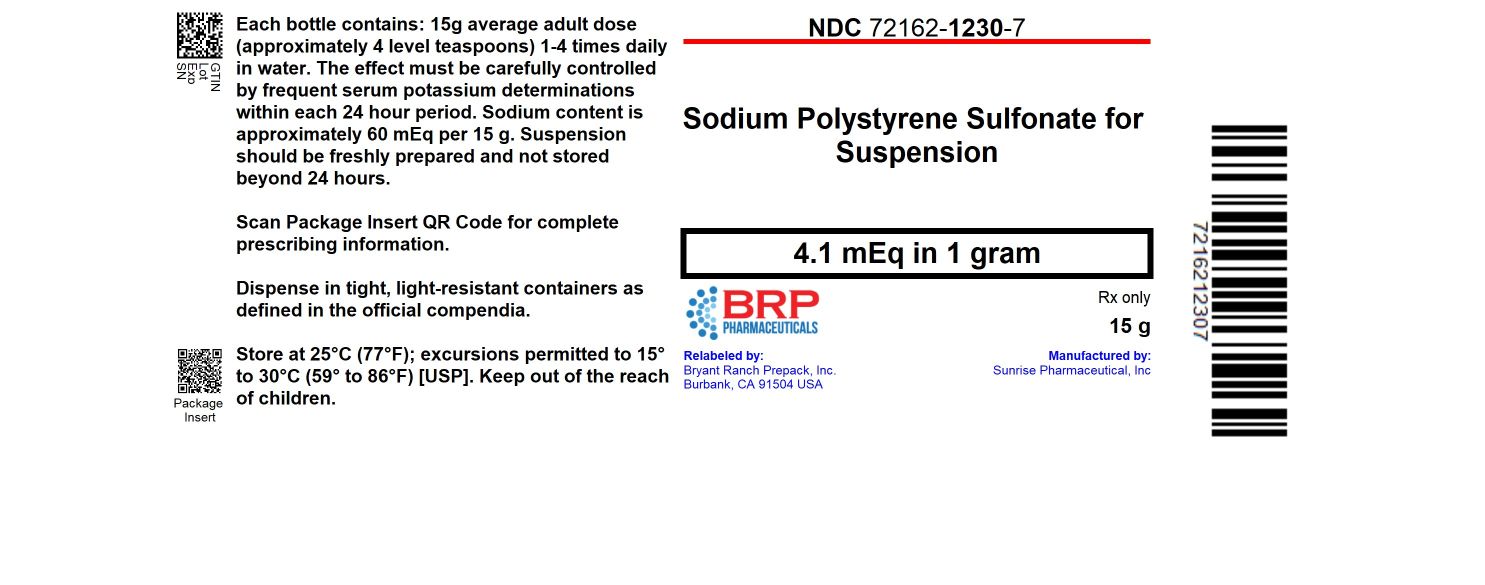
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension is indicated for the treatment of hyperkalemia.
Limitation of Use:
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension should not be used as an emergency treatment for life-threatening hyperkalemia because of its delayed onset of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension is a potassium binder indicated for the treatment of hyperkalemia ( 1).
Limitation of Use:
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate for suspension should not be used an emergency treatment for life threatening hyperkalemia because of its delayed onset of action ( 1).
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- Hypersensitivity to polystyrene sulfonate resins
- Obstructive bowel disease
- Neonates with reduced gut motility
- Hypersensitivity to polystyrene sulfonate resins ( 4)
- Obstructive bowel disease ( 4)
- Neonates with reduced gut motility ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Intestinal Necrosis
Cases of intestinal necrosis, some fatal, and other serious gastrointestinal adverse events (bleeding, ischemic colitis, perforation) have been reported in association with sodium polystyrene sulfonate use. The majority of these cases reported the concomitant use of sorbitol. Risk factors for gastrointestinal adverse events were present in many of the cases including prematurity, history of intestinal disease or surgery, hypovolemia, and renal insufficiency and failure. Concomitant administration of sorbitol is not recommended.
- Use only in patients who have normal bowel function. Avoid use in patients who have not had a bowel movement post-surgery.
- Avoid use in patients who are at risk for developing constipation or impaction (including those with history of impaction, chronic constipation, inflammatory bowel disease, ischemic colitis, vascular intestinal atherosclerosis, previous bowel resection, or bowel obstruction). Discontinue use in patients who develop constipation.
5.2 Electrolyte Disturbances
Monitor serum potassium during therapy because severe hypokalemia may occur.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is not totally selective for potassium, and small amounts of other cations such as magnesium and calcium can also be lost during treatment. Monitor calcium and magnesium in patients receiving sodium polystyrene sulfonate.
5.3 Fluid Overload in Patients Sensitive to High Sodium Intake
Each 15 g dose of sodium polystyrene sulfonate contains 1500 mg (60 mEq) of sodium. Monitor patients who are sensitive to sodium intake (heart failure, hypertension, edema) for signs of fluid overload. Adjustment of other sources of sodium may be required.
5.4 Risk of Aspiration
Cases of acute bronchitis or bronchopneumonia caused by inhalation of sodium polystyrene sulfonate particles have been reported. Patients with impaired gag reflex, altered level of consciousness, or patients prone to regurgitation may be at increased risk. Administer sodium polystyrene sulfonate with the patient in an upright position.
5.5 Binding to Other Orally Administered Medications
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate may bind orally administered medications, which could decrease their gastrointestinal absorption and lead to reduced efficacy. Administer other oral medications at least 3 hours before or 3 hours after sodium polystyrene sulfonate. Patients with gastroparesis may require a 6 hour separation. [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)and Drug Interactions (7)].
- Intestinal Necrosis: cases of intestinal necrosis and other serious gastrointestinal events have been reported ( 5.1).
- Electrolyte Disturbances: Severe hypokalemia can occur. ( 5.2).
- Fluid overload in patient sensitive to high sodium intake: Monitor patients who are sensitive to sodium intake for signs of fluid overload. ( 5.3).
- Risk of aspiration: Acute bronchitis or bronchopneumonia caused by inhalation of sodium polystyrene sulfonate particles has been reported. ( 5.4).
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 General Interactions
No formal drug interaction studies have been conducted in humans.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate has the potential to bind other drugs. In in vitrobinding studies, sodium polystyrene sulfonate was shown to significantly bind the oral medications (n=6) that were tested. Decreased absorption of lithium and thyroxine have also been reported with co-administration of sodium polystyrene sulfonate. Binding of sodium polystyrene sulfonate to other oral medications could cause decreased gastrointestinal absorption and loss of efficacy when taken close to the time sodium polystyrene sulfonate is administered. Administer sodium polystyrene sulfonate at least 3 hours before or 3 hours after other oral medications. Patients with gastroparesis may require a 6 hour separation. Monitor for clinical response and/or blood levels where possible.
7.2 Cation-Donating Antacids
The simultaneous oral administration of sodium polystyrene sulfonate with nonabsorbable cation-donating antacids and laxatives may reduce the resin's potassium exchange capability and increase the risk of systemic alkalosis.
7.3 Sorbitol
Sorbitol may contribute to the risk of intestinal necrosis [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] and concomitant use is not recommended.
- Take other orally administered drugs at least 3 hours before or 3 hours after sodium polystyrene sulfonate ( 7.1).
- Cation-Donating Antacids: may reduce the resin’s potassium exchange capability and increase risk of systemic alkalosis ( 7.2).
- Sorbitol: Concomitant use may contribute to the risk of intestinal necrosis and is not recommended ( 7.3).
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Information
Administer sodium polystyrene sulfonate at least 3 hours before or 3 hours after other oral medications. Patients with gastroparesis may require a 6 hour separation [see Warnings and Precautions(5.5)andDrug Interaction(7)]
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The intensity and duration of therapy depend upon the severity and resistance of hyperkalemia.
Oral
The average total daily adult dose of sodium polystyrene sulfonate is 15 g to 60 g, administered as a 15-g dose (four level teaspoons), one to four times daily.
Rectal
The average adult dose is 30 g to 50 g every six hours.
2.3 Preparation and Administration
Prepare suspension fresh and use within 24 hours.
Do not heat sodium polystyrene sulfonate as it could alter the exchange properties of the resin.
One level teaspoon contains approximately 3.5 g of sodium polystyrene sulfonate and 15 mEq of sodium.
Oral Suspension
Suspend each dose in a small quantity of water or syrup, approximately 3 to 4 mL of liquid per gram of resin. Administer with patient in an upright position [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Enema
After an initial cleansing enema, insert a soft, large size (French 28) rubber tube into the rectum for a distance of about 20 cm, with the tip well into the sigmoid colon, and tape in place.
Administer as a warm (body temperature) emulsion in 100 mL of aqueous vehicle and flush with 50 to 100 ml of fluid. A somewhat thicker suspension may be used, but do not form a paste.
Agitate the emulsion gently during administration. The resin should be retained for as long as possible and follow by a cleansing enema with a nonsodium containing solution. Ensure an adequate volume of cleansing solution (up to 2 liters) is utilized.
Oral: The average total daily adult dose of sodium polystyrene sulfonate is 15 g to 60 g, administered as a 15-g dose (four level teaspoons), one to four times daily ( 2.1).
Rectal: The average adult dose is 30 g to 50 g every six hours ( 2.1).
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is not absorbed systemically following oral or rectal administration and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal risk.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is not absorbed systemically by the mother, so breastfeeding is not expected to result in risk to the infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Studies of safety and efficacy have not been conducted in pediatric patients.
In pediatric patients, as in adults, sodium polystyrene sulfonate is expected to bind potassium at the practical exchange ratio of 1mEq potassium per 1 gram of resin.
In neonates, sodium polystyrene sulfonate should not be given by the oral route. In both children and neonates, excessive dosage or inadequate dilution could result in impaction of the resin. Premature infants or low birth weight infants may have an increased risk for gastrointestinal adverse effects with sodium polystyrene sulfonate use [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a benzene, diethenyl- polymer, with
ethenylbenzene,
sulfonated, sodium salt and has the following structural formula:
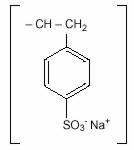 n
n
The drug is a golden brown finely ground, powdered form of sodium polystyrene sulfonate, a cation-exchange resin prepared in the sodium phase with an in vitroexchange capacity of approximately 3.1 mEq ( in vivoapproximately 1 mEq) of potassium per gram. The sodium content is approximately 100 mg (4.1 mEq) per gram of the drug. It can be administered orally or in an enema.
One gram of sodium polystyrene sulfonate contains 4.1 mEq of sodium.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is a non-absorbed, cation exchange polymer that contains a sodium counterion.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate increases fecal potassium excretion through binding of potassium in the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. Binding of potassium reduces the concentration of free potassium in the gastrointestinal lumen, resulting in a reduction of serum potassium levels. The practical exchange ratio is 1 mEq K per 1 gram of resin.
As the resin passes along the intestine or is retained in the colon after administration by enema, the sodium ions are partially released and are replaced by potassium ions. This action occurs primarily in the large intestine, which excretes potassium ions to a greater degree than does the small intestine. The efficiency of this process is limited and unpredictably variable.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The effective lowering of serum potassium with sodium polystyrene sulfonate may take hours to days.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The in vivoefficiency of sodium-potassium exchange resins is approximately 33 percent; hence, about one third of the resin's actual sodium content is delivered to the body.
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate is not absorbed systemically.
Drug Interactions
In vitrobinding studies showed that sodium polystyrene sulfonate bound significantly to the following tested drugs – warfarin, metoprolol, phenytoin, furosemide, amlodipine and amoxicillin.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Drug Interactions
Advise patients who are taking other oral medication to separate the dosing of sodium polystyrene sulfonate by at least 3 hours (before or after) [ see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.5), and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
Rx Only
Manufactured & Distributed by:
Sunrise Pharmaceutical, Inc.
Rahway, NJ 07065
Revised August 2022
5368/00
