Carglumic acid
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CARGLUMIC ACID TABLETS FOR ORAL SUSPENSION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CARGLUMIC ACID TABLETS FOR ORAL SUSPENSION.CARGLUMIC ACID tablets for oral suspensionInitial U.S. Approval: 2010
2aee4281-402b-4cd6-9e6a-08945262e1a1
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 19, 2024
Burel Pharmaceuticals, LLC
DUNS: 609436204
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Carglumic acid
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Bottle label - 60 Tablets in Bottle
NDC 35573-459-60
Carglumic Acid
Tablets for Oral
Suspension
200 mg
Store at 20° to 25°C (68°F to 77°F);
excursions permitted between 15°C
and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
60 Tablets
Rx only

Carton label - 60 Tablets in Bottle
NDC 35573-459-60
Carglumic Acid
Tablets for Oral
Suspension
200 mg
Disperse Carglumic Acid Tablets in water.
Do not swallow whole or crushed.
Discard one month after first opening.
Date of first opening:
60 Tablets
Rx only
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Acute and Chronic Hyperammonemia due to N-acetylglutamate Synthase
(NAGS) Deficiency
Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension is indicated in adult and pediatric patients as:
- Adjunctive therapy to standard of care for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia due to NAGS deficiency.
- Maintenance therapy for the treatment of chronic hyperammonemia due to NAGS deficiency.
Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension is a carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS 1) activator indicated in pediatric and adult patients as:
- Adjunctive therapy to standard of care for the treatment of acute hyperammonemia due to N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS) deficiency. (1.1)
- Maintenance therapy for the treatment of chronic hyperammonemia due to NAGS deficiency. (1.1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None
None. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Acute and Chronic Hyperammonemia due to NAGS Deficiency
In a retrospective case series of 23 NAGS deficiency patients treated with Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, 17 of the 23 patients reported an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions (occurring in ≥ 13% of patients) were vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, tonsillitis, anemia, diarrhea, ear infection, infections, nasopharyngitis, hemoglobin decreased, and headache.
Table 1 summarizes adverse reactions occurring in 2 or more patients treated with carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 2 Patients with NAGS deficiency Treated with Carglumic Acid Tablets for Oral Suspension in the Retrospective Case Series|
** Adverse Reaction** |
** Number of Patients (N) (%)** |
|
Vomiting |
6 (26) |
|
Abdominal pain |
4 (17) |
|
Pyrexia |
4 (17) |
|
Tonsillitis |
4 (17) |
|
Anemia |
3 (13) |
|
Diarrhea |
3 (13) |
|
Ear infection |
3 (13) |
|
Infections |
3 (13) |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
3 (13) |
|
Hemoglobin decreased |
3 (13) |
|
Headache |
3 (13) |
|
Dysgeusia |
2 (9) |
|
Asthenia |
2 (9) |
|
Hyperhidrosis |
2 (9) |
|
Influenza |
2 (9) |
|
Pneumonia |
2 (9) |
|
Weight decreased |
2 (9) |
|
Anorexia |
2 (9) |
|
Somnolence |
2 (9) |
|
Rash |
2 (9) |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Psychiatric disorders: mania
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: pruritus, rash including rash erythematous, rash maculopapular, rash pustular
- NAGS deficiency : Most common adverse reactions (≥13%) are vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, tonsillitis, anemia, diarrhea, ear infection, infections, nasopharyngitis, hemoglobin decreased, and headache. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Navinta LLC at 1-609-883-1135, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Carglumic acid is a synthetic structural analogue of N-acetylglutamate (NAG) which is produced from glutamate and acetyl-CoA in a reaction catalyzed by N-acetylglutamate synthase (NAGS), a mitochondrial liver enzyme. NAG acts as the essential allosteric activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS 1), a mitochondrial liver enzyme which catalyzes the first reaction of the urea cycle. The urea cycle, whose role is the disposition of ammonia, includes a series of biochemical reactions in the liver resulting in the conversion of ammonia into urea, which is then excreted through the urine. Carglumic acid acts as a CPS1 activator, improves or restores the function of the urea cycle, and facilitates ammonia detoxification and urea production.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a retrospective review of the clinical course in 23 patients with NAGS deficiency, carglumic acid reduced plasma ammonia levels within 24 hours when administered with and without concomitant ammonia lowering therapies. No dose- response relationship has been identified.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of carglumic acid was evaluated in a Phase 1, randomized study in 76 healthy volunteers. The study suggests a lack of clinically relevant QT prolongation effect at the highest therapeutic dose level (250 mg/kg/day).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of carglumic acid in healthy subjects following an intravenous (IV) infusion over 2 hours at 8 mg/kg or an oral administration at 100 mg/kg are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3: Mean (SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameter Values of Carglumic Acid in Healthy Subjects
Median (range); N/A, not applicable | ||
|
PK parameter |
IV infusion 8 mg/kg |
Oral 100 mg/kg |
|
Cmax (ng/mL) |
8613 (558) |
3284 (321) |
|
Tmax (hr)# |
2 (1-2) |
3 (2-4) |
|
AUC (ng*hr/mL) |
24501 (1613) |
31426 (2150) |
|
T1/2 (hr) |
31 (3) |
25 (2) |
|
CL (L/hr/kg) |
0.34 (0.02) |
N/A |
|
Vd (L/kg) |
15 (1) |
N/A |
Absorption
Following an oral administration of Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension 100 mg/kg in healthy subjects, the absolute bioavailability was approximately 10%.
Distribution
Carglumic acid is not bound to plasma proteins.
Elimination
Carglumic acid is predominantly excreted by the kidneys as unchanged product.
Metabolism
A proportion of carglumic acid may be metabolized by the intestinal bacterial flora.
The likely end product of carglumic acid metabolism is carbon dioxide, eliminated through the lungs.
Excretion
Following an oral administration of radiolabeled carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension at 100 mg/kg, 9% of the dose is excreted unchanged in the urine and up to 60% of the dose is recovered unchanged in the feces.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of carglumic acid in subjects with renal impairment were compared with healthy subjects with normal renal function following oral administration of a single dose of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension 40 mg/kg or 80 mg/kg. The Cmax and AUC0-t of carglumic acid are summarized in Table 4. The geometric mean ratio (90% CI) of Cmax in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment relative to those in their matched control subjects with normal renal function were approximately 1.3 (0.95, 1.86), 2.0 (1.62, 2.50), and 4.4 (3.11, 6.28) respectively. The geometric mean ratio (90% CI) of AUC0-t in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment relative to those in their matched control subjects with normal renal function were approximately 1.4 (1.09, 1.73), 2.8 (2.27, 3.47), and 6.9 (5.21, 9.24), respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Table 4: Mean (SD) Cmax and AUC0-t of Carglumic Acid Following Single Oral Dose Administration of Carglumic Acid Tablets for Oral Suspension 80 mg/kg or 40 mg/kg in Subjects with Renal Impairment and Matched Healthy Control Subjects with Normal Renal Function|
Treatment groups 1a and 1b represent two separate matched control groups of healthy subjects with normal renal function. | |||||
|
** PK Parameters** |
** Normal Renal Function1a: eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m2 (N=8)** |
** Mild Renal Impairment: eGFR 60-89 mL/min/1.73m****2** |
** Moderate Renal Impairment: eGFR 30-59 mL/min/1.73m2 (N=8)** |
** Normal Renal Function1b: eGFR ≥90 mL/min/1.73m2 (N=8)** |
** Severe Renal Impairment: eGFR 15-29**** mL/min/1.73m****2** |
|
** 80 mg/kg** |
** 40 mg/kg** | ||||
|
Cmax (ng/mL) |
2983 (552) |
4310 (1937) |
6129 (1854) |
1890 (901) |
8377 (3815) |
|
AUC0-t (ng*hr/mL) |
28313 (6204) |
39545 (12109) |
79766 (19708) |
20212 (6186) |
143075 (55910) |
Drug Interaction Studies
Based on in vitro studies, carglumic acid is not an inducer of CYP1A1/2, CYP2B6, CYP2C, and CYP3A4/5 enzymes, and not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4/5 enzymes.
Based on in vitro studies, carglumic acid is a substrate of the human OAT1 transporter. Carglumic acid is not a substrate of MDR1, BCRP, MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, and OCT2. Carglumic acid is not an inhibitor of human BSEP, BCRP, MDR1, MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, and OCT2 transporters.
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension 200 mg are white to off-white elongated tablets, functionally scored with 3 lines (for splitting into 4 equal portions) and engraved "N" on one side.
Tablets for oral suspension: 200 mg, functionally scored. (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Although rare case reports of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes, untreated NAGS deficiency can result in irreversible neurologic damage and death in pregnant women (see Clinical Considerations).
In an animal reproduction study, decreased survival and growth occurred in offspring born to rats that received carglumic acid at a dose approximately 38 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, miscarriage, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Pregnant women with urea cycle disorders may experience an increase in catabolic stress which can trigger a hyperammonemic crisis both in the intrapartum and in the post-partum (3 - 14 days post-partum) periods. Maternal complications related to hyperammonemic crisis can include neurological impairment, coma and in some cases death.
Data
Animal Data
No effects on embryo-fetal development were observed in pregnant rats treated with up to 2000 mg/kg/day (approximately 38 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC [area under the plasma concentration-time curve]) from two weeks prior to mating through organogenesis or in pregnant rabbits treated with up to 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 6 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC) during organogenesis.
In a pre- and post-natal developmental study, female rats received oral carglumic acid from organogenesis through lactation at doses of 500 mg/kg/day and 2000 mg/kg/day. Decreased growth of offspring was observed at 500 mg/kg/day and higher (approximately 38 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC), and reduction in offspring survival during lactation was observed at 2000 mg/kg/day (approximately 38 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC). No effects on physical and sexual development, learning and memory, or reproductive performance were observed through maturation of the surviving offspring at maternal doses up to 2000 mg/kg/day. The high dose (2000 mg/kg/day) produced maternal toxicity (impaired weight gain and approximately 10% mortality).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether carglumic acid is present in human milk. There are no available data on the effects of carglumic acid on the breastfed infant or the effects on milk production. Carglumic acid is present in milk from treated rats. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension for the treatment of pediatric patients (birth to 17 years of age) with acute or chronic hyperammonemia due to NAGS deficiency have been established, and the information on these uses are discussed throughout the labeling. There are insufficient data to determine if there is a difference in clinical or biochemical responses between adult and pediatric patients treated with Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension did not include patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Plasma concentrations of carglumic acid increased in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Reduce the carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension dosage in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. The pharmacokinetics of carglumic acid have not been evaluated in patients with end stage renal disease.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
One patient treated with 650 mg/kg/day of Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension developed symptoms resembling monosodium glutamate intoxication- like syndrome and characterized by tachycardia, profuse sweating, increased bronchial secretion, increased body temperature, and restlessness.
These symptoms resolved upon reduction of the dose.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of carglumic acid was assessed in a 2-year carcinogenicity study in rats. Carglumic acid was not tumorigenic at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 34 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC).
Carglumic acid was negative in the Ames test, chromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes, and the in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
There were no effects on fertility or reproductive performance in female rats at oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg/day (approximately 38 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC). In a separate study, mating and fertility were unaffected in male rats at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 34 times the maximum reported human maintenance dose [100 mg/kg/day] based on AUC).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension 200 mg are white to off-white elongated tablets, functionally scored with 3 lines for splitting into 4 equal portions, and engraved 'N's on one side.
Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension is supplied in a high-density polyethylene bottle with child resistant polypropylene cap and desiccant unit. Each bottle contains 60 tablets.
Bottles of 60 tablets: NDC 35573-459-60
Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
After first opening of the bottle:
- Store at room temperature between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F). Do not refrigerate.
- Keep the bottle tightly closed between openings in order to protect from moisture.
- Write the date of opening on the bottle.
- Do not use carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension after the expiration date stated on the bottle.
- Discard bottle one month after first opening.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Advise the patient or caregiver on the following:
Preparation and Administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]
- Disperse carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension in water. Do not swallow whole or crushed.
- Take carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension immediately before meals or feedings.
- Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension dispersed in water can be administered orally or via a nasogastric tube or gastrostomy tube as described in the Instructions for Use.
Storage [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
- Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- After first opening of the bottle: Do not refrigerate. Store at room temperature between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). Keep the bottle tightly closed in order to protect from moisture. Write the date of opening on the bottle.
- Discard bottle one month after first opening. Do not use carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension after the expiration date stated on the bottle.
Manufactured for:
Burel Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Mason, OH 45040 USA
Revised: 03/2024
31230922 R2
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Carglumic Acid Tablets for Oral Suspension
Important information:
***Carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension must be mixed in water before taking.**Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension should not be mixed in any other food or liquid. *Do notswallow carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension whole. *Do notcrush carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
- Take carglumic acid tablets for oral suspensionright beforemeals or feedings.
- The carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture has a slightly sour taste.
You may need to ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a medicine cup to measure the correct amount of water you will need to prepare the dose of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
**The Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension has 3 lines used for splitting the tablet into 4 equal parts in order to get the prescribed dose. **Ask your healthcare provider if you have any questions about how to split the tablet the right way or have any questions about the prescribed dose.
Taking carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension by mouth using a cup:
Children and Adults
1. Add a minimum of 2.5 mL of water into a small cup for each carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension, or each ½ or ¼ carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension, needed for the prescribed dose. For example:
● If the prescribed dose is 2 carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 5 mL of water into the cup.
● If the prescribed dose is 2 and a ¼ carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 7.5 mL of water into the cup.
● If the prescribed dose is 2 and a ½ carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 7.5 mL of water into the cup.
● Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure of how much water you should use for the prescribed dose of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
2. Place the prescribed number of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension into the water in the cup.
3. Carefully stir the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture in the cup to avoid spilling the mixture. Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension do not dissolve completely in water.
4. Swallow the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture right away.
5. Pieces of the tablet may remain in the cup. Add more water to the cup to rinse the cup and swallow the mixtureright away.
6. Repeat step 5 until there are no pieces of the tablet left in the cup.
Taking carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension by mouth using an oral syringe:
Children
1. Add a minimum of 2.5 mL of water into a small cup for each carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension, or each ½ or ¼ carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension, needed for the prescribed dose. For example:
● If the prescribed dose is 2 carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 5 mL of water into the cup.
● If the prescribed dose is 2 and a ¼ carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 7.5 mL of water into the cup.
● If the prescribed dose is 2 and a ½ carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 7.5 mL of water into the cup.
● Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure of how much water you should use for the prescribed dose of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
2. Place the prescribed number of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension into the water in the cup.
3. Carefully stir the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture in the cup to avoid spilling the mixture. Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension do not dissolve completely in water.
4. Draw up all of the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture in the cup into an oral syringe.
5. Give your child the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixtureright away by placing the tip of the oral syringe along the inner cheek of their mouth, on either the right or left side. Slowly push all the way down on the plunger to give the medicine.
6. Pieces of the tablet may remain in the oral syringe. Refill the oral syringe with a minimum of 1 mL to 2 mL of water and give your child the mixtureright away.
7. Repeat step 6 until there are no pieces of the tablet left in the oral syringe.
Giving carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension through a nasogastric (NG) tube or gastrostomy tube (G-tube):
Children and Adults
1. Add a minimum of 2.5 mL of water into a small cup for each carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension, or each ½ or ¼ carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension, needed for the prescribed dose. For example:
● If the prescribed dose is 2 carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 5 mL of water into the cup.
● If the prescribed dose is 2 and a ¼ carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 7.5 mL of water into the cup.
● If the prescribed dose is 2 and a ½ carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension, add a minimum of 7.5 mL of water into the cup.
● Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure of how much water you should use for the prescribed dose of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension.
2. Place the prescribed number of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension into the water in the cup.
3. Carefully stir the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture in the cup to avoid spilling the mixture. Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension do not dissolve completely in water.
4. Draw up all of the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture in the cup into a catheter-tip syringe.
5. Connect the catheter-tip syringe to the NG tube or G-tube.
6. Give the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension and water mixture through the NG tube or G-tuberight away.
7. Pieces of the tablet may remain in the catheter-tip syringe or NG tube or G-tube.
8. Refill the catheter-tip syringe with 1 mL to 2 mL of water and flush the NG tube or G-tuberight away.
9. Repeat step 8 until there are no pieces of the tablet left in the catheter-tip syringe or NG tube or G-tube.
How should I store carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension?
*Before opening, store carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension at controlled room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) in the bottle it comes in. *After opening, store carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension at room temperature between 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).Do notstore carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension in a refrigerator after opening. * Keep carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension in a tightly closed bottle to protect the tablets from moisture. * Write the date the carglumic acid tablet for oral suspension bottle is opened on the bottle label. Throw away any unused tablets one month after opening the bottle.
- Do not use carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension after the expiration date on the bottle. *Keep carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Burel Pharmaceuticals, LLC
Mason, OH 45040 USA
Revised: 03/2024
31230922 R2
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
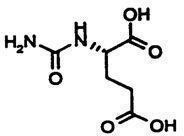
Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension contain 200 mg of carglumic acid. Carglumic acid, the active substance, is a carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS 1) activator and is soluble in dimethyl formamide and sparingly soluble in water.
The chemical name of carglumic acid is N-carbamoyl-L-glutamic acid or (2S)-2-(carbamoylamino) pentanedioic acid. The empirical formula is C6H10N2O5 and the molecular weight is 190.16.
The structural formula is:
The inactive ingredients of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension are croscarmellose sodium, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium lauryl sulfate, colloidal silicon dioxide and sodium stearyl fumarate.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Acute and Chronic Hyperammonemia due to NAGS Deficiency
The efficacy of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension in the treatment of acute and chronic hyperammonemia due to NAGS deficiency was evaluated in a retrospective case series of 23 NAGS deficiency patients treated with Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension over a median duration of 7.9 years (range 0.6 to 20.8 years). For acute treatment, patients received Carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension at 100 mg/kg/day to 250 mg/kg/day orally administered in 2 to 4 divided doses. For maintenance treatment, the dosage was reduced over time based on plasma ammonia level and clinical response.
The baseline characteristics of the patient population are shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Baseline Characteristics of 23 NAGS Deficiency Patients Treated with Carglumic Acid Tablets for Oral Suspension|
Patients | ||
|
Sex |
Male |
14 (61%) |
|
Female |
9 (39%) | |
|
Age at initiation of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension therapy (years) |
Mean (SD) |
2 (4) |
|
Min - Max |
0 - 13 | |
|
Age groups at initiation of carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension therapy |
<30 days |
9 (39%) |
|
9 (39%) | |
|
≥1 - 13 years |
5 (22%) | |
|
NAGS gene mutations by DNA testing |
Homozygous |
14 (61%) |
|
Heterozygous |
4 (17%) | |
|
Not available |
5 (22%) | |
|
Patients current treatment status |
On-going |
18 (78%) |
|
Discontinued |
5 (22%) |
The clinical and biochemical data in the 23-patient case series were retrospectively collected, unblinded, and uncontrolled and preclude formal statistical testing. Short-term efficacy was evaluated using mean and median change in plasma ammonia levels from baseline to days 1 to 3. Persistence of the effect was evaluated using long-term mean and median change in plasma ammonia level. Of the 23 NAGS deficiency patients in the case series, 13 patients had documented plasma ammonia levels prior to carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension treatment and after long-term treatment with carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension and were evaluable.
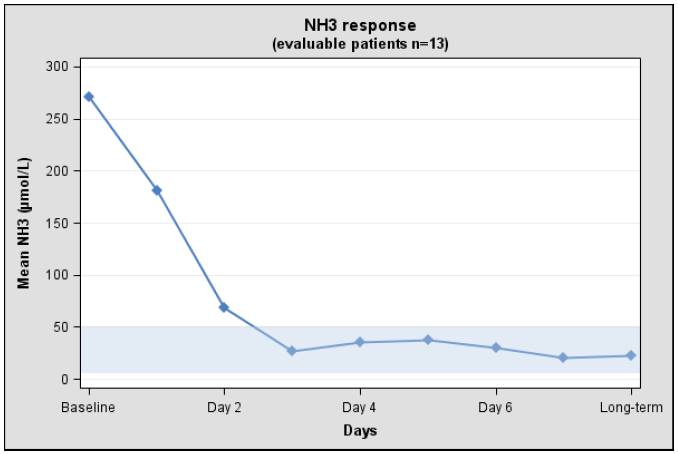
Table 6 summarizes the plasma ammonia levels at baseline, days 1 to 3 post- carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension treatment, and long-term carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension treatment (mean 8 years) in the 13 evaluable patients.
All 13 patients had increased plasma ammonia levels at baseline (mean 271 micromol/L; normal range: 5 to 50 micromol/L). By day 3 and with long-term treatment, normal plasma ammonia levels were attained (Table 6).
Table 6: Plasma Ammonia Levels in NAGS Deficiency Patients at Baseline and After Treatment with Carglumic Acid Tablets for Oral Suspension|
** Time point** |
** Patients** |
** Ammonia****level |
|
** Baseline** |
N |
13 |
|
Mean (SD) |
271 (359) | |
|
Median |
157 | |
|
Range |
72-1428 | |
|
Missing Data |
0 | |
|
** Day 1** |
N |
10 |
|
Mean (SD) |
181 (358) | |
|
Median |
65 | |
|
Range |
25-1190 | |
|
Missing Data |
3 | |
|
** Day 2** |
N |
8 |
|
Mean (SD) |
69 (78) | |
|
Median |
44 | |
|
Range |
11-255 | |
|
Missing Data |
5 | |
|
** Day 3** |
N |
5 |
|
Mean (SD) |
27 (11) | |
|
Median |
25 | |
|
Range |
12-42 | |
|
Missing Data |
8 | |
|
** Long-term treatment** |
N |
13 |
|
Mean (SD) |
23 (7) | |
|
Median |
24 | |
|
Range |
9-34 | |
|
Missing Data |
0 |
The mean plasma ammonia level at baseline and the decline that is observed after treatment with carglumic acid tablets for oral suspension in 13 evaluable patients with NAGS deficiency is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure** 1: Mean Plasma Ammonia in 13 Evaluable NAGS Deficiency Patients at Baseline and After Treatment with Carglumic Acid Tablets for Oral Suspension**