Gefitinib
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GEFITINIB TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GEFITINIB TABLETS.GEFITINIB tablets, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 2015
6402435f-9f6a-4f02-91a2-6267d783fa78
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Dec 28, 2023
Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC
DUNS: 833250017
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Gefitinib
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL – 250mg tablets, 30 count, bottle
NDC 50742-366-30
30 tablets
Gefitinib Tablets
250 mg
Manufactured for:
Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Orlando, FL 32811-7193
Manufactured by:
Qilu Pharmaceutical (Hainan) Co., Ltd.
Haikou, 570314, China

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Gefitinib tablets are indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Limitation of Use: Safety and efficacy of gefitinib tablets have not been established in patients with metastatic NSCLC whose tumors have EGFR mutations other than exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Gefitinib tablets are a tyrosine kinase inhibitor indicated for the first-line treatment of patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) whose tumors have epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations as detected by an FDA-approved test. (1)
Limitation of Use: Safety and efficacy of gefitinib tablets have not been established in patients whose tumors have EGFR mutations other than exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) substitution mutations. (1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
ILD or ILD-like adverse drug reactions (e.g., lung infiltration, pneumonitis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or pulmonary fibrosis) occurred in 1.3% of the 2462 patients who received gefitinib tablets across clinical trials; of these, 0.7% were Grade 3 or higher and 3 cases were fatal.
Withhold gefitinib tablets and promptly investigate for ILD in any patient who presents with worsening of respiratory symptoms such as dyspnea, cough and fever. Permanently discontinue gefitinib tablets if ILD is confirmed [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
In patients who received gefitinib tablets across clinical trials, 11.4% of patients had increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT), 7.9% of patients had increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and 2.7% of patients had increased bilirubin. Grade 3 or higher liver test abnormalities occurred in 5.1% (ALT), 3.0% (AST), and 0.7% (bilirubin) of patients. The incidence of fatal hepatotoxicity was 0.04%.
Obtain periodic liver function testing. Withhold gefitinib tablets in patients with worsening liver function and discontinue in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
5.3 Gastrointestinal Perforation
Gastrointestinal perforation occurred in three (0.1%) of the 2462 gefitinib tablets-treated patients across clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Permanently discontinue gefitinib tablets in patients who develop gastrointestinal perforation [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Severe or Persistent Diarrhea
Grade 3 or 4 diarrhea occurred in 3% of 2462 gefitinib tablets-treated patients across clinical trials. Withhold gefitinib tablets for severe or persistent (up to 14 days) diarrhea [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Ocular Disorders including Keratitis
Ocular disorders [keratitis (0.1%), corneal erosion and aberrant eyelash growth (0.2%), conjunctivitis, blephritis and dry eye (6.7%)] occurred in the 2462 gefitinib tablets-treated patients across clinical trials. The incidence of Grade 3 ocular disorders was 0.1% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Interrupt or discontinue gefitinib tablets for severe, or worsening ocular disorders [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.6 Bullous and Exfoliative Skin Disorders
Bullous conditions including toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme have been reported from treatment with gefitinib tablets. Erythema multiforme and dermatitis bullous have been reported in two patients (0.08%) across NSCLC trials (Study 2, Study 3 and Study 4). Gefitinib tablets treatment should be interrupted or discontinued if the patient develops severe bullous, blistering or exfoliating conditions.
5.7 Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and data from animal reproduction studies gefitinib tablets can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproductive studies, oral administration of gefitinib from organogenesis through weaning resulted in fetotoxicity and neonatal death at doses below the recommended human dose. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with gefitinib tablets and for at least two weeks following completion of therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Interstitial lung disease (ILD): ILD occurred in patients taking gefitinib tablets. Withhold gefitinib tablets for worsening of respiratory symptoms. Discontinue gefitinib tablets if ILD is confirmed. (2.4, 5.1)
- Hepatotoxicity: Obtain periodic liver function testing. Withhold gefitinib tablets for Grade 2 or higher for ALT and/or AST elevations. Discontinue for severe hepatic impairment. (2.4, 5.2)
- Gastrointestinal perforation: Discontinue gefitinib tablets for gastrointestinal perforation. (2.4, 5.3)
- Diarrhea: Withhold gefitinib tablets for Grade 3 or higher diarrhea. (2.4, 5.4)
- Ocular Disorders including Keratitis: Withhold gefitinib tablets for signs and symptoms of severe or worsening ocular disorders including keratitis. Discontinue for persistent ulcerative keratitis. (2.4, 5.5)
- Bullous and Exfoliative Skin Disorders: Withhold gefitinib tablets for Grade 3 or higher skin reactions or exfoliative conditions. (2.4, 5.6)
- Embryo-fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise of potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception. (5.7, 8.1, 8.3)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Affecting Gefitinib Exposure
CYP3A4 Inducer
Drugs that are strong inducers of CYP3A4 increase the metabolism of gefitinib and decrease gefitinib plasma concentrations. Increase gefitinib tablets to 500 mg daily in patients receiving a strong CYP3A4 inducer (e.g., rifampicin, phenytoin, or tricyclic antidepressant) and resume gefitinib tablets at 250 mg 7 days after discontinuation of the strong inducer [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
CYP3A4 Inhibitor
Drugs that are strong inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., ketoconazole and itraconazole) decrease gefitinib metabolism and increase gefitinib plasma concentrations. Monitor adverse reactions when administering strong CYP3A4 inhibitors with gefitinib tablets.
Drugs Affecting Gastric pH
Drugs that elevate gastric pH (e.g., proton pump inhibitors, histamine H2-receptor antagonists, and antacids) may reduce plasma concentrations of gefitinib. Avoid concomitant use of gefitinib tablets with proton pump inhibitors, if possible. If treatment with a proton-pump inhibitor is required, take gefitinib tablets 12 hours after the last dose or 12 hours before the next dose of the proton-pump inhibitor. Take gefitinib tablets 6 hours after or 6 hours before an H2-receptor antagonist or an antacid [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Hemorrhage in Patients taking Warfarin
International Normalized Ratio (INR) elevations and/or hemorrhage have been reported in some patients taking warfarin while on gefitinib tablets therapy. Patients taking warfarin should be monitored regularly for changes in prothrombin time or INR.
- CYP3A4 Inducer: Increase gefitinib tablets to 500 mg daily in patients receiving a strong CYP3A4 inducer. (2.4, 7.1)
- CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Monitor adverse reactions if concomitant use with gefitinib tablets. (7.1)
- Drugs Affecting Gastric pH: Avoid concomitant use of gefitinib tablets with proton pump inhibitors, if possible. (7.1)
- Hemorrhage in patients taking warfarin: Monitor changes in prothrombin time or INR. (7.2)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Gefitinib is a kinase inhibitor.
The chemical name of gefitinib is 4-Quinazolinamine N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl)-7-methoxy-6-[3-(4-morpholinyl) propoxy] and the following structural formula:
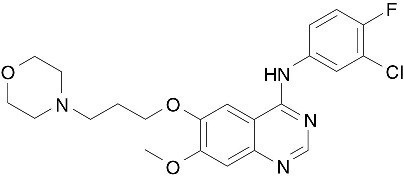
Gefitinib has the molecular formula C22H24ClFN4O3, a relative molecular mass of 446.9 daltons and is a white-colored powder. Gefitinib is a free base. The molecule has pKas of 5.4 and 7.2. Gefitinib can be defined as sparingly soluble at pH 1, but is practically insoluble above pH 7, with the solubility decreasing sharply between pH 4 and pH 6. In non-aqueous solvents, gefitinib is freely soluble in glacial acetic acid and dimethyl sulfoxide, soluble in pyridine, sparingly soluble in tetrahydrofuran, and slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol (99.5%), ethyl acetate, propan-2-ol and acetonitrile.
Gefitinib tablets are available as brown film-coated tablets, containing 250 mg of gefitinib, for oral administration. The inactive ingredients of the tablet core of gefitinib tablets are lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium, povidone, sodium lauryl sulfate and magnesium stearate. The tablet coating is composed of polyvinyl alcohol-part hydrolysed, polyethylene glycol 3350, talc, titanium dioxide, red ferric oxide, ferrosoferric oxide and yellow ferric oxide.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Gefitinib has been tested for genotoxicity in a series of in vitro (bacterial mutation, mouse lymphoma, and human lymphocyte) assays and an in vivo rat micronucleus test. Under the conditions of these assays, gefitinib did not cause genetic damage.
In a two-year carcinogenicity study in mice, administration of gefitinib at a dose of 270 mg/m2/day (approximately twice the recommended daily dose of 250 mg on a mg/m2 basis; dose reduced from 375 mg/m2/day from week 22) caused hepatocellular adenomas in females. In a two-year carcinogenicity study in rats, administration of gefitinib at 60 mg/m2/day (approximately 0.4 times the recommended daily clinical dose on a mg/m2 basis) caused hepatocellular adenomas and hemangiomas/hemagiosarcomas of the mesenteric lymph nodes in female rats. The clinical relevance of these findings is unknown.
In a dedicated fertility study in rats at doses ≥120 mg/m2 (approximately equal to the recommended human dose of gefitinib on a mg/m2 basis), animals presented with an increased incidence of irregular estrous, decreased corpora lutea, and decreases in uterine implants and live embryos per litter.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Gefitinib is available as 250 mg tablets.
Gefitinib tablets 250 mg are round, biconvex face, brown film-coated, debossed with “QL” on one side and plain on the other side.
Gefitinib tablets are supplied as:
Bottles of 30 Tablets (NDC 50742-366-30)
Store at controlled room temperature 20°C-25°C (68°F-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labelling (Patient Information).
Interstitial Lung Disease: Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new onset or worsening of pulmonary symptoms such as dyspnea, cough and fever [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients that they will need to undergo lab tests to monitor for liver function. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider to report any new symptoms indicating hepatic toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Gastrointestinal Perforation: Advise patients that gefitinib tablets can increase the risk of gastrointestinal perforation and to seek immediate medical attention for severe abdominal pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Severe or Persistent Diarrhea: Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for severe or persistent diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Ocular Disorders including Keratitis: Advise patients promptly to contact their healthcare provider if they develop eye symptoms, lacrimation, light sensitivity, blurred vision, eye pain, red eye or changes in vision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Bullous and Exfoliative Skin Disorders: Advise patients that gefitinib tablets can increase the risk of bullous and exfoliative skin disorders and to seek immediately medical attention for severe skin reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Embryo-fetal Toxicity: Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus or potential risk for loss of the pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with gefitinib tablets and for at least two weeks following completion of therapy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation: Advise women to discontinue breast-feeding during treatment with gefitinib tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured for:
Ingenus Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Orlando, FL 32811-7193

Manufactured by:
Qilu Pharmaceutical (Hainan) Co., Ltd.
Haikou, 570314, China
34120057011A
