Deferoxamine Mesylate
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEFEROXAMINE MESYLATE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEFEROXAMINE MESYLATE. Initial U.S. Approval: 1968
f9ab6b1c-98d0-4373-0e9b-b10cb4a67543
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 15, 2024
Hospira, Inc.
DUNS: 141588017
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Deferoxamine Mesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
Deferoxamine Mesylate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
Drug Labeling Information
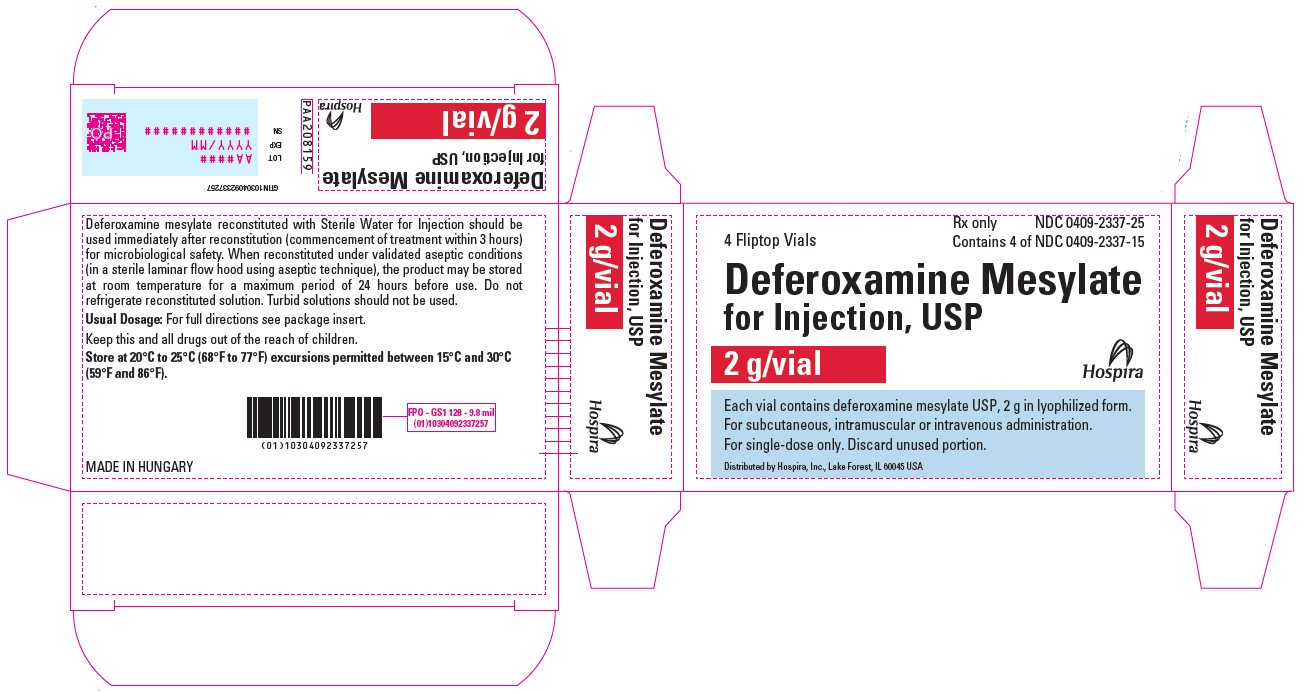
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 2 g Vial Carton
4 Fliptop Vials
Rx only
NDC 0409-2337-25
Contains 4 of NDC 0409-2337-15
Deferoxamine Mesylate
for Injection, USP
2 g/vial
Hospira
Each vial contains deferoxamine mesylate USP, 2 g in lyophilized form.
For subcutaneous, intramuscular or intravenous administration.
For single-dose only. Discard unused portion.
Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Acute Iron Intoxication
Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection is indicated as an adjunct to standard measures for the treatment of acute iron intoxication.
1.2 Chronic Iron Overload
Deferoxamine mesylate is indicated for the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with chronic anemia.
1.3 Limitations of Use
Deferoxamine mesylate is not indicated for the treatment of primary hemochromatosis (since phlebotomy is the method of choice for removing excess iron in this disorder).
Deferoxamine mesylate is an iron-chelating agent indicated:
•
As an adjunct to standard measures for the treatment of acute iron intoxication. (1.1)
•
For the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with chronic anemia. (1.2)
Limitations of Use
Deferoxamine mesylate is not indicated for the treatment of primary hemochromatosis (since phlebotomy is the method of choice for removing excess iron in this disorder).
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection is contraindicated in patients with:
•
A history of a hypersensitivity reaction to deferoxamine or any of its inactive ingredients [see Description (11)]. Reactions have included anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
•
Severe renal disease or anuria since the drug and the iron chelate are excreted primarily by the kidney [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
•
Known hypersensitivity to the active substance. (4)
•
Patients with severe renal disease or anuria. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
•
Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Auditory and Ocular Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Respiratory Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Growth Suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Cardiac Dysfunction with Concomitant Use of Vitamin C [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Risks of Deferoxamine mesylate Treatment in Patients with Aluminum Overload [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
•
Effects on Ability to Drive and Use Machines [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of Deferoxamine mesylate were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
At the Injection Site: Localized irritation, pain, burning, swelling, induration, infiltration, pruritus, erythema, wheal formation, eschar, crust, vesicles, local edema. Injection site reactions may be associated with systemic allergic reactions (see Body as a Whole, below)
Hypersensitivity Reactions and Systemic Allergic Reactions: Generalized rash, urticaria, anaphylactic reaction with or without shock, angioedema
Body as a Whole: Local injection site reactions may be accompanied by systemic reactions like arthralgia, fever, headache, myalgia, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or asthma
Infections: Yersinia, mucormycosis
Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, hypotension, shock
Digestive: Abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting
Hematologic: Blood dyscrasia (thrombocytopenia, leukopenia)
Hepatic: Increased transaminases, hepatic dysfunction
Musculoskeletal: Muscle spasms. Growth retardation and bone changes (e.g., metaphyseal dysplasia)
Nervous System: Neurological disturbances, including dizziness, peripheral sensory, motor, or mixed neuropathy, paresthesias, seizures; exacerbation or precipitation of aluminum-related dialysis encephalopathy
Special Senses: High-frequency sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, visual disturbances including acuity, blurred vision, loss of vision, dyschromatopsia, night blindness, visual field defects, scotoma, retinopathy (pigmentary degeneration), optic neuritis, and cataracts
Respiratory: Acute respiratory distress syndrome (with dyspnea, cyanosis, and/or interstitial infiltrates)
Skin: Generalized rash
Urogenital: Dysuria, acute renal failure, increased serum creatinine and renal tubular disorders
Most common adverse reactions are injection reactions (local and systemic), hypersensitivity reactions, infections with Yersinia and Mucormycosis, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, hematologic, hepatic, musculoskeletal, urogenital, nervous, respiratory, ocular and hearing. (6)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactPfizer Inc. at 1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Prochlorperazine
Concurrent treatment with deferoxamine mesylate and prochlorperazine, a phenothiazine derivative, may lead to temporary impairment of consciousness.
7.2 Gallium-67
Imaging results may be distorted because of the rapid urinary excretion of deferoxamine mesylate-bound gallium-67. Discontinue deferoxamine mesylate 48 hours prior to scintigraphy.
•
Concurrent treatment with prochlorperazine may lead to temporary impairment of consciousness. (7.1)
•
Imaging results may be distorted due to rapid urinary excretion of Deferoxamine mesylate bound gallium-67. Discontinue Deferoxamine mesylate 48 hours prior to scintigraphy. (7.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Dosage and Administration, Preparation (2.3) |
11/2023 |
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 500 mg of deferoxamine mesylate (corresponding to 426.82 mg of deferoxamine as free base) as a white to off-white lyophilized powder in single-dose fliptop vial for reconstitution.
For injection: 2 g of deferoxamine mesylate (corresponding to 1707.28 mg of deferoxamine as free base) as a white to off-white lyophilized powder in single-dose fliptop vial for reconstitution.
For injection: 500 mg of deferoxamine mesylate as a lyophilized powder in single-dose fliptop vial for reconstitution. (3)
For injection: 2 g of deferoxamine mesylate as a lyophilized powder in single- dose fliptop vial for reconstitution. (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on Deferoxamine mesylate use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriages or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies subcutaneous administration of deferoxamine to pregnant animals (mice or rabbits) during organogenesis at doses approximately ≥0.2- (mice) and ≥0.7 (rabbits) times the maximum recommended human dose resulted in maternal toxicity and adverse developmental outcomes (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Consider the benefits and risks of Deferoxamine mesylate for the mother and possible risks to the fetus when prescribing Deferoxamine mesylate to a pregnant woman.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population(s) is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal developmental study in mice, pregnant animals administered subcutaneous doses of deferoxamine at 180, and 540 mg/kg/day from gestation day 7 to gestation day 12 resulted in a dose dependent delay and irregularities of fetal skeletal maturation at doses ≥0.2 times the MRHD. At the highest dose of 540 mg/kg, in 1/23 fetuses had a unilateral lesion to the eye lens (approximately 0.5 times the MRHD).
In the embryo-fetal developmental studies in rabbits, pregnant animals administered subcutaneous doses of deferoxamine either 200 mg/kg or 200, 300, and 540 mg/kg from gestation day 6 to gestation day 14 resulted in maternal toxicity and embryo-fetal developmental effects at 0.7 times the MRHD. Maternal toxicity included reduced fetal body weights and embryo-fetal effects included malformations of spina bifida, and increased incidence of abnormally ossified ribs and vertebrae.
No maternal toxicity or embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats at deferoxamine doses tested (up to 0.9 times the MRHD).
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of deferoxamine or its metabolite in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. It is not known whether deferoxamine is excreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise patients not to breastfeed during treatment with Deferoxamine mesylate, and for one week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on animal data, Deferoxamine mesylate can cause malformations at doses less than the human dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
Deferoxamine mesylate can cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Deferoxamine mesylate and for one month after the last dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients 3 years of age and older have been established for the treatment of acute iron intoxication and for the treatment of transfusional iron overload in patients with chronic anemia. Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients under the age of 3 years have not been established.
Iron mobilization with Deferoxamine mesylate is relatively poor in patients under the age of 3 years with relatively little iron overload. Deferoxamine mesylate is not recommended for use. The drug should ordinarily not be given to these patients unless significant iron mobilization (e.g., 1 mg or more of iron per day) can be demonstrated.
High doses of Deferoxamine mesylate and concomitant low ferritin levels have been associated with growth suppression in pediatric patients. Monitor weight and height in pediatric patients receiving Deferoxamine mesylate every 3 months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical Studies of deferoxamine mesylate did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from the younger subjects. Postmarketing reports suggest a possible trend for an increased risk of eye disorders in the geriatric population, specifically the occurrence of color blindness, maculopathy, and scotoma. However, it is unclear if these eye disorders were dose related. Although the number of reports was very small, certain elderly patients may be predisposed to eye disorders when taking deferoxamine mesylate. Postmarketing reports also suggest that there may be an increased risk of deafness and hearing loss in the geriatric population [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Deferoxamine mesylate is contraindicated in patients with severe renal disease [see Contraindications (4)].
For patients with renal impairment, dose selection should usually start at the low end of the dosing range.
Deferoxamine can cause increases in serum creatinine (possibly dose-related), acute renal failure and renal tubular disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Monitor patients for changes in renal function.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
For patients with hepatic impairment, dose selection should usually start at the low end of the dosing range.
•
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
•
Geriatric Use: Increased risk of ocular disorders. (8.5)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Acute Toxicity
Intravenous LD50s (mg/kg): mice, 287; rats, 329.
Inadvertent administration of an overdose or inadvertent intravenous bolus administration/rapid intravenous infusion may be associated with hypotension, tachycardia and gastrointestinal disturbances; acute but transient loss of vision, aphasia, agitation, headache, nausea, pallor, CNS depression, including coma, bradycardia and acute renal failure have been reported.
Acute respiratory distress syndrome has been reported following treatment with excessively high intravenous doses of Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection in patients with acute iron intoxication and in patients with thalassemia.
There is no specific antidote for Deferoxamine mesylate overdose. In case of overdose, discontinue Deferoxamine mesylate and provide symptomatic supportive care.
Deferoxamine mesylate is readily dialyzable.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
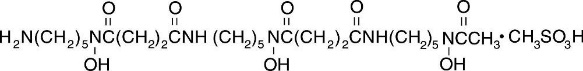
Deferoxamine Mesylate for Injection, USP, is an iron-chelating agent, available in vials for injection via intramuscular, subcutaneous, and intravenous administration. Deferoxamine mesylate is supplied as vials containing 500 mg of deferoxamine mesylate USP (corresponding to 426.82 mg of deferoxamine as free base) and 2 g of deferoxamine mesylate USP (corresponding to 1707.28 mg of deferoxamine as free base) in sterile, lyophilized form. Deferoxamine mesylate is N-[5-[3-[(5-aminopentyl)hydroxycarbamoyl]propionamido]pentyl]-3-[[5-(N-hydroxyacetamido)pentyl]carbamoyl]propionohydroxamic acid monomethanesulfonate (salt), and its structural formula is:
Deferoxamine mesylate USP is a white to off-white powder. It is freely soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol. Its molecular weight is 656.79 g/mol.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
|
Unit of Sale |
Concentration |
|
NDC 0409-2336-10 Carton of 4 Single-dose Fliptop vials |
500 mg |
|
NDC 0409-2337-25 Carton of 4 Single-dose Fliptop vials |
2 g |
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F).
Discard unused portion.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Deferoxamine mesylate chelates iron by forming a stable complex that prevents the iron from entering into further chemical reactions. It readily chelates iron from ferritin and hemosiderin but not readily from transferrin; it does not combine with the iron from cytochromes and hemoglobin.
Deferoxamine mesylate does not cause any demonstrable increase in the excretion of electrolytes or trace metals. Theoretically, 100 parts by weight of deferoxamine mesylate is capable of binding approximately 8.5 parts by weight of ferric iron.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Deferoxamine mesylate is metabolized principally by plasma enzymes, but the pathways have not yet been defined. The chelate is readily soluble in water and passes easily through the kidney, giving the urine a characteristic reddish color. Some is also excreted in the feces via the bile.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed with deferoxamine mesylate. Cytotoxicity may occur, since deferoxamine mesylate has been shown to inhibit DNA synthesis in vitro.
Deferoxamine mesylate was not mutagenic when tested in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) and was not genotoxic in an in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Animal studies to assess fertility effects have not been conducted.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Caution patients about the potential allergic reactions associated with rapid intravenous administration of Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection and the need for monitoring allergic reactions during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Caution patients about the potential auditory and ocular toxicities due to prolonged use of Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection, conduct auditory testing and ophthalmic testing at regular intervals. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they develop visual or auditory changes during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Caution patients about the potential for kidney toxicity when taking Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection and the need for kidney function test to monitor for increase in serum creatinine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Inform patients that if they have difficulty in breathing during treatment, they should inform the health care provider as this is a symptom of acute respiratory distress syndrome which can occur with excessively high intravenous doses of Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Caution pediatric patients and their caregivers that child treated with Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection could have slower than normal growth and the need to monitor for body weight and height every 3 months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Caution patients about the increased risk of bacterial infections (Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis) with Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection treatment and the need for treatment discontinuation until the infection is resolved [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Caution patients about the potential risk of fungal infections (Mucormycosis) when receiving Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection treatment and the need for treatment discontinuation, mycological tests and required treatment for treating the infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Caution patients about the potential impairment of cardiac function when taking Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection concomitantly with high doses of Vitamin C (more than 500 mg daily in adults). Inform adult patients not to exceed a daily Vitamin C dose of 200 mg given in divided doses. Inform pediatric patients under 10 years of age and older pediatric patients or their care takers not to exceed a daily Vitamin C of 50 mg and 100 mg, respectively [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Inform patients with cardiac failure not to take Vitamin C supplements when on treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Caution patients with aluminum-related encephalopathy and receiving dialysis about potential neurological dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Cautions patients that treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection in the presence of aluminum overload may result in decreased serum calcium and aggravation of hyperparathyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Inform patients that they should refrain from driving or operating potentially hazardous machines if they experience dizziness or other nervous system disturbances, or impairment of vision or hearing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Advise patients to inform the healthcare provider if they have received prochlorperazine prior to Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection treatment as this may lead to temporary impairment of consciousness [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Inform patients that if they are going for any imaging tests while receiving Gallium-67 and Deferoxamine mesylate concomitantly it can result in reports with distorted images [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Inform patients that their urine may occasionally show a reddish discoloration.
Embryo-fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraceptive during treatment with Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection and for one month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise patients to avoid breastfeeding while taking Deferoxamine Mesylate for injection and for one week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA

LAB-1006-5.0
