Diclofenac Epolamine
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%. DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
45e191b6-c6c9-45f9-96d5-cf30f8aa910c
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Feb 26, 2024
Asclemed USA, Inc.
DUNS: 059888437
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Diclofenac Epolamine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR and GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
*Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (5.1) *DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4,5.1) *NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events (5.2)
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is indicated for the topical treatment of acute pain due to minor strains, sprains, and contusions in adults and pediatric patients 6 years and older.
- DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), and is indicated for the topical treatment of acute pain due to minor strains, sprains, and contusions in adults and pediatric patients 6 years and older. ( 1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to diclofenac or any components of the drug product [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9) ]
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8) ]
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is contraindicated for use on non-intact or damaged skin resulting from any etiology, including exudative dermatitis, eczema, infection lesions, burns or wounds.
- Known hypersensitivity to diclofenac or any components of the drug product ( 4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs ( 4)
- In the setting of CABG surgery ( 4)
- For use on non-intact or damaged skin ( 4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Clinical Trials Experience
In controlled trials during the premarketing development of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, approximately 600 patients with minor sprains, strains, and contusions were treated with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% for up to two weeks.
Adverse Events Leading to Discontinuation of Treatment
In the controlled trials, 3% of patients in both the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and placebo groups discontinued treatment due to an adverse event. The most common adverse events leading to discontinuation were application site reactions, occurring in 2% of both the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and placebo groups. Application site reactions leading to dropout included pruritus, dermatitis, and burning.
Common Adverse Events
Overall, the most common adverse events associated with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% treatment were skin reactions at the site of treatment. Table 1lists all adverse events, regardless of causality, occurring in ≥ 1% of patients in controlled trials of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%. A majority of patients treated with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% had adverse events with a maximum intensity of "mild" or "moderate."
Table 1. Common Adverse Events (by body system and preferred term) in ≥ 1% of Patients treated with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% or Placebo *|
Category |
Diclofenac |
Placebo | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
N |
Percent |
N |
Percent | |
| ||||
|
Application Site Conditions |
64 |
11 |
70 |
12 |
|
Pruritus |
31 |
5 |
44 |
8 |
|
Dermatitis |
9 |
2 |
3 |
<1 |
|
Burning |
2 |
<1 |
8 |
1 |
|
Other † |
22 |
4 |
15 |
3 |
|
Gastrointestinal Disorders |
49 |
9 |
33 |
6 |
|
Nausea |
17 |
3 |
11 |
2 |
|
Dysgeusia |
10 |
2 |
3 |
<1 |
|
Dyspepsia |
7 |
1 |
8 |
1 |
|
Other ‡ |
15 |
3 |
11 |
2 |
|
Nervous System Disorders |
13 |
2 |
18 |
3 |
|
Headache |
7 |
1 |
10 |
2 |
|
Paresthesia |
6 |
1 |
8 |
1 |
|
Somnolence |
4 |
1 |
6 |
1 |
|
Other § |
4 |
1 |
3 |
<1 |
Foreign labeling describes that dermal allergic reactions may occur with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% treatment. Additionally, the treated area may become irritated or develop itching, erythema, edema, vesicles, or abnormal sensation.
Pediatric Clinical Trials Experience
In one open-label trial, 104 male and female pediatric patients 6 years and older presenting with minor strains, sprains, and contusions received DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % twice a day for as many as 16 days. The most commonly reported adverse events (incidence ≥ 2%) were headache (9%), application site pruritus (7%), nausea (3%), and dyspepsia (3%). No adverse events led to discontinuation of treatment.
The most common adverse reactions in DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % and placebo-treated adult patients were pruritus (5% and 8%, respectively) and nausea (3% and 2%, respectively) ( 6.1). The most common adverse reactions in DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % treated pediatric patients were headache (9%) and application site pruritus (7%) ( 6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Yaral Pharma Professional Information Service at 1-866-218-9009 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Warning and Precautions, Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS) ( 5.10) |
04/2021 |
|
Warning and Precautions: Fetal Toxicity ( 5.11) |
04/2021 |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Instructions
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [ see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
The recommended dose of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is one (1) topical system to the most painful area twice a day both in adults and pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
2.2 Special Precautions
- Inform patients that, if DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% begins to peel-off, the edges of the topical system may be taped down. If problems with adhesion persist, patients may overlay the topical system with a mesh netting sleeve, where appropriate (e.g. to secure topical systems applied to ankles, knees, or elbows). The mesh netting sleeve (e.g. Curad® Hold Tite™, Surgilast® Tubular Elastic Dressing) must allow air to pass through and not be occlusive (non-breathable).
- Do not apply DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% to non-intact or damaged skin resulting from any etiology e.g. exudative dermatitis, eczema, infected lesion, burns or wounds.
- Do not wear a DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% when bathing or showering.
- Wash your hands after applying, handling or removing the topical system.
- Avoid eye contact.
- Do not use combination therapy with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and an oral NSAID unless the benefit outweighs the risk and conduct periodic laboratory evaluations.
- Use the lowest effective dosage for shortest duration consist with the individual patient treatment goals ( 2.1)
- The recommended dose of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% for adults and pediatric patients 6 years and older is one (1) topical system to the most painful area twice a day. ( 2)
- DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% should not be applied to damaged or non-intact skin. ( 2)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Diclofenac has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action of diclofenac, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Diclofenac is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Diclofenac concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because diclofenac is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% applied to intact skin provides local analgesia by releasing diclofenac epolamine from the topical system into the skin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption- Adults
Following a single application of the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% on the upper inner arm, peak plasma concentrations of diclofenac (range 0.7 – 6 ng/mL) were noted between 10 – 20 hours of application. Plasma concentrations of diclofenac in the range of 1.3 – 8.8 ng/mL were noted after five days with twice-a-day DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% application.
Systemic exposure (AUC) and maximum plasma concentrations of diclofenac, after repeated dosing for four days with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, were lower (<1%) than after a single oral 50-mg diclofenac sodium tablet.
The pharmacokinetics of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% has been tested in healthy volunteers at rest or undergoing moderate exercise (cycling 20 min/h for 12 h at a mean HR of 100.3 bpm). No clinically relevant differences in systemic absorption were observed, with peak plasma concentrations in the range of 2.2 – 8.1 ng/mL while resting, and 2.7 – 7.2 ng/mL during exercise.
Absorption– Pediatrics
Diclofenac plasma concentration was assessed in pediatric patients 6 years and older at a fixed time point 24-hours after the initial application and at the final visit (Day 3 – 15). The resulting average concentrations were 1.65 ng/mL and 1.80 ng/mL, respectively, both of which are similar to the values observed in adults.
Distribution
Diclofenac has a very high affinity (>99%) for human serum albumin. Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses, and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of diclofenac.
Elimination
Metabolism
Five diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5-dihydroxy- and 3'-hydroxy-4'-methoxy diclofenac. The major diclofenac metabolite, 4'hydroxy-diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4'-hydroxy diclofenac is primarily mediated by CPY2C9. Both diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CPY2C8 may also play a role in diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy and 3'-hydroxy- diclofenac.
Excretion
The plasma elimination half-life of diclofenac after application of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is approximately 12 hours. Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged diclofenac plus metabolites.
Specific Populations
The pharmacokinetics of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% has not been investigated in children less than 6 years old, patients with hepatic or renal impairment, or specific racial groups.
Drug Interaction Studies
Aspirin:When NSAIDs were administered with aspirin, the protein binding of NSAIDs were reduced, although the clearance of free NSAID was not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. See Table 1for clinically significant drug interactions of NSAIDs with aspirin [ see Drug Interactions (7)] .
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Diclofenac Epolamine Topical System is a 10 cm × 14 cm topical system that
contains 1.3% diclofenac epolamine, and is debossed with YARAL
DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, for topical use. Each individual topical system is debossed. ( 3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Use of NSAIDs, including DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus and fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and, in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. Because of these risks, limit dose and duration of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% use between about 20 and 30 weeks of gestation, and avoid DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% use at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy ( see Clinical Considerations, Data).
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Use of NSAIDs, including DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, at about 30 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment
Use of NSAIDs at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy has been associated with cases of fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment.
Data from observational studies regarding other potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive.
In animal reproduction studies, diclofenac epolamine administered orally to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis produced embryotoxicity at approximately 3 and 7 times, respectively, the topical exposure from the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%. In rats, increased incidences of skeletal anomalies and maternal toxicity were also observed at this dose. Diclofenac epolamine administered orally to both male and female rats prior to mating and throughout the mating period, and during gestation and lactation in females produced embryotoxicity at doses approximately 3 and 7 times, respectively, the topical exposure from the MRHD (see Data) .
Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as diclofenac, resulted in increased pre- and post- implantation loss. Prostaglandins also have been shown to have an important role in fetal kidney development. In published animal studies, prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors have been reported to impair kidney development when administered at clinically relevant doses.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Avoid use of NSAIDs in women at about 30 weeks gestation and later in pregnancy, because NSAIDs, including DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, can cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus ( see Data).
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
If an NSAID is necessary at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy, limit the use to the lowest effective dose and shortest duration possible. If DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% treatment extends beyond 48 hours, consider monitoring with ultrasound for oligohydramnios. If oligohydramnios occurs, discontinue DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and follow up according to clinical practice ( see Data).
Data
Human Data
Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus:
Published literature reports that the use of NSAIDs at about 30 weeks of gestation and later in pregnancy may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus.
Oligohydramnios/Neonatal Renal Impairment:
Published studies and postmarketing reports describe maternal NSAID use at about 20 weeks gestation or later in pregnancy associated with fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios, and in some cases, neonatal renal impairment. These adverse outcomes are seen, on average, after days to weeks of treatment, although oligohydramnios has been infrequently reported as soon as 48 hours after NSAID initiation. In many cases, but not all, the decrease in amniotic fluid was transient and reversible with cessation of the drug. There have been a limited number of case reports of maternal NSAID use and neonatal renal dysfunction without oligohydramnios, some of which were irreversible. Some cases of neonatal renal dysfunction required treatment with invasive procedures, such as exchange transfusion or dialysis.
Methodological limitations of these postmarketing studies and reports include lack of a control group; limited information regarding dose, duration, and timing of drug exposure; and concomitant use of other medications. These limitations preclude establishing a reliable estimate of the risk of adverse fetal and neonatal outcomes with maternal NSAID use. Because the published safety data on neonatal outcomes involved mostly preterm infants, the generalizability of certain reported risks to the full-term infant exposed to NSAIDs through maternal use is uncertain.
Animal Data
Pregnant Sprague Dawley rats were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage daily from gestation days 6 to 15. Maternal toxicity, embryotoxicity, and increased incidence of skeletal anomalies were noted with 6 mg/kg/day diclofenac epolamine, which corresponds to 3 times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison. Pregnant New Zealand White rabbits were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage daily from gestation days 6 to 18. No maternal toxicity was noted; however, embryotoxicity was evident at 6 mg/kg/day group which corresponds to 7 times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison.
Male rats were orally administered diclofenac epolamine (1, 3, 6 mg/kg) for 60 days prior to mating and throughout the mating period, and females were given the same doses 14 days prior to mating and through mating, gestation, and lactation. Embryotoxicity was observed at 6 mg/kg diclofenac epolamine (3 times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison), and was manifested as an increase in early resorptions, post-implantation losses, and a decrease in live fetuses. The number of live born and total born were also reduced as was F1 postnatal survival, but the physical and behavioral development of surviving F1 pups in all groups was the same as the deionized water control, nor was reproductive performance adversely affected despite a slight treatment-related reduction in body weight.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Data from published literature reports with oral preparations of diclofenac indicate the presence of small amounts of diclofenac in human milk (see Data) . There are no data on the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
One woman treated orally with a diclofenac salt, 150 mg/day, had a milk diclofenac level of 100 mcg/L, equivalent to an infant dose of about 0.03 mg/kg/day. Diclofenac was not detectable in breast milk in 12 women using diclofenac (after either 100 mg/day orally for 7 days or a single 50 mg intramuscular dose administered in the immediate postpartum period). The relative bioavailability for DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is <1% of a single 50 mg diclofenac tablet.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Females
Based on the mechanism of action, the use of prostaglandin-mediated NSAIDs, including DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% may delay or prevent rupture of ovarian follicles, which has been associated with reversible infertility in some women [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. Published animal studies have shown that administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors has the potential to disrupt prostaglandin- mediated follicular rupture required for ovulation. Small studies in women treated with NSAIDs have also shown a reversible delay in ovulation. Consider withdrawal of NSAIDs, including DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, in women who have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% have been established in pediatric patients 6 years and older based on evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % in adults, as well as an open-label study in pediatric patients 6 years and older. The pediatric study enrolled 104 patients, 6 years of age and older with minor soft tissue injuries. One DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % was applied to the injury site twice daily for a maximum of 14 days or until treatment was no longer required for pain management, whichever occurred first. Based on the available data from the pediatric study, the safety profile of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % topical system in pediatric patients is similar to that in adults. The safety and effectiveness of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3 % has not been investigated in pediatric patients less than 6 years old. [ see Clinical Trials Experience (6.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID- associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.14)].
Clinical studies of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
- Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% in women who have difficulties conceiving ( 8.3)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug for topical application. DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is a 10 cm × 14 cm topical system comprised of an adhesive material containing 1.3% diclofenac epolamine which is applied to a non-woven polyester felt backing and covered with a polypropylene film release liner. The release liner is removed prior to topical application to the skin.
The chemical name of diclofenac epolamine is 2-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl) amino] benzeneacetic acid, (2-(pyrrolidin-1-yl) ethanol salt, with a molecular formula of C 20H 24Cl 2N 2O 3,and molecular weight 411.3, an n-octanol/water partition coefficient of 8 at pH 8.5, and the following chemical structure:
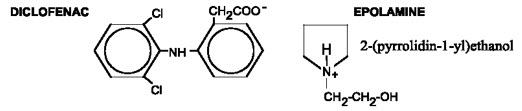
Each adhesive topical system contains 180 mg of diclofenac epolamine (13 mg per gram adhesive) in an aqueous base. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: butylene glycol, carboxymethylcellulose sodium, dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate, edetate disodium, fragrance (Dalin PH), gelatin, kaolin, methylparaben, polysorbate 80, povidone, propylene glycol, propylparaben, sodium polyacrylate, sorbitol solution, tartaric acid, titanium dioxide, and purified water.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Relabeled by:
Enovachem PHARMACEUTICALS
Torrance, CA 90501
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) | ||
|---|---|---|
|
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)? ** NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:** *Increased risk of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase: * with increasing doses of NSAIDs * with longer use of NSAIDs Do not take NSAIDs right before or after a heart surgery called a "coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)." Avoid taking NSAIDs after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack. *Increased risk of bleeding, ulcers, and tears (perforation) of the esophagus (tube leading from the mouth to the stomach), stomach and intestines: * anytime during use * without warning symptoms * that may cause death The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with: | ||
|
| |
|
NSAIDs should only be used: | ||
| ||
|
What are NSAIDs? NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain. | ||
|
Who should not take NSAIDs? ** Do not take NSAIDs:**
| ||
|
Before taking NSAIDS, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
**Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the-counter medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements.**NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects.Do not start taking any new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider first. | ||
|
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs? ** NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:** **See "**What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms: | ||
|
| |
|
Stop taking your NSAID and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms: | ||
|
| |
|
**If you take too much of your NSAID, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.**These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | ||
|
Other information about NSAIDs
| ||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals. |
Relabeled by:
Enovachem PHARMACEUTICALS
Torrance, CA 90501
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.6) ].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of either diclofenac epolamine or DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%.
Mutagenesis
Diclofenac epolamine is not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimuriumstrains, nor does it induce an increase in metabolic aberrations in cultured human lymphocytes, or the frequency of micronucleated cells in the bone marrow micronucleus test performed in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
Male and female Sprague Dawley rats were administered 1, 3, or 6 mg/kg/day diclofenac epolamine via oral gavage (males treated for 60 days prior to conception and during mating period, females treated for 14 days prior to mating through day 19 of gestation). Diclofenac epolamine treatment with 6 mg/kg/day resulted in increased early resorptions and post-implantation losses; however, no effects on the mating and fertility indices were found. The 6 mg/kg/day dose corresponds to 3 times the maximum recommended daily exposure in humans based on a body surface area comparison.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Strains, Sprains, and Contusions
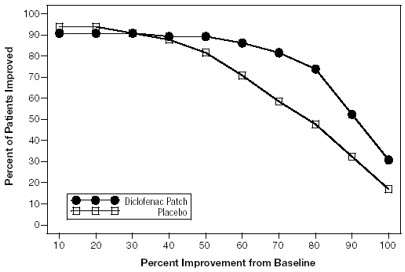
Efficacy of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% was demonstrated in two of four studies of patients with minor strains, sprains, and contusions. Patients were randomly assigned to treatment with the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, or a placebo identical to the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% minus the active ingredient. In the first of these two studies, patients with ankle sprains were treated once daily for a week. In the second study, patients with strains, sprains and contusions were treated twice daily for up to two weeks. Pain was assessed over the period of treatment. Patients treated with the DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% experienced a greater reduction in pain as compared to patients randomized to placebo as evidenced by the responder curves presented below (Figures 1-4).
Figure 1: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at Day 3; 14-Day Study
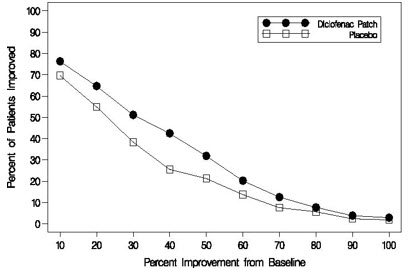
Figure 2: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at End of Study; 14-Day Study
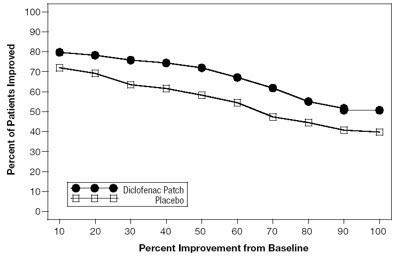
Figure 3: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at Day 3; 7-Day Study
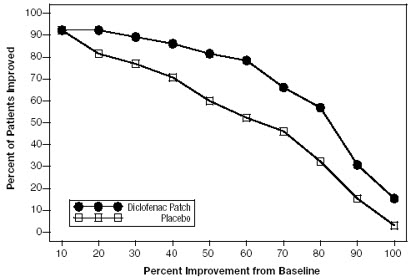
Figure 4: Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief at End of Study; 7-Day Study
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
The DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is supplied in resealable envelopes, each containing 5 topical systems (10 cm × 14 cm), with 6 envelopes per box (NDC 76420-673-30 [relabeled from NDC 82347-0405-5]). Each individual topical system is debossed with "YARAL < DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM > 1.3%".
- The product is intended for topical use only.
- Keep out of reach of children and pets.
- Envelopes should be sealed at all times when not in use.
- Curad® Hold Tite™ is a trademark of Medline Industries, Inc., and Surgilast® Tubular Elastic Dressing is a trademark of Derma Sciences, Inc.
Storage
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed, as well as the Directions for Use on the product packaging. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurring of speech, and to report any of these symptoms to their health care provider immediately [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Advise patients to report symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis to their health care provider. In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, inform patients of the increased risk for and the signs and symptoms of GI bleeding [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, diarrhea, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If these occur, instruct patients to stop DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and seek immediate medical therapy [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Heart Failure and Edema
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of congestive heart failure including shortness of breath, unexplained weight gain, or edema and to contact their healthcare provider if such symptoms occur [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Anaphylactic Reactions
Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). Instruct patients to seek immediate emergency help if these occur [ see Contraindications (4)and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Serious Skin Reactions including DRESS
Advise patients to stop using DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% immediately if they develop any type of rash or fever and to contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible [ see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.105.9)].
Female Fertility
Advise females of reproductive potential who desire pregnancy that NSAIDs, including DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3%, may delay or prevent rupture of ovarian follicles, which has been associated with reversible infertility in some women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)]
Fetal Toxicity
Inform pregnant women to avoid use of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% and other NSAIDs starting at 30 weeks of gestation because of the risk of the premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. If treatment with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% is needed for a pregnant woman between about 20 to 30 weeks gestation, advise her that she may need to be monitored for oligohydramnios, if treatment continues for longer than 48 hours [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)] .
Avoid Concomitant Use of NSAIDs
Inform patients that the concomitant use of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) is not recommended due to the increased risk of gastrointestinal toxicity, and little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)and Drug Interactions (7)]. Alert patients that NSAIDs may be present in "over the counter" medications for treatment of colds, fever, or insomnia.
Use of NSAIDS and Low-Dose Aspirin
Inform patients not to use low-dose aspirin concomitantly with DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% until they talk to their healthcare provider [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Eye Exposure
Instruct patients to avoid contact of DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% with the eyes and mucosa. Advise patients that if eye contact occurs, immediately wash out the eye with water or saline and consult a physician if irritation persists for more than an hour [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
Special Application Instructions
- Instruct patients that, if DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% begins to peel-off, the edges of the topical system may be taped down. If problems with adhesion persist, patients may overlay the topical system with a mesh netting sleeve, where appropriate (e.g. to secure topical systems applied to ankles, knees, or elbows). The mesh netting sleeve (e.g. Curad® Hold Tite™, Surgilast® Tubular Elastic Dressing) must allow air to pass through and not be occlusive (non-breathable).
- Instruct patients not to apply DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% to non-intact or damaged skin resulting from any etiology e.g. exudative dermatitis, eczema, infected lesion, burns or wounds.
- Instruct patients not to wear a DICLOFENAC EPOLAMINE TOPICAL SYSTEM 1.3% when bathing or showering.
- Instruct patients to wash hands after applying, handling or removing the topical system.
