Xepi
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use XEPI™ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for XEPI™. XEPI™ (ozenoxacin) cream, for topical useInitial U.S. Approval: 2017
2765b37b-4862-473f-b4cd-8da908088e8b
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 25, 2023
Biofrontera Inc.
DUNS: 080213133
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
ozenoxacin
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 g Tube Carton
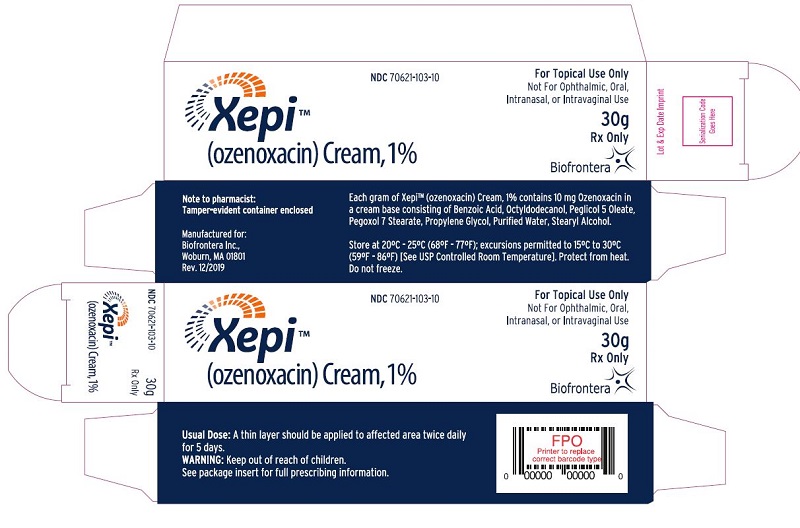
Xepi****TM
(ozenoxacin) Cream, 1%
NDC 70621-103-10
For Topical Use Only
Not for Ophthalmic, Oral, Intranasal, or Intravaginal Use
30g
Rx Only
Biofrontera
Note to pharmacist:
Tamper-evident container enclosed
Manufactured for:
Biofrontera Inc.,
Woburn, MA 01801
Rev. 12/2019
Each gram of XepiTM (ozenoxacin) Cream, 1% contains 10 mg Ozenoxacin in a cream base consisting of Benzoic Acid, Octyldodecanol, Peglicol 5 Oleate, Pegoxol 7 Stearate, Propylene Glycol, Purified Water, Stearyl Alcohol.
Store at 20ºC - 25ºC (68ºF - 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF
- 86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from heat. Do not freeze.
Usual Dose: A thin layer should be applied to affected area twice daily
for 5 days.
Warning: Keep out of reach of children.
See package insert for full prescribing information.
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety profile of XEPI was assessed in two clinical trials (Trial 1 and Trial 2) in 362 adult and pediatric patients two months of age and older with impetigo. The patients used at least one dose from a 5-day, twice a day regimen of XEPI. Control groups included 361 patients who used placebo and 152 patients who used retapamulin ointment. The median age of the patients enrolled in the clinical trials was 10 years; 3 % of patients were 2 months to less than 2 years of age, 55 % of patients were 2 to less than 12 years of age, 11 % of patients were 12 to less than 18 years of age, and 31 % of patients were 18 years of age or older.
Adverse reactions (rosacea and seborrheic dermatitis) were reported in 1 adult patient treated with XEPI.
Adverse reactions (rosacea and seborrheic dermatitis) were reported in 1 adult patient treated with XEPI (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Biofrontera, Inc. at 1-844-829-7434 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
XEPI is an antimicrobial drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Exposure-Response Relationship
The exposure response relationship for ozenoxacin following topical application has not been studied, however; a relationship is unlikely because systemic exposure following topical application is negligible [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Four pharmacokinetic studies were conducted in 110 patients utilizing varying strengths of ozenoxacin cream, up to 2% (twice the concentration of the marketed formulation). Three of these studies assessed systemic absorption in healthy subjects and in subjects with impetigo. These studies were conducted with either single or repeated application of up to 1 g ozenoxacin cream to intact or abraded skin (up to 200 cm2 surface area). No systemic absorption was observed in 84 of 86 subjects, and negligible systemic absorption was observed at the level of detection (0.489 ng/mL) in 2 subjects.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of [14C]-ozenoxacin was moderate (~80 to 85%) and did not appear to be dependent on concentration. Since negligible systemic absorption was observed in clinical studies, tissue distribution has not been investigated in humans.
Elimination
Metabolism: Ozenoxacin was not metabolized in the presence of fresh human skin discs and was minimally metabolized in human hepatocytes.
Excretion: Studies have not been investigated in humans due to the negligible systemic absorption observed in clinical studies.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Ozenoxacin is a quinolone antimicrobial drug. The mechanism of action involves the inhibition of bacterial DNA replication enzymes, DNA gyrase A and topoisomerase IV. Ozenoxacin has been shown to be bactericidal against S. aureus and S. pyogenes organisms.
Resistance
The mechanism of quinolone resistance can arise through mutations of one or more of the genes that encode DNA gyrase or topoisomerase IV. Resistant organisms will typically carry a combination of mutations within gyrA and parC subunits.
Overall the frequency of resistant mutants selected by ozenoxacin is ≤10-10.
Interaction with Other Antimicrobials
Ozenoxacin has been tested in combination with 17 other commonly used antimicrobial agents against S. aureus and S.pyogenes. Antagonism interactions with ozenoxacin were observed with ciprofloxacin against S. aureus.
Antimicrobial Activity
Ozenoxacin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)]:
Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant isolates)
Streptococcus pyogenes
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted with ozenoxacin.
Ozenoxacin demonstrated no genotoxicity when evaluated in vitro for gene mutation and/or chromosomal effects in the Ames test, mouse lymphoma cell assay, or when evaluated in vivo in a rat micronucleus test with demonstrated systemic exposure.
Oral doses of ozenoxacin did not affect mating and fertility in male and female rats treated up to 500 mg/kg/day (about 8500 and 16,000 times respectively, the maximum human plasma concentration seen with dermal application of ozenoxacin 1% cream).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of XEPI for the treatment of impetigo was evaluated in two multi-center, randomized, double-blind placebo controlled clinical trials (Trial 1, (NCT01397461) and Trial 2, (NCT02090764)). Seven-hundred twenty- three (723) subjects two months of age and older with an affected body surface area of up to 100 cm2, and not exceeding 2% for subjects aged 2 months to 11 years were randomized to XEPI or placebo. Subjects applied XEPI or placebo twice daily for 5 days. Subjects with underlying skin disease (e.g., preexisting eczematous dermatitis), skin trauma, clinical evidence of secondary infection, or systemic signs and symptoms of infection (such as fever), were excluded from these studies.
Overall clinical success was defined as no need for additional antimicrobial therapy of the baseline affected area(s) and absence/reduction in clinical signs and symptoms assessed at the end of therapy (Day 6-7), as follows: absence of exudates/pus, crusting, tissue warmth, and pain; and erythema/inflammation, tissue edema, and itching assessed as less than mild in Trial 1; and absence of blistering, exudates/pus, crusting, and itching/pain, and mild or improved erythema/inflammation in Trial 2. Table 2 below presents the results for clinical response at the end of therapy.
Table 2 Clinical Response at End of Therapy in Trial 1 and Trial 2 in All Randomized Subjects|
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
XEPI |
Placebo |
XEPI |
Placebo | |
|
(N = 155) |
(N = 156) |
(N = 206) |
(N = 206) | |
|
a The success rates for ozenoxacin were significantly different than placebo in Study 1 and Study 2 (p = 0.002 and p = 0.001). | ||||
|
Clinical success |
54 (34.8) |
30 (19.2) |
112 (54.4) |
78 (37.9) |
|
Clinical failure |
98 (63.2) |
120 (76.9) |
91 (44.2) |
121 (58.7) |
|
Unable to determine |
3 (1.9) |
6 (3.8) |
3 (1.5) |
7 (3.4) |
The most commonly identified bacteria were S. aureus and S. pyogenes. Table 3 below presents the results for clinical success at end of therapy in subjects with S.aureus or S.pyogenes at baseline.
Table 3 Clinical Success at End of Therapy in Trial 1 and Trial 2 in Subjects with S. aureus or S. pyogenes|
Trial 1 |
Trial 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
XEPI |
Placebo |
XEPI |
Placebo | |
|
Clinical success |
n/N (%) |
n/N (%) |
n/N (%) |
n/N (%) |
|
S. aureus |
35/93 (37.6) |
16/98 (16.3) |
66/115 (57.4) |
36/108 (33.3) |
|
S. pyogenes |
29/73 (39.7) |
7/67 (10.4) |
15/19 (78.9) |
8/20 (40.0) |
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
XEPI cream, 1% is a pale yellow cream supplied in a 30-gram tube. Each gram of cream contains 10 mg of ozenoxacin.
NDC 70621-103-01 (30-gram tube)
NDC 70621-103-10 (Cardbox containing one 30-gram tube)
Store at 20ºC - 25ºC (68ºF - 77ºF); excursions permitted to 15ºC to 30ºC (59ºF
- 86ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
