Methamphetamine Hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use METHAMPHETAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for METHAMPHETAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS.METHAMPHETAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE tablets, for oral use, CIIInitial U.S. Approval: 1943
90c02ac6-e5e2-4c97-8c68-81e4e389a195
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Nov 17, 2023
Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
DUNS: 080189610
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Methamphetamine Hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0054-0389-25 100 Tablets
Methamphetamine
Hydrochloride
Tablets, USP CII
5 mg
**PHARMACIST:**Dispense with
attached Medication Guide.
Rx only

Boxed Warning section
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older.
•
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets are a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in pediatric patients 6 years of age and older. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with:
•
known hypersensitivity to amphetamine, or other components of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Hypersensitivity reactions such as angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients treated with other amphetamine products [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
•
taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days following discontinuation of treatment with an MAOIs (including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue), because of the risk of hypertensive crisis [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
•
Known hypersensitivity to amphetamine, or other components of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. (4)
•
Concomitant use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or use of an MAOI within the preceding 14 days. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets have a high potential for abuse and misuse. The use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets exposes individuals to the risks of abuse and misuse, which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction. Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels or distribution [see Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)]. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, including methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)], and this risk is increased with higher doses or unapproved methods of administration, such as snorting or injection.
Before prescribing methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction. Educate patients and their families about these risks and proper disposal of any unused drug. Advise patients to store methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets in a safe place, preferably locked, and instruct patients to not give methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets to anyone else. Throughout methamphetamine treatment, reassess each patient’s risk of abuse, misuse, and addiction and frequently monitor for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction.
5.2 Risks to Patients with Serious Cardiac Disease
Sudden death has been reported in patients with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious cardiac disease who were treated with CNS stimulants at the recommended ADHD dosages.
Avoid methamphetamine use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart arrhythmia, coronary artery disease, or other serious heart problems.
5.3 Increased Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
CNS stimulants cause an increase in blood pressure (mean increase about 2 to 4 mm Hg) and heart rate (mean increase about 3 to 6 bpm). Some patients may have larger increases.
Monitor all methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets-treated patients for potential tachycardia and hypertension [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
5.4 Psychiatric Adverse Reactions
Exacerbation of Pre-Existing Psychosis
CNS stimulants may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance and thought disorder in patients with a pre-existing psychotic disorder.
Induction of a Manic Episode in Patients with Bipolar Illness
CNS stimulants may induce a mixed or manic episode in patients with bipolar disorder. Prior to initiating methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets treatment, screen patients for risk factors for developing a manic episode (e.g., comorbid or has a history of depressive symptoms or a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, or depression).
New Psychotic or Manic Symptoms
CNS stimulants, at recommended doses, may cause psychotic or manic symptoms (e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania) in patients without prior history of psychotic illness or mania. In a pooled analysis of multiple short-term, placebo-controlled studies of CNS stimulants, psychotic or manic symptoms occurred in 0.1% of CNS stimulant-treated patients compared to 0% in placebo-treated patients. If such symptoms occur, consider discontinuing methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets.
5.5 Long-Term Suppression of Growth in Pediatric Patients
CNS stimulants have been associated with weight loss and slowing of growth rate in pediatric patients. Closely monitor growth (weight and height) in methamphetamine-treated pediatric patients treated with CNS stimulants.
Pediatric patients who are not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted.
5.6 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon
CNS stimulants, including methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of CNS stimulant.
Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during methamphetamine treatment. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for methamphetamine-treated patients who develop signs or symptoms of peripheral vasculopathy.
5.7 Seizures
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may lower the convulsive threshold in patients with prior history of seizure, in patients with prior EEG abnormalities in the absence of seizures, and in patients without a history of seizures and no prior EEG evidence of seizures. In the presence of seizures, methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets should be discontinued.
5.8 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening reaction, may occur when amphetamines are used in combination with other drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter systems such as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John’s Wort [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. The coadministration with cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) inhibitors may also increase the risk with increased exposure to methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. In these situations, consider an alternative nonserotonergic drug or an alternative drug that does not inhibit CYP2D6 [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
Concomitant use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets with MAOI drugs is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
Discontinue treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if the above symptoms occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets with other serotonergic drugs or CYP2D6 inhibitors is clinically warranted, initiate methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets with lower doses, monitor patients for the emergence of serotonin syndrome during drug initiation or titration, and inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome.
5.9 Motor and Verbal Tics, and Worsening of Tourette’s Syndrome
CNS stimulants, including amphetamine, have been associated with the onset or exacerbation of motor and verbal tics. Worsening of Tourette’s syndrome has also been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Before initiating methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, assess the family history and clinically evaluate patients for tics or Tourette’s syndrome. Regularly monitor methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets-treated patients for the emergence or worsening of tics or Tourette’s syndrome, and discontinue treatment if clinically appropriate.
•
Risks to Patients with Serious Cardiac Disease: Avoid use in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious cardiac arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, or other serious cardiac disease. (5.2)
•
Increased Blood Pressure and Heart Rate: Monitor blood pressure and pulse. (5.3)
•
Psychiatric Adverse Reactions: Prior to initiating methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, screen patients for risk factors for developing a manic episode. If new psychotic or manic symptoms occur, consider discontinuing methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. (5.4)
•
Long-Term Suppression of Growth in Pediatric Patients: Closely monitor growth (height and weight) in pediatric patients. Pediatric patients not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted. (5.5)
•
Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon: Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets treatment. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for patients who develop signs or symptoms of peripheral vasculopathy. (5.6)
•
Seizures: May lower the convulsive threshold. If a seizure occurs, discontinue methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. (5.7)
•
Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when coadministered with serotonergic agents (e.g., SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans), but also during overdosage situations. If it occurs, discontinue methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and initiate supportive treatment. (5.8)
•
Motor and Verbal Tics, and Worsening of Tourette’s Syndrome: Before initiating methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, assess the family history and clinically evaluate patients for tics or Tourette’s syndrome. Regularly monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of tics or Tourette’s syndrome. Discontinue treatment if clinically appropriate. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
•
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2, 9.3)]
•
Hypersensitivity to amphetamine products or other ingredients of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets [see Contraindications (4)]
•
Hypertensive Crisis When Used Concomitantly with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7.1)]
•
Risks to Patient with Serious Cardiac Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Increased Blood Pressure and Heart Rate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Psychiatric Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Long-Term Suppression of Growth in Pediatric Patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
•
Motor and Verbal Tics, and Worsening of Tourette’s Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets were identified in clinical trials or postmarketing reports. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Elevation of blood pressure, tachycardia and palpitation. Fatal cardiorespiratory arrest has been reported, mostly in the context of abuse/misuse
Central Nervous System: Psychotic episodes reported at recommended doses. Dizziness, dysphoria, overstimulation, euphoria, insomnia, tremor, restlessness and headache. Exacerbation of motor and verbal tics and Tourette’s syndrome
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, constipation, dryness of mouth, unpleasant taste, intestinal ischemia, and other gastrointestinal disturbances
Hypersensitivity: Urticaria
Endocrine: Impotence and changes in libido; frequent or prolonged erections
Musculoskeletal: Rhabdomyolysis
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders: Suppression of growth has been reported with the long-term use of stimulants in pediatric patients
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of amphetamines:
Allergic: Rash, hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema and anaphylaxis. Serious skin rashes, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis have been reported.
Cardiovascular: Dyspnea, sudden death, myocardial infarction. There have been isolated reports of cardiomyopathy associated with chronic amphetamine use
Central Nervous System: dyskinesia, fatigue, aggression, anger, logorrhea, dermatillomania, and paresthesia (including formication)
Eye Disorders: Mydriasis
Vascular Disorders: Raynaud’s phenomenon
Common adverse reactions include: palpitation, dizziness, insomnia, tremor, headache, diarrhea, dryness of mouth. (6)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactHikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. at 1-800-962-8364 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with Methamphetamine
Hydrochloride Tablets
Table 1 presents clinically important drug interactions with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets.
Table 1: Clinically Important Drug Interactions with Methamphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets|
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOI) | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
MAOI antidepressants slow amphetamine metabolism, increasing amphetamines effect on the release of norepinephrine and other monoamines from adrenergic nerve endings causing headaches and other signs of hypertensive crisis. Toxic neurological effects and malignant hyperpyrexia can occur, sometimes with fatal results. |
|
Intervention: |
Concomitant use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) or within 14 days after discontinuing MAOI treatment is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. |
|
Serotonergic Drugs | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of amphetamines, including methamphetamine, and serotonergic drugs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
|
Intervention: |
Initiate methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets initiation or dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and the concomitant serotonergic drug(s) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. |
|
Alkalinizing Agents | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Alkalinizing agents may increase exposure to amphetamines and potentiate the action of amphetamine. |
|
Intervention: |
Avoid co-administration of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and gastrointestinal and urinary alkalinizing agents. |
|
Acidifying Agents | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Acidifying agents lower blood levels and efficacy of amphetamines. |
|
Intervention: |
Increase dose of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets based on clinical response. |
|
Tricyclic Antidepressants | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
May enhance the activity of tricyclic or sympathomimetic agents causing sustained increases in the concentration of d-amphetamine in the brain; cardiovascular effects can be potentiated. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor frequently and adjust methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets dose or use alternative therapy based on clinical response. |
|
CYP2D6 Inhibitors | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Concomitant use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and CYP2D6 inhibitors may increase the exposure of methamphetamine compared to the use of the drug alone, and increase the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
|
Intervention: |
Start with lower doses and monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome particularly during methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets initiation and after a dosage increase. If serotonin syndrome occurs, discontinue methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and the CYP2D6 inhibitor [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. |
|
Gastric pH Modulators | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Time to maximum concentration (Tmax) of amphetamine is decreased compared to when administered alone. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for changes in clinical effect and use alternative therapy based on clinical response. |
|
Guanethidine | |
|
Clinical Impact: |
Methamphetamine may decrease the hypotensive effect of guanethidine. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients and adjust therapy based on clinical response. |
Insulin requirements in diabetes mellitus may be altered in association with the use of methamphetamine and the concomitant dietary regimen.
7.2 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Amphetamines can cause a significant elevation in plasma corticosteroid levels. This increase is greatest in the evening. Amphetamines may interfere with urinary steroid determinations.
Acidifying and Alkalinizing Agents: Agents that alter GI and urinary pH can alter blood levels of amphetamine. Acidifying agents can decrease amphetamine blood levels, while alkalinizing agents can increase amphetamine blood levels. (7.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Boxed Warning 10/2023
Dosage and Administration (2.1) 10/2023
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.9) 10/2023
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
MEDICATION GUIDE Methamphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets, USP, CII (meth″ am fet′ a meen hye″ droe klor′ ide) Rx only |
|
What is the most important information I should know about methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets? Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may cause serious side effects, including: • o o o o o • Your child’s healthcare provider should check your child carefully for heart problems before starting treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Tell your child’s healthcare provider if your child has any heart problems, heart disease, or heart defects. Call your child’s healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away if your child has any signs of heart problems such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. • • o o o Tell your child’s healthcare provider about any mental problems your child has, or about a family history of suicide, bipolar illness, or depression. Call your child’s healthcare provider right away if your child has any new or worsening mental symptoms or problems during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, especially hearing voices, seeing or believing things that are not real, or new manic symptoms. |
|
What are methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets? Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets are a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant prescription medicine used for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children 6 years to 17 years of age. Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in people with ADHD. It is not known if methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets are safe and effective in children under 6 years of age. Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets are a federally controlled substance (CII) because it contains methamphetamine that can be a target for people who abuse prescription medicines or street drugs. Keep methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets in a safe place to protect it from theft. Never give your methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets to anyone else because it may cause death or harm them. Selling or giving away methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may harm others and is against the law. |
|
Do not take methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets if your child is: • • |
|
Before taking methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, tell your child’s healthcare provider about all your child’s medical conditions, including if your child: • • • • • • o • Tell your child’s healthcare provider about all of the medicines that your child takes including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and some medicines may interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines will need to be changed during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Your child’s healthcare provider will decide whether methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets can be taken with other medicines. Especially tell your child’s healthcare provider if your child takes: • • • • • • • • • Ask your child’s healthcare provider if you are not sure if your child takes any of these medicines. Know the medicines your child takes. Keep a list of your child’s medicines with you to show your child’s healthcare provider and pharmacist.Do not start any new medicine during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets without talking to your child’s healthcare provider first. |
|
How should methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets be taken? • • • If your child takes too many methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, call your child’s healthcare provider or Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away. |
|
What are possible side effects of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets? Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may cause serious side effects, including: • • • o o Tell your child’s healthcare provider if your child has numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in your fingers or toes or if your child has any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. • o o o o o o o o o o o o • |
|
The most common side effects with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets include: • • • • • • • These are not all the possible side effects of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Call your child’s healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets? • • • Keep methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets for a condition for which they were not prescribed. Do not give methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that your child has. They may harm them and it is against the law. You can ask your child’s pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets that is written for healthcare professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets? Active Ingredient: methamphetamine hydrochloride, USP Inactive Ingredients: crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and povidone. For more information about methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, go to www.hikma.com or call Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. at 1-800-962-8364. Distributed by: Berkeley Heights, NJ 07922 C50000760/04 |
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: 09/2024
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 5 mg of methamphetamine hydrochloride as a round, white to off-white, biconvex, debossed tablet with “54” on one side and “681” on the other side.
Tablets: 5 mg (3)
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Methamphetamine Hydrochloride Tablets, USP
How Supplied
5 mg tablets are supplied as a round, white to off-white, biconvex, debossed
tablet with “54” on one side and “681” on the other side.
NDC 0054-0389-25: Bottle of 100 tablets
Storage and Handling
Recommended Storage:Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Dispense in a tight, light resistant, child-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
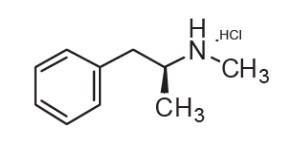
Methamphetamine hydrochloride, USP, chemically known as (αS)-α-Methylbenzeneethan-(N-methyl)-amine Hydrochloride, is a member of the amphetamine group of sympathomimetic amines. It has the following structural formula:
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, USP contain 5 mg of methamphetamine hydrochloride, USP for oral administration. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: crospovidone, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and povidone.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Amphetamines are non-catecholamine sympathomimetic amines with CNS stimulant activity. The exact mode of therapeutic action in the treatment of ADHD is not known.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Amphetamines block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Methamphetamine is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract.
Elimination
Metabolism
The primary site of metabolism is in the liver by aromatic hydroxylation, N-dealkylation and deamination. At least seven metabolites have been identified in the urine. The biological half-life has been reported in the range of 4 to 5 hours.
Excretion
Excretion occurs primarily in the urine and is dependent on urine pH. Alkaline urine will significantly increase the drug half-life. Approximately 62% of an oral dose is eliminated in the urine within the first 24 hours with about one- third as intact drug and the remainder as metabolites.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE SECTION
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets contain methamphetamine hydrochloride, a Schedule II controlled substance.
9.2 Abuse
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets have a high potential for abuse and misuse which can lead to the development of a substance use disorder, including addiction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets can be diverted for non-medical use into illicit channels or distribution.
Abuse is the intentional non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, to achieve a desired psychological or physiological effect. Misuse is the intentional use, for therapeutic purposes, of a drug by an individual in a way other than prescribed by a healthcare provider or for whom it was not prescribed. Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving a higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence.
Misuse and abuse of methamphetamine may cause increased heart rate, respiratory rate, or blood pressure; sweating; dilated pupils; hyperactivity; restlessness; insomnia; decreased appetite; loss of coordination; tremors; flushed skin; vomiting; and/or abdominal pain. Anxiety, psychosis, hostility, aggression, and suicidal or homicidal ideation have also been observed with CNS stimulants abuse and/or misuse. Misuse and abuse of CNS stimulants, including methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, can result in overdose and death [see Overdosage (10)], and this risk is increased with higher doses or unapproved methods of administration, such as snorting or injection.
9.3 Dependence
Physical Dependence
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may produce physical dependence. Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug.
Withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or dose reduction following prolonged use of CNS stimulants including methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets include dysphoric mood; depression; fatigue; vivid, unpleasant dreams; insomnia or hypersomnia; increased appetite; and psychomotor retardation or agitation.
Tolerance
Methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may produce tolerance. Tolerance is a physiological state characterized by a reduced response to a drug after repeated administration (i.e., a higher dose of a drug is required to produce the same effect that was once obtained at a lower dose).
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Effects of Overdose
Overdose of CNS stimulants is characterized by the following sympathomimetic effects:
•
Cardiovascular effects including tachyarrhythmias, and hypertension or hypotension. Vasospasm, myocardial infarction, or aortic dissection may precipitate sudden cardiac death. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy may develop.
•
CNS effects including psychomotor agitation, confusion, and hallucinations. Serotonin syndrome, seizures, cerebral vascular accidents, and coma may occur.
•
Life-threatening hyperthermia (temperatures greater than 104°F) and rhabdomyolysis may develop.
Overdose Management
Consider the possibility of multiple drug ingestion. D-amphetamine is not dialyzable.
Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdose management recommendations.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Pretreatment Screening
Prior to treating patients with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, assess:
•
for the presence of cardiac disease (i.e., perform a careful history, family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia, and physical examination) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
•
the family history and clinically evaluate patients for motor or verbal tics or Tourette’s syndrome before initiating methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
2.2 Important Dosing Information
Administer methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets orally once daily or in two divided doses daily. Avoid taking methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets late in the evening due to the risk of insomnia.
2.3 Recommended Dosage
For pediatric patients 6 years of age and older, the recommended starting dosage is 5 mg methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets once or twice daily. The daily dosage may be increased in increments of 5 mg at weekly intervals based on clinical response of the patient. The recommended dosage range is 20 mg to 25 mg daily.
2.4 Dosage Modifications Due to Drug Interactions
Agents that alter urinary pH can impact excretion and alter blood levels of amphetamine. Acidifying agents (e.g., ascorbic acid) decrease blood levels, while alkalinizing agents (e.g., sodium bicarbonate) increase blood levels. Adjust methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets dosage based on clinical response [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
•
Administer methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets orally once daily or in two divided doses daily. Avoid administration late in the evening due to the risk of insomnia. (2.2)
•
Recommended starting dosage is 5 mg once or twice daily. (2.3)
•
Daily dosage may be increased in 5 mg increments at weekly intervals depending on clinical response. (2.3)
•
The recommended dosage range is 20 mg to 25 mg daily. (2.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to ADHD medications, including methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to advise patients to register by contacting the National Pregnancy Registry for ADHD Medications at 1-866-961-2388 or visiting online at www.womensmentalhealth.org/research/pregnancyregistry/adhd-medications/.
Risk Summary
Available data from epidemiologic studies and postmarketing reports on use of methamphetamine and amphetamine in pregnant women over decades of use have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects or miscarriage. Neonates exposed to amphetamines in utero are at risk for withdrawal symptoms following delivery. Adverse pregnancy outcomes including premature delivery and low birth weight have been seen in infants born to mothers taking amphetamines during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations).
In animals, administration of methamphetamine during organogenesis resulted in developmental toxicity, including neonatal death and fetal malformations, at doses equivalent to the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis. Oral administration of methamphetamine to rats during pregnancy, pregnancy and lactation, or lactation resulted in developmental toxicity in the offspring, including, neonatal mortality and delayed development, at a maternal dose similar to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
Amphetamines, such as methamphetamine, cause vasoconstriction and thereby decrease placental perfusion. In addition, amphetamines can stimulate uterine contractions, increasing the risk of premature delivery. Infants born to mothers taking amphetamines during pregnancy have an increased risk of premature delivery and low birth weight.
Monitor infants born to mothers taking methamphetamine for symptoms of withdrawal such as feeding difficulties, irritability, agitation, and excessive drowsiness.
Data
Animal Data
Based on published data, methamphetamine administration during the period of organogenesis caused malformations and pup mortality in mammals at doses equivalent to the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis. Oral administration of methamphetamine (0, or 3.75 mg/kg) to pregnant rats during gestation, throughout gestation and lactation, or only during lactation resulted in an increase in neonatal pup mortality. Delayed somatic development (pinna unfolding and eye opening) and impairments in neurobehavioral development (righting reflex, incline plane test, and forelimb grip strength) were observed in the pups. The dose with adverse effects was equivalent to the MRHD of 25 mg on a mg/m2 basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on limited case reports in the published literature, methamphetamine and its active metabolite, amphetamine, are present in human milk. There are no reports of adverse effects on the breastfed infant. Long-term neurodevelopmental effects on infants from amphetamine exposure are unknown. It is possible that large doses of amphetamine might interfere with milk production, especially in women whose lactation is not well established. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets for the treatment of ADHD have been established in pediatric patients aged 6 years and older.
The safety and effectiveness of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 6 years old.
Growth Suppression
Growth should be monitored during treatment with stimulants, including methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Pediatric patients who are not growing or gaining weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Adverse Reactions (6)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects age 65 years and over to determine whether elderly subjects respond differently from younger subjects.
•
Pregnancy: May cause fetal harm. (8.1)
•
Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended. (8.2)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and Mutagenesis
Carcinogenicity, mutagenic, or genotoxic potential of methamphetamine has not been fully characterized.
Impairment of Fertility
There have been no adequate studies performed in animals at current standards to evaluate the effect of methamphetamine treatment on fertility. However, published studies in mice and rats exposed to repeated daily dosing of methamphetamine report irregular estrous cycling and decreased ovarian reserve in females, and decreased sperm density, motility, and percent of sperm with normal morphology in males. The clinical significance of these findings is not clear.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
Educate patients and their families about the risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, which can lead to overdose and death, and proper disposal of any unused drug [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Abuse and Dependence (9.2), Overdosage (10)]. Advise patients to store methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets in a safe place, preferably locked, and instruct patients to not give methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets to anyone else.
Risks to Patients with Serious Cardiac Disease
Advise patients that there are potential risks to patients with serious cardiac disease, including sudden death with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets use. Instruct patients to contact a healthcare provider immediately if they develop symptoms such as exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Increased Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
Instruct patients that methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets can cause elevations of their blood pressure and pulse rate and they should be monitored for such effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Psychiatric Adverse Risks
Advise patients that methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets, at recommended doses, may cause psychotic or manic symptoms even in patients without prior history of psychotic symptoms or mania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Long-Term Suppression of Growth in Pediatric Patients
Advise patients, family members, and caregivers that methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may cause slowing of growth including weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Circulation problems in fingers and toes (peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s phenomenon)
Instruct patients beginning treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets about the risk of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud’s Phenomenon, and associated signs and symptoms: fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful, and/or may change color from pale, to blue, to red. Instruct patients to report to their physician any new numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in fingers or toes. Instruct patients to call their physician immediately with any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes while taking methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Seizures
Caution patient that methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets may lower the convulsive threshold. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider immediately and to discontinue methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets if a seizure occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Serotonin Syndrome
Caution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome with concomitant use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets and other serotonergic drugs including SSRIs, SNRIs, triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, St. John’s Wort, and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others such as linezolid [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider or report to the emergency room if they experience signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome.
Motor and Verbal Tics, and Worsening of Tourette’s Syndrome
Advise patients that motor and verbal tics and worsening of Tourette’s syndrome may occur during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Instruct patients to notify their healthcare provider if emergence of new tics or worsening of tics or Tourette’s syndrome occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to notify their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter drugs because there is a potential for interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Pregnancy
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets during pregnancy. Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets. Advise patients of the potential fetal effects from the use of methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed if they are taking methamphetamine hydrochloride tablets [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Distributed by:
Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Berkeley Heights, NJ 07922
C50000760/04
Revised September 2024
