Thiola
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use THIOLA® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for THIOLA. THIOLA (tiopronin) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1988
494a714e-923c-cd57-df6c-12886afb265a
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 25, 2025
Mission Pharmacal Company
DUNS: 008117095
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
tiopronin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (14)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL

Manufactured and packaged by Mission Pharmacal Company, San Antonio, TX 78230
1355
Distributed by Travere Therapeutics, Inc., San Diego, CA 92130
Copyright © 2024 Mission Pharmacal Company. All rights reserved.
L090201R0824
THL_T13758R0824

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
THIOLA is indicated, in combination with high fluid intake, alkali, and diet
modification, for the prevention of
cystine stone formation in adults and pediatric patients 20 kg and greater
with severe homozygous cystinuria,
who are not responsive to these measures alone.
(1)
(1)
(1)
--------------------------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE----------------------------------------- (1)
THIOLA is a reducing and complexing thiol indicated, in combination with high
fluid intake, alkali, and diet
modification, for the prevention of cystine stone formation in adults and
pediatric patients 20 kg and greater
with severe homozygous cystinuria, who are not responsive to these measures
alone. (1) (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
THIOLA is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to tiopronin or
any other components of THIOLA
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
----------------------------------------------CONTRAINDICATIONS------------------------------------------ (4)
• Hypersensitivity to tiopronin or any component of THIOLA (4) (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Proteinuria
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.1 Proteinuria
Proteinuria, including nephrotic syndrome, and membranous nephropathy, have
been reported with tiopronin
use. Pediatric patients receiving greater than 50 mg/kg of tiopronin per day
may be at increased risk for
proteinuria [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Monitor patients for the development of proteinuria and discontinue
therapy in patients who develop
proteinuria [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions (drug fever, rash, fever, arthralgia and
lymphadenopathy) have been reported [see Contraindications (4)].
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other
sections of the labeling:
• Proteinuria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
• Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, the
adverse reaction rates observed in
the clinical trials of the drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the
clinical trials of another drug and may
not reflect the rates observed in practice.
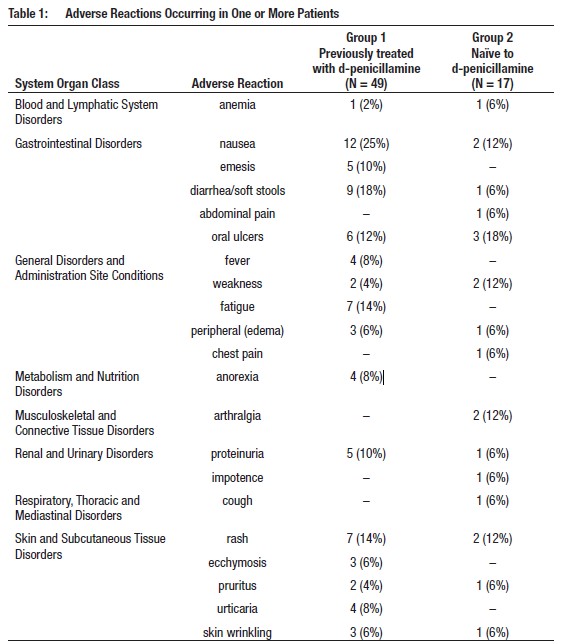
Adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of ≥5% in an uncontrolled trial in
66 patients with cystinuria
age 9 to 68 years are shown in the table below. Patients in group 1 had
previously been treated with
d-penicillamine; those in group 2 had not. Of those patients who had stopped
taking d-penicillamine due to
toxicity (34 out of 49 patients in group 1), 22 were able to continue
treatment with THIOLA. In those without
prior history of d-penicillamine treatment, 6% developed reactions of
sufficient severity to require THIOLA
withdrawal.
Table 1 presents adverse reactions ≥5% in either treatment group occurring in
this trial.
Taste Disturbance
A reduction in taste perception may develop. It is believed to be the result
of chelation of trace metals by
tiopronin. Hypogeusia is often self-limited.
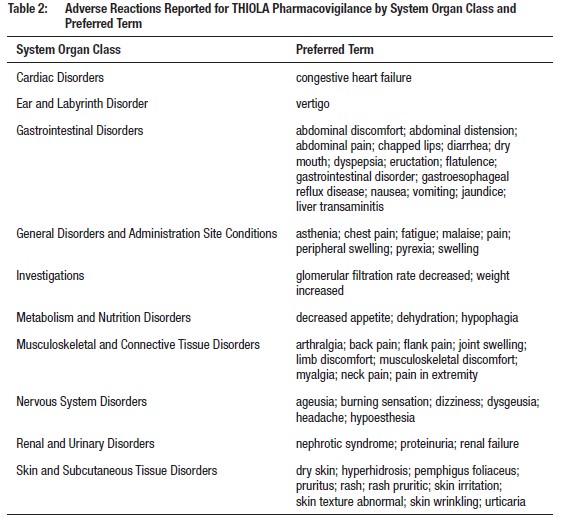
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Adverse reactions have been reported from the literature, as well as during
post-approval use of THIOLA.
Because the post-approval reactions are reported voluntarily from a population
of uncertain size, it is not
always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal
relationship to THIOLA exposure.
Adverse reactions reported during the postmarketing use of THIOLA are listed
by body system inTable 2.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The goal of therapy is to reduce urinary cystine concentration below its
solubility limit. Tiopronin is an active
reducing agent which undergoes thiol-disulfide exchange with cystine to form a
mixed disulfide of tiopronincysteine.
From this reaction, a water-soluble mixed disulfide is formed and the amount
of sparingly soluble
cystine is reduced.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The decrement in urinary cystine produced by tiopronin is generally
proportional to the dose. A reduction in
urinary cystine of 250-350 mg/day at tiopronin dosage of 1 g/day, and a
decline of approximately 500 mg/day
at a dosage of 2 g/day, might be expected. Tiopronin has a rapid onset and
offset of action, showing a fall in
cystine excretion on the first day of administration and a rise on the first
day of drug withdrawal.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
THIOLA Tablets
When THIOLA single doses were given to fasted healthy subjects (n = 39), the
median time to peak plasma
level (T max) was 1 (range: 0.5 to 2.1) hours.
Elimination
Excretion
When tiopronin is given orally, up to 48% of dose appears in urine during the
first 4 hours and up to 78% by
72 hours.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
THIOLA (tiopronin) immediate-release tablets are a reducing and cystine-
binding thiol drug (CBTD) for oral
use. Tiopronin is N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl) glycine and has the following
structure:
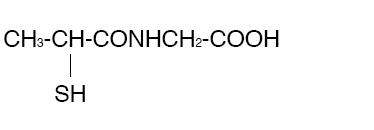
Tiopronin has the empirical formula C 5H 9NO 3S and a molecular weight of
163.20. In this drug product tiopronin
exists as a dl racemic mixture.
Tiopronin is a white crystalline powder, which is freely soluble in water.
Each THIOLA tablet contains 100 mg of tiopronin. The inactive ingredients in
THIOLA tablets include calcium
carbonate, carnauba wax, ethyl cellulose, dimethylaminoethyl methacrylate:
butyl methacrylate: methyl
methacrylate copolymer (Eudragit E 100), hydroxy-propyl cellulose, lactose
monohydrate, magnesium
stearate, povidone, sugar, talc, titanium dioxide.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Monitoring
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Adults: The recommended initial dosage in adult patients is 800 mg/day. In
clinical studies, the average
dosage was about 1,000 mg/day.
Pediatrics: The recommended initial dosage in pediatric patients weighing 20
kg and greater is 15 mg/kg/day.
Avoid dosages greater than 50 mg/kg per day in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Administer THIOLA in 3 divided doses at the same times each day at least one
hour before or 2 hours after
meals.
Consider starting THIOLA at a lower dosage in patients with history of severe toxicity to d-penicillamine.
2.2 Monitoring
Measure urinary cystine 1 month after starting THIOLA and every 3 months
thereafter. Adjust THIOLA dosage
to maintain urinary cystine concentration less than 250 mg/L.
Assess for proteinuria before treatment and every 3 to 6 months during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Discontinue THIOLA in patients who develop proteinuria, and monitor urinary
protein and renal function.
Consider restarting THIOLA treatment at a lower dosage after resolution of
proteinuria.
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets for oral use:
100 mg tablets: round, white and imprinted in red with “M” on one side
-----------------------------------------DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS----------------------------------- (3)
Tablets: 100 mg (3) (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available published case report data with tiopronin have not identified a
drug-associated risk for major birth
defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Renal stones in
pregnancy may result in adverse
pregnancy outcomes (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction
studies, there were no adverse
developmental outcomes with oral administration of tiopronin to pregnant mice
and rats during organogenesis
at doses up to 2 times a 2 grams/day human dose (based on mg/m 2). The
estimated background risk of major
birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All
pregnancies have a background
risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general
population, the estimated background
risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized
pregnancies are 2% to 4% and 15% to
20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Renal stones in pregnancy may increase the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes,
such as preterm birth and
low birth weight.
Data
Animal Data
No findings of fetal malformations could be attributed to the drug in
reproduction studies in mice and rats at
doses up to 2 times the highest recommended human dose of 2 grams/day (based
on mg/m 2).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of tiopronin in either human or animal milk
or on the effects of the
breastfed child. A published study suggests that tiopronin may suppress milk
production. Because of the
potential for serious adverse reactions, including nephrotic syndrome, advise
patients that breastfeeding is not
recommended during treatment with THIOLA.
8.4 Pediatric Use
THIOLA is indicated in pediatric patients weighing 20 kg or more with severe
homozygous cystinuria, in
combination with high fluid intake, alkali, and diet modification, for the
prevention of cystine stone formation
who are not responsive to these measures alone. This indication is based on
safety and efficacy data from a
trial in patients 9 years to 68 years of age and clinical experience.
Proteinuria, including nephrotic syndrome,
has been reported in pediatric patients. Pediatric patients receiving greater
than 50 mg/kg tiopronin per day
may be at greater risk [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
THIOLA tablets are not approved for use in pediatric patients weighing less
than 20 kg or in pediatric patients
unable to swallow tablets [see Recommended Dosage (2.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of
adverse reactions to this drug
may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly
patients are more likely to have
decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may
be useful to monitor renal
function.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no information on overdosage with tiopronin.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in animals have not been performed.
Mutagenesis
Tiopronin was not genotoxic in the chromosomal aberration, sister chromatid
exchange, and in vivo
micronucleus assays.
Impairment of Fertility
High doses of tiopronin in experimental animals have been shown to interfere
with maintenance of pregnancy
and viability of the fetus. In 2 published male fertility studies in rats,
tiopronin at 20 mg/kg/day intramuscular
(IM) for 60 days induced reductions in testis, epididymis, vas deferens, and
accessory sex glands weights and
in the count and motility of cauda epididymal sperm.
PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Lactation
Advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with THIOLA [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
100 mg round, white, immediate-release tablet imprinted in red with “M” on one
side and blank on the other
side: Bottles of 100NDC0178-0900-01.
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
