Simponi
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SIMPONI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SIMPONI. SIMPONI (golimumab) injection, for subcutaneous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2009
f86cb4a7-c358-4136-ae57-b32bda9bba00
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 9, 2025
Janssen Biotech, Inc.
DUNS: 099091753
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
golimumab
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
golimumab
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mg/mL Autoinjector Syringe Carton
NDC 57894-071-02
FOR SUBCUTANEOUS INJECTION
Sterile solution in a single-dose
SmartJect ®autoinjector.
Discard unused portion.
See package insert for dosing information.
No U.S. standard of potency.
This Product Contains
** Dry Natural Rubber.**
Rx only.
Simponi**®******
** golimumab**
100 mg/mL
One single-dose SmartJect ®autoinjector

CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Rheumatoid Arthritis
The efficacy and safety of SIMPONI were evaluated in 3 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, controlled trials (Trials RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3) in 1542 patients ≥ 18 years of age with moderately to severely active RA, diagnosed according to the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) criteria, for at least 3 months prior to administration of trial agent. Patients were required to have at least 4 swollen and 4 tender joints. SIMPONI was administered subcutaneously at doses of 50 mg or 100 mg every 4 weeks. Double- blinded controlled efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 24. Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone a day) and/or NSAIDs and patients may have received oral MTX during the trials.
Trial RA-1 evaluated 445 patients who were previously treated (at least 8 to 12 weeks prior to administration of trial agent) with one or more doses of a biologic TNF blocker without a serious adverse reaction. Patients may have discontinued the biologic TNF blocker for a variety of reasons. Patients were randomized to receive placebo (N=150), SIMPONI 50 mg (N=147), or SIMPONI 100 mg (N=148). Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant MTX, sulfasalazine (SSZ), and/or hydroxychloroquine (HCQ) during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
Trial RA-2 evaluated 444 patients who had active RA despite a stable dose of at least 15 mg/week of MTX and who had not been previously treated with a biologic TNF blocker. Patients were randomized to receive background MTX (N=133), SIMPONI 50 mg + background MTX (N=89), SIMPONI 100 mg + background MTX (N=89), or SIMPONI 100 mg monotherapy (N=133). The use of other DMARDs including SSZ, HCQ, cytotoxic agents, or other biologics was prohibited.
Trial RA-3 evaluated 637 patients with active RA who were MTX naïve and had not previously been treated with a biologic TNF blocker. Patients were randomized to receive MTX (N=160), SIMPONI 50 mg + MTX (N=159), SIMPONI 100 mg
- MTX (N=159), or SIMPONI 100 mg monotherapy (N=159). For patients receiving MTX, MTX was administered at a dose of 10 mg/week beginning at Week 0 and increased to 20 mg/week by Week 8. The use of other DMARDs including SSZ, HCQ, cytotoxic agents, or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint in Trial RA-1 and Trial RA-2 was the percentage of patients achieving an ACR 20 response at Week 14 and the primary endpoint in Trial RA-3 was the percentage of patients achieving an ACR 50 response at Week 24.
In Trials RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3, the median duration of RA disease was 9.4, 5.7, and 1.2 years and 99%, 75%, and 54% of the patients used at least one DMARD in the past, respectively. Approximately 77% and 57% of patients received concomitant NSAIDs and low dose corticosteroids, respectively, in the 3 pooled RA trials.
Clinical Response
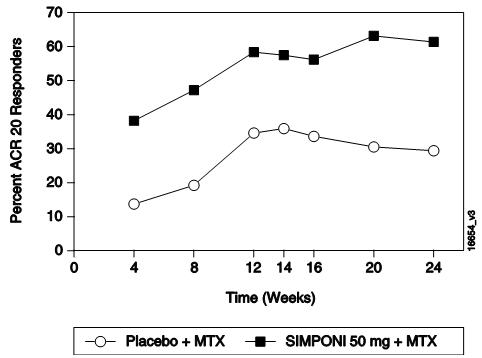
In the 3 RA trials, a greater percentage of patients treated with the combination of SIMPONI and MTX achieved ACR responses at Week 14 (Trials RA-1 and RA-2) and Week 24 (Studies RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3) versus patients treated with the MTX alone. There was no clear evidence of improved ACR response with the higher SIMPONI dose group (100 mg) compared to the lower SIMPONI dose group (50 mg). In Trials RA-2 and RA-3, the SIMPONI monotherapy groups were not statistically different from the MTX monotherapy groups in ACR responses. Table 2 shows the proportion of patients with the ACR response for the SIMPONI 50-mg and control groups in Trials RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3. In the subset of patients who received SIMPONI in combination with MTX in Trial RA-1, the proportion of patients achieving ACR 20, 50 and 70 responses at Week 14 were 40%, 18%, and 12%, respectively, in the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX group (N=101) compared with 17%, 6%, and 2%, respectively, in the placebo + MTX group (N=103). Table 3 shows the percent improvement in the components of the ACR response criteria for the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX and MTX groups in Trial RA-2. The percentage of patients achieving ACR 20 responses by visit for Trial RA-2 is shown in Figure 1. ACR 20 responses were observed in 38% of patients in the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX group at the first assessment (Week 4) after the initial SIMPONI administration.
Table 2: Trials RA-1, RA-2, and RA-3 Proportion of Patients with an ACR Response *|
Trial RA-1 |
Trial RA-2 |
Trial RA-3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Placebo ± DMARDs † |
SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs † |
Background MTX |
SIMPONI 50 mg + Background MTX |
MTX |
SIMPONI 50 mg + MTX | |
| ||||||
|
N ‡ |
150 |
147 |
133 |
89 |
160 |
159 |
|
ACR 20 | ||||||
|
Week 14 |
18% |
35% |
33% |
55% |
NA § |
NA § |
|
Week 24 |
16% |
31% |
28% |
60% |
49% |
62% |
|
ACR 50 | ||||||
|
Week 14 |
7% |
15% |
10% |
35% |
NA § |
NA § |
|
Week 24 |
4% |
16% |
14% |
37% |
29% |
40% |
|
ACR 70 | ||||||
|
Week 14 |
2% |
10% |
4% |
13% |
NA § |
NA § |
|
Week 24 |
2% |
9% |
5% |
20% |
16% |
24% ¶ |
|
Background MTX |
SIMPONI 50 mg + Background MTX | |
|---|---|---|
|
Note: Baseline values are medians. | ||
| ||
|
N † |
133 |
89 |
|
Number of swollen joints (0–66) | ||
|
Baseline |
12 |
13 |
|
Week 14 |
38% |
62% |
|
Number of tender joints (0–68) | ||
|
Baseline |
21 |
26 |
|
Week 14 |
30% |
60% |
|
Patient's assessment of pain (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
5.7 |
6.1 |
|
Week 14 |
18% |
55% |
|
Patient's global assessment of disease activity (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
5.3 |
6.0 |
|
Week 14 |
15% |
45% |
|
Physician's global assessment of disease activity (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
5.7 |
6.1 |
|
Week 14 |
35% |
55% |
|
HAQ score (0–3) | ||
|
Baseline |
1.25 |
1.38 |
|
Week 14 |
10% |
29% |
|
CRP (mg/dL) | ||
|
Baseline |
0.8 |
1.0 |
|
Week 14 |
2% |
44% |
|
|
Figure 1: Trial RA-2 – Percentage of Patients Achieving ACR 20 Response by Visit: Randomized Patients***** |
|
|
Physical Function Response in Patients with RA
In Trials RA-1 and RA-2, the SIMPONI 50-mg groups demonstrated a greater improvement compared to the control groups in the change in mean Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score from baseline to Week 24: 0.23 vs. 0.03 in RA-1, 0.47 vs. 0.13 in RA-2, respectively. Also in Trials RA-1 and RA-2, the SIMPONI 50-mg groups compared to the control groups had a greater proportion of HAQ responders (change from baseline > 0.22) at Week 24: 43% vs. 27%, 65% vs. 35%, respectively.
14.2 Psoriatic Arthritis
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 405 adult patients with moderately to severely active PsA (≥ 3 swollen joints and ≥ 3 tender joints) despite NSAID or DMARD therapy (Trial PsA). Patients in this trial had a diagnosis of PsA for at least 6 months with a qualifying psoriatic skin lesion of at least 2 cm in diameter. Previous treatment with a biologic TNF blocker was not allowed. Patients were randomly assigned to placebo (N=113), SIMPONI 50 mg (N=146), or SIMPONI 100 mg (N=146) given subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Patients were allowed to receive stable doses of concomitant MTX (≤ 25 mg/week), low dose oral corticosteroids (equivalent to ≤ 10 mg of prednisone a day), and/or NSAIDs during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including SSZ, HCQ, cytotoxic agents, or other biologics was prohibited. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving ACR 20 response at Week 14. Placebo- controlled efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 24.
Patients with each subtype of PsA were enrolled, including polyarticular arthritis with no rheumatoid nodules (43%), asymmetric peripheral arthritis (30%), distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint arthritis (15%), spondylitis with peripheral arthritis (11%), and arthritis mutilans (1%). The median duration of PsA disease was 5.1 years, 78% of patients received at least one DMARD in the past, and approximately 48% of patients received MTX, and 16% received low dose oral steroids.
Clinical Response in Patients with PsA
SIMPONI ± MTX, compared with placebo ± MTX, resulted in significant improvement in signs and symptoms as demonstrated by the proportion of patients with an ACR 20 response at Week 14 in Trial PsA (see Table 4). There was no clear evidence of improved ACR response with the higher SIMPONI dose group (100 mg) compared to the lower SIMPONI dose group (50 mg). ACR responses observed in the SIMPONI-treated groups were similar in patients receiving and not receiving concomitant MTX. Similar ACR 20 responses at Week 14 were observed in patients with different PsA subtypes. However, the number of patients with arthritis mutilans was too small to allow meaningful assessment. SIMPONI 50-mg treatment also resulted in significantly greater improvement compared with placebo for each ACR component in Trial PsA (Table 5). Treatment with SIMPONI resulted in improvement in enthesitis and skin manifestations in patients with PsA. However, the safety and efficacy of SIMPONI in the treatment of patients with plaque psoriasis has not been established.
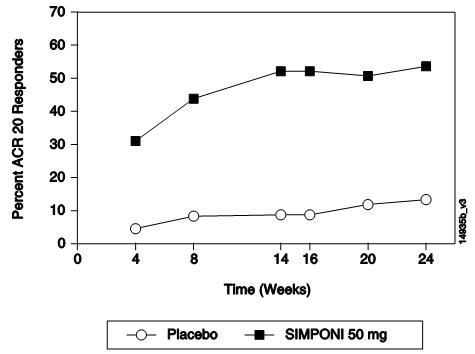
The percentage of patients achieving ACR 20 responses by visit for Trial PsA is shown in Figure 2. ACR 20 responses were observed in 31% of patients in the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX group at the first assessment (Week 4) after the initial SIMPONI administration.
Table 4: Trial PsA - Proportion of Patients with ACR Responses|
Placebo ± MTX * |
SIMPONI 50 mg ± MTX * | |
|---|---|---|
|
Bold text indicates primary endpoint. | ||
| ||
|
N † |
113 |
146 |
|
ACR 20 | ||
|
Week 14 |
9% |
51% |
|
Week 24 |
12% |
52% |
|
ACR 50 | ||
|
Week 14 |
2% |
30% |
|
Week 24 |
4% |
32% |
|
ACR 70 | ||
|
Week 14 |
1% |
12% |
|
Week 24 |
1% |
19% |
|
Placebo ± MTX * |
SIMPONI 50 mg ± MTX * | |
|---|---|---|
|
Note: Baseline are median values. | ||
| ||
|
N**†** |
113 |
146 |
|
Number of swollen joints (0–66) | ||
|
Baseline |
10.0 |
11.0 |
|
Week 14 |
8% |
60% |
|
Number of tender joints (0–68) | ||
|
Baseline |
18.0 |
19.0 |
|
Week 14 |
0% |
54% |
|
Patient's assessment of pain (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
5.4 |
5.8 |
|
Week 14 |
-1% |
48% |
|
Patient's global assessment of disease activity (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
5.2 |
5.2 |
|
Week 14 |
2% |
49% |
|
Physician's global assessment of disease activity (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
5.2 |
5.4 |
|
Week 14 |
7% |
59% |
|
HAQ score (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
1.0 |
1.0 |
|
Week 14 |
0% |
28% |
|
CRP (mg/dL) (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
0.6 |
0.6 |
|
Week 14 |
0% |
40% |
|
|
Figure 2: Trial PsA – Percentage of ACR 20 PsA Responders by Visit: Randomized Patients***** |
|
|
Physical Function Response in Patients with PsA
In Trial PsA, SIMPONI 50 mg demonstrated a greater improvement compared to placebo in the change in mean Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) score from baseline to Week 24 (0.33 and -0.01, respectively). In addition, the SIMPONI 50-mg group compared to the placebo group had a greater proportion of HAQ responders (≥ 0.3 change from baseline) at Week 24: 43% vs. 22%, respectively.
14.3 Ankylosing Spondylitis
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 356 adult patients with active ankylosing spondylitis according to modified New York criteria for at least 3 months (Trial AS). Patients had symptoms of active disease [defined as a Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) ≥ 4 and VAS for total back pain of ≥ 4, on scales of 0 to 10 cm] despite current or previous NSAID therapy. Patients were excluded if they were previously treated with a biologic TNF blocker or if they had complete ankylosis of the spine. Patients were randomly assigned to placebo (N=78), SIMPONI 50 mg (N=138), or SIMPONI 100 mg (N=140) administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Patients were allowed to continue stable doses of concomitant MTX, sulfasalazine (SSZ), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), low dose corticosteroids (equivalent to < 10 mg of prednisone a day), and/or NSAIDs during the trial. The use of other DMARDs including cytotoxic agents or other biologics was prohibited.
The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients achieving an ASsessment in Ankylosing Spondylitis (ASAS) 20 response at Week 14. Placebo-controlled efficacy data were collected and analyzed through Week 24.
In Trial AS, the median duration of AS disease was 5.6 years, median duration of inflammatory back pain was 12 years, 83% were HLA-B27 positive, 24% had prior joint surgery or procedure, and 55% received at least one DMARD in the past. During the trial, the use of concomitant DMARDs and/or NSAIDs was as follows: MTX (20%), SSZ (26%), HCQ (1%), low dose oral steroids (16%), and NSAIDs (90%).
Clinical Response in Patients with AS
In Trial AS, SIMPONI ± DMARDs treatment, compared with placebo ± DMARDs, resulted in a significant improvement in signs and symptoms as demonstrated by the proportion of patients with an ASAS 20 response at Week 14 (see Table 6). There was no clear evidence of improved ASAS response with the higher SIMPONI dose group (100 mg) compared to the lower SIMPONI dose group (50 mg). Table 7 shows the percent improvement in the components of the ASAS response criteria for the SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs and placebo ± DMARDs groups in Trial AS.
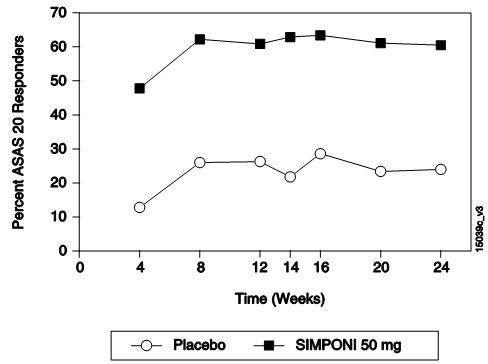
The percentage of patients achieving ASAS 20 responses by visit for Trial AS is shown in Figure 3. ASAS 20 responses were observed in 48% of patients in the SIMPONI 50-mg + MTX group at the first assessment (Week 4) after the initial SIMPONI administration.
Table 6: Trial AS – Proportion of ASAS Responders at Weeks 14 and 24|
Placebo ± DMARDs * |
SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs * | |
|---|---|---|
|
Bold text indicates primary endpoint. | ||
| ||
|
N † |
78 |
138 |
|
Responders, % of patients | ||
|
ASAS 20 | ||
|
Week 14 |
22% |
59% |
|
Week 24 |
23% |
56% |
|
ASAS 40 | ||
|
Week 14 |
15% |
45% |
|
Week 24 |
15% |
44% |
|
Placebo ± DMARDs * |
SIMPONI 50 mg ± DMARDs * | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
N † |
78 |
138 |
|
ASAS components | ||
|
Patient global assessment (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
7.2 |
7.0 |
|
Week 14 |
13% |
47% |
|
Total back pain (0–10) | ||
|
Baseline |
7.6 |
7.5 |
|
Week 14 |
9% |
50% |
|
BASFI (0–10)****‡ | ||
|
Baseline |
4.9 |
5.0 |
|
Week 14 |
-3% |
37% |
|
Inflammation (0–10)****§ | ||
|
Baseline |
7.1 |
7.1 |
|
Week 14 |
6% |
59% |
|
|
**Figure 3:**Trial AS – Percentage of AS Patients Achieving ASAS 20 Response by Visit: Randomized Patients * |
|
|
14.4 Ulcerative Colitis
The safety and efficacy of SIMPONI were evaluated in 2 multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials in patients ≥ 18 years of age (Trials UC-1 and UC-2).
Trial UC-1 was an induction trial conducted in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC), defined as a Mayo score of 6 to 12 [the Mayo score ranges from 0 to 12 and has 4 subscales that are each scored from 0 (normal) to 3 (most severe): stool frequency, rectal bleeding, findings on endoscopy, and physician global assessment]. At baseline, subjects also had an endoscopy subscore of 2 or 3 on a 3-point scale (an endoscopy score of 2 is defined by marked erythema, absent vascular pattern, friability, erosions; and a score of 3 is defined by spontaneous bleeding, ulceration). Patients were corticosteroid dependent (i.e., an inability to successfully taper corticosteroids without a return of the symptoms of UC) or had an inadequate response to or had failed to tolerate at least one of the following therapies: oral aminosalicylates, oral corticosteroids, azathioprine, or 6-mercaptopurine.
Trial UC-1 was divided into 2 parts. In Part 1 (dose finding), patients were randomized to one of 4 treatment groups: 400 mg SIMPONI administered subcutaneously (SC) at Week 0 and 200 mg at Week 2 (400/200 mg), 200-mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 100 mg at Week 2 (200/100 mg), 100-mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 50 mg at Week 2 (100/50 mg), or placebo SC at Weeks 0 and 2. In Part 2 (dose confirming), efficacy was evaluated in 761 patients who were randomized to receive either 400 mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 200 mg at Week 2, 200-mg SIMPONI SC at Week 0 and 100 mg at Week 2, or placebo SC at Weeks 0 and 2. SIMPONI 100/50-mg SC was not evaluated in Part 2; its safety and effectiveness has not been established in UC. Concomitant stable doses of oral aminosalicylates (5-ASA), oral corticosteroids (less than 40 mg/day), azathioprine (AZA), 6-mercaptopurine (6-MP), and/or methotrexate (MTX) were permitted. Patients who received previous TNF inhibitors were excluded. The primary endpoint was the percent of patients in clinical response at Week 6, defined as a decrease from baseline in the Mayo score by ≥ 30% and ≥ 3 points, accompanied by a decrease in the rectal bleeding subscore of ≥ 1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 (no blood seen) or 1 (streaks of blood with stool less than half the time).
Trial UC-2 was a randomized-withdrawal maintenance trial that evaluated 456 patients who achieved clinical response with SIMPONI induction and tolerated SIMPONI treatment. Patients were randomized to receive SIMPONI 50 mg, SIMPONI 100 mg or placebo administered subcutaneously every 4 weeks. Concomitant stable doses of oral aminosalicylates, azathioprine, 6-mercaptopurine, and/or methotrexate were permitted. Corticosteroids were to be tapered at the start of the maintenance trial. The primary endpoint was the percent of patients maintaining clinical response through Week 54.
Clinical Response, Clinical Remission and Improvement of Endoscopic Appearance of the Mucosa
In Trial UC-1, a greater proportion of patients achieved clinical response, clinical remission and had improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa at Week 6 in the SIMPONI 200/100-mg group compared with the placebo group. The SIMPONI 400/200-mg group did not demonstrate additional clinical benefit over the SIMPONI 200/100-mg group. Clinical response was defined as a decrease from baseline in the Mayo score of ≥ 30% and ≥ 3 points, accompanied by a decrease in the rectal bleeding subscore of ≥ 1 or a rectal bleeding subscore of 0 or
- Clinical remission was defined as a Mayo score ≤ 2 points, with no individual subscore > 1. Improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa was defined as a Mayo endoscopy subscore of 0 (normal or inactive disease) or 1 (erythema, decreased vascular pattern, mild friability).
In Trial UC-2, a greater proportion of patients maintained clinical response through Week 54 in the SIMPONI 100-mg group compared with the placebo group. In Trial UC-2, SIMPONI-treated patients in clinical response (which included the subset of patients in clinical remission) in Trial UC-1, were again assessed for clinical remission at Week 30 and Week 54. A greater proportion of patients had clinical remission at both Weeks 30 and 54 without demonstrating a loss of response at any time point through Week 54 in the SIMPONI 100-mg group compared with the placebo group.
These results are shown in Table 8 below.
Table 8: The Proportion of Patients with UC in Clinical Response, Clinical Remission and with Improvement of Endoscopic Appearance of the Mucosa in Trials UC-1 and UC-2
Þ ß | |||
|
Trial UC-1 (6-Week Induction Trial) | |||
|
Placebo |
SIMPONI |
Treatment difference | |
|
Clinical response *at Week 6 |
30% |
51% |
21% |
|
Clinical remission *at Week 6 |
6% |
18% |
11% |
|
Improvement of endoscopic appearance of the mucosa at Week 6 * |
29% |
42% |
14% |
|
Trial UC-2 (54-Week Maintenance Trial)****§ | |||
|
Placebo |
SIMPONI |
Treatment difference | |
|
Clinical response *through Week 54 ¶ |
31% |
50% |
19% |
|
Clinical remission *at both Week 30 and Week 54 Þ |
16% |
28% |
12% |
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
Instructions for Use
** SIMPONI****®**
(SIM-po-nee)
(golimumab)
Prefilled Syringe


Important
SIMPONI comes as a single-dose prefilled syringe containing one 50 mg or one 100 mg dose. Each SIMPONI prefilled syringe can only be used one time. Throw away (dispose of) the used prefilled syringe (See Step 3) after one dose, even if there is medicine left in it. Do not reuse your SIMPONI prefilled syringe.
If your healthcare provider decides that you or a caregiver may be able to give your injections of SIMPONI at home, you should receive training on the right way to prepare and inject SIMPONI using the prefilled syringe before attempting to inject. Do not try to inject yourself until you have been shown the right way to give the injections by your healthcare provider.
Read this Instructions for Use before using your SIMPONI prefilled syringe and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
The SIMPONI prefilled syringe is intended for injection under the skin, not into the muscle or vein. After injection, the needle will retract into the body of the device and lock into place.
 Storage
information
Storage
information
Store SIMPONI in the refrigerator at36° to 46°F(2° to 8°C).
If needed, store SIMPONI at room temperature, up to 77°F (25°C) for one period of time up to 30 days. Do not return it to the refrigerator. Throw away if not used within 30 days at room temperature.
Do notfreeze SIMPONI prefilled syringe.
Do notshake SIMPONI prefilled syringe.
Keep SIMPONI prefilled syringe in the original carton to protect from light before use.
Keep SIMPONI prefilled syringe and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Prefilled syringe parts
Before use
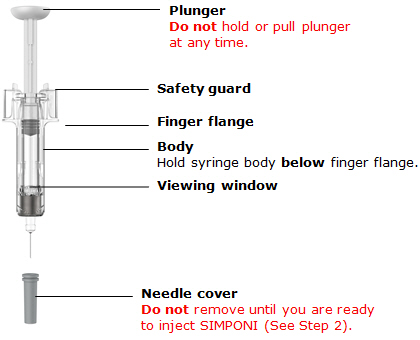
After use
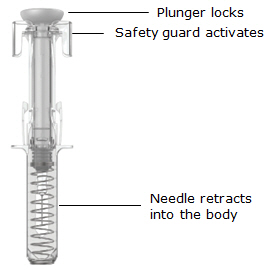
|
You will need these supplies: *1 SIMPONI prefilled syringe |
|
Not provided in the SIMPONI prefilled syringe carton: *1 Alcohol swab *1 Cotton ballorgauze pad *1 Adhesive bandage *1 Sharps container(See Step 3) |

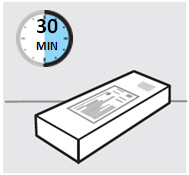
Inspect carton
Remove your SIMPONI prefilled syringe carton from the refrigerator.
Remove the prefilled syringe from the carton and let it sit on a flat surface at room temperature forat least 30 minutesbefore use.
Do notwarm the prefilled syringe any other way.
**Check the expiration date ('EXP')**on the back panel of the carton and on the prefilled syringe (through the viewing window).
Do notuse your prefilled syringe if the expiration date has passed.
Do notinject SIMPONI if the perforations on the carton are broken. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a refill.
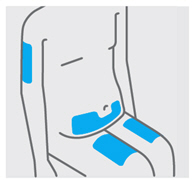
Choose injection site
Select from the following areas for your injection:
*Front of thighs(recommended)
- Lower stomach area (lower abdomen), except for a 2-inch area right around your navel (belly-button)
- Back of upper arms (only if someone else is giving you the injection)
Choose a different site within your preferred area for each injection.
Do notinject into skin that is tender, bruised, red, hard, thick or scaly.
Do notinject into areas with scars or stretch marks.
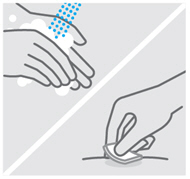
Clean injection site
Wash your hands well with soap and warm water.
Wipe your chosen injection site with an alcohol swab and allow it to dry.
Do nottouch, fan, or blow on the injection site after you have cleaned it.
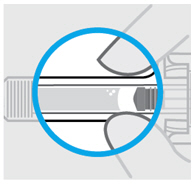
Inspect liquid
Check the SIMPONI prefilled syringe liquid in the viewing window. It should be clear to slightly yellow and may contain tiny white or clear particles. You may also see one or more air bubbles. This is normal.
Do notinject if the liquid is cloudy or discolored, or has large particles. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a refill.

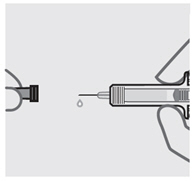
Remove needle cover
Hold your prefilled syringe by the body and pull needle cover straight off. It is normal to see a drop of liquid.
Inject SIMPONI within 5 minutes of removing the needle cover.
Do notput needle cover back on, as this may damage the needle or cause a needle stick injury.
Do nottouch needle or let it touch any surface.
Do notuse a SIMPONI prefilled syringe if it is dropped. Call your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a refill.
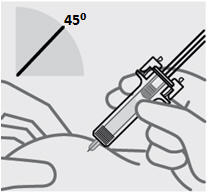
Position fingers and insert needle
Place your thumb, index and middle fingersdirectly under the finger flange, as shown.
Do nottouch plunger or area above finger flange as this may cause the needle safety device to activate.
Use your other hand to pinch skin at the injection site. Position syringe at about a 45 degree angle to the skin.
It is important to pinch enough skin toinject under the skinand not into the muscle.
Insert needle with a quick, dart-like motion.
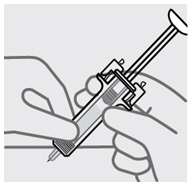
Release pinch and reposition hand
Use your free hand to grasp the body of the prefilled syringe.
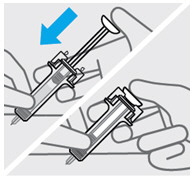
Press plunger
Place thumb from the opposite hand on the plunger and press the plungerall the way down until it stops.
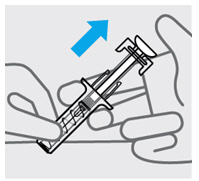
Release pressure from plunger
The safety guard will cover the needle and lock into place, removing the needle from your skin.

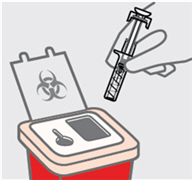
Dispose of your prefilled syringe
Put your used SIMPONI prefilled syringe in an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use.
Do notthrow away (dispose of) your SIMPONI prefilled syringe in your household trash.
Do notrecycle your used sharps disposal container.
For more information, see "How should I dispose of the used prefilled syringe?"
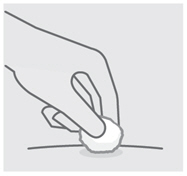
Check injection site
There may be a small amount of blood or liquid at the injection site. Hold pressure over your skin with a cotton ball or gauze pad until any bleeding stops.
Do notrub the injection site.
If needed, cover injection site with a bandage.
 Need help?
Need help?
Call your healthcare provider to talk about any questions you may have. For additional assistance or to share your feedback call 800-JANSSEN (800-526-7736).
How should I dispose of the used prefilled syringe?
If you do not have an FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out
- upright and stable during use
- leak-resistant
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container
When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes.
For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Janssen Biotech, Inc. Horsham, PA 19044
US License No. 1864
Revised: May 2018
janssen