Registrants1
Companies and organizations registered with the FDA for this drug approval, including their contact information and regulatory details.
080025838
Manufacturing Establishments1
FDA-registered manufacturing facilities and establishments involved in the production, packaging, or distribution of this drug product.
Casper Pharma LLC
Casper Pharma LLC
725656438
Products1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Edetate Calcium Disodium
Product Details
Drug Labeling Information
Complete FDA-approved labeling information including indications, dosage, warnings, contraindications, and other essential prescribing details.
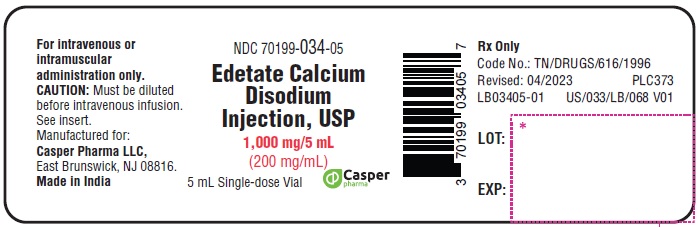
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
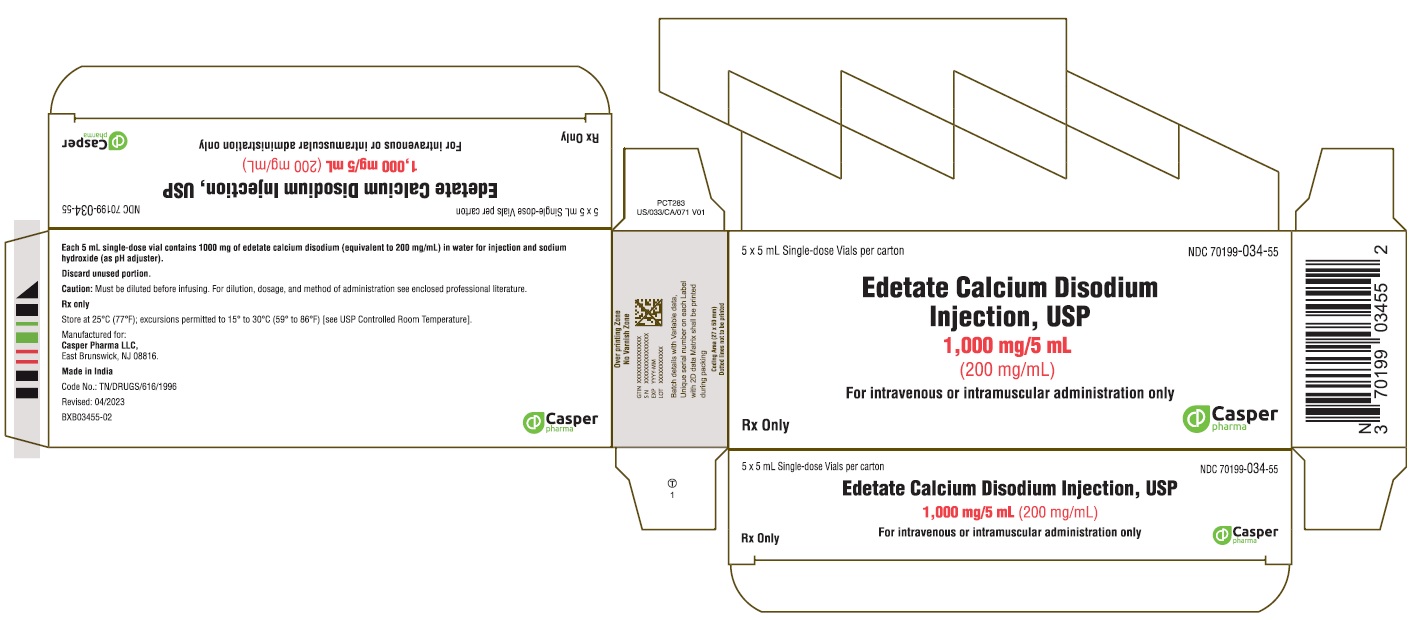
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 x 5 mL single-dose vials per carton
** Casper Pharma LLC**
Edetate Calcium Disodium Injection, USP
1000 mg/5 mL (200 mg/mL)
NDC 70199-034-05
5 mL single-dose vial
** NDC 70199-034-55**
5 x 5 mL single-dose vials per carton
For intravenous or intramuscular administration only
Rx Only
****
****
DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION
Edetate Calcium Disodium injection, USP is a sterile, injectable, chelating agent in concentrated solution for intravenous infusion or intramuscular injection. Each 5 mL single-dose vial contains 1000 mg of edetate calcium disodium (equivalent to 200 mg/mL) in water for injection and sodium hydroxide (as pH adjuster). Chemically, this product is called [N,N'-1,2-ethanediyl- bis[N-(carboxymethyl)-glycinato]-N,N',O,O',ON,ON']-, disodium, hydrate, (OC-6-21)-Calciate(2-).
Structural Formula:
****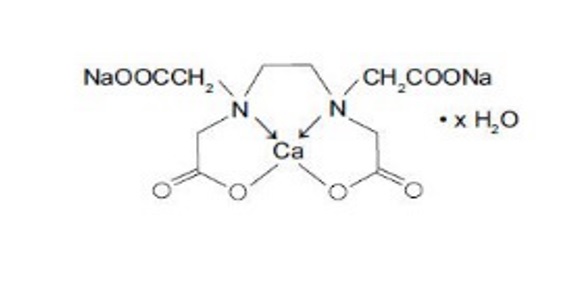
C10H12CaN2Na2O8 • × H2O
Molecular weight 374.27 (anhydrous)
PRECAUTIONS SECTION
PRECAUTIONS
General Precautions
Edetate calcium disodium may produce the same renal damage as lead poisoning, such as proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Treatment-induced nephrotoxicity is dose-dependent and may be reduced by assuring adequate diuresis before therapy begins. Urine flow must be monitored throughout therapy which must be stopped if anuria or severe oliguria develop. The proximal tubule hydropic degeneration usually recovers upon cessation of therapy. Edetate calcium disodium must be used in reduced doses in patients with pre-existing mild renal disease. Patients should be monitored for cardiac rhythm irregularities and other ECG changes during intravenous therapy.
Information for patients
Patients should be instructed to immediately inform their physician if urine output stops for a period of 12 hours.
Laboratory Tests
Urinalysis and urine sediment, renal and hepatic function and serum electrolyte levels should be checked before each course of therapy and then be monitored daily during therapy in severe cases, and in less serious cases after the second and fifth day of therapy. Therapy must be discontinued at the first sign of renal toxicity. The presence of large renal epithelial cells or increasing number of red blood cells in urinary sediment or greater proteinuria call for immediate stopping of edetate calcium disodium administration. Alkaline phosphatase values are frequently depressed (possibly due to decreased serum zinc levels), but return to normal within 48 hours after cessation of therapy. Elevated erythrocyte protoporphyrin levels (> 35 mcg/dl of whole blood) indicate the need to perform a venous blood lead determination. If the whole blood lead concentration is between 25 to 55 mcg/dl a mobilization test can be considered.7,8 (SeeDiagnostic Test.) An elevation of urinary coproporphyrin (adults: > 250 mcg/day; pediatric patients under 80 lbs: > 75 mcg/day) and elevation of urinary delta aminolevulinic acid (ALA) (adults: > 4 mg/day; pediatric patients: > 3 mg/m2/day) are associated with blood lead levels > 40 mcg/dl. Urinary coproporphyrin may be falsely negative in terminal patients and in severely iron-depleted pediatric patients who are not regenerating heme.9 In growing pediatric patients long bone x-rays showing lead lines and abdominal x-rays showing radio-opaque material in the abdomen may be of help in estimating the level of exposure to lead.
Drug Interactions
There is no known drug interference with standard clinical laboratory tests. Steroids enhance the renal toxicity of edetate calcium disodium in animals.7 Edetate calcium disodium interferes with the action of zinc insulin preparations by chelating the zinc.7
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long term animal studies have not been conducted with edetate calcium disodium to evaluate its carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or its effect on fertility.
Pregnancy
Category B
One reproduction study was performed in rats at doses up to 13 times the human dose and revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to edetate calcium disodium.10 Another reproduction study performed in rats at doses up to about 25 to 40 times the human dose revealed evidence of fetal malformations due to edetate calcium disodium, which were prevented by simultaneous supplementation of dietary zinc.11 There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
Edetate calcium disodium has no recognized use during labor and delivery, and its effects during these processes are unknown.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when edetate calcium disodium is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Since lead poisoning occurs in pediatric populations and adults but is frequently more severe in pediatric patients, edetate calcium disodium is used in patients of all ages. The intramuscular route is preferred by some for young pediatric patients. In cases where the intravenous route is necessary, avoid rapid infusion. (SeeWARNINGS.) Urine flow must be monitored throughout therapy; Edetate Calcium Disodium therapy must be stopped if anuria or severe oliguria develops. (SeeGeneral Precautions.) At no time should the recommended daily dosage be exceeded. (SeeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
