Diclofenac Sodium
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DICLOFENAC SODIUM TOPICAL SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DICLOFENAC SODIUM TOPICAL SOLUTION. DICLOFENAC SODIUM topical solution 2% w/w, for topical use Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
f104f8fb-066f-4bbf-8894-3b3ed1b8266d
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 1, 2024
Proficient Rx LP
DUNS: 079196022
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Diclofenac Sodium
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2% w/w Container Carton Label (112
grams Bottle)
NDC 82804-074-12
** Diclofenac Sodium**
** Topical Solution, USP**
2% w/w
** FOR EXTERNAL USE ONLY**
** Alcohol Content (31.07% v/v)**
Pharmacist: Dispense the
** enclosed Medication**
** Guide to each patient.**
Usual dosage:
Apply two pump activations
to affected
knee(s) two times a day.
Rx only 3.8 FL.OZ.
** (112 grams)**

Boxed Warning section
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1. INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Diclofenac sodium topical solution is indicated for the treatment of the pain of osteoarthritis of the knee(s).
Diclofenac sodium topical solution is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug indicated for the treatment of the pain of osteoarthritis of the knee(s). (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4. CONTRAINDICATIONS
Diclofenac sodium topical solution****is contraindicated in the following patients:
•
Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to diclofenac or any components of the drug product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9)]
•
History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)]
•
In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Known hypersensitivity to diclofenac or any components of the drug product. (4)
•
History of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. (4)
•
In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6. ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
•
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
•
Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution
The data described below reflect exposure to diclofenac sodium topical solution of 130 patients treated for 4 weeks (mean duration of 28 days) in one Phase 2 controlled trial. This population’s mean age was approximately 60 years, 85% of patients were Caucasian, 65% were females, and all patients had primary osteoarthritis. The most common adverse events with diclofenac sodium topical solution were application site skin reactions. These events were the most common reason for withdrawing from the study.
Application Site Reactions:
In this controlled trial, application site reactions were characterized by one or more of the following: dryness (22%), exfoliation (7%), erythema (4%), pruritus (2%), pain (2%), induration (2%), rash (2%), and scabbing (<1%).
Other Common Adverse Reactions:
Table 1 lists all adverse reactions occurring in >1% of patients receiving diclofenac sodium topical solution, where the rate in the diclofenac sodium topical solution group exceeded vehicle, from a controlled study conducted in patients with osteoarthritis.
Table 1: Incidence of Adverse Reactions Occurring in >1% of Subjects with Osteoarthritis Using Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution and More Often than in Subjects with OA Using Vehicle Control (Pooled)|
Adverse Reaction |
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution |
Vehicle Control |
|---|---|---|
|
Urinary tract infection |
4 (3%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Application site induration |
2 (2%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Contusion |
2 (2%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Sinus congestion |
2 (2%) |
1 (<1%) |
|
Nausea |
2 (2%) |
0 |
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution 1.5%
The safety of diclofenac sodium topical solution 2% is based in part, on prior experience with diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5%. The data described below reflect exposure to diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% of 911 patients treated between 4 and 12 weeks (mean duration of 49 days) in seven Phase 3 controlled trials, as well as exposure of 793 patients treated in an open-label study, including 463 patients treated for at least 6 months, and 144 patients treated for at least 12 months. The population mean age was approximately 60 years, 89% of patients were Caucasian, 64% were females, and all patients had primary osteoarthritis. The most common adverse events with diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% were application site skin reactions. These events were the most common reason for withdrawing from the studies.
Application Site Reactions:
In controlled trials, application site reactions were characterized by one or more of the following: dryness, erythema, induration, vesicles, paresthesia, pruritus, vasodilation, acne, and urticaria. The most frequent of these reactions were dry skin (32%), contact dermatitis characterized by skin erythema and induration (9%), contact dermatitis with vesicles (2%) and pruritus (4%). In one controlled trial, a higher rate of contact dermatitis with vesicles (4%) was observed after treatment of 152 subjects with the combination of diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% and oral diclofenac. In the open-label uncontrolled long-term safety study, contact dermatitis occurred in 13% and contact dermatitis with vesicles in 10% of patients, generally within the first 6 months of exposure, leading to a withdrawal rate for an application site event of 14%.
Other Common Adverse Reactions:
In controlled trials, subjects treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% experienced some adverse events associated with the NSAID class more frequently than subjects using placebo (constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, nausea, flatulence, abdominal pain, edema; see Table 2). The combination of diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% and oral diclofenac, compared to oral diclofenac alone, resulted in a higher rate of rectal hemorrhage (3% vs. less than 1%), and more frequent abnormal creatinine (12% vs. 7%), urea (20% vs. 12%), and hemoglobin (13% vs. 9%), but no difference in elevation of liver transaminases.
Table 2 lists all adverse reactions occurring in ≥1% of patients receiving diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5%, where the rate in the diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% group exceeded placebo, from seven controlled studies conducted in patients with osteoarthritis. Since these trials were of different durations, these percentages do not capture cumulative rates of occurrence.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥1% of Patients Treated with Diclofenac Sodium 1.5% Topical Solution in Placebo and Oral Diclofenac- Controlled Trials|
Treatment Group: |
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution 1.5% N=911 |
Topical Placebo |
|
Adverse Reaction |
N (%) |
N (%) |
|
Dry Skin (Application Site) |
292 (32) |
17 (5) |
|
Contact Dermatitis (Application Site) |
83 (9) |
6 (2) |
|
Dyspepsia |
72 (8) |
13 (4) |
|
Abdominal Pain |
54 (6) |
10 (3) |
|
Flatulence |
35 (4) |
1 (<1) |
|
Pruritus (Application Site) |
34 (4) |
7 (2) |
|
Diarrhea |
33 (4) |
7 (2) |
|
Nausea |
33 (4) |
3 (1) |
|
Pharyngitis |
40 (4) |
13 (4) |
|
Constipation |
29 (3) |
1 (<1) |
|
Edema |
26 (3) |
0 |
|
Rash (Non-Application Site) |
25 (3) |
5 (2) |
|
Infection |
25 (3) |
8 (2) |
|
Ecchymosis |
19 (2) |
1 (<1) |
|
Dry Skin (Non-Application Site) |
19 (2) |
1 (<1) |
|
Contact Dermatitis, vesicles (Application Site) |
18 (2) |
0 |
|
Paresthesia (Non-Application Site) |
14 (2) |
3 (<1) |
|
Accidental Injury |
22 (2) |
7 (2) |
|
Pruritus (Non-Application Site) |
15 (2) |
2 (<1) |
|
Sinusitis |
10 (1) |
2 (<1) |
|
Halitosis |
11 (1) |
1 (<1) |
|
Application Site Reaction (not otherwise specified) |
11 (1) |
3 (<1) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In postmarketing surveillance, the following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5%. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Body as a Whole: abdominal pain, accidental injury, allergic reactions, asthenia, back pain, body odor, chest pain, edema, face edema, halitosis, headache, neck rigidity, pain
Cardiovascular: palpitation, cardiovascular disorder
Gastrointestinal: diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspepsia, gastroenteritis, decreased appetite, lip swelling, mouth ulceration, nausea, rectal hemorrhage, ulcerative stomatitis, swollen tongue
Metabolic and Nutritional: creatinine increased
Musculoskeletal: leg cramps, myalgia
Nervous: depression, dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy, paresthesia at application site
Respiratory: asthma, dyspnea, laryngismus, laryngitis, pharyngitis, throat swelling
Skin and Appendages: At the Application Site: rash, skin burning sensation;
Other Skin and Appendages Adverse Reactions: eczema, skin discoloration, urticaria
Special Senses: abnormal vision, blurred vision, cataract, ear pain, eye disorder, eye pain, taste perversion
Vascular: blood pressure increased, hypertension
The most common adverse reactions with diclofenac sodium topical solution are application site reactions. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Instructions
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
For relief of the pain of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee(s), the recommended dose is 40 mg of diclofenac sodium (2 pump actuations) on each painful knee, 2 times a day.
Apply diclofenac sodium topical solution to clean, dry skin.
The pump must be primed before first use. Instruct patients to fully depress the pump mechanism (actuation) 4 times while holding the bottle in an upright position. This portion should be discarded to ensure proper priming of the pump. No further priming of the bottle should be required.
After the priming procedure, diclofenac sodium topical solution is properly dispensed by completely depressing the pump 2 times to achieve the prescribed dosage for one knee. Deliver the product directly into the palm of the hand and then apply evenly around front, back, and sides of the knee.
Application of diclofenac sodium topical solution in an amount exceeding or less than the recommended dose has not been studied and is therefore not recommended.
2.2 Special Precautions
•
Avoid showering/bathing for at least 30 minutes after the application of diclofenac sodium topical solution to the treated knee.
•
Wash and dry hands after use.
•
Do not apply diclofenac sodium topical solution to open wounds.
•
Avoid contact of diclofenac sodium topical solution with eyes and mucous membranes.
•
Do not apply external heat and/or occlusive dressings to treated knees.
•
Avoid wearing clothing over the diclofenac sodium topical solution-treated knee(s) until the treated knee is dry.
•
Protect the treated knee(s) from natural and artificial sunlight.
•
Wait until the treated area is dry before applying sunscreen, insect repellant, lotion, moisturizer, cosmetics, or other topical medication to the same knee you have just treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution.
•
Until the treated knee(s) is completely dry, avoid skin-to-skin contact between other people and the treated knee(s).
•
Do not use combination therapy with diclofenac sodium topical solution and an oral NSAID unless the benefit outweighs the risk and conduct periodic laboratory evaluations.
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals.
The recommended dose is 2 pump actuations on each painful knee, 2 times a day. (2)
•
Apply diclofenac sodium topical solution, to clean, dry skin. (2.1)
•
Dispense 40 mg (2 pump actuations) directly onto the knee or first into the hand and then onto the knee. Spread evenly around front, back and sides of the knee. (2.1)
•
Wash hands completely after administering the product. (2.2)
•
Wait until the area is completely dry before covering with clothing or applying sunscreen, insect repellent, cosmetics, topical medications, or other substances. (2.2)
•
Until the treated knee(s) is completely dry, avoid skin-to-skin contact between other people and the treated knee(s). (2.2)
•
Do not get diclofenac sodium topical solution in your eyes, nose, or mouth (2.2).
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Diclofenac sodium topical solution, USP: 2% w/w
•
Diclofenac sodium topical solution, USP 2% w/w (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8. USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium topical solution, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus and fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. Because of these risks, limit dose and duration of diclofenac sodium topical solution use between about 20 and 30 weeks of gestation, and avoid diclofenac sodium topical solution use at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations, Data).
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Use of NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium topical solution, at about 30 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy has been associated with cases of fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment.
Data from observational studies regarding other potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive. In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of malformations were observed in mice, rats, or rabbits given diclofenac during the period of organogenesis at doses up to approximately 0.6, 0.6, and 1.3 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 162 mg diclofenac sodium via diclofenac sodium topical solution, despite the presence of maternal and fetal toxicity at these doses [see Data]. Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as diclofenac, resulted in increased pre- and post-implantation loss. Prostaglandins also have been shown to have an important role in fetal kidney development. In published animal studies, prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors have been reported to impair kidney development when administered at clinically relevant doses.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Premature Closure of the Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy, because NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium topical solution, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus (see Data).
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
If an NSAID is necessary at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy, limit the use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. If diclofenac sodium topical solution treatment extends beyond 48 hours, consider monitoring with ultrasound for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, discontinue diclofenac sodium topical solution and follow up according to clinical practice (see Data).
Labor or Delivery
There are no studies on the effects of diclofenac sodium topical solution during labor or delivery. In animal studies, NSAIDs, including diclofenac inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, cause delayed parturition, and increase the incidence of stillbirth.
Data
Human Data
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Published literature reports that the use of NSAIDs at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Published studies and postmarketing reports describe maternal NSAID use at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy associated with fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. In many cases, but not all, the decrease in amniotic fluid was transient and reversible with cessation of the drug. There have been a limited number of case reports of maternal NSAID use and neonatal renal dysfunction without oligohydramnios, some of which were irreversible. Some cases of neonatal renal dysfunction required treatment with invasive procedures, such as exchange transfusion or dialysis.
Methodological limitations of these postmarketing studies and reports include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and concomitant use of other medications. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal NSAID use. Because the published safety data on neonatal outcomes involved mostly preterm infants, the generalizability of certain reported risks to the full-term infant exposed to NSAIDs through maternal use is uncertain.
Animal data
Reproductive and developmental studies in animals demonstrated that diclofenac sodium administration during organogenesis did not produce malformations despite the induction of maternal toxicity and fetal toxicity in mice at oral doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of diclofenac sodium topical solution, 162 mg diclofenac sodium/day, based on body surface area (BSA) comparison), and in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 and 1.3-times, respectively, the MRHD based on BSA comparison). Published reproductive and developmental studies of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, the solvent used in diclofenac sodium topical solution) are equivocal as to potential teratogenicity.
In a study in which pregnant rats were orally administered 2 or 4 mg/kg diclofenac (0.12 and 0.24 times the MRHD, respectively, based on BSA comparison) from Gestation Day 15 through Lactation Day 21, significant maternal toxicity (peritonitis, mortality) was noted. These maternally toxic doses were associated with dystocia, prolonged gestation, reduced fetal weights and growth, and reduced fetal survival. Diclofenac has been shown to cross the placental barrier in mice and rats.
In published studies, diclofenac administration to pregnant rats prolonged gestation and produced liver toxicity and neuronal loss in offspring (1 mg/kg, IP; 0.06 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison), impaired nephrogenesis in the kidney (3.6 mg/kg, IP; 0.2 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison), and caused adverse effects on the developing testes (6.1 mg/kg, oral; 0.4 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on available data, diclofenac may be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for diclofenac and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from the diclofenac or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
One woman treated orally with a diclofenac salt, 150 mg/day, had a milk diclofenac level of 100 mcg/L, equivalent to an infant dose of about 0.03 mg/kg/day. Diclofenac was not detectable in breast milk in 12 women using diclofenac (after either 100 mg/day orally for 7 days or a single 50 mg intramuscular dose administered in the immediate postpartum period).
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Females
Based on the mechanism of action, the use of prostaglandin-mediated NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium topical solution, may delay or prevent rupture of ovarian follicles, which has been associated with reversible infertility in some women. Published animal studies have shown that administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors has the potential to disrupt prostaglandin- mediated follicular rupture required for ovulation. Small studies in women treated with NSAIDs have also shown a reversible delay in ovulation. Consider withdrawal of NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium topical solution, in women who have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility.
Males
Published studies in adult male rodents report that diclofenac, at clinically relevant doses, can produce adverse effects on male reproductive tissues. The impact of these findings on male fertility is not clear [See Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID- associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.14)].
Of the 911 patients treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% in seven controlled, Phase 3 clinical trials, 444 subjects were 65 years of age and over. There was no age-related difference in the incidence of adverse events. Of the 793 patients treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% in one open-labeled safety trial, 334 subjects were 65 years of age and over including 107 subjects 75 and over. There was no difference in the incidence of adverse events with long-term exposure to diclofenac sodium topical solution 1.5% for this elderly population.
•
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of diclofenac sodium topical solution in women who have difficulties conceiving. (8.3)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10. OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.6)].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Emesis is not recommended due to a possibility of aspiration and subsequent respiratory irritation by DMSO contained in diclofenac sodium topical solution. Consider activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment, contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Diclofenac has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action of diclofenac sodium topical solution, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Diclofenac is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Diclofenac concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because diclofenac is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
After administration of diclofenac sodium topical solution (40 mg/knee every 12 h; total daily diclofenac exposure: 80 mg/knee) for 7.5 days, the mean (SD) AUC0-12 and mean (SD) Cmax were 77.27 (49.89) ng•h/mL and 12.16 (7.66) ng/mL, respectively, on Day 1; and 204.58 (111.02) ng•h/mL and 25.24 (12.95) ng/mL, respectively, at steady state on Day 8. After administration of diclofenac sodium 1.5% topical solution (19.3 mg/knee every 6 h; total daily diclofenac exposure 77.2 mg/knee), the mean (SD) AUC0-12 and mean (SD) Cmax were 27.46 (23.97) ng•h/mL and 2.30 (2.02) ng/mL, respectively, on Day 1; and 141.49 (92.47) ng•h/mL and 17.04 (11.28) ng/mL, respectively, at steady state on Day 8.
The pharmacokinetics and effect of diclofenac sodium topical solution were not evaluated under the conditions of heat application, occlusive dressings overlay, or exercise following product application. Therefore, concurrent use of diclofenac sodium topical solution under these conditions is not recommended.
Distribution:
Diclofenac is more than 99% bound to human serum proteins, primarily to albumin.
Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of diclofenac.
Elimination
Metabolism:
Five diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5-dihydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxy diclofenac. The major diclofenac metabolite, 4'-hydroxy-diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4'-hydroxy diclofenac is primarily mediated by CYP2C9. Both diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CYP2C8 may also play a role in diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy and 3'-hydroxy-diclofenac.
Excretion:
Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites.
Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine.
Specific Populations:
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetics of diclofenac sodium topical solution has not been investigated in pediatric patients.
Race: Pharmacokinetic differences due to race have not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
Aspirin: When NSAIDs were administered with aspirin, the protein binding of NSAIDs were reduced, although the clearance of free NSAID was not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. See Table 3 for clinically significant drug interactions of NSAIDs with aspirin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Diclofenac sodium 2% topical solution, contains diclofenac sodium, a benzeneacetic acid derivative that is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, and is available as a clear, colorless to faintly pink or orange solution for topical application. The chemical name is 2[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)amino]-benzeneacetic acid, monosodium salt. The molecular weight is 318.14. Its molecular formula is C14H10Cl2NNaO2, and it has the following chemical structure.

Each 1 gram of solution contains 20 mg of diclofenac sodium USP. The inactive ingredients: dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 45.5% w/w), ethanol 96%, hydroxypropyl cellulose, propylene glycol and purified water.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution, USP 2% w/w, is supplied as a clear, colorless to faintly pink or orange solution containing 20 mg of diclofenac sodium per gram of solution, in a white polypropylene-dose pump bottle with a cap. Each pump actuation delivers 20 mg of diclofenac sodium in 1 gram of solution.
112 g bottle NDC 82804-074-12
Storage
Store at20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with diclofenac sodium topical solution and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurring of speech, and to report any of these symptoms to their health care provider immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Advise patients to report symptoms of ulceration and bleeding, including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis to their health care provider. In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, inform patients of the increased risk for and the signs and symptoms of GI bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, instruct patients to stop diclofenac sodium topical solution and seek immediate medical therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Heart Failure and Edema
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of congestive heart failure including shortness of breath, unexplained weight gain, or edema and to contact their healthcare provider if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Anaphylactic Reactions
Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). Instruct patients to seek immediate emergency help if these occur [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Serious Skin Reactions, including DRESS
Advise patients to stop using diclofenac sodium topical solution immediately if they develop any type of rash or fever and contact their health care provider as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9, 5.10)].
Female Fertility
Advise females of reproductive potential who desire pregnancy that NSAIDs, including diclofenac sodium topical solution, may be associated with a reversible delay in ovulation [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
Fetal Toxicity
Inform pregnant women to avoid use of diclofenac sodium topical solution and other NSAIDs starting at 30 weeks gestation because of the risk of the premature closing of the fetal ductus arteriosus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. If treatment with diclofenac sodium topical solution is needed for a pregnant woman between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, advise her that she may need to be monitored for oligohydramnios, if treatment continues for longer than 48 hours [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Avoid Concomitant Use of NSAIDs
Inform patients that the concomitant use of diclofenac sodium topical solution with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) is not recommended due to the increased risk of gastrointestinal toxicity, and little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7)]. Alert patients that NSAIDs may be present in “over the counter” medications for treatment of colds, fever, or insomnia.
Use of NSAIDs and Low-Dose Aspirin
Inform patients not to use low-dose aspirin concomitantly with diclofenac sodium topical solution until they talk to their healthcare provider [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Eye Exposure
Instruct patients to avoid contact of diclofenac sodium topical solution with the eyes and mucosa. Advise patients that if eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and consult a physician if irritation persists for more than an hour.
Prevention of Secondary Exposure
Instruct patients to avoid skin-to-skin contact between other people and the knee(s) to which diclofenac sodium topical solution was applied until the knee(s) is completely dry.
Special Application Instructions
Instruct patients not to apply diclofenac sodium topical solution to open skin wounds, infections, inflammations, or exfoliative dermatitis, as it may affect absorption and reduce tolerability of the drug.
Instruct patients to wait until the area treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution is completely dry before applying sunscreen, insect repellant, lotion, moisturizer, cosmetics, or other topical medication.
Instruct patients to minimize or avoid exposure of treated knee(s) to natural or artificial sunlight.
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Relabeled by:
Proficient Rx LP
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Issued: November 2022
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Instructions for Use
Diclofenac Sodium (dye kloe' fen ak soe' dee um) Topical Solution, USP 2%
Read the Medication Guide that comes with diclofenac sodium topical solution first. Be sure that you read, understand and follow these Instructions for Use before you use diclofenac sodium topical solution for the first time.
Important: For use on the skin only (topical). Do not get diclofenac sodium topical solution in your eyes, nose or mouth.
Before you use diclofenac sodium topical solution:
•
Apply diclofenac sodium topical solution exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure.
•
Only use diclofenac sodium topical solution to treat pain from osteoarthritis in your knee or knees.
•
Apply diclofenac sodium topical solution on clean, dry skin that does not have any cuts, infections or rashes.
•
Use diclofenac sodium topical solution two times a day on your knee or knees as prescribed.
•
If you get diclofenac sodium topical solution in your eyes, rinse your eyes right away with water or saline. Call your healthcare provider if your eyes are irritated for more than one hour.
Diclofenac sodium topical solution comes in a pump bottle from your healthcare provider.
** If you are using a diclofenac sodium topical solution pump bottle follow the steps below:**
** Before you use diclofenac sodium topical solution pump bottle for the first time, you will need to prime the pump.To prime the pump, remove the cap (SeeFigure A**) and fully press the top of the pump all the way down 4 times while holding the bottle in an upright position (SeeFigure B). Dispense this portion of the medicine into a tissue or paper towel and throw it away in a trash can. The pump is now ready to use. You should not need to prime the pump again.

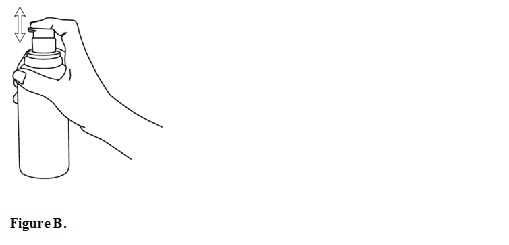
Steps for using diclofenac sodium topical solution pump bottle:
Step 1: Wash your hands with soap and water before applying diclofenac sodium topical solution.
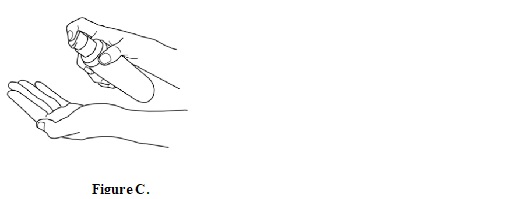
Step 2: Remove the bottle cap and press the pump head down firmly and fully to dispense diclofenac sodium topical solution into the palm of your hand. Release the pump head and then press the pump head down firmly and fully a second time. When you use your diclofenac sodium topical solution pump bottle, you can hold the bottle at an angle. Put 2 pumps of diclofenac sodium topical solution on your hand (SeeFigure C).
Step 3: Apply diclofenac sodium topical solution evenly around the front, back, and sides of your knee. Diclofenac sodium topical solution should be applied without massaging the knee (SeeFigures DandE).


Step 4: Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for your other knee if your healthcare provider has prescribed diclofenac sodium topical solution for both knees.
Step 5: Wash your hands with soap and water right away after applying diclofenac sodium topical solution.
Step 6: Replace the cap on the bottle and store in an upright position.
After you use diclofenac sodium topical solution:
Do not:
•
cover your knee with clothing until your knee is completely dry.
•
put sunscreen, insect repellant, lotion, moisturizer, cosmetics, or other topical medicines on your knee until it is completely dry.
•
take a shower or a bath for at least 30 minutes after you put diclofenac sodium topical solution on your knee(s).
•
use heating pads or cover the treated area with bandages where you have applied diclofenac sodium topical solution.
•
exercise following application of diclofenac sodium topical solution.
•
use sunlamp and tanning beds. Protect your treated knee from sunlight. Wear clothes that cover your skin if you have to be in the sunlight.
How should I store diclofenac sodium topical solution?
•
Store diclofenac sodium topical solution at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
Keep diclofenac sodium topical solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc.
279 Princeton-Hightstown Road
East Windsor, NJ 08520
Relabeled by:
Proficient Rx LP
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
Issued: November 2022
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) |
|
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including: • o o Do not take NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a “coronary artery bypass graft (CABG).” Avoid taking NSAIDs after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack. • o o o The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with: • • • • • • • • • • NSAIDs should only be used: • • • |
|
What are NSAIDs? NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain. |
|
Who should not take NSAIDs? Do not take NSAIDS: • • |
|
Before taking NSAIDs, tell your health care provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: • • • • • Tell your health care provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects.** Do not start taking new medicine without talking to your health care provider first.** |
|
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs? NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including: See “What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?” • • • • • • • • |
|
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms: • • • • • Stop taking your NSAID and call your health care provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms: • • • • • • • • • • • • If you take too much of your NSAID, call your health care provider or get medical help right away. These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your health care provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
Other information about NSAIDs • • |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your health care provider. You can ask your pharmacist or health care provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals. |
|
For more information, call Aurobindo Pharma USA, Inc. at 1-866-850-2876. |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats administered diclofenac sodium as a dietary constituent for 2 years resulted in no significant increases in tumor incidence at doses up to 2 mg/kg/day approximately 0.85 and 1.7 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human topical dose of diclofenac sodium topical solution (based on apparent bioavailability and body surface area comparison).
In a dermal carcinogenicity study conducted in albino mice, daily topical applications of diclofenac sodium for two years at concentrations up to 0.035% diclofenac sodium (a 57-fold lower diclofenac sodium concentration than present in diclofenac sodium topical solution) did not increase neoplasm incidence.
In a photococarcinogenicity study conducted in hairless mice, topical application of diclofenac sodium at doses up to 0.035% diclofenac sodium (a 57-fold lower diclofenac sodium concentration than present in diclofenac sodium topical solution) resulted in an earlier median time of onset of tumors.
Mutagenesis
Diclofenac was not mutagenic or clastogenic in a battery of genotoxicity tests that included the bacterial reverse mutation assay, in vitro mouse lymphoma point mutation assay, chromosomal aberration studies in Chinese hamster ovarian cells in vitro, and in vivo rat chromosomal aberration assay of bone marrow cells.
Impairment of Fertility
Fertility studies have not been conducted with diclofenac sodium topical solution. Diclofenac sodium administered to male and female rats at doses up to 4 mg/kg/day (approximately 3.4 times the MRHD of diclofenac sodium topical solution based on apparent bioavailability and body surface area comparison) did not affect fertility. Studies conducted in rats found no effect of dermally applied DMSO on fertility, reproductive performance, or offspring performance.
However, published studies report that treatment of adult male rats with diclofenac by the oral route at 10 mg/kg (0.6 times the MRHD) for 14 days and at 0.25 mg/kg (0.01 times the MRHD) for 30 days produced adverse effects on male reproductive hormones and testes.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Ocular Effects
No adverse effects were observed using indirect ophthalmoscopy after multiple- daily dermal application to rats for 26 weeks and minipigs for 52 weeks of DMSO at twice the concentration found in diclofenac sodium topical solution. Published studies of dermal or oral administration of DMSO to rabbits, dogs and pigs described refractive changes of lens curvature and cortical fibers indicative of myopic changes and/or incidences of lens opacity or discoloration when evaluated using slit-lamp biomicroscopy examination, although no ocular abnormalities were observed in rhesus monkeys during daily oral or dermal treatment with DMSO for 9 to 18 months.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Study in Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution
The use of diclofenac sodium topical solution for the treatment of pain of osteoarthritis of the knee was evaluated in a single double-blind controlled trial conducted in the US, involving patients treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution at a dose of 2 pumps twice a day for 4 weeks. Diclofenac sodium topical solution was compared to topical vehicle, applied directly to the study knee. In this trial, patients treated with diclofenac sodium topical solution experienced a greater reduction in the Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index (WOMAC) pain subscale compared to patients treated with vehicle. Numerical results of the WOMAC pain subscale are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: Change in Treatment Outcomes after 4 Weeks of Treatment with Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution
| ||
|
Efficacy Variable |
Treatment | |
|
|
Diclofenac Sodium Topical Solution |
Vehicle Control |
|
WOMAC Pain Subscale***** | ||
|
Baseline |
12.4 |
12.6 |
|
Mean Change from Baseline |
-4.5 |
-3.6 |
