Colesevelam hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use COLESEVELAM HYDROCHLORIDE FOR ORAL SUSPENSION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for COLESEVELAM HYDROCHLORIDE FOR ORAL SUSPENSION. COLESEVELAM HYDROCHLORIDE for oral suspension Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
dbed6967-b261-44a1-bee4-638810e2efe9
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 12, 2024
Bryant Ranch Prepack
DUNS: 171714327
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Colesevelam hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Drug Labeling Information
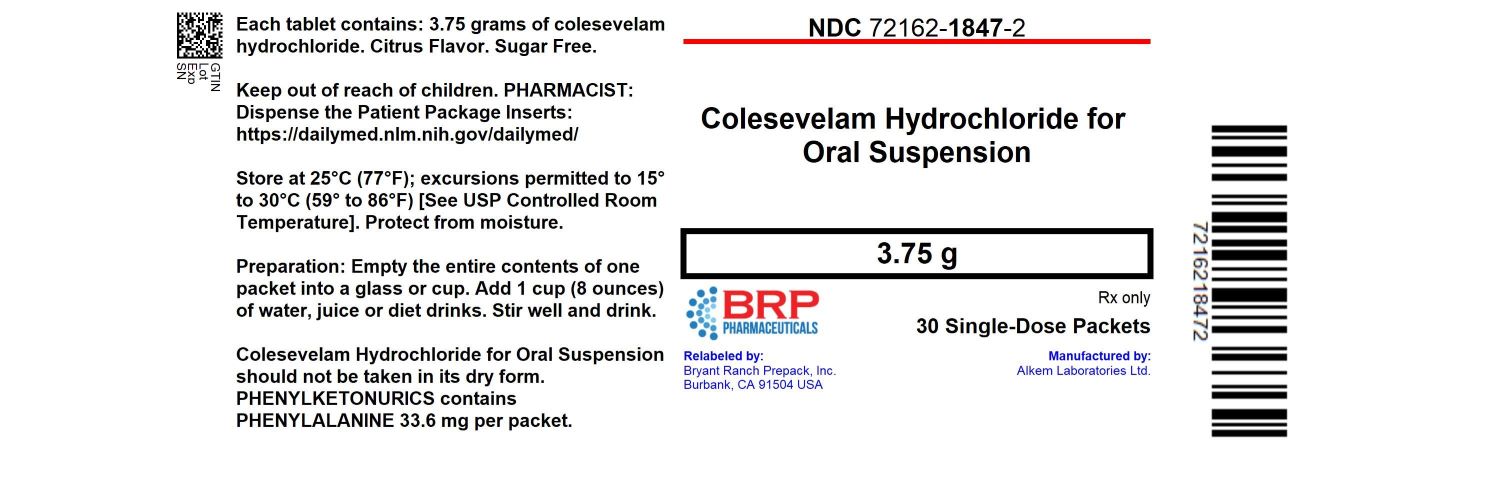
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Colesevelam Hcl 3.75 g for Oral Susp #30
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
Colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia.
Colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension is indicated to reduce LDL-C levels in boys and postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH) who are unable to reach LDL-C target levels despite an adequate trial of dietary therapy and lifestyle modification.
1.3 Limitations of Use
- Colesevelam hydrochloride should not be used for the treatment of type 1 diabetes or for the treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Colesevelam hydrochloride has not been studied in Fredrickson Type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias.
Colesevelam hydrochloride is a bile acid sequestrant indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to:
- reduce elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in adults with primary hyperlipidemia (1.1).
- reduce LDL-C levels in boys and postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age, with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH), unable to reach LDL-C target levels despite an adequate trial of diet and lifestyle modification (1.1).
Limitations of Use (1.3):
- Do not use for treatment of type 1 diabetes or for diabetic ketoacidosis.
- Not studied in Fredrickson Type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Colesevelam hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with:
- Serum TG concentrations greater than 500 mg/dL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- History of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- A history of bowel obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Patients with serum triglyceride levels greater than 500 mg/dL (4)
- Patients with a history of hypertriglyceridemia-induced pancreatitis (4)
- Patients with a history of bowel obstruction (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypertriglyceridemia and Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Gastrointestinal Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Vitamin K or Fat-Soluble Vitamin Deficiencies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
** Primary Hyperlipidemia**
****In 7 double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials, 807 patients with
primary hyperlipidemia (age range 18 to 86 years, 50% women, 90% Caucasians,
7% Blacks, 2% Hispanics, 1% Asians) and elevated LDL-C were treated with
colesevelam hydrochloride 1.5 g/day to 4.5 g/day from 4 to 24 weeks (total
exposure 199 patient-years).
Table 1
Clinical Studies of Colesevelam Hydrochloride for Primary Hyperlipidemia: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 2% of Patients and More Commonly than in Placebo
|
Colesevelam hydrochloride |
Placebo | |
|
Constipation |
11.0% |
7.0% |
|
Dyspepsia |
8.3% |
3.5% |
|
Nausea |
4.2% |
3.9% |
|
Accidental injury |
3.7% |
2.7% |
|
Asthenia |
3.6% |
1.9% |
|
Pharyngitis |
3.2% |
1.9% |
|
Flu syndrome |
3.2% |
3.1% |
|
Rhinitis |
3.2% |
3.1% |
|
Myalgia |
2.1% |
0.4% |
** Pediatric Patients 10 to 17 Years of Age**
****In an 8-week double-blind, placebo-controlled study, boys and post-
menarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age, with HeFH (n=194), were treated with
colesevelam hydrochloride tablets (1.9 to 3.8 g, daily) or placebo tablets.
Table 2
Clinical Study ofColesevelam Hydrochloride for Primary Hyperlipidemia in HeFH Pediatric Patients: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥2% of Patients and More Commonly than in Placebo
|
Colesevelam Hydrochloride |
Placebo | |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
6.2% |
4.6% |
|
Headache |
3.9% |
3.1% |
|
Fatigue |
3.9% |
1.5% |
|
Creatine Phosphokinase Increase |
2.3% |
0.0% |
|
Rhinitis |
2.3% |
0.0% |
|
Vomiting |
2.3% |
1.5% |
The reported adverse reactions during the additional 18-week open-label treatment period with colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g per day were similar to those during the double-blind period and included headache (7.6%), nasopharyngitis (5.4%), upper respiratory tract infection (4.9%), influenza (3.8%), and nausea (3.8%).
6.2 Post-marketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post- approval use of colesevelam hydrochloride. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse Reactions Resulting from Drug Interactions[see Drug Interactions (7)]: Increased seizure activity or decreased phenytoin levels in patients receiving phenytoin, reduced International Normalized Ratio (INR) in patients receiving warfarin therapy, and elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in patients receiving thyroid hormone replacement therapy
Gastrointestinal: Bowel obstruction (in patients with a history of bowel obstruction or resection), dysphagia or esophageal obstruction (occasionally requiring medical intervention), fecal impaction, pancreatitis, abdominal distension, exacerbation of hemorrhoids, and increased transaminases
Laboratory Abnormalities: Hypertriglyceridemia
In clinical trials, the most common (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) adverse reactions with Colesevelam hydrochloride included constipation, dyspepsia, and nausea (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ascend Laboratories, LLC at 1-877-ASC-RX01 (877-272-7901) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch**.**
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Colesevelam Hydrochloride Drug Interactions that Decrease the Exposure
of the Concomitant Medication
Table 4 includes a list of drugs that decrease exposure of the concomitant medication when administered concomitantly with colesevelam hydrochloride and instructions for preventing or managing them.
Table 4
Colesevelam Hydrochloride Drug Interactions that Decrease the Exposure of the
Concomitant Medication
|
Drugs with a Narrow Therapeutic Index | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Concomitant use with colesevelam hydrochloride may decrease the exposure of the narrow therapeutic index drug. In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in exposure of cyclosporine when coadministered with colesevelam hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Administer the narrow therapeutic index drug at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. Monitor drug levels when appropriate. |
|
Examples: |
Cyclosporine |
|
Phenytoin | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
There have been postmarketing reports of increased seizure activity or decreased phenytoin levels in patients receiving phenytoin [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Administer phenytoin 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. |
|
Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in exposure of levothyroxine when coadministered with colesevelam hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. There have been postmarketing reports of elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in patients receiving thyroid hormone replacement therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Administer thyroid hormone replacement therapy 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. |
|
Warfarin | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
There have been postmarketing reports of reduced INR in patients receiving warfarin therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor INR frequently during colesevelam hydrochloride initiation then periodically thereafter. |
|
Oral Contraceptives Containing Ethinyl Estradiol and Norethindrone | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in exposure of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone when coadministered with colesevelam hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Administer oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. |
|
Olmesartan Medoxomil | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in olmesartan medoxomil when coadministered with colesevelam hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Administer olmesartan medoxomil 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. |
|
Sulfonylureas | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
In vivo drug interactions studies showed a decrease in sulfonylureas when coadministered with colesevelam hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Administer sulfonylureas 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. |
|
Examples: |
Glimepiride, glipizide, and glyburide |
|
Oral Vitamin Supplements | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Colesevelam hydrochloride may decrease the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Patients on oral vitamin supplementation should take their vitamins at least 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride. |
7.2 Colesevelam Hydrochloride Drug Interactions that Increase the Exposure
of the Concomitant Medication
Table 5
Colesevelam Hydrochloride Drug Interactions that Increase the Exposure of the Concomitant Medication
|
Metformin Extended Release (ER) | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
In vivo drug interactions studies showed an increase in metformin extended release (ER) when coadministered with colesevelam hydrochloride [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients' glycemic control. |
Concomitant use with colesevelam hydrochloride may decrease the exposure of the following drugs: Drugs with a narrow therapeutic index (e.g., cyclosporine), phenytoin, thyroid hormone replacement therapy, warfarin, oral contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone, olmesartan medoxomil, and sulfonylureas (glimepiride, glipizide, glyburide). Administer these drugs 4 hours prior to colesevelam hydrochloride tablets. For patients on warfarin, monitor International Normalized Ratio (INR) frequently during initiation then periodically (7.1).
Concomitant use with colesevelam hydrochloride may increase the exposure of the following drugs: Metformin extended release. Monitor patients glycemic control (7.2).
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- Colesevelam Hydrochloride for Oral Suspension: a white to yellow granular powder containing yellow granules packaged in single-dose packets: 3.75 gram single-dose packet.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Colesevelam hydrochloride is not absorbed systemically following oral administration, and maternal use is not expected to result in fetal exposure to the drug. Limited available data on the use of colesevelam hydrochloride are insufficient to determine a drug-associated risk of major congenital malformations or miscarriage. In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of either maternal or fetal toxicity was found in rats or rabbits exposed to colesevelam hydrochloride during the period of fetal organogenesis at 8 and 5 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 3.75 g/day, based on body surface area (mg/m2). No adverse effects on offspring survival and development were observed in rats administered 5 times the MRHD (see Data).Colesevelam hydrochloride may decrease the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. There are no data available on the effect of colesevelam hydrochloride on the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins in pregnant women. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking colesevelam hydrochloride, the patient should be advised of the lack of known clinical benefit with continued use during pregnancy.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of colesevelam hydrochloride use in pregnant women.
In the postmarketing setting there have been infrequent reports of pregnancy with use of colesevelam hydrochloride and a causal association with congenital anomalies has not been established.
Animal Data
In pregnant rats given dietary doses of 0.3, 1.0, 3.0 g/kg/day colesevelam hydrochloride from gestation days 7 through 17, no teratogenic effects were observed. Exposures at 3.0 g/kg/day were 8 times the human exposure at 3.75 g/day MRHD, based on body surface area (mg/m2).
In pregnant rabbits given oral gavage doses of 0.1, 0.5, 1.0 g/kg/day colesevelam hydrochloride from gestation days 6 through 18, no teratogenic effects were observed. Exposures at 1.0 g/kg/day were 5 times the human exposure at 3.75 g/day MRHD, based on body surface area (mg/m2).
In pregnant rats given oral gavage doses of 0.1, 0.3, 1.0 g/kg/day colesevelam hydrochloride from gestation day 6 through lactation day 21 (weaning), no adverse effects on survival and development were observed. Exposures at 1.0 g/kg/day were 5 times the human exposure at 3.75 g/day MRHD, based on body surface area (mg/m2).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Colesevelam hydrochloride is not absorbed systemically by the mother following oral administration, and breastfeeding is not expected to result in exposure of the child to colesevelam hydrochloride.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Use of colesevelam hydrochloride may reduce the efficacy of oral contraceptives. Advise patients to take oral contraceptives at least 4 hours prior to taking colesevelam hydrochloride [see Drug Interactions (7)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Primary Hyperlipidemia
The safety and effectiveness of colesevelam hydrochloride to reduce LDL-C levels in boys and postmenarchal girls 10 to 17 years of age with HeFH who are unable to reach LDL-C target levels despite an adequate trial of dietary therapy and lifestyle modification have been established. Use of colesevelam hydrochloride for this indication is supported by a study in 129 colesevelam hydrochloride-treated pediatric patients aged 10 to 17 years with HeFH [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Adverse reactions commonly observed in pediatric patients compared to placebo, but not in adults, included headache (3.9%), creatine phosphokinase increase (2.3%), and vomiting (2.3%) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. There were no significant effects on fat-soluble vitamin levels or clotting factors in the adolescent boys or girls relative to placebo. Due to colesevelam hydrochloride tablet size, colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension is recommended for use in the pediatric population [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4)]. The safety and effectiveness of colesevelam hydrochloride in pediatric patients with HeFH less than 10 years of age or in premenarchal females have not been established.
Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
The safety and effectiveness of colesevelam hydrochloride to improve glycemic control in pediatric patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus have not been established.
Pediatric information describing a clinical study in which efficacy was not demonstrated is approved for Daiichi Sankyo Inc.’s Welchol® (colesevelam hydrochloride) powder for oral suspension. However, due to Daiichi Sankyo Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this product is not labeled with that information.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Primary Hyperlipidemia
Of the 1350 patients enrolled in the hyperlipidemia clinical studies, 349
(26%) were ≥65 years old, and 58 (4%) were ≥75 years old. No overall
differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects
and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not
identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients,
but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Colesevelam hydrochloride is not absorbed and the risk of systemic toxicity is low. Excessive doses of colesevelam hydrochloride may cause more severe local gastrointestinal effects (e.g., constipation).
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Colesevelam hydrochloride is a non-absorbed, polymeric, lipid-lowering and glucose-lowering agent for oral administration. Colesevelam hydrochloride is a high-capacity bile acid-binding molecule.
Colesevelam hydrochloride is poly(allylamine hydrochloride) cross-linked with
epichlorohydrin and alkylated with 1-bromodecane and
(6-bromohexyl)-trimethylammonium bromide. The chemical name (IUPAC) of
colesevelam hydrochloride is allylamine polymer with
1-chloro-2,3-epoxypropane, [6-(allylamino)-hexyl]trimethylammonium chloride
and N-allyldecylamine, hydrochloride. The chemical structure of colesevelam
hydrochloride is represented by the following formula:
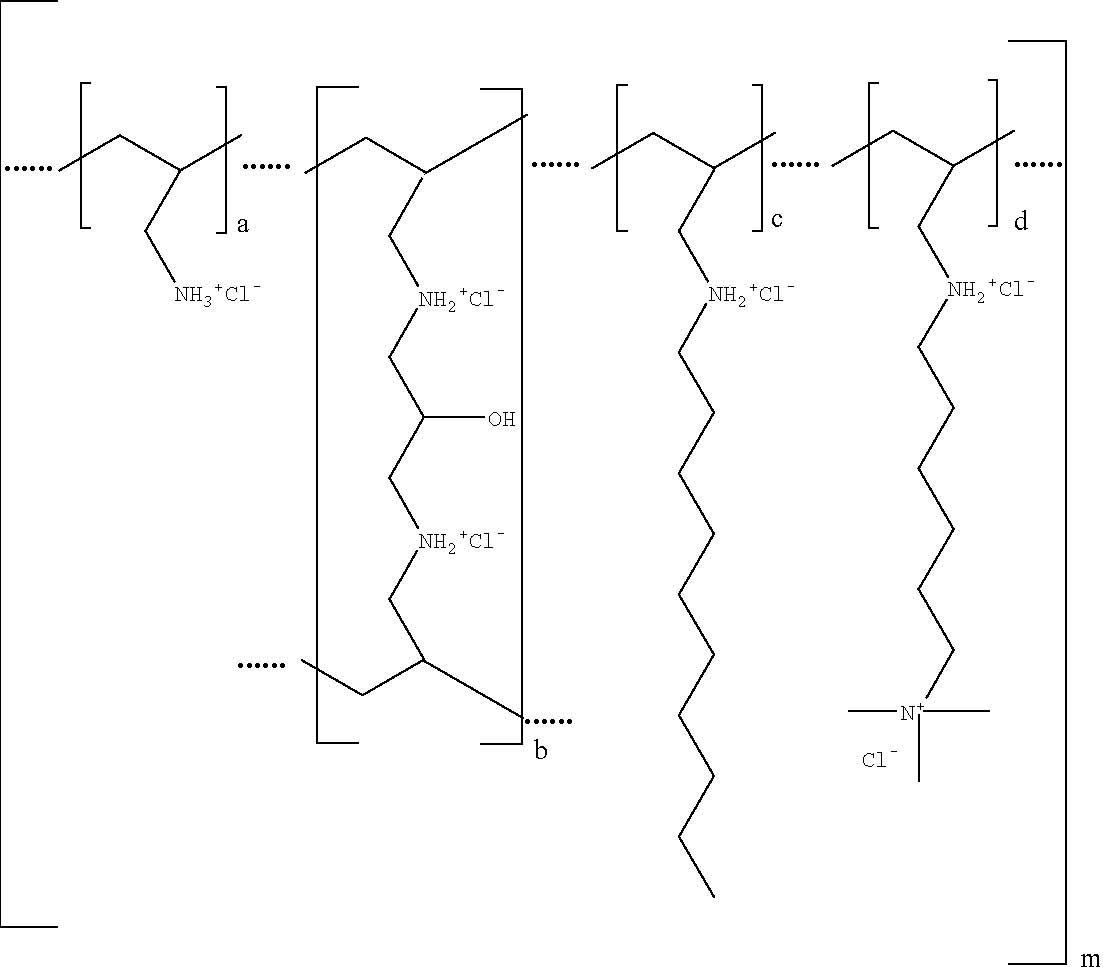
wherein (a) represents allyl amine monomer units that have not been alkylated by either of the 1-bromodecane or (6-bromohexyl)-trimethylammonium bromide alkylating agents or cross-linked by epichlorohydrin; (b) represents allyl amine units that have undergone cross-linking with epichlorohydrin; (c) represents allyl amine units that have been alkylated with a decyl group; (d) represents allyl amine units that have been alkylated with a (6-trimethylammonium) hexyl group, and m represents a number ≥ 100 to indicate an extended polymer network. A small amount of the amines are dialkylated and are not depicted in the formula above. No regular order of the groups is implied by the structure; cross-linking and alkylation are expected to occur randomly along the polymer chains. A large amount of the amines are protonated. The polymer is depicted in the hydrochloride form; a small amount of the halides are bromide. Colesevelam hydrochloride is hydrophilic and insoluble in water.
Colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension is a citrus-flavored, a white to yellow granular powder containing yellow granules packaged in single-dose packets containing 3.75 gram colesevelam hydrochloride. In addition, each packet contains the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, medium chain triglycerides, simethicone emulsion, colloidal silicon dioxide, propylene glycol alginate, magnesium trisilicate, lemon-lime flavor, orange flavor, citric acid monohydrate, and aspartame (<5 calories per 3.75 gram single-dose packet).PHENYLKETONURICS: colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension contains 33.6 mg phenylalanine per 3.75 gram dose.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Primary Hyperlipidemia: Colesevelam hydrochloride, the active pharmaceutical ingredient in colesevelam hydrochloride, is a non-absorbed, lipid-lowering polymer that binds bile acids in the intestine, impeding their reabsorption. As the bile acid pool becomes depleted, the hepatic enzyme, cholesterol 7-α-hydroxylase, is upregulated, which increases the conversion of cholesterol to bile acids. This causes an increased demand for cholesterol in the liver cells, resulting in the dual effect of increasing transcription and activity of the cholesterol biosynthetic enzyme, HMG-CoA reductase, and increasing the number of hepatic LDL receptors. These compensatory effects result in increased clearance of LDL-C from the blood, resulting in decreased serum LDL-C levels. Serum TG levels may increase or remain unchanged.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
A maximum therapeutic response to the lipid-lowering effects of colesevelam hydrochloride was achieved within 2 weeks and was maintained during long-term therapy. In the diabetes clinical studies, a therapeutic response to colesevelam hydrochloride, as reflected by a reduction in HbA1c, was initially noted following 4 to 6 weeks of treatment and reached maximal or near-maximal effect after 12 to 18 weeks of treatment.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Colesevelam hydrochloride is a hydrophilic, water-insoluble polymer that is
not hydrolyzed by digestive enzymes and is not absorbed.
Distribution
Colesevelam hydrochloride is not absorbed, and therefore, its distribution is
limited to the gastrointestinal tract.
Elimination
Metabolism
Colesevelam hydrochloride is not metabolized systemically and does not
interfere with systemic drug-metabolizing enzymes such as cytochrome P450.
Excretion
In 16 healthy volunteers, an average of 0.05% of administered radioactivity
from a single 14C-labeled colesevelam hydrochloride dose was excreted in the
urine.
Drug Interaction Studies
Drug interactions between colesevelam and concomitantly administered drugs
were screened through in vitro studies and confirmed in in vivo studies. In
vitro studies demonstrated that cephalexin, metformin, and ciprofloxacin had
negligible binding to colesevelam hydrochloride. Therefore, an in vivo
pharmacokinetic interaction of colesevelam hydrochloride with these drugs is
unlikely. Colesevelam hydrochloride was found to have no significant effect on
the bioavailability of aspirin, atenolol, digoxin, enalapril, fenofibrate,
lovastatin, metoprolol, phenytoin, pioglitazone, quinidine, rosiglitazone,
sitagliptin, valproic acid, and warfarin. The results of additional in vivo
drug interactions of colesevelam hydrochloride are presented in Table 6.
** Table 6**
Mean Change in Drug Exposure (AUC0 to ∞ and Cmax) when Administered withColesevelam Hydrochloride (3.75 g)*****
|
Drug |
Dose |
Co-administered |
1 hr prior to |
4 hr prior to | |||
|
AUC0 to ∞ |
Cmax |
AUC0 to ∞ |
Cmax |
AUC0 to ∞ |
Cmax | ||
|
Cyclosporine |
200 mg |
-34% |
-44% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Ethinyl |
0.035 mg |
-24% |
-24% |
-18% |
-1% |
-12% |
0% |
|
Glimepiride |
4 mg |
-18% |
-8% |
N/A |
N/A |
-6% |
3% |
|
Glipizide |
20 mg |
-12% |
-13% |
N/A |
N/A |
-4% |
0% |
|
Glyburide |
3 mg |
-32% |
-47% |
-20% |
-15% |
-7% |
4% |
|
Levothyroxine |
600 μg |
-22% |
-33% |
6% |
-2% |
1% |
8% |
|
Metformin ER |
1500 mg |
44% |
8% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Norethindrone† |
1 mg |
-1% |
-20% |
5% |
-3% |
6% |
7% |
|
Olmesartan Medoxomil |
40 mg |
-39% |
-28% |
N/A |
N/A |
-15% |
-4% |
|
Repaglinide |
2 mg |
-7% |
-19% |
-6% |
-1% |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Verapamil sustained-release |
240 mg |
-31% |
-11% |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
N/A |
*With verapamil, the dose of colesevelam hydrochloride was 4.5 g.
†Oral contraceptive containing norethindrone and ethinyl estradiol
N/A – not available
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
Colesevelam hydrochloride reduces total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, apolipoprotein B (Apo B), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non- HDL-C) when administered alone or in combination with a statin in patients with primary hyperlipidemia.
Approximately 1,600 patients were studied in 9 clinical trials with treatment durations ranging from 4 to 50 weeks. With the exception of one open-label, uncontrolled, long-term extension study, all studies were multicenter, randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. A maximum therapeutic response to colesevelam hydrochloride was achieved within 2 weeks and was maintained during long-term therapy.
Monotherapy
In a study in patients with LDL-C between 130 mg/dL and 220 mg/dL (mean 158 mg/dL), colesevelam hydrochloride was given for 24 weeks in divided doses with the morning and evening meals.
As shown in Table 7, the mean LDL-C reductions were 15% and 18% at the 3.8 g and 4.5 g doses. The respective mean TC reductions were 7% and 10%. The mean Apo B reductions were 12% in both treatment groups. colesevelam hydrochloride at both doses increased HDL-C by 3%. Increases in TG of 9 to 10% were observed at both colesevelam hydrochloride doses, but the changes were not statistically different from placebo.
Table 7
Response toColesevelam Hydrochloride Monotherapy in a 24-Week Trial -Percent Change in Lipid Parameters from Baseline
|
Grams/ |
** N** |
** TC** |
** LDL-C** |
** Apo B** |
** HDL-C******* |
Non-HDL-C |
** TG*********** |
|
Placebo |
88 |
+1 |
0 |
0 |
–1 |
+1 |
+5 |
|
3.8 g |
95 |
–7† |
–15† |
–12† |
+3† |
–10† |
+10 |
|
4.5 g |
94 |
–10† |
–18† |
–12† |
+3 |
–13† |
+9 |
*Median % change from baseline.
†p less than 0.05 for lipid parameters compared to placebo, for Apo B compared to baseline.
In a study in 98 patients with LDL-C between 145 mg/dL and 250 mg/dL (mean 169 mg/dL), colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g was given for 6 weeks as a single dose with breakfast, as a single dose with dinner, or as divided doses with breakfast and dinner. The mean LDL-C reductions were 18%, 15%, and 18% for the 3 dosing regimens, respectively. The reductions with these 3 regimens were not statistically different from one another.
Combination Therapy
Co-administration of colesevelam hydrochloride and a statin (atorvastatin, lovastatin, or simvastatin) in 3 clinical studies demonstrated an additive reduction of LDL-C. The mean baseline LDL-C was 184 mg/dL in the atorvastatin study (range 156 to 236 mg/dL), 171 mg/dL in the lovastatin study (range 115 to 247 mg/dL), and 188 mg/dL in the simvastatin study (range 148 to 352 mg/dL). As demonstrated in Table 8, colesevelam hydrochloride doses of 2.3 g to 3.8 g resulted in an additional 8% to 16% reduction in LDL-C above that seen with the statin alone.
** Table 8**
Response toColesevelam Hydrochloride in Combination with Atorvastatin, Simvastatin, or Lovastatin -Percent Change in Lipid Parameters
|
** Dose/Day** |
** N** |
** TC** |
** LDL-C** |
** Apo B** |
** HDL-C******* |
Non-HDL-C |
** TG*********** |
|
Atorvastatin Trial (4-week) | |||||||
|
Placebo |
19 |
+4 |
+3 |
–3 |
+4 |
+4 |
+10 |
|
Atorvastatin 10 mg |
18 |
–27† |
–38† |
–32† |
+8 |
–35† |
–24† |
|
Colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g/ |
18 |
–31† |
–48† |
–38† |
+11 |
–40† |
–1 |
|
Atorvastatin 80 mg |
20 |
–39† |
–53† |
–46† |
+6 |
–50† |
–33† |
|
Simvastatin Trial (6-week) | |||||||
|
Placebo |
33 |
–2 |
–4 |
–4† |
–3 |
–2 |
+6† |
|
Simvastatin 10 mg |
35 |
–19† |
–26† |
–20† |
+3† |
–24† |
–17† |
|
Colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g/ |
34 |
–28† |
–42† |
–33† |
+10† |
–37† |
–12† |
|
Simvastatin 20 mg |
39 |
–23† |
–34† |
–26† |
+7† |
–30† |
–12† |
|
Colesevelam hydrochloride 2.3 g/ |
37 |
–29† |
–42† |
–32† |
+4† |
–37† |
–12† |
|
Lovastatin Trial (4-week) | |||||||
|
Placebo |
26 |
+1 |
0 |
0 |
+1 |
+1 |
+1 |
|
Lovastatin 10 mg |
26 |
–14† |
–22† |
–16† |
+5 |
–19† |
0 |
|
Colesevelam hydrochloride 2.3 g/ Lovastatin 10 mg Together |
27 |
–21† |
–34† |
–24† |
+4 |
–27† |
–1 |
|
Colesevelam hydrochloride 2.3 g/ Lovastatin 10 mg Apart |
23 |
–21† |
–32† |
–24† |
+2 |
–28† |
–2 |
*Median % change from baseline
† p less than 0.05 for lipid parameters compared to placebo, for Apo B compared to baseline
In all 3 studies, the LDL-C reduction achieved with the combination of colesevelam hydrochloride and any given dose of statin therapy was statistically superior to that achieved with colesevelam hydrochloride or that dose of the statin alone. The LDL-C reduction with atorvastatin 80 mg was not statistically significantly different from the combination of colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g and atorvastatin 10 mg.
Pediatric Therapy
The safety and efficacy of colesevelam hydrochloride in pediatric patients were evaluated in an 8-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled, parallel-group study followed by an open-label phase, in 194 boys and postmenarchal girls 10 to 17 years of age (mean age 14.1 years) with HeFH, taking a stable dose of an FDA-approved statin (with LDL-C greater than 130 mg/dL) or naïve to lipid-lowering therapy (with LDL-C greater than 160 mg/dL). This study had 3 periods: a single-blind, placebo stabilization period; an 8-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo-controlled treatment period; and an 18-week, open-label treatment period. Forty-seven (24%) patients were taking statins and 147 (76%) patients were statin-naïve at screening. The mean baseline LDL-C at Day 1 was approximately 199 mg/dL.
During the double-blind treatment period, patients were assigned randomly to treatment: colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g/day (n=64), colesevelam hydrochloride 1.9 g/day (n=65), or placebo (n=65). In total, 186 patients completed the double-blind treatment period. After 8 weeks of treatment, colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g/day significantly decreased plasma levels of LDL-C, non-HDL-C, TC, and Apo B and significantly increased HDL-C. A moderate, non-statistically significant increase in TG was observed versus placebo (Table 9).
** Table 9**
Response toColesevelam Hydrochloride 3.8 g Compared to Placebo in Pediatric Patients 10 to 17 Years of Age – Mean Percent Change in Lipid Parameters from Baseline to Week 8
|
Treatment |
** TC** |
** LDL-C** |
** Apo B** |
** HDL-C** |
** Non-HDL-C** |
TG***** |
|
Colesevelam Hydrochloride |
-7† |
-13† |
-8† |
+6† |
-11† |
+5 |
*For triglycerides, median % change from baseline
†p≤0.05 for lipid parameters compared to placebo
Values represent LS mean. Only patients with values at both study baseline and endpoint are included in this table. Study baseline was defined as the last value measured before or on Day 1 prior to the first dose of randomized study medication.
Results were based on the ITT population with LOCF.
During the open-label treatment period patients were treated with colesevelam hydrochloride 3.8 g/day. In total, 173 (89%) patients completed 26 weeks of treatment. Results at Week 26 were consistent with those at Week 8.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension is a white to yellow granular powder containing yellow granules.
3.75 gram single-dose packet
NDC: 72162-1847-2: 30 single-dose packet
Store at 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].Protect from moisture.
Repackaged/Relabeled by:
Bryant Ranch Prepack, Inc.
Burbank, CA 91504
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation of Colesevelam Hydrochloride
Obtain lipid parameters, including triglyceride (TG) levels, before starting colesevelam hydrochloride. Colesevelam hydrochloride is contraindicated in patients with TG levels greater than 500 mg/dL [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Primary Hyperlipidemia
The recommended dosage of colesevelam hydrochloride for adults and for boys and postmenarchal girls aged 10 to 17 years with primary hyperlipidemia is 3.75 grams daily.
Colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension should be taken as follows:
For Oral Suspension
Take one packet once daily.
2.3 Important Dosing Information for Primary Hyperlipidemia
Colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension can be dosed at the same time as a statin, or colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension and the statin can be dosed apart. Monitor lipid levels within 4 to 6 weeks after initiation of colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension.
2.4 Administration Instructions
For Oral Suspension
To prepare, empty the entire contents of one packet into a glass or cup. Add 1 cup (8 ounces) of water, fruit juice, or diet soft drinks. Stir well and drink. Take colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension with meals. Do not take colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension in its dry form. Due to tablet size, colesevelam hydrochloride for oral suspension is recommended for use in the pediatric population.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment Of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
A 104-week carcinogenicity study with colesevelam hydrochloride was conducted
in CD-1 mice, at oral dietary doses up to 3 g/kg/day. This dose was
approximately 50 times the maximum recommended human dose of 4.5 g/day, based
on body weight, mg/kg. There were no significant drug-induced tumor findings
in male or female mice. In a 104-week carcinogenicity study with colesevelam
hydrochloride in Harlan Sprague-Dawley rats, a statistically significant
increase in the incidence of pancreatic acinar cell adenoma was seen in male
rats at doses greater than 1.2 g/kg/day (approximately 20 times the maximum
human dose, based on body weight, mg/kg) (trend test only). A statistically
significant increase in thyroid C-cell adenoma was seen in female rats at 2.4
g/kg/day (approximately 40 times the maximum human dose, based on body weight,
mg/kg).
Mutagenesis
Colesevelam hydrochloride and 4 degradants present in the drug substance have
been evaluated for mutagenicity in the Ames test and a mammalian chromosomal
aberration test. The 4 degradants and an extract of the parent compound did
not exhibit genetic toxicity in an in vitro bacterial mutagenesis assay in S.
typhimurium and E. coli (Ames assay) with or without rat liver metabolic
activation. An extract of the parent compound was positive in the Chinese
Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell chromosomal aberration assay in the presence of
metabolic activation and negative in the absence of metabolic activation. The
results of the CHO cell chromosomal aberration assay with 2 of the 4
degradants, decylamine HCl and aminohexyltrimethyl ammonium chloride HCl, were
equivocal in the absence of metabolic activation and negative in the presence
of metabolic activation. The other 2 degradants, didecylamine HCl and
6-decylamino-hexyltrimethyl ammonium chloride HCl, were negative in the
presence and absence of metabolic activation.
Impairment of Fertility
Colesevelam hydrochloride did not impair fertility in rats at doses up to 3
g/kg/day (approximately 50 times the maximum human dose, based on body weight,
mg/kg).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Reproductive Toxicology Studies
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at doses up to 3 g/kg/day and 1 g/kg/day, respectively (approximately 50 and 17 times the maximum human dose, based on body weight, mg/kg) and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to colesevelam hydrochloride.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hypertriglyceridemia and Pancreatitis
Inform patients that colesevelam hydrochloride may increase their serum
triglycerides which can lead to hypertriglyceridemia and pancreatitis.
Instruct patients to discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride and seek prompt
medical attention if the symptoms of acute pancreatitis occur (e.g., severe
abdominal pain with or without nausea and vomiting) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal
Inform patients that colesevelam hydrochloride may cause bowel obstruction.
Instruct patients to promptly discontinue colesevelam hydrochloride and seek
medical attention if severe abdominal pain or severe constipation occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Drug and Vitamin Interactions
Advise patients that colesevelam hydrochloride has drug interactions, and
colesevelam hydrochloride may decrease the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
A, D, E, and K. Instruct patients to take oral vitamins at least 4 hours prior
to colesevelam hydrochloride. Instruct patients to inform their physician
about all the drugs and vitamins that they are prescribed or take over the
counter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Hypertriglyceridemia and Cardiovascular Disease
Inform patients that colesevelam hydrochloride may increase serum
triglycerides and that the long-term effect of hypertriglyceridemia on the
risk of coronary artery disease is uncertain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4)]:
For Oral Suspension
Instruct patients to empty the entire contents of one packet into a glass or
cup and add 1 cup (8 ounces) of water, fruit juice, or diet soft drinks. Stir
well and drink. Advise patients to take colesevelam hydrochloride oral
suspension with meals. Advise patient to not take colesevelam hydrochloride
oral suspension in its dry form.
Females of Reproductive Potential
Advise females of reproductive potential that colesevelam hydrochloride may
reduce the effectiveness of oral contraceptives, and to take oral
contraceptives at least 4 hours before taking colesevelam hydrochloride [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Manufactured by:
Alkem Laboratories Ltd.,
INDIA.
Distributed by:
Ascend Laboratories, LLC
Parsippany, NJ 07054
Revised: June, 2022
** PT 2768-05**
