Renvela
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RENVELA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RENVELA. RENVELA (sevelamer carbonate) tablets, for oral use RENVELA (sevelamer carbonate) powder, for oral suspension Initial U.S. Approval: 2000
e6328460-a57b-450b-a48c-6dcd4b476360
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 3, 2025
Genzyme Corporation
DUNS: 025322157
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
SEVELAMER CARBONATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
SEVELAMER CARBONATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
SEVELAMER CARBONATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
SEVELAMER CARBONATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label - Principal Display Panel - 800 mg Tablets, 30 per Bottle
NDC 58468-0130-2
Rx only
Renvela®
sevelamer carbonate
tablets
800 mg
30 film-Coated Tablets
USUAL DOSAGE:
SEE PACKAGE INSERT
FOR DOSAGE INFORMATION.
Manufactured by:
Genzyme Ireland Ltd.
For: Genzyme Corporation
Cambridge, MA 02142 USA

DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
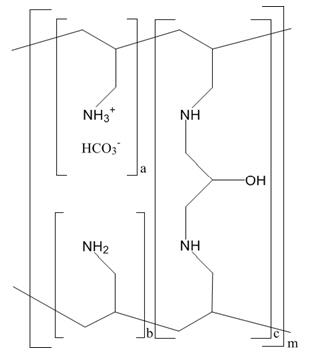
The active ingredient in Renvela is sevelamer carbonate, a polymeric amine that binds phosphate and is meant for oral administration. It was developed as a pharmaceutical alternative to sevelamer hydrochloride (Renagel ®). Sevelamer carbonate is an anion exchange resin, with the same polymeric structure as sevelamer hydrochloride, in which carbonate replaces chloride as the counterion. While the counterions differ for the two salts, the polymer itself, the active moiety involved in phosphate binding, is the same.
Renvela (sevelamer carbonate) is known chemically as poly(allylamine- co-N,N′-diallyl-1,3-diamino-2-hydroxypropane) carbonate salt. Sevelamer carbonate is hygroscopic, but insoluble in water. The structure is represented in Figure 1.
|
Figure 1: Chemical Structure of Sevelamer Carbonate | |
|
| |
|
a, b = number of primary amine groups |
a + b = 9 |
|
c = number of cross-linking groups |
c = 1 |
|
m = large number to indicate extended polymer network |
**Renvela Tablets:**Each film-coated tablet of Renvela contains 800 mg of sevelamer carbonate on an anhydrous basis. The inactive ingredients are hypromellose, diacetylated monoglycerides, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium chloride, and zinc stearate.
**Renvela Powder:**Each packet of Renvela powder contains 0.8 or 2.4 g of sevelamer carbonate on an anhydrous basis. The inactive ingredients are natural and artificial citrus flavor, propylene glycol alginate, sodium chloride, sucralose, and ferric oxide (yellow).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The ability of sevelamer to control serum phosphorus in CKD patients on dialysis was predominantly determined from the effects of the hydrochloride salt to bind phosphate. Six clinical trials used sevelamer hydrochloride and three clinical trials used sevelamer carbonate. The sevelamer hydrochloride studies include one double-blind, placebo-controlled 2-week study (sevelamer N=24); two open-label, uncontrolled, 8-week studies (sevelamer N=220); and three active-controlled open-label studies with treatment durations of 8 to 52 weeks (sevelamer N=256). The sevelamer carbonate studies include one double- blind, active-controlled, cross-over study with two 8-week treatment periods using sevelamer carbonate tablets (N=79); one open-label, active-controlled, cross-over study with two 4-week treatment periods using sevelamer carbonate powder (N=31); and one randomized, parallel, open-label study using sevelamer carbonate powder (N=144) dosed once daily or sevelamer hydrochloride tablets (N=73) dosed three times daily for 24 weeks. Six of the active-controlled studies are described here (three sevelamer carbonate and three sevelamer hydrochloride studies).
14.1 Cross-Over Study of Sevelamer Carbonate (Renvela) 800 mg Tablets and
Sevelamer Hydrochloride (Renagel) 800 mg Tablets
Stage 5 CKD patients on hemodialysis were entered into a five-week sevelamer hydrochloride run-in period and 79 patients received, in random order, sevelamer carbonate 800 mg tablets and sevelamer hydrochloride 800 mg tablets for eight weeks each, with no intervening washout. Study dose during the cross-over period was determined based on the sevelamer hydrochloride dose during the run-in period on a gram-per-gram basis. The phosphorus levels at the end of each of the two cross-over periods were similar. Average actual daily dose was 6 g/day divided among meals for both treatments. Thirty-nine of those completing the cross-over portion of the study were entered into a two- week washout period during which patients were instructed not to take any phosphate binders; this confirmed the activity of sevelamer in this study.
14.2 Cross-Over Study of Sevelamer Carbonate (Renvela) Powder and Sevelamer
Hydrochloride (Renagel) Tablets
Stage 5 CKD patients on hemodialysis were entered into a four-week sevelamer hydrochloride run-in period and 31 patients received, in random order, sevelamer carbonate powder and sevelamer hydrochloride tablets for four weeks each with no intervening washout. Study dose during the cross-over period was determined based on the sevelamer hydrochloride dose during the run-in period on a gram-per-gram basis. The phosphorus levels at the end of each of the two cross-over periods were similar. Average actual daily dose was 6.0 g/day divided among meals for sevelamer carbonate powder and 6.4 g/day divided among meals for sevelamer hydrochloride tablets.
14.3 Clinical Study of Sevelamer Carbonate (Renvela) Powder and Tablets in
Pediatric Patients
A clinical study with sevelamer carbonate was conducted in 101 patients 6 to 18 years of age with chronic kidney disease. This study included a washout period for patients on a phosphate binder, a 2-week, double-blind, fixed-dose period (FDP) in which patients were randomized to sevelamer carbonate (n=50) or placebo (n=51), and a 26-week, open-label, sevelamer carbonate dose titration period (DTP). Most patients were 13 to 18 years of age (73%) and had a BSA ≥1.2 m 2(84%). Approximately 78% of patients were CKD patients on dialysis.
Sevelamer carbonate significantly reduced serum phosphorus through Week 2 (primary endpoint) by an LS Mean difference of -0.90 (SE 0.27) mg/dL compared to placebo (p=0.001). A similar treatment response was observed in patients who received sevelamer carbonate during the 6-month open-label DTP. Approximately 30% of subjects reached their target serum phosphorus. The median prescribed daily dose was approximately 7.0 g per day during the titration period.
The results of the primary efficacy endpoint were consistent by BSA subgroup. In contrast, a treatment effect was not observed in subjects with a baseline serum phosphorus below 7 mg/dL, many of whom were the subjects 6 to <13 years of age or the subjects not on dialysis (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Change in Serum Phosphorus (mg/dL) from Baseline to Week 2 by Subgroup
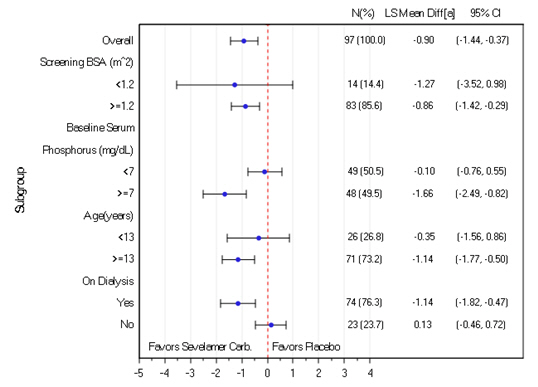
[a]: LS Mean difference of Sevelamer Carbonate – Placebo, based on ANCOVA within subgroup and with treatment as fixed effect and screening BSA and baseline serum phosphorus as covariates.
14.4 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active-Control, Cross-Over Study in
Hemodialysis Patients
Eighty-four CKD patients on hemodialysis who were hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus >6.0 mg/dL) following a two-week phosphate binder washout period were randomized in a cross-over design to receive in random order sevelamer hydrochloride and active control for eight weeks each. Treatment periods were separated by a two-week phosphate binder washout period. Patients started on treatment three times per day with meals. Over each eight-week treatment period, at three separate time points the dose of sevelamer hydrochloride could be titrated up to control serum phosphorus, the dose of active control could also be altered to attain phosphorus control. Both treatments significantly decreased mean serum phosphorus by about 2 mg/dL (Table 6).
Table 6: Mean Serum Phosphorus (mg/dL) at Baseline and Endpoint|
Sevelamer Hydrochloride |
Active Control | |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Baseline at End of Washout |
8.4 |
8.0 |
|
Endpoint |
6.4 |
5.9 |
|
Change from Baseline at Endpoint |
-2.0 * |
-2.1 * |
|
(95% Confidence Interval) |
(-2.5, -1.5) |
(-2.6, -1.7) |
The distribution of responses is shown in Figure 3. The distributions are similar for sevelamer hydrochloride and active control. The median response is a reduction of about 2 mg/dL in both groups. About 50% of subjects have reductions between 1 and 3 mg/dL.
Figure 3: Percentage of Patients (Y-axis) Attaining a Phosphorus Reduction from Baseline (mg/dL) at Least as Great as the Value of the X-axis
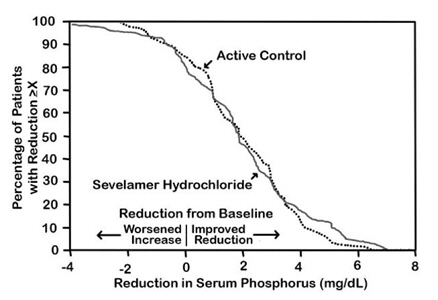
Average daily sevelamer hydrochloride dose at the end of treatment was 4.9 g (range of 0.0 to 12.6 g).
14.5 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active Control in Hemodialysis Patients
Two hundred CKD patients on hemodialysis who were hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus >5.5 mg/dL) following a two-week phosphate-binder washout period were randomized to receive sevelamer hydrochloride 800 mg tablets (N=99) or an active control (N=101). At week 52, using last observation carried forward, sevelamer and active control both significantly decreased mean serum phosphorus (Table 7).
Table 7: Mean Serum Phosphorus (mg/dL) and Ion Product at Baseline and Change from Baseline to End of Treatment|
Sevelamer HCl |
Active Control | |
|---|---|---|
|
Phosphorus | ||
|
Baseline |
7.5 |
7.3 |
|
Change from Baseline at Endpoint |
-2.1 |
-1.8 |
|
Ca × Phosphorus Ion Product | ||
|
Baseline |
70.5 |
68.4 |
|
Change from Baseline at Endpoint |
-19.4 |
-14.2 |
Sixty-one percent of sevelamer hydrochloride patients and 73% of the control patients completed the full 52 weeks of treatment.
Figure 4, a plot of the phosphorus change from baseline for the completers, illustrates the durability of response for patients who are able to remain on treatment.
Figure 4: Mean Phosphorus Change from Baseline for Patients who Completed 52 Weeks of Treatment
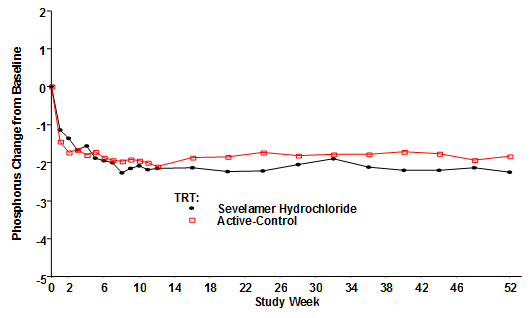
Average daily sevelamer hydrochloride dose at the end of treatment was 6.5 g (range of 0.8 to 13 g).
14.6 Sevelamer Hydrochloride versus Active Control in Peritoneal Dialysis
Patients
One hundred and forty-three patients on peritoneal dialysis who were hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus >5.5 mg/dL) following a two-week phosphate binder washout period were randomized to receive sevelamer hydrochloride (N=97) or active control (N=46) open label for 12 weeks. Average daily sevelamer hydrochloride dose at the end of treatment was 5.9 g (range 0.8 to 14.3 g). Thirteen patients (14%) in the sevelamer group and 9 patients (20%) in the active-control group discontinued, mostly for gastrointestinal adverse reactions. There were statistically significant changes in serum phosphorus (p<0.001) for sevelamer hydrochloride (-1.6 mg/dL from baseline of 7.5 mg/dL), similar to the active control.
14.7 Once-Daily versus Three-Times-Per-Day Dosing
Stage 5 CKD patients on hemodialysis with a serum phosphate level of >5.5 mg/dL after washout from baseline therapies were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to receive either sevelamer carbonate powder once daily (N=144) or sevelamer hydrochloride as a tablet with the dose divided three times per day (N=73) for 24 weeks. The initial dose for the two groups was 4.8 g/day. At the end of the study, the total daily dose was 6.2 g/day of sevelamer carbonate powder once daily and 6.7 g/day of sevelamer hydrochloride tablets three times per day. A greater percentage of subjects on the once-daily dose than three-times-per-day regimen discontinued therapy prematurely, 35% versus 15%. The reasons for discontinuation were largely driven by adverse events and withdrawal of consent in the once-daily dosing regimen. Serum phosphate levels and calcium- phosphate product were better controlled on the three-times-per-day regimen than on the once-daily regimen. Mean serum phosphorus decreased 2.0 mg/dL for sevelamer carbonate powder once daily and 2.9 mg/dL for sevelamer hydrochloride tablets three times per day.