FABHALTA
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FABHALTA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FABHALTA. FABHALTA (iptacopan) capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2023
a76b5845-6e21-4d3b-ad07-cd8df1b60bee
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 13, 2024
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
DUNS: 002147023
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
iptacopan
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0078-1189-20
Rx only
FABHALTA®
(iptacopan) capsules
200 mg
Dispense with accompanying Medication Guide.
60 capsules
Swallow the capsules whole. Do not open, break, or chew capsules.
NOVARTIS

Boxed Warning section
WARNING: SERIOUS INFECTIONS CAUSED BY ENCAPSULATED BACTERIA
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
FABHALTA increases the risk of serious and life-threatening infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, includingStreptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, andHaemophilus influenzae type B.
*Complete or update vaccination for encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to the first dose of FABHALTA, unless the risks of delaying FABHALTA outweigh the risk of developing a serious infection. Comply with the most current Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommendations for vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria in patients receiving a complement inhibitor. (5.1) *Patients receiving FABHALTA are at increased risk for invasive disease caused by encapsulated bacteria, even if they develop antibodies following vaccination. Monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infections and evaluate immediately if infection is suspected. (5.1)
FABHALTA is available only through a restricted program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called FABHALTA REMS. (5.2)
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FABHALTA is indicated for the treatment of adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH).
FABHALTA is a complement factor B inhibitor, indicated for the treatment of adults with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH). (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
FABHALTA is contraindicated:
- in patients with serious hypersensitivity to iptacopan or any of the excipients.
- for initiation in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, or Haemophilus influenzae type B.
- Serious hypersensitivity to iptacopan or any of the excipients. (4)
- Initiation in patients with unresolved serious infection caused by encapsulated bacteria. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria
FABHALTA, a complement inhibitor, increases a patient’s susceptibility to serious, life-threatening, or fatal infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis (caused by any serogroup, including non-groupable strains), and Haemophilus influenzae type B. Life-threatening and fatal infections with encapsulated bacteria have occurred in both vaccinated and unvaccinated patients treated with complement inhibitors. The initiation of FABHALTA treatment is contraindicated in patients with unresolved serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
Complete or update vaccination against encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to administration of the first dose of FABHALTA, according to the current ACIP recommendations for patients receiving a complement inhibitor. Revaccinate patients in accordance with ACIP recommendations considering the duration of therapy with FABHALTA. Note that ACIP recommends an administration schedule in patients receiving complement inhibitors that differs from the administration schedule in the vaccine prescribing information. If urgent FABHALTA therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines against encapsulated bacteria according to ACIP recommendations, provide the patient with antibacterial drug prophylaxis and administer these vaccines as soon as possible. Various durations and regimens of antibacterial drug prophylaxis have been considered, but the optimal durations and drug regimens for prophylaxis and their efficacy have not been studied in unvaccinated or vaccinated patients receiving complement inhibitors, including FABHALTA. The benefits and risks of treatment with FABHALTA, as well as the benefits and risks of antibacterial drug prophylaxis in unvaccinated or vaccinated patients, must be considered against the known risks for serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
Vaccination does not eliminate the risk of serious encapsulated bacterial infections, despite development of antibodies following vaccination. Closely monitor patients for early signs and symptoms of serious infection and evaluate patients immediately if an infection is suspected. Inform patients of these signs and symptoms and instruct patients to seek immediate medical care if these signs and symptoms occur. Promptly treat known infections. Serious infection may become rapidly life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early. Consider interruption of FABHALTA in patients who are undergoing treatment for serious infections.
FABHALTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
5.2 FABHALTA REMS
FABHALTA is available only through a restricted program under a REMS called FABHALTA REMS, because of the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Notable requirements of the FABHALTA REMS include the following:
- Prescribers must enroll in the REMS.
- Prescribers must counsel patients about the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
- Prescribers must provide patients with the REMS educational materials.
- Prescribers must assess patient vaccination status for vaccines against encapsulated bacteria and vaccinate if needed according to current ACIP recommendations two weeks prior to the first dose of FABHALTA.
- Prescribers must provide a prescription for antibacterial drug prophylaxis if treatment must be started urgently, and the patient is not up to date with vaccines against encapsulated bacteria according to current ACIP recommendations at least two weeks prior to the first dose of FABHALTA.
- Pharmacies that dispense FABHALTA must be certified in the FABHALTA REMS and must verify prescribers are certified.
- Patients must receive counseling from the prescriber about the need to receive vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria per ACIP recommendations, the need to take antibiotics as directed by the prescriber, and the early signs and symptoms of serious infections.
- Patients must be instructed to carry the Patient Safety Card with them at all times during treatment and for 2 weeks following the last dose of FABHALTA.
Further information is available by telephone: 1-833-99FABHA or online at www.FABHALTA-REMS.com.
5.3 Monitoring of PNH Manifestations After FABHALTA Discontinuation
After discontinuing treatment with FABHALTA, closely monitor patients for at least 2 weeks after the last dose for signs and symptoms of hemolysis. These signs include elevated lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels along with a sudden decrease in hemoglobin or PNH clone size, fatigue, hemoglobinuria, abdominal pain, dyspnea, major adverse vascular events (such as thrombosis, stroke and myocardial infarction), dysphagia, or erectile dysfunction. If discontinuation of FABHALTA is necessary, consider alternative therapy.
If hemolysis occurs after discontinuation of FABHALTA, consider restarting treatment with FABHALTA, if appropriate, or initiating another treatment for PNH.
5.4 Hyperlipidemia
FABHALTA increases total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, and serum triglycerides.
Of the 54 FABHALTA-treated patients who had a normal total cholesterol level at baseline in APPLY-PNH, 43% developed Grade 1 hypercholesterolemia during the randomized treatment period. One FABHALTA-treated patient in APPLY-PNH experienced increased total cholesterol that worsened to Grade 2 from Grade 1 at baseline.
Of the 34 FABHALTA-treated patients who had a normal cholesterol level at baseline in APPOINT-PNH, 24% developed Grade 1 hypercholesterolemia during the core treatment period.
Of the 60 FABHALTA-treated patients who had LDL-cholesterol ≤130 mg/dL at baseline in APPLY-PNH, 17% developed LDL-cholesterol >130-160 mg/dL, 8% developed LDL-cholesterol >160-190 mg/dL, and 7% developed LDL-cholesterol
190 mg/dL during the randomized treatment period. Of the 36 FABHALTA-treated patients who had LDL-cholesterol ≤130 mg/dL at baseline in APPOINT-PNH, 11% developed LDL-cholesterol >130-160 mg/dL and 3% developed LDL-cholesterol 160-190 mg/dL.
Of the 52 patients with normal triglyceride levels at baseline in APPLY-PNH, 23% developed Grade 1 elevated triglycerides during the randomized treatment period. Three FABHALTA-treated patients in APPLY-PNH experienced an increase in triglycerides from Grade 1 to Grade 2.
Of the 37 FABHALTA-treated patients who had a normal triglyceride level at baseline in APPOINT-PNH, 27% developed Grade 1 elevated triglycerides in the core treatment period.
Some patients required cholesterol-lowering medications.
Monitor serum lipid parameters periodically during treatment with FABHALTA and initiate cholesterol-lowering medication, if indicated.
- Monitoring of PNH Manifestations After FABHALTA Discontinuation: Monitor for signs of hemolysis after discontinuation. (5.3)
- Hyperlipidemia: Monitor serum lipid parameters periodically during treatment and initiate cholesterol-lowering medication, if indicated. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reaction is discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Hyperlipidemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
The data described below reflects the exposure in adults with PNH who received FABHALTA (n = 62) or anti-C5 treatment (US-approved and non-US-approved eculizumab product or US-approved and non-US-approved ravulizumab product, n = 35) in APPLY-PNH [NCT04558918] and adults who received FABHALTA (n = 40) in APPOINT-PNH [NCT04820530] at the recommended dosing regimen for 24 weeks. In APPLY-PNH, serious adverse reactions were reported in 2 (3%) patients with PNH receiving FABHALTA. Serious adverse reactions included pyelonephritis, urinary tract infection and COVID-19. In APPOINT-PNH, serious adverse reactions were reported in 2 (5%) patients with PNH receiving FABHALTA. Serious adverse reactions included COVID-19 and bacterial pneumonia. The most common adverse reactions (≥ 10%) with FABHALTA were headache, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bacterial infection, viral infection, nausea, and rash.
Table 1 describes the adverse reactions that occurred in > 5% of patients treated with FABHALTA in the APPLY-PNH or APPOINT-PNH studies.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported in > 5% of Patients Treated with FABHALTA in APPLY-PNH or APPOINT-PNH Studies (24-Week Treatment Period)|
aIncludes similar terms. | |||
|
Adverse reactions |
APPLY-PNH |
APPOINT-PNH | |
|
FABHALTA |
Anti-C5 |
FABHALTA | |
|
Headachea |
12 (19) |
1 (3) |
11 (28) |
|
Nasopharyngitisb |
10 (16) |
6 (17) |
6 (15) |
|
Diarrhea |
9 (15) |
2 (6) |
3 (8) |
|
Abdominal paina |
9 (15) |
1 (3) |
3 (8) |
|
Bacterial infectionc |
7 (11) |
4 (11) |
2 (5) |
|
Nausea |
6 (10) |
1 (3) |
2 (5) |
|
Viral infectiond |
6 (10) |
11 (31) |
7 (18) |
|
Arthralgia |
5 (8) |
1 (3) |
0 |
|
Thrombocytopeniaa |
4 (6) |
0 |
0 |
|
Dizziness |
4 (6) |
0 |
1 (3) |
|
Systemic hypertensiona |
4 (6) |
0 |
0 |
|
Lipid disordere |
4 (6) |
0 |
3 (8) |
|
Rashf |
2 (3) |
0 |
4 (10) |
Clinically relevant adverse reactions reported in less than or equal to 5% of patients includes urticaria in one patient (3%) in APPOINT-PNH.
Description of Select Adverse Reactions (graded per NCI CTCAE Version 4.03 unless noted otherwise)
Platelet Count Decreased
Of the 37 FABHALTA-treated patients who had normal platelet counts at baseline in APPLY-PNH, 43% experienced any Grade thrombocytopenia during the randomized treatment period. Three FABHALTA-treated patients in APPLY-PNH experienced decreased platelets that worsened to Grade ≥ 3 from baseline (one patient with normal platelets that worsened to Grade 4, one patient with baseline Grade 1 that worsened to Grade 4; and one patient with baseline Grade 3 that worsened to Grade 4).
Most common adverse reactions in adults with PNH (incidence ≥ 10%) were headache, nasopharyngitis, diarrhea, abdominal pain, bacterial infection, viral infection, nausea and rash. (6.1)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP2C8 Inducers
Concomitant use of CYP2C8 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may decrease iptacopan exposure, which may result in loss of or reduced efficacy of FABHALTA. Monitor the clinical response and discontinue use of the CYP2C8 inducer if loss of efficacy of FABHALTA is evident.
7.2 Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
Concomitant use of strong CYP2C8 inhibitors (e.g., gemfibrozil) may increase iptacopan exposure, which may result in an increased risk for adverse reactions with FABHALTA. Coadministration with a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor is not recommended.
- CYP2C8 inducers (e.g., rifampin): May decrease iptacopan exposure. Monitor for loss of efficacy. (7.1)
- Strong CYP2C8 inhibitors (e.g., gemfibrozil): May increase iptacopan exposure. Coadministration not recommended. (7.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Dosage and Administration (2.1) |
3/2024 |
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 200 mg of iptacopan in pale yellow, opaque, hard gelatin capsules imprinted with “LNP200” on the body and “NVR” on the cap.
Capsules: 200 mg (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from clinical trials with FABHALTA use in pregnant women are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with untreated PNH in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). The use of FABHALTA in pregnant women or women planning to become pregnant may be considered following an assessment of the risks and benefits.
In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of iptacopan to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at exposures 4 to 6-times the human exposure (based on AUC) at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 200 mg twice daily did not induce embryo or fetal toxicity (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of major birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriages in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-Associated Maternal and/or Embryo/Fetal Risk
PNH in pregnancy is associated with adverse maternal outcomes, including worsening cytopenias, thrombosis, infections, bleeding, miscarriages, increased maternal mortality, and adverse fetal outcomes, including fetal death and premature delivery.
Data
Animal Data
In an embryo-fetal development study in rats, oral administration of iptacopan during organogenesis did not cause embryo-fetal toxicity when given up to the highest dose of 1,000 mg/kg/day, which corresponds to 4-times the MRHD based on AUC.
In an embryo-fetal development study in rabbits, oral administration of iptacopan during organogenesis did not cause embryo-fetal toxicity when given up to the highest dose of 450 mg/kg/day, which corresponds to 6-times the MRHD based on AUC.
In a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, oral administration of iptacopan during gestation, parturition, and lactation did not cause adverse effects in offspring when given up to the highest dose of 1,000 mg/kg/day, which corresponds to 4-times the MRHD based on AUC.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of iptacopan or its metabolite in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child or on milk production. Since many medicinal products are secreted into human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, breastfeeding should be discontinued during treatment and for 5 days after the final dose.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients with PNH have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There were 29 PNH patients 65 years of age and older in APPLY-PNH and APPOINT- PNH [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Of the total number of FABHALTA-treated patients during the 24-week treatment period in these studies, 21 (20.6%) were 65 years of age and older, while 7 (6.9%) were 75 years of age and older. Clinical studies of FABHALTA did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
8.6 Renal Impairment
The use of FABHALTA is not recommended in patients with severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) with or without hemodialysis. No dose adjustment is required in patients with mild (eGFR 60 to < 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The use of FABHALTA is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C). No dose adjustment is required for patients with mild (Child-Pugh class A) or moderate (Child-Pugh class B) hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Severe renal impairment: Use not recommended. (8.6)
- Severe hepatic impairment: Use not recommended. (8.7)
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
200 mg capsules: pale yellow opaque hard capsules, imprinted with “LNP200” on one half and “NVR” on the other half, packaged in a high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with induction seal and child-resistant cap. Each bottle contains 60 capsules (NDC 0078-1189-20).
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: 3/2024 |
|
MEDICATION GUIDE | |
|
What is the most important information I should know about FABHALTA? *FABHALTA increases your chance of getting serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae, Neisseria meningitidis, and Haemophilus influenzae type B. These serious infections may quickly become life-threatening or fatal if not recognized and treated early. * You must complete or be up to date with the vaccines against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis at least 2 weeks before your first dose of FABHALTA. * If you have not completed your vaccinations and FABHALTA must be started right away, you should receive the required vaccinations as soon as possible. * If you have not been vaccinated and FABHALTA must be started right away, you should also receive antibiotics to take for as long as your healthcare provider tells you. * If you have been vaccinated against these bacteria in the past, you might need additional vaccinations before starting FABHALTA. Your healthcare provider will decide if you need additional vaccinations. * Vaccines do not prevent all infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.Call your healthcare provider or get emergency medical care right away if you have any of these signs and symptoms of a serious infection: | |
|
▪ fever with or without shivers or chills |
▪ fever and a rash |
|
Your healthcare provider will give you a Patient Safety Card about the risk
of serious infections. Carry it with you at all times during treatment and
for 2 weeks after your last dose of FABHALTA. Your risk of serious infections
may continue for a few weeks after your last dose of FABHALTA. It is important
to show this card to any healthcare provider who treats you. This will help
them diagnose and treat you quickly.
FABHALTA may increase your cholesterol and triglycerides and your healthcare provider will do blood tests to check them periodically during treatment. | |
|
What is FABHALTA? | |
|
Who should not take FABHALTA?
| |
|
Before you take FABHALTA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Taking FABHALTA with certain other medicines may affect the way FABHALTA works
and may cause side effects. | |
|
How should I take FABHALTA?
Symptoms or problems that can happen due to breakdown of red blood cells include: | |
|
○ decreased hemoglobin level in your blood |
○ tiredness |
|
*It is important that you take FABHALTA exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to lower the possibility of breakdown of red blood cells due to PNH. | |
|
What are the possible side effects of FABHALTA?
The most common side effects of FABHALTA include: | |
|
|
|
Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you or that
does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of FABHALTA. | |
|
How should I store FABHALTA?
Keep FABHALTA and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of FABHALTA. | |
|
What are the ingredients in FABHALTA? Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, New Jersey
07936 |
T2024-11
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Vaccination and Prophylaxis for Encapsulated Bacterial
Infections
Vaccinate patients against encapsulated bacteria, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis (serogroups A, C, W, Y and B), according to current ACIP recommendations at least 2 weeks prior to initiation of FABHALTA [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
If urgent FABHALTA therapy is indicated in a patient who is not up to date with vaccines for Streptococcus pneumoniae and Neisseria meningitidis according to ACIP recommendations, provide the patient with antibacterial drug prophylaxis and administer these vaccines as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Healthcare providers who prescribe FABHALTA must enroll in the FABHALTA REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dosage of FABHALTA is 200 mg orally twice daily without regard to food.
Swallow capsules whole. Do not open, break, or chew capsules.
If a dose or doses are missed, advise the patient to take one dose of FABHALTA as soon as possible (even if it is soon before the next scheduled dose) and then to resume the regular dosing schedule.
2.3 Patients Switching from Anti-C5 (eculizumab, ravulizumab) to FABHALTA
To reduce the potential risk of hemolysis with abrupt discontinuation of other PNH therapies:
- For patients switching from eculizumab, initiate FABHALTA no later than 1 week after the last dose of eculizumab.
- For patients switching from ravulizumab, initiate FABHALTA no later than 6 weeks after the last dose of ravulizumab.
There is no available information regarding the timeframe for initiation of FABHALTA after other PNH therapies.
200 mg orally twice daily with or without food. (2.2)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
FABHALTA contains iptacopan, a complement Factor B inhibitor. The molecular weight of iptacopan hydrochloride monohydrate is approximately 477 g/mol. The chemical name is (2S,4S)-2-(4-Carboxyphenyl)-4-ethoxy-1-[(5-methoxy-7-methyl-1H-indol-4-yl)methyl]piperidin-1-ium chloride―water (1/1). The molecular formula is C25H30N2O4·HCl H2O. The structure is shown below.
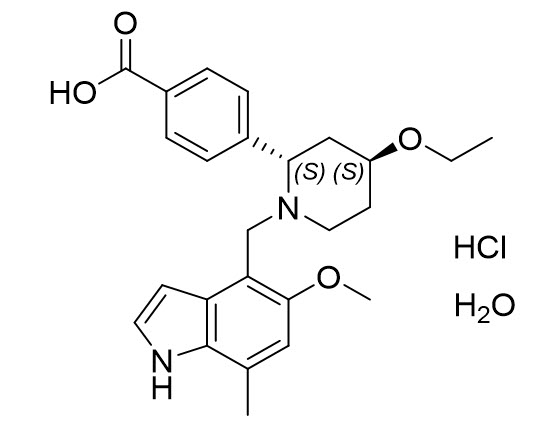
Iptacopan hydrochloride monohydrate is a white or almost white to pale purplish-pink powder.
FABHALTA is supplied as hard gelatin capsules for oral administration. The capsules are packaged in high-density polyethylene (HDPE) bottles with induction seals and child resistant caps. Each FABHALTA capsule contains 200 mg iptacopan (provided as 225.8 mg iptacopan hydrochloride monohydrate) and the capsule shell contains the following inactive ingredients: gelatin, red ferric oxide, titanium dioxide, yellow ferric oxide. The black printing ink contains ferrosoferric oxide, potassium hydroxide, propylene glycol, shellac, and strong ammonia solution.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Iptacopan binds to Factor B of the alternative complement pathway and regulates the cleavage of C3, generation of downstream effectors, and the amplification of the terminal pathway.
In PNH, intravascular hemolysis (IVH) is mediated by the downstream membrane attack complex (MAC), while extravascular hemolysis (EVH) is facilitated by C3b opsonization. Iptacopan acts proximally in the alternative pathway of the complement cascade to control both C3b-mediated EVH and terminal complement- mediated IVH.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Inhibition of the alternative complement pathway biomarkers, in vitro alternative pathway assay and plasma Bb (fragment Bb of Factor B), started approximately 2 hours after a single iptacopan dose in healthy volunteers.
In PNH patients receiving concomitant anti-C5 treatment and FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily, the in vitro alternative pathway assay and plasma Bb decreased from baseline by 54.1% and 56.1%, respectively, on the first observation on Day 8. In treatment naïve PNH patients, these same biomarkers decreased from baseline by 78.4% and 58.9%, respectively, on the first observation after 4 weeks of treatment with FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily.
In PNH patients on concomitant anti-C5 treatment and FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily, the mean PNH red blood cell (RBC) clone size was 54.8% at baseline and increased to 89.2% after 13 weeks; the proportion of PNH Type II + III RBCs with C3 deposition was 12.4% at baseline and decreased to 0.2% after 13 weeks. In treatment naïve PNH patients, the mean PNH RBC clone size was 49.1% at baseline and increased to 91.1% after 12 weeks; there were negligible PNH Type II + III RBCs with C3 deposition in this population due to the predominance of IVH.
Iptacopan reduces serum LDH levels. In PNH patients previously treated with eculizumab, all patients treated with FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily achieved a reduction of LDH levels to < 1.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN) at 13 weeks. In treatment naïve PNH patients, FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily reduced LDH by > 60% compared to baseline after 12 weeks and maintained the effect through the end of the study at 2 years.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a QTc clinical study in healthy volunteers, single supra-therapeutic iptacopan doses up to 1,200 mg (which provided greater than 4-fold peak concentration of the MRHD) showed no effect on cardiac repolarization or QT interval.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following oral administration, iptacopan reached peak plasma concentrations approximately 2 hours post dose. At the recommended dosing regimen of 200 mg twice daily, steady state is achieved in approximately 5 days with minor accumulation (1.4-fold).
Effect of Food
Based on a food-effect study in healthy volunteers, a high-fat meal did not affect the exposure of iptacopan to a clinically meaningful degree.
Distribution
Iptacopan showed concentration-dependent plasma protein binding due to binding to the target Factor B in the systemic circulation. Iptacopan was 75% to 93% protein bound in vitro at the relevant clinical plasma concentrations. After administration of iptacopan 200 mg twice daily, the apparent volume of distribution at steady state was approximately 288 L.
Elimination
The half-life (t1/2) of iptacopan at steady state is approximately 25 hours after administration of FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily. The clearance of iptacopan at steady state is 7.96 L/h after administration of FABHALTA 200 mg twice daily.
Metabolism
Metabolism is a predominant elimination pathway for iptacopan with approximately 50% of the dose attributed to oxidative pathways. Metabolism of iptacopan includes N-dealkylation, O-deethylation, oxidation, and dehydrogenation, mostly driven by CYP2C8 (98%) with a small contribution from CYP2D6 (2%). Iptacopan undergoes Phase 2 metabolism through glucuronidation by UGT1A1, UGT1A3, and UGT1A8. In plasma, iptacopan was the major component, accounting for 83% of the drug related species. Two acyl glucuronides were the only metabolites detected in plasma and were minor, accounting for 8% and 5% of the drug related species. Iptacopan metabolites are not pharmacologically active.
Excretion
In a human study, following a single 100 mg oral dose of [14C]-iptacopan, mean total excretion of radioactivity (iptacopan and metabolites) was 71.5% in the feces and 24.8% in the urine, for a total mean excretion of >96% of the dose. Specifically, 17.9% of the dose was excreted as parent iptacopan in the urine, and 16.8% of the dose was excreted as parent iptacopan in feces.
Linearity/Non-linearity
At doses between 25 mg and 200 mg twice daily, iptacopan was overall less than dose proportional. However, oral doses of 100 mg and 200 mg were approximately dose proportional.
Specific Populations
A population pharmacokinetic (PK) analysis was conducted on iptacopan data from 234 patients. Age, body weight, race, and gender did not have a clinically significant effect on iptacopan PK.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the exposure of iptacopan was assessed using a population pharmacokinetic analysis. Renal function was estimated as eGFR using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation. There were no clinically relevant differences in the exposure of iptacopan between patients with normal renal function compared to patients with mild (eGFR 60 to < 90 mL/min/1.73 m2) or moderate (eGFR 30 to < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) renal impairment. The population pharmacokinetic analysis did not include a sufficient number of patients with severe renal impairment with or without hemodialysis.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In a study in subjects with normal hepatic function and patients with mild (Child-Pugh class A), moderate (Child-Pugh class B), or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class C), there was a negligible effect of hepatic impairment on the total (bound+unbound) exposure of iptacopan. However, unbound iptacopan AUCinf increased by 1.5, 1.6, and 3.7-fold in patients with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment, respectively, compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Based on a clinical drug interaction study in healthy volunteers, iptacopan exposure did not change to a clinically relevant degree when coadministered with clopidogrel (a moderate CYP2C8 inhibitor) or cyclosporine (a P-gp, BCRP, and OATP 1B1/1B3 inhibitor). The exposure of digoxin (a P-gp substrate) and rosuvastatin (an OATP substrate) did not change to a clinically relevant degree when coadministered with iptacopan.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Iptacopan was not genotoxic or mutagenic in a battery of in vitro and in vivo assays.
Carcinogenicity studies conducted with oral administration of iptacopan in RasH2 transgenic mice with doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day for 6 months and in rats with doses up to 750 mg/kg/day for 2 years did not identify any carcinogenic potential. The highest exposure to iptacopan in rats corresponds to ~9-times the MRHD based on AUC.
In a fertility study in male rats, iptacopan did not adversely impact fertility up to the highest tested dose of 750 mg/kg/day, which corresponds to 4-times the MRHD based on AUC. Reversible effects on the male reproductive system (testicular tubular degeneration and cellular debris in epididymis) were observed in repeat-dose toxicity studies with oral administration in dogs at doses ≥ 2-times the MRHD based on AUC, with no clear effects on sperm numbers, morphology or motility. In a fertility and early embryonic developmental study in female rats, oral administration of iptacopan caused increased pre- and post-implantation losses when given at the highest dose of 1,000 mg/kg/day orally, which corresponds to ~11-times the MRHD based on AUC.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
APPLY-PNH: Anti-C5 treatment Experienced Patients With PNH
The efficacy of FABHALTA administered orally in adults with PNH was evaluated in a multi-center, open-label, 24-week, active comparator-controlled trial (APPLY-PNH; NCT04558918).
The study enrolled adults with PNH and residual anemia (hemoglobin < 10 g/dL) despite previous treatment with a stable regimen of anti-C5 treatment (either eculizumab or ravulizumab) for at least 6 months prior to randomization.
Ninety-seven patients were randomized in an 8:5 ratio to switch to FABHALTA 200 mg orally twice daily (n = 62) or to continue anti-C5 treatment (US- approved and non-US-approved eculizumab product n = 23 or US-approved and non- US-approved ravulizumab product n = 12) throughout the duration of the 24-week randomized controlled period. Randomization was stratified based on prior anti-C5 treatment and transfusion history within the last 6 months. Following completion of the 24-week randomized controlled period, all patients were eligible to enroll in a 24-week treatment extension period and receive FABHALTA monotherapy. Subsequently, patients were eligible to enter a separate long-term extension study.
Patients were required to be vaccinated against Neisseria meningitidis and recommended to be vaccinated against Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae type B. If the patient had not been previously vaccinated or if a booster was required, vaccination was administered at least 2 weeks prior to the first dose of study medication. If FABHALTA treatment was initiated earlier than 2 weeks after vaccination, antibacterial drug prophylaxis was administered.
Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were generally well balanced between treatment groups (see Table 2). The mean time on prior anti-C5 treatment was 3.8 and 4.2 years for the FABHALTA and anti-C5 groups, respectively. The baseline mean PNH RBC clone size (Type II + III) was 64.6% for FABHALTA and 57.4% for the anti-C5 group.
Table 2: Patient Baseline Demographics and Characteristics in APPLY- PNH|
Abbreviations: LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MAVEs, major adverse vascular events (includes thrombosis, stroke and myocardial infarction); SD, standard deviation. | |||
|
Parameters |
Statistics |
FABHALTA |
Anti-C5 |
|
Age (years) |
Mean (SD) |
51.7 (16.9) |
49.8 (16.7) |
|
Sex |
n (%) |
43 (69.4) |
24 (68.6) |
|
Race |
n (%) |
48 (77.4) |
26 (74.3) |
|
Ethnicity |
n (%) |
51 (82.3) |
27 (77.1) |
|
Hemoglobin level (g/dL) |
Mean (SD) |
8.9 (0.7) |
8.9 (0.9) |
|
LDH level (U/L) |
Mean (SD) |
269 (70) |
273 (85) |
|
Absolute reticulocyte count (ARC) (109/L) |
Mean (SD) |
193 (84) |
191 (81) |
|
At least one transfusion in 6 months prior to randomization |
n (%) |
35 (56.5) |
21 (60.0) |
|
History of MAVEs in the last 12 months |
n (%) |
12 (19.4) |
10 (28.6) |
|
Disease duration (years) |
Mean (SD) |
11.9 (9.8) |
13.5 (10.9) |
Efficacy was established based on demonstration of superiority of switching to FABHALTA compared to continuing on anti-C5 therapy in achieving hematological response after 24 weeks of treatment, without a need for transfusion, by assessing the proportion of patients demonstrating: 1) sustained increase of ≥ 2 g/dL in hemoglobin levels from baseline (hemoglobin improvement) and 2) sustained hemoglobin levels ≥ 12 g/dL. Additional efficacy endpoints included transfusion avoidance, change from baseline in hemoglobin levels and change from baseline in absolute reticulocyte counts.
The efficacy results from the APPLY-PNH trial are provided in Table 3.
Table 3: Efficacy Results for the 24-week Randomized Treatment Period for APPLY-PNH|
Abbreviations: RR, rate ratio | |||
|
Endpoints |
FABHALTA |
Anti-C5 |
Difference |
|
Primary endpoints | |||
|
Patients with sustained increase of hemoglobin levels ≥ 2 g/dLa from baseline in the absence of transfusions Response rate (%) |
51/62 82.3 |
0/35 0 |
81.5b |
|
Patients with sustained hemoglobin level ≥ 12 g/dLa in the absence of transfusions Response rate (%) |
42/62 67.7 |
0/35 0 |
66.6b |
|
Secondary endpoints | |||
|
Patients avoiding transfusionc,d Transfusion avoidance rate (%) |
59/62 95.2 |
16/35 45.7 |
49.5b |
|
Hemoglobin change from baseline (g/dL) (adjusted meane,f) |
3.6 |
-0.1 |
3.7 |
|
Absolute reticulocyte count change from baseline (109/L) (adjusted meane) |
-116 |
0 |
-116 |
APPOINT-PNH: Complement Inhibitor Naïve Patients with PNH
Study APPOINT-PNH (NCT04820530) is a single arm study in adults with PNH who were not previously treated with a complement inhibitor. This study enrolled a total of 40 adults with PNH (RBC clone size ≥ 10%), hemoglobin < 10 g/dL, and LDH > 1.5 times upper limit of normal (ULN). All 40 patients received FABHALTA 200 mg orally twice daily during the 24-week open-label core treatment period. Subsequently, patients were eligible to enroll in a 24-week treatment extension period and continue to receive FABHALTA, followed by a separate long-term extension study.
The mean age of the patients was 42.1 years and 42.5% were female. The mean disease duration was 4.7 years. The baseline mean PNH RBC clone size (Type II
- III) was 42.7%, mean baseline hemoglobin was 8.2 g/dL, and approximately 70% of patients required a transfusion in the 6 months prior to treatment. The baseline mean LDH level was 1,699 U/L and the mean absolute reticulocyte count was 154 X 109/L. About 13% of patients had a history of MAVEs. No patients discontinued from the core treatment period of the study.
In total, 77.5% (95% CI: 61.5%, 89.2%) of patients (31/40) achieved a sustained increase (between Day 126 and Day 168) in hemoglobin levels from baseline of ≥ 2 g/dL in the absence of RBC transfusions, based on central laboratory hemoglobin values. In a sensitivity analysis, 87.5% (95% CI: 73.2%, 95.8%) of patients (35/40) achieved a sustained increase (between Day 126 and Day 168) in hemoglobin levels from baseline of ≥ 2 g/dL in the absence of RBC transfusions, including local laboratory hemoglobin values when central laboratory hemoglobin values were not available.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Serious Infections Caused by Encapsulated Bacteria
Advise patients of the risk of serious infection. Inform patients of the need to complete or update their vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria at least 2 weeks prior to receiving the first dose of FABHALTA or receive antibacterial drug prophylaxis if FABHALTA treatment must be initiated immediately and they have not been previously vaccinated. Inform patients of the requirement to be revaccinated according to current ACIP recommendations for encapsulated bacteria while on FABHALTA therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Inform patients that vaccination may not prevent serious infection and to seek immediate medical attention if the following signs or symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]:
- fever with or without shivers or chills
- fever and a rash
- fever with chest pain and cough
- fever with breathlessness/fast breathing
- fever with high heart rate
- headache with nausea or vomiting
- headache and a fever
- headache with a stiff neck or stiff back
- confusion
- body aches with flu-like symptoms
- clammy skin
- eyes sensitive to light
Inform patients that they will be given a Patient Safety Card for FABHALTA that they should carry with them at all times during and for 2 weeks following treatment with FABHALTA. This card describes symptoms which, if experienced, should prompt the patient to seek immediate medical evaluation.
FABHALTA REMS
FABHALTA is available only through a restricted program called FABHALTA REMS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Inform the patient of the following notable requirements:
- Patients must receive counseling about the risk of serious infections caused by encapsulated bacteria.
- Patients must receive written educational materials about this risk.
- Patients must be instructed to carry the Patient Safety Card with them at all times during and for 2 weeks following treatment with FABHALTA.
- Patients must be instructed to complete or update vaccines against encapsulated bacteria per ACIP recommendations as directed by the prescriber prior to treatment with FABHALTA.
- Patients must receive antibiotics as directed by the prescriber if they are not up to date on vaccinations against encapsulated bacteria and have to start FABHALTA right away.
Importance of Adherence to Dosing Schedule
Inform patients with PNH of the importance of taking FABHALTA as prescribed in order to minimize the risk of hemolysis.
Discontinuation
Inform patients with PNH that they may develop serious hemolysis due to PNH if FABHALTA is discontinued and that they should be monitored by their healthcare providers for at least 2 weeks following discontinuation of FABHALTA.
Inform patients who discontinue FABHALTA to keep the Patient Safety Card with them for 2 weeks after the last dose of FABHALTA. The increased risk of serious infection may continue for a few weeks after the last dose of FABHALTA.
Hyperlipidemia
Inform patients that FABHALTA may increase their cholesterol and triglycerides and that monitoring of these parameters will be needed periodically during treatment.
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, New Jersey 07936
For more information, visit www.FABHALTA.com or call 1-888-669-6682.
© Novartis
T2024-10
