PREZISTA
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PREZISTA safely and effectively. See Full Prescribing Information for PREZISTA. PREZISTA (darunavir) oral suspension PREZISTA (darunavir) tablet, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2006
814301f9-c990-46a5-b481-2879a521a16f
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 15, 2023
Janssen Products LP
DUNS: 804684207
Products 5
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
darunavir
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
darunavir
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
darunavir
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
darunavir
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
darunavir
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 200 mL Bottle Carton
200 mL
NDC 59676-565-01
PREZISTA**®**
(darunavir) Oral Suspension
100 mg per mL
Store at 25°C (77°F); with excursions
permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F).
Do not refrigerate or freeze.
Shake well before each usage.
**RECOMMENDED DOSAGE:**See
Prescribing Information
**Dispensing:**For information concerning
proper usage of the oral dosing syringe,
see accompanying patient instructions.
Keep out of reach of children.
ALERT
** Find out about medicines that**
** should NOT be taken with**
** PREZISTA.**
Rx only
janssen

CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (narrow therapeutic index). Examples of these drugs and other contraindicated drugs (which may lead to reduced efficacy of darunavir) are listed below [see Drug Interactions (7.3)] . Due to the need for co-administration of PREZISTA with ritonavir, please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for a description of ritonavir contraindications.
- Alpha 1-adrenoreceptor antagonist: alfuzosin
- Anti-gout: colchicine, in patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment
- Antimycobacterial: rifampin
- Antipsychotics: lurasidone, pimozide
- Cardiac Disorders: dronedarone, ivabradine, ranolazine
- Ergot derivatives, e.g. dihydroergotamine, ergotamine, methylergonovine
- Herbal product: St. John's wort ( Hypericum perforatum)
- Hepatitis C direct acting antiviral: elbasvir/grazoprevir
- Lipid modifying agents: lomitapide, lovastatin, simvastatin
- Opioid Antagonist: naloxegol
- PDE-5 inhibitor: sildenafil when used for treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Sedatives/hypnotics: orally administered midazolam, triazolam
- Co-administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir is contraindicated with drugs that are highly dependent on CYP3A for clearance and for which elevated plasma concentrations are associated with serious and/or life-threatening events (narrow therapeutic index). ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Importance of Co-administration with Ritonavir
PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir and food to achieve the desired antiviral effect. Failure to administer PREZISTA with ritonavir and food may result in a loss of efficacy of darunavir.
Please refer to ritonavir prescribing information for additional information on precautionary measures.
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
Drug-induced hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis) has been reported with PREZISTA/ritonavir. During the clinical development program (N=3063), hepatitis was reported in 0.5% of patients receiving combination therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Patients with pre-existing liver dysfunction, including chronic active hepatitis B or C, have an increased risk for liver function abnormalities including severe hepatic adverse events.
Post-marketing cases of liver injury, including some fatalities, have been reported. These have generally occurred in patients with advanced HIV-1 disease taking multiple concomitant medications, having co-morbidities including hepatitis B or C co-infection, and/or developing immune reconstitution syndrome. A causal relationship with PREZISTA/ritonavir therapy has not been established.
Appropriate laboratory testing should be conducted prior to initiating therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir and patients should be monitored during treatment. Increased AST/ALT monitoring should be considered in patients with underlying chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases, especially during the first several months of PREZISTA/ritonavir treatment.
Evidence of new or worsening liver dysfunction (including clinically significant elevation of liver enzymes and/or symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, nausea, jaundice, dark urine, liver tenderness, hepatomegaly) in patients on PREZISTA/ritonavir should prompt consideration of interruption or discontinuation of treatment.
5.3 Severe Skin Reactions
During the clinical development program (n=3063), severe skin reactions, accompanied by fever and/or elevations of transaminases in some cases, have been reported in 0.4% of subjects. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome was rarely (less than 0.1%) reported during the clinical development program. During post- marketing experience toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms, and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis have been reported. Discontinue PREZISTA/ritonavir immediately if signs or symptoms of severe skin reactions develop. These can include but are not limited to severe rash or rash accompanied with fever, general malaise, fatigue, muscle or joint aches, blisters, oral lesions, conjunctivitis, hepatitis and/or eosinophilia.
Rash (all grades, regardless of causality) occurred in 10.3% of subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir [see Adverse Reactions (6)] . Rash was mostly mild-to-moderate, often occurring within the first four weeks of treatment and resolving with continued dosing. The discontinuation rate due to rash in subjects using PREZISTA/ritonavir was 0.5%.
Rash occurred more commonly in treatment-experienced subjects receiving regimens containing PREZISTA/ritonavir + raltegravir compared to subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir without raltegravir or raltegravir without PREZISTA/ritonavir. However, rash that was considered drug related occurred at similar rates for all three groups. These rashes were mild to moderate in severity and did not limit therapy; there were no discontinuations due to rash.
5.4 Sulfa Allergy
Darunavir contains a sulfonamide moiety. PREZISTA should be used with caution in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy. In clinical studies with PREZISTA/ritonavir, the incidence and severity of rash were similar in subjects with or without a history of sulfonamide allergy.
5.5 Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions due to Drug Interactions
Initiation of PREZISTA/ritonavir, a CYP3A inhibitor, in patients receiving medications metabolized by CYP3A or initiation of medications metabolized by CYP3A in patients already receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir, may increase plasma concentrations of medications metabolized by CYP3A and reduce plasma concentrations of active metabolite(s) formed by CYP3A.
Initiation of medications that inhibit or induce CYP3A may increase or decrease concentrations of PREZISTA/ritonavir, respectively.
These interactions may lead to:
- Clinically significant adverse reactions, potentially leading to severe, life threatening, or fatal events from greater exposures of concomitant medications.
- Clinically significant adverse reactions from greater exposures of PREZISTA/ritonavir.
- Loss of therapeutic effect of the concomitant medications from lower exposures of active metabolite(s).
- Loss of therapeutic effect of PREZISTA/ritonavir and possible development of resistance from lower exposures of PREZISTA/ritonavir.
See Table 10for steps to prevent or manage these possible and known significant drug interactions, including dosing recommendations [see Drug Interactions (7)] . Consider the potential for drug interactions prior to and during PREZISTA/ritonavir therapy; review concomitant medications during PREZISTA/ritonavir therapy; and monitor for the adverse reactions associated with the concomitant drugs [see Contraindications (4)and Drug Interactions (7)] .
5.6 Diabetes Mellitus/Hyperglycemia
New onset diabetes mellitus, exacerbation of pre-existing diabetes mellitus, and hyperglycemia have been reported during postmarketing surveillance in HIV- infected patients receiving protease inhibitor (PI) therapy. Some patients required either initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents for treatment of these events. In some cases, diabetic ketoacidosis has occurred. In those patients who discontinued PI therapy, hyperglycemia persisted in some cases. Because these events have been reported voluntarily during clinical practice, estimates of frequency cannot be made and causal relationships between PI therapy and these events have not been established.
5.7 Fat Redistribution
Redistribution/accumulation of body fat, including central obesity, dorsocervical fat enlargement (buffalo hump), peripheral wasting, facial wasting, breast enlargement, and "cushingoid appearance" have been observed in patients receiving antiretroviral therapy. The mechanism and long-term consequences of these events are currently unknown. A causal relationship has not been established.
5.8 Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune reconstitution syndrome has been reported in patients treated with combination antiretroviral therapy, including PREZISTA. During the initial phase of combination antiretroviral treatment, patients whose immune systems respond may develop an inflammatory response to indolent or residual opportunistic infections (such as Mycobacterium aviuminfection, cytomegalovirus, Pneumocystis jiroveciipneumonia [PCP], or tuberculosis), which may necessitate further evaluation and treatment.
Autoimmune disorders (such as Graves' disease, polymyositis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and autoimmune hepatitis) have also been reported to occur in the setting of immune reconstitution; however, the time to onset is more variable, and can occur many months after initiation of antiretroviral treatment.
5.9 Hemophilia
There have been reports of increased bleeding, including spontaneous skin hematomas and hemarthrosis in patients with hemophilia type A and B treated with PIs. In some patients, additional factor VIII was given. In more than half of the reported cases, treatment with PIs was continued or reintroduced if treatment had been discontinued. A causal relationship between PI therapy and these episodes has not been established.
5.10 Not Recommended in Pediatric Patients Below 3 Years of Age
PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age is not recommended in view of toxicity and mortality observed in juvenile rats dosed with darunavir (from 20 mg/kg to 1000 mg/kg) up to days 23 to 26 of age [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1and 8.4)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- Drug-induced hepatitis (e.g., acute hepatitis, cytolytic hepatitis) has been reported with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Monitor liver function before and during therapy, especially in patients with underlying chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases. Post-marketing cases of liver injury, including some fatalities, have been reported. ( 5.2)
- Skin reactions ranging from mild to severe, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, have been reported. Discontinue treatment if severe reaction develops. ( 5.3)
- Use with caution in patients with a known sulfonamide allergy. ( 5.4)
- Patients may develop new onset diabetes mellitus or hyperglycemia. Initiation or dose adjustments of insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents may be required. ( 5.6)
- Patients may develop redistribution/accumulation of body fat or immune reconstitution syndrome. ( 5.7, 5.8)
- Patients with hemophilia may develop increased bleeding events. ( 5.9)
- PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended in pediatric patients below 3 years of age in view of toxicity and mortality observed in juvenile rats dosed with darunavir up to days 23 to 26 of age. ( 5.10)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Darunavir was evaluated for carcinogenic potential by oral gavage administration to mice and rats up to 104 weeks. Daily doses of 150, 450 and 1000 mg/kg were administered to mice and doses of 50, 150 and 500 mg/kg was administered to rats. A dose-related increase in the incidence of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas were observed in males and females of both species as well as an increase in thyroid follicular cell adenomas in male rats. The observed hepatocellular findings in rodents are considered to be of limited relevance to humans. Repeated administration of darunavir to rats caused hepatic microsomal enzyme induction and increased thyroid hormone elimination, which predispose rats, but not humans, to thyroid neoplasms. At the highest tested doses, the systemic exposures to darunavir (based on AUC) were between 0.4- and 0.7-fold (mice) and 0.7- and 1-fold (rats), relative to those observed in humans at the recommended therapeutic doses (600/100 mg twice daily or 800/100 mg once daily).
Darunavir was not mutagenic or genotoxic in a battery of in vitroand in vivoassays including bacterial reserve mutation (Ames), chromosomal aberration in human lymphocytes and in vivomicronucleus test in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
No effects on fertility or early embryonic development were observed with darunavir in rats.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PREZISTA ®(darunavir) 100 mg per mL oral suspension is a white to off-white opaque liquid supplied in amber-colored multiple-dose bottles containing 100 mg of darunavir per mL packaged with a 6 mL oral dosing syringe with 0.2 mL gradations.
PREZISTA ®(darunavir) 75 mg tablets are supplied as white, caplet-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with "75" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA ®(darunavir) 150 mg tablets are supplied as white, oval-shaped, film- coated tablets debossed with "150" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA ®(darunavir) 600 mg tablets are supplied as orange, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with "600MG" on one side and "TMC" on the other side.
PREZISTA ®(darunavir) 800 mg tablets are supplied as dark red, oval-shaped, film-coated tablets debossed with "800" on one side and "T" on the other side.
PREZISTA is packaged in bottles in the following configuration:
- 100 mg/mL oral suspension – 200 mL bottles (NDC 59676-565-01)
- 75 mg tablets — bottles of 480 (NDC 59676-563-01)
- 150 mg tablets — bottles of 240 (NDC 59676-564-01)
- 600 mg tablets — bottles of 60 (NDC 59676-562-01)
- 800 mg tablets — bottles of 30 (NDC 59676-566-30)
Storage
PREZISTA Oral Suspension
- Store at 25°C (77°F); with excursions permitted to 15°–30°C (59°–86°F).
- Do not refrigerate or freeze. Avoid exposure to excessive heat.
- Store in the original container.
- Shake well before each usage.
PREZISTA Tablets
- Store at 25°C (77°F); with excursions permitted to 15°–30°C (59°–86°F).
Keep PREZISTA out of reach of children.
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
PREZISTA (pre-ZIS-ta)
(darunavir)
oral suspension
Be sure that you read, understand, and follow these Instructions for Use so that you measure and take PREZISTA oral suspension correctly. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
|
Each PREZISTA oral suspension carton contains:
|
|
Important information for use:
*Shake PREZISTA oral suspension well before each use. *PREZISTA oral suspension should be given with the oral dosing syringe provided to make sure you measure the right amount. The oral dosing syringe provided with your PREZISTA oral suspension should not be used for any other medicines.
|
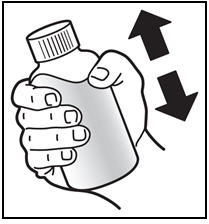
*Shake the bottle. * Shake the bottle well before each use (See Figure A). |
Figure A: Shake the bottle | |
|
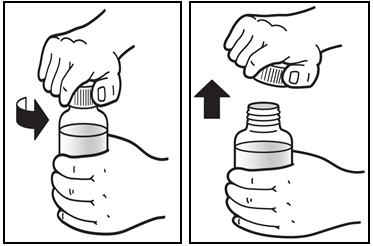
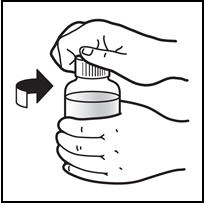
*Open the bottle of PREZISTA oral suspension. * Open the bottle by pushing downward on the cap and twisting it in the direction of the arrow (counter-clockwise) (See Figure B). |
Figure B: Opening the bottle | |
|
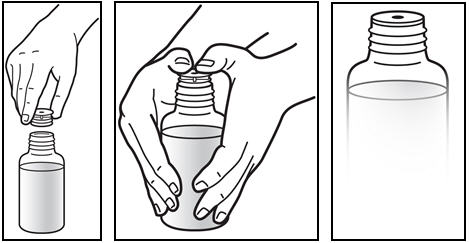
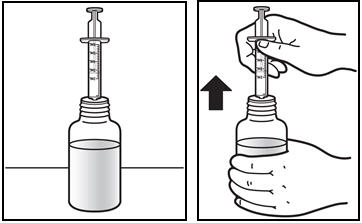
*The first time a bottle of PREZISTA oral suspension is used: * Insert the oral syringe adapter into the bottle. Press on the adapter until it is even with the top of the bottle (See Figure C). *Do notremove the oral syringe adapter from the bottle once inserted. |
Figure C: Inserting the adapter | |
|
*Insert the oral dosing syringe. * Fully push down (depress) the plunger of the syringe. * Insert the syringe into the opening of the oral syringe adapter until it is firmly in place (See Figure D). |
Figure D: Inserting the syringe | |
|
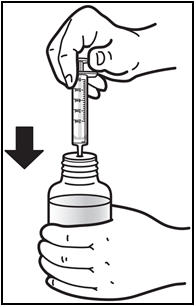
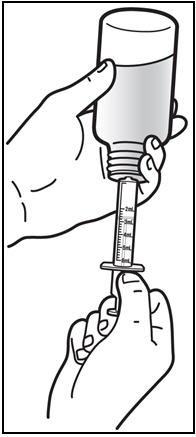
*Withdraw the prescribed amount of PREZISTA oral suspension. * Turn the bottle upside down. Gently pull back the plunger of the syringe until the bottom of the plunger is even with the markings on the syringe for the prescribed dose (See Figure E). If you see air bubbles in the syringe, push the plunger in to empty the oral suspension back into the bottle. Then repeat steps 4 and 5. * If you or your child's dose of PREZISTA oral suspension is more than 6 mL, you will need to divide the dose. Follow the instructions given to you by your healthcare provider or pharmacist about how to divide the dose. |
Figure E: Withdrawing the Oral Suspension | |
|
Turn the bottle upright and remove the syringe from the bottle by pulling straight up on the oral dosing syringe (See**Figure F***).** |
Figure F: Removing the syringe | |
|
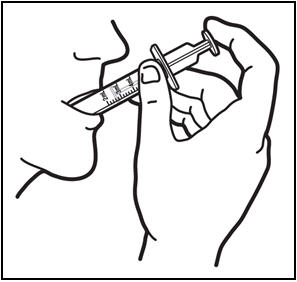
*Take the dose of PREZISTA. * Place the tip of the oral dosing syringe in the mouth. * Press on the plunger of the syringe towards the mouth (See Figure G). If you or your child's dose is more than 6 mL you will need to divide the dose. Follow the instructions given to you by your healthcare provider or pharmacist about how to divide the dose, and repeat steps 4 through 7. |
Figure G: Taking the dose of PREZISTA | |
|
*Close the bottle with the cap after use. * Close the bottle by twisting the cap in the direction of the arrow (clockwise) (See Figure H). |
Figure H: Closing the bottle | |
|
Remove the plunger from the barrel by pulling the plunger and barrel away from each other (See**Figure I***). Rinse both parts of the syringe with water and allow to air dry after each use.** |
Figure I: Removing the plunger from the barrel | |
|
After air drying, put the oral dosing syringe back together by inserting the plunger into the barrel (See**Figure J***). Store the oral dosing syringe with PREZISTA oral suspension.** |
Figure J: Putting the syringe back together |
How should I store PREZISTA?
- Store PREZISTA oral suspension and the oral dosing syringe at room temperature 77°F (25°C).
- Do not refrigerate or freeze PREZISTA oral suspension.
- Keep PREZISTA oral suspension away from high heat.
- Store PREZISTA oral suspension in the original container.
Keep PREZISTA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This Instruction for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Janssen Products, LP, Horsham PA 19044
Revised: May 2022
©2006 Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Testing Prior to Initiation of PREZISTA/ritonavir
In treatment-experienced patients, treatment history, genotypic and/or phenotypic testing is recommended to assess drug susceptibility of the HIV-1 virus [see Microbiology (12.4)]. Refer to Dosage and Administration (2.3), (2.4)and (2.5)for dosing recommendations.
Appropriate laboratory testing such as serum liver biochemistries should be conducted prior to initiating therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
2.2 Monitoring During Treatment with PREZISTA/ritonavir
Patients with underlying chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, or in patients who have pre-treatment elevations of transaminases should be monitored for elevation in serum liver biochemistries, especially during the first several months of PREZISTA/ritonavir treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] .
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients
PREZISTA must be co-administered with ritonavir to exert its therapeutic effect. Failure to correctly co-administer PREZISTA with ritonavir will result in plasma levels of darunavir that will be insufficient to achieve the desired antiviral effect and will alter some drug interactions.
Patients who have difficulty swallowing PREZISTA tablets can use the 100 mg per mL PREZISTA oral suspension.
Treatment-Naïve Adult Patients
The recommended oral dose of PREZISTA is 800 mg (one 800 mg tablet or 8 mL of the oral suspension) taken with ritonavir 100 mg (one 100 mg tablet or capsule or 1.25 mL of a 80 mg per mL ritonavir oral solution) once daily and with food. An 8 mL PREZISTA dose should be taken as two 4 mL administrations with the included oral dosing syringe.
Treatment-Experienced Adult Patients
The recommended oral dosage for treatment-experienced adult patients is summarized in Table 1.
Baseline genotypic testing is recommended for dose selection. However, when genotypic testing is not feasible, PREZISTA 600 mg taken with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily is recommended.
Table 1: Recommended PREZISTA/ritonavir Dosage in Treatment- Experienced Adult Patients|
Formulation and Recommended Dosing | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Baseline Resistance |
PREZISTA tablets with ritonavir tablets or capsule |
PREZISTA oral suspension (100 mg/mL) with ritonavir oral solution (80 mg/mL) |
| ||
|
With no darunavir resistance associated substitutions * |
One 800 mg PREZISTA tablet with one 100 mg ritonavir tablet/capsule, taken once daily with food |
8 mL †PREZISTA oral suspension with 1.25 mL ritonavir oral solution, taken once daily with food |
|
With at least one darunavir resistance associated substitutions *, or with no baseline resistance information |
One 600 mg PREZISTA tablet with one 100 mg ritonavir tablet/capsule, taken twice daily with food |
6 mL PREZISTA oral suspension with 1.25 mL ritonavir oral solution, taken twice daily with food |
2.4 Recommended Dosage During Pregnancy
The recommended dosage in pregnant patients is PREZISTA 600 mg taken with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily with food.
PREZISTA 800 mg taken with ritonavir 100 mg once daily should only be considered in certain pregnant patients who are already on a stable PREZISTA 800 mg with ritonavir 100 mg once daily regimen prior to pregnancy, are virologically suppressed (HIV-1 RNA less than 50 copies per mL), and in whom a change to twice daily PREZISTA 600 mg with ritonavir 100 mg may compromise tolerability or compliance.
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients (age 3 to less than 18 years)
Healthcare professionals should pay special attention to accurate dose selection of PREZISTA, transcription of the medication order, dispensing information and dosing instruction to minimize risk for medication errors, overdose, and underdose.
Prescribers should select the appropriate dose of PREZISTA/ritonavir for each individual child based on body weight (kg) and should not exceed the recommended dose for adults.
Before prescribing PREZISTA, children weighing greater than or equal to 15 kg should be assessed for the ability to swallow tablets. If a child is unable to reliably swallow a tablet, the use of PREZISTA oral suspension should be considered.
The recommended dose of PREZISTA/ritonavir for pediatric patients (3 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg is based on body weight (see Tables 2, 3, 4, and 5) and should not exceed the recommended adult dose. PREZISTA should be taken with ritonavir and with food.
The recommendations for the PREZISTA/ritonavir dosage regimens were based on pediatric clinical trial data and population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dosing Recommendations for Treatment-Naïve Pediatric Patients or Antiretroviral Treatment-Experienced Pediatric Patients with No Darunavir Resistance Associated Substitutions
Pediatric Patients Weighing At Least 10 kg but Less than 15 kg
The weight-based dose in antiretroviral treatment-naïve pediatric patients or antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric patients with no darunavir resistance associated substitutions is PREZISTA 35 mg/kg once daily with ritonavir 7 mg/kg once daily using the following table:
Table 2: Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients Weighing 10 kg to Less Than 15 kg Who are Treatment-Naïve or Treatment-Experienced with No Darunavir Resistance Associated Substitutions *|
Body weight (kg) |
Formulation: PREZISTA oral suspension (100 mg/mL) and ritonavir oral solution (80 mg/mL) |
|---|---|
|
Dose: once daily with food | |
| |
|
Greater than or equal to 10 kg to less than 11 kg |
PREZISTA 3.6 mL †(350 mg) with ritonavir 0.8 mL (64 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 11 kg to less than 12 kg |
PREZISTA 4 mL †(385 mg) with ritonavir 0.8 mL (64 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 12 kg to less than 13 kg |
PREZISTA 4.2 mL (420 mg) with ritonavir 1 mL (80 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 13 kg to less than 14 kg |
PREZISTA 4.6 mL †(455 mg) with ritonavir 1 mL (80 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 14 kg to less than 15 kg |
PREZISTA 5 mL †(490 mg) with ritonavir 1.2 mL (96 mg) |
Pediatric Patients Weighing At Least 15 kg
Pediatric patients weighing at least 15 kg can be dosed with PREZISTA oral tablet(s) or suspension using the following table:
Table 3: Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients Weighing At Least 15 kg Who are Treatment-Naïve or Treatment-Experienced with No Darunavir Resistance Associated Substitutions *|
Body weight (kg) |
Formulation: PREZISTA tablet(s) and ritonavir capsules or tablets (100 mg) |
Formulation: PREZISTA oral suspension (100 mg/mL) and ritonavir oral solution (80 mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
|
Dose: once daily with food |
Dose: once daily with food | |
| ||
|
Greater than or equal to 15 kg to less than 30 kg |
PREZISTA 600 mg with ritonavir 100 mg |
PREZISTA 6 mL (600 mg) with ritonavir 1.25 mL (100 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 30 kg to less than 40 kg |
PREZISTA 675 mg with ritonavir 100 mg |
PREZISTA 6.8 mL †‡(675 mg) with ritonavir 1.25 mL (100 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 40 kg |
PREZISTA 800 mg with ritonavir 100 mg |
PREZISTA 8 mL ‡(800 mg) with ritonavir 1.25 mL (100 mg) |
Dosing Recommendations for Treatment-Experienced Pediatric Patients with At Least One Darunavir Resistance Associated Substitutions
Pediatric Patients Weighing At Least 10 kg but Less than 15 kg
The weight-based dose in antiretroviral treatment-experienced pediatric patients with at least one darunavir resistance associated substitution is PREZISTA 20 mg/kg twice daily with ritonavir 3 mg/kg twice daily using the following table:
Table 4: Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients Weighing 10 kg to Less Than 15 kg Who are Treatment-Experienced with At Least One Darunavir Resistance Associated Substitution *|
Body weight (kg) |
Formulation: PREZISTA oral suspension (100 mg/mL) and ritonavir oral solution (80 mg/mL) |
|---|---|
|
Dose: twice daily with food | |
| |
|
Greater than or equal to 10 kg to less than 11 kg |
PREZISTA 2 mL (200 mg) with ritonavir 0.4 mL (32 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 11 kg to less than 12 kg |
PREZISTA 2.2 mL (220 mg) with ritonavir 0.4 mL (32 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 12 kg to less than 13 kg |
PREZISTA 2.4 mL (240 mg) with ritonavir 0.5 mL (40 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 13 kg to less than 14 kg |
PREZISTA 2.6 mL (260 mg) with ritonavir 0.5 mL (40 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 14 kg to less than 15 kg |
PREZISTA 2.8 mL (280 mg) with ritonavir 0.6 mL (48 mg) |
Pediatric Patients Weighing At Least 15 kg
Pediatric patients weighing at least 15 kg can be dosed with PREZISTA oral tablet(s) or suspension using the following table:
Table 5: Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients Weighing At Least 15 kg Who are Treatment-Experienced with At Least One Darunavir Resistance Associated Substitution *|
Body weight (kg) |
Formulation: PREZISTA tablet(s) and ritonavir tablets, capsules (100 mg) or oral solution (80 mg/mL) |
Formulation: PREZISTA oral suspension (100 mg/mL) and ritonavir oral solution (80 mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|
|
Dose: twice daily with food |
Dose: twice daily with food | |
| ||
|
Greater than or equal to 15 kg to less than 30 kg |
PREZISTA 375 mg with ritonavir 0.6 mL (48 mg) |
PREZISTA 3.8 mL (375 mg) †with ritonavir 0.6 mL (48 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 30 kg to less than 40 kg |
PREZISTA 450 mg with ritonavir 0.75 mL (60 mg) |
PREZISTA 4.6 mL (450 mg) †with ritonavir 0.75 mL (60 mg) |
|
Greater than or equal to 40 kg |
PREZISTA 600 mg with ritonavir 100 mg |
PREZISTA 6 mL (600 mg) with ritonavir 1.25 mL (100 mg) |
The use of PREZISTA/ritonavir in pediatric patients below 3 years of age is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] .
2.6 Not Recommended in Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. No data are available regarding the use of PREZISTA/ritonavir when co-administered to subjects with severe hepatic impairment; therefore, PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
- Testing:
- In treatment-experienced patients, treatment history genotypic and/or phenotypic testing is recommended prior to initiation of therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir to assess drug susceptibility of the HIV-1 virus ( 2.1, 12.4)
- Monitor serum liver chemistry tests before and during therapy with PREZISTA/ritonavir. ( 2.1, 2.2, 5.2)
- Treatment-naïve adult patients and treatment-experienced adult patients with no darunavir resistance associated substitutions: 800 mg (one 800 mg tablet) taken with ritonavir 100 mg once daily and with food. ( 2.3)
- Treatment-experienced adult patients with at least one darunavir resistance associated substitution: 600 mg (one 600 mg tablet) taken with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily and with food. ( 2.3)
- Pregnant patients: 600 mg (one 600 mg tablet) taken with ritonavir 100 mg twice daily and with food. ( 2.4)
- Pediatric patients (3 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg): dosage of PREZISTA and ritonavir is based on body weight and should not exceed the adult dose. PREZISTA should be taken with ritonavir and with food. ( 2.5)
- PREZISTA/ritonavir is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. ( 2.6)
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Darunavir is an HIV-1 antiviral drug [see Microbiology (12.4)] .
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
In a thorough QT/QTc study in 40 healthy subjects, PREZISTA/ritonavir doses of 1.33 times the maximum recommended dose did not affect the QT/QTc interval.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics in Adults
General
Darunavir is primarily metabolized by CYP3A. Ritonavir inhibits CYP3A, thereby increasing the plasma concentrations of darunavir. When a single dose of PREZISTA 600 mg was given orally in combination with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily, there was an approximate 14-fold increase in the systemic exposure of darunavir. Therefore, PREZISTA should only be used in combination with 100 mg of ritonavir to achieve sufficient exposures of darunavir.
The pharmacokinetics of darunavir, co-administered with low dose ritonavir (100 mg), has been evaluated in healthy adult volunteers and in HIV-1-infected subjects. Table 11 displays the population pharmacokinetic estimates of darunavir after oral administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily (based on sparse sampling in 285 patients in trial TMC114-C214, 278 patients in trial TMC114-C229 and 119 patients [integrated data] from trials TMC114-C202 and TMC114-C213) and PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily (based on sparse sampling in 335 patients in trial TMC114-C211 and 280 patients in trial TMC114-C229) to HIV-1-infected patients.
Table 11: Population Pharmacokinetic Estimates of Darunavir at PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg Once Daily (Trial TMC114-C211, 48-Week Analysis and Trial TMC114-C229, 48-Week Analysis) and PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg Twice Daily (Trial TMC114-C214, 48-Week Analysis, Trial TMC114-C229, 48-Week Analysis and Integrated Data from Trials TMC114-C213 and TMC114-C202, Primary 24-Week Analysis)|
PREZISTA/ritonavir |
PREZISTA/ritonavir | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Parameter |
TMC114-C211 |
TMC114-C229 |
TMC114-C214 |
TMC114-C229 |
TMC114-C213 + TMC114-C202 (integrated data) |
|
N=number of subjects with data | |||||
| |||||
|
AUC 24h(ng.h/mL) * | |||||
|
Mean ± Standard Deviation |
93026 ± 27050 |
93334 ± 28626 |
116796 ± 33594 |
114302 ± 32681 |
124698 ± 32286 |
|
Median |
87854 |
87788 |
111632 |
109401 |
123336 |
|
C 0h(ng/mL) | |||||
|
Mean ± Standard Deviation |
2282 ± 1168 |
2160 ± 1201 |
3490 ± 1401 |
3386 ± 1372 |
3578 ± 1151 |
|
Median |
2041 |
1896 |
3307 |
3197 |
3539 |
Absorption and Bioavailability
Darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily, was absorbed following oral administration with a T maxof approximately 2.5–4 hours. The absolute oral bioavailability of a single 600 mg dose of darunavir alone and after co-administration with 100 mg ritonavir twice daily was 37% and 82%, respectively. In vivodata suggest that PREZISTA/ritonavir is an inhibitor of the P-glycoprotein (P-gp) transporters.
Effects of Food on Oral Absorption
When PREZISTA tablets were administered with food, the C maxand AUC of darunavir, co-administered with ritonavir, is approximately 40% higher relative to the fasting state. Within the range of meals studied, darunavir exposure is similar. The total caloric content of the various meals evaluated ranged from 240 Kcal (12 gms fat) to 928 Kcal (56 gms fat).
Distribution
Darunavir is approximately 95% bound to plasma proteins. Darunavir binds primarily to plasma alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG).
Metabolism
In vitroexperiments with human liver microsomes (HLMs) indicate that darunavir primarily undergoes oxidative metabolism. Darunavir is extensively metabolized by CYP enzymes, primarily by CYP3A. A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after a single dose administration of 400 mg 14C-darunavir, co- administered with 100 mg ritonavir, the majority of the radioactivity in the plasma was due to darunavir. At least 3 oxidative metabolites of darunavir have been identified in humans; all showed activity that was at least 90% less than the activity of darunavir against wild-type HIV-1.
Elimination
A mass balance study in healthy volunteers showed that after single dose administration of 400 mg 14C-darunavir, co-administered with 100 mg ritonavir, approximately 79.5% and 13.9% of the administered dose of 14C-darunavir was recovered in the feces and urine, respectively. Unchanged darunavir accounted for approximately 41.2% and 7.7% of the administered dose in feces and urine, respectively. The terminal elimination half-life of darunavir was approximately 15 hours when co-administered with ritonavir. After intravenous administration, the clearance of darunavir, administered alone and co- administered with 100 mg twice daily ritonavir, was 32.8 L/h and 5.9 L/h, respectively.
Special Populations
Hepatic Impairment
Darunavir is primarily metabolized by the liver. The steady-state pharmacokinetic parameters of darunavir were similar after multiple dose co- administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily to subjects with normal hepatic function (n=16), mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, n=8), and moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class B, n=8). The effect of severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of darunavir has not been evaluated [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)] .
Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Virus Co-infection
The 48-week analysis of the data from Studies TMC114-C211 and TMC114-C214 in HIV-1-infected subjects indicated that hepatitis B and/or hepatitis C virus co-infection status had no apparent effect on the exposure of darunavir.
Renal Impairment
Results from a mass balance study with 14C-PREZISTA/ritonavir showed that approximately 7.7% of the administered dose of darunavir is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug. As darunavir and ritonavir are highly bound to plasma proteins, it is unlikely that they will be significantly removed by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed that the pharmacokinetics of darunavir were not significantly affected in HIV-1-infected subjects with moderate renal impairment (CrCL between 30–60 mL/min, n=20). There are no pharmacokinetic data available in HIV-1-infected patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)] .
Gender
Population pharmacokinetic analysis showed higher mean darunavir exposure in HIV-1-infected females compared to males. This difference is not clinically relevant.
Race
Population pharmacokinetic analysis of darunavir in HIV-1-infected subjects indicated that race had no apparent effect on the exposure to darunavir.
Geriatric Patients
Population pharmacokinetic analysis in HIV-1-infected subjects showed that darunavir pharmacokinetics are not considerably different in the age range (18 to 75 years) evaluated in HIV-1-infected subjects (n=12, age greater than or equal to 65) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)] .
Pediatric Patients
PREZISTA/ritonavir administered twice daily
The pharmacokinetics of darunavir in combination with ritonavir in 93 antiretroviral treatment-experienced HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 3 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 10 kg showed that the administered weight-based dosages resulted in similar darunavir exposure when compared to the darunavir exposure achieved in treatment-experienced adults receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
PREZISTA/ritonavir administered once daily
The pharmacokinetics of darunavir in combination with ritonavir in 12 antiretroviral treatment-naïve HIV-1-infected pediatric subjects 12 to less than 18 years of age and weighing at least 40 kg receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily resulted in similar darunavir exposures when compared to the darunavir exposure achieved in treatment-naïve adults receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
Based on population pharmacokinetic modeling and simulation, the proposed PREZISTA/ritonavir once daily dosing regimens for pediatric patients 3 to less than 12 years of age is predicted to result in similar darunavir exposures when compared to the darunavir exposures achieved in treatment-naïve adults receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)] .
The population pharmacokinetic parameters in pediatric subjects with PREZISTA/ritonavir administered once or twice daily are summarized in the table below:
Table 12: Population Pharmacokinetic Estimates of Darunavir Exposure (Trials TMC114-C230, TMC114-C212 and TMC114-C228) Following Administration of Doses in Tables 2 and 3|
PREZISTA/ritonavir |
PREZISTA/ritonavir | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
TMC114-C228 * | ||||
|
Parameter |
TMC114-C230 † |
TMC114-C212 | ||
|
10 to less than 15 kg ‡ |
15 to less than 20 kg § | |||
|
N=number of subjects with data. | ||||
| ||||
|
AUC 24h(ng∙h/mL) ¶) | ||||
|
Mean ± Standard Deviation |
84390 ± 23587 |
126377 ± 34356 |
137896 ± 51420 |
157760 ± 54080 |
|
Median |
86741 |
127340 |
124044 |
132698 |
|
C 0h(ng/mL) | ||||
|
Mean ± Standard Deviation |
2141 ± 865 |
3948 ± 1363 |
4510 ± 2031 |
4848 ± 2143 |
|
Median |
2234 |
3888 |
4126 |
3927 |
Pregnancy and Postpartum
The exposure to total darunavir and ritonavir after intake of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily and PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily as part of an antiretroviral regimen was generally lower during pregnancy compared with postpartum (see Table 13, Table 14and Figure 1).
Table 13: Pharmacokinetic Results of Total Darunavir After Administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir at 600/100 mg Twice Daily as Part of an Antiretroviral Regimen, During the 2 ndTrimester of Pregnancy, the 3 rdTrimester of Pregnancy and Postpartum|
Pharmacokinetics of total darunavir |
2 ndTrimester of pregnancy |
3 rdTrimester of pregnancy |
Postpartum (6–12 Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
C max, ng/mL |
4668 ± 1097 |
5328 ± 1631 |
6659 ± 2364 |
|
AUC 24h, ng.h/mL † |
78740 ± 19194 |
91760 ± 34720 |
113780 ± 52680 |
|
C min, ng/mL |
1922 ± 825 |
2661 ± 1269 |
2851 ± 2216 |
|
Pharmacokinetics of total darunavir |
2 ndTrimester of pregnancy |
3 rdTrimester of pregnancy |
Postpartum (6–12 Weeks) |
|---|---|---|---|
|
C max, ng/mL |
4964 ± 1505 |
5132 ± 1198 |
7310 ± 1704 |
|
AUC 24h, ng.h/mL |
62289 ± 16234 |
61112 ± 13790 |
92116 ± 29241 |
|
C min, ng/mL |
1248 ± 542 |
1075 ± 594 |
1473 ± 1141 |
Due to an increase in the unbound fraction of darunavir during pregnancy compared to postpartum, unbound darunavir exposures were less reduced during pregnancy as compared to postpartum. Exposure reductions during pregnancy were greater for the once daily regimen as compared to the twice daily regimen (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Pharmacokinetic Results (Within-Subject Comparison) of Total and Unbound Darunavir After Administration of PREZISTA/ritonavir at 600/100 mg Twice Daily or 800/100 mg Once Daily as Part of an Antiretroviral Regimen, During the 2ndand 3rdTrimester of Pregnancy Compared to Postpartum
|
Legend: 90% CI: 90% confidence interval; GMR: geometric mean ratio. Solid vertical line: ratio of 1.0; dotted vertical lines: reference lines of 0.8 and 1.25. |
|
|
Drug Interactions
[See also Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.5)and Drug Interactions (7). ]
Darunavir co-administered with ritonavir is an inhibitor of CYP3A, CYP2D6, and P-gp. Co-administration of darunavir and ritonavir with drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A and CYP2D6, or are transported by P-gp, may result in increased plasma concentrations of such drugs, which could increase or prolong their therapeutic effect and adverse events.
Darunavir and ritonavir are metabolized by CYP3A. In vitrodata indicate that darunavir may be a P-gp substrate. Drugs that induce CYP3A activity would be expected to increase the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir, resulting in lowered plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir. Co-administration of darunavir and ritonavir and other drugs that inhibit CYP3A or P-gp may decrease the clearance of darunavir and ritonavir and may result in increased plasma concentrations of darunavir and ritonavir.
Drug interaction studies were performed with darunavir and other drugs likely to be co-administered and some drugs commonly used as probes for pharmacokinetic interactions. The effects of co-administration of darunavir on the AUC, C max, and C minvalues are summarized in Table 15 (effect of other drugs on darunavir) and Table 16 (effect of darunavir on other drugs). For information regarding clinical recommendations, see Drug Interactions (7).
Several interaction studies have been performed with a dose other than the recommended dose of the co-administered drug or darunavir; however, the results are applicable to the recommended dose of the co-administered drug and/or darunavir.
Table 15: Drug Interactions: Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Darunavir in the Presence of Co-Administered Drugs|
Co-administered drug |
Dose/Schedule |
N |
PK |
LS Mean ratio (90% CI) of darunavir | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Co-administered Drug |
Darunavir/ritonavir |
C max |
AUC |
C min | |||
|
N = number of subjects with data | |||||||
| |||||||
|
Co-administration with other HIV protease inhibitors | |||||||
|
Atazanavir |
300 mg q.d. * |
400/100 mg b.i.d. † |
13 |
↔ |
1.02 |
1.03 |
1.01 |
|
Indinavir |
800 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
9 |
↑ |
1.11 |
1.24 |
1.44 |
|
Lopinavir/ritonavir |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
1200/100 mg b.i.d. ‡ |
14 |
↓ |
0.79 |
0.62 |
0.49 |
|
533/133.3 mg b.i.d. |
1200 mg b.i.d. ‡ |
15 |
↓ |
0.79 |
0.59 |
0.45 | |
|
Saquinavir hard gel capsule |
1000 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 |
↓ |
0.83 |
0.74 |
0.58 |
|
Co-administration with other HIV antiretrovirals | |||||||
|
Didanosine |
400 mg q.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
17 |
↔ |
0.93 |
1.01 |
1.07 |
|
Efavirenz |
600 mg q.d. |
300/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↓ |
0.85 |
0.87 |
0.69 |
|
Etravirine |
200 mg b.i.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↔ |
1.11 |
1.15 |
1.02 |
|
Nevirapine |
200 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
8 |
↑ |
1.40 § |
1.24 § |
1.02 § |
|
Rilpivirine |
150 mg q.d. |
800/100 mg q.d. |
15 |
↔ |
0.90 |
0.89 |
0.89 |
|
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
300 mg q.d. |
300/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↑ |
1.16 |
1.21 |
1.24 |
|
Co-administration with other drugs | |||||||
|
Artemether/lumefantrine |
80/480 mg (6 doses at 0, 8, 24, 36, 48, and 60 hours) |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 |
↔ |
1.00 |
0.96 |
0.87 |
|
Carbamazepine |
200 mg b.i.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↔ |
1.04 |
0.99 |
0.85 |
|
Clarithromycin |
500 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
17 |
↔ |
0.83 |
0.87 |
1.01 |
|
Ketoconazole |
200 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 |
↑ |
1.21 |
1.42 |
1.73 |
|
Omeprazole |
20 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↔ |
1.02 |
1.04 |
1.08 |
|
Paroxetine |
20 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↔ |
0.97 |
1.02 |
1.07 |
|
Pitavastatin |
4 mg q.d. |
800/100 mg q.d. |
27 |
↔ |
1.06 |
1.03 |
NA |
|
Ranitidine |
150 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↔ |
0.96 |
0.95 |
0.94 |
|
Rifabutin |
150 mg q.o.d. ¶ |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
11 |
↑ |
1.42 |
1.57 |
1.75 |
|
Sertraline |
50 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
13 |
↔ |
1.01 |
0.98 |
0.94 |
|
Co-administered drug |
Dose/Schedule |
N |
PK |
LS Mean ratio (90% CI) of co-administered drug | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Co-administered drug |
Darunavir/ritonavir |
C max |
AUC |
C min | |||
|
N = number of subjects with data;- = no information available | |||||||
Þ ß | |||||||
|
Co-administration with other HIV protease inhibitors | |||||||
|
Atazanavir |
300 mg q.d. */100 mg ritonavir q.d. when administered alone |
400/100 mg b.i.d. † |
13 |
↔ |
0.89 |
1.08 |
1.52 |
|
300 mg q.d. when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
|
Indinavir |
800 mg b.i.d. /100 mg ritonavir b.i.d. when administered alone |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
9 |
↑ |
1.08 |
1.23 |
2.25 |
|
800 mg b.i.d. when administered with darunavir/ | |||||||
|
Lopinavir/ritonavir |
400/100 mg b.i.d. ‡ |
1200/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 |
↔ |
0.98 |
1.09 |
1.23 |
|
533/133.3 mg b.i.d.. ‡ |
1200 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↔ |
1.11 |
1.09 |
1.13 | |
|
Saquinavir hard gel capsule |
1000 mg b.i.d. /100 mg ritonavir b.i.d. when administered alone |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↔ |
0.94 |
0.94 |
0.82 |
|
1000 mg b.i.d. when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
|
Co-administration with other HIV antiretrovirals | |||||||
|
Didanosine |
400 mg q.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
17 |
↔ |
0.84 |
0.91 |
|
|
Dolutegravir |
30 mg q.d |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↓ |
0.89 |
0.78 |
0.62 § |
|
Dolutegravir |
50 mg q.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. with 200 mg b.i.d. etravirine |
9 |
↓ |
0.88 |
0.75 |
0.63 § |
|
Efavirenz |
600 mg q.d. |
300/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↑ |
1.15 |
1.21 |
1.17 |
|
Etravirine |
100 mg b.i.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 |
↓ |
0.68 |
0.63 |
0.51 |
|
Nevirapine |
200 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
8 |
↑ |
1.18 |
1.27 |
1.47 |
|
Rilpivirine |
150 mg q.d. |
800/100 mg q.d. |
14 |
↑ |
1.79 |
2.30 |
2.78 |
|
Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate |
300 mg q.d. |
300/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↑ |
1.24 |
1.22 |
1.37 |
|
Maraviroc |
150 mg b.i.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↑ |
2.29 |
4.05 |
8.00 |
|
600/100 mg b.i.d. with 200 mg b.i.d. etravirine |
10 |
↑ |
1.77 |
3.10 |
5.27 | ||
|
Co-administration with other drugs | |||||||
|
Atorvastatin |
40 mg q.d. when administered alone |
300/100 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↑ |
0.56 |
0.85 |
1.81 |
|
10 mg q.d. when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
|
Artemether |
80 mg single dose |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↓ |
0.85 |
0.91 |
|
|
Dihydroartemisinin |
15 |
↑ |
1.06 |
1.12 |
| ||
|
Artemether |
artemether/lumefantrine 80/480 mg (6 doses at 0, 8, 24, 36, 48, and 60 hours) |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↓ |
0.82 |
0.84 |
0.97 |
|
Dihydroartemisinin |
15 |
↓ |
0.82 |
0.82 |
1.00 | ||
|
Lumefantrine |
15 |
↑ |
1.65 |
2.75 |
2.26 | ||
|
Buprenorphine/Naloxone |
8/2 mg to 16/4 mg q.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
17 |
↔ |
0.92 ¶ |
0.89 ¶ |
0.98 ¶ |
|
Norbuprenorphine |
17 |
↑ |
1.36 |
1.46 |
1.71 | ||
|
Carbamazepine |
200 mg b.i.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↑ |
1.43 |
1.45 |
1.54 |
|
Carbamazepine epoxide |
16 |
↓ |
0.46 |
0.46 |
0.48 | ||
|
Clarithromycin |
500 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
17 |
↑ |
1.26 |
1.57 |
2.74 |
|
Dabigatran etexilate |
150 mg |
800/100 mg single dose |
14 |
↑ |
1.64 |
1.72 |
|
|
800/100 mg q.d. # |
13 |
↑ |
1.22 |
1.18 |
| ||
|
Dextromethorphan |
30 mg |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↑ |
2.27 |
2.70 |
|
|
Dextrorphan |
↓ |
0.87 |
0.96 |
| |||
|
Digoxin |
0.4 mg |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
8 |
↑ |
1.15 |
1.36 |
|
|
Ethinyl estradiol (EE) |
Ortho-Novum 1/35 |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
11 |
↓ |
0.68 |
0.56 |
0.38 |
|
Norethindrone (NE) |
11 |
↓ |
0.90 |
0.86 |
0.70 | ||
|
Ketoconazole |
200 mg b.i.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
15 |
↑ |
2.11 |
3.12 |
9.68 |
|
R-Methadone |
55–150 mg q.d. |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↓ |
0.76 |
0.84 |
0.85 |
|
Omeprazole |
40 mg single dose |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↓ |
0.66 |
0.58 |
|
|
5-hydroxy omeprazole |
↓ |
0.93 |
0.84 |
| |||
|
Paroxetine |
20 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↓ |
0.64 |
0.61 |
0.63 |
|
Pitavastatin |
4 mg q.d. |
800/100 mg q.d. |
27 |
↓ |
0.96 |
0.74 |
NA |
|
Pravastatin |
40 mg single dose |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
14 |
↑ |
1.63 |
1.81 |
|
|
Rifabutin |
150 mg q.o.d. Þwhen administered with PREZISTA/ritonavir |
600/100 mg b.i.d. ß |
11 |
↑ |
0.72 |
0.93 |
1.64 |
|
25- O-desacetyl-rifabutin |
300 mg q.d. when administered alone |
11 |
↑ |
4.77 |
9.81 |
27.1 | |
|
Sertraline |
50 mg q.d. |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
13 |
↓ |
0.56 |
0.51 |
0.51 |
|
Sildenafil |
100 mg (single dose) administered alone |
400/100 mg b.i.d. |
16 |
↑ |
0.62 |
0.97 |
|
|
25 mg (single dose)when administered with darunavir/ritonavir | |||||||
|
S-warfarin |
10 mg single dose |
600/100 mg b.i.d. |
12 |
↓ |
0.92 |
0.79 |
|
|
7-OH-S-warfarin |
12 |
↑ |
1.42 |
1.23 |
|
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Darunavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease. It selectively inhibits the cleavage of HIV-1 encoded Gag-Pol polyproteins in infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature virus particles.
Antiviral Activity
Darunavir exhibits activity against laboratory strains and clinical isolates of HIV-1 and laboratory strains of HIV-2 in acutely infected T-cell lines, human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and human monocytes/macrophages with median EC 50values ranging from 1.2 to 8.5 nM (0.7 to 5.0 ng/mL). Darunavir demonstrates antiviral activity in cell culture against a broad panel of HIV-1 group M (A, B, C, D, E, F, G), and group O primary isolates with EC 50values ranging from less than 0.1 to 4.3 nM. The EC 50value of darunavir increases by a median factor of 5.4 in the presence of human serum. Darunavir did not show antagonism when studied in combination with the PIs amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, or tipranavir, the N(t)RTIs abacavir, didanosine, emtricitabine, lamivudine, stavudine, tenofovir, zalcitabine, or zidovudine, the NNRTIs delavirdine, rilpivirine, efavirenz, etravirine, or nevirapine, and the fusion inhibitor enfuvirtide.
Resistance
Cell Culture: HIV-1 isolates with a decreased susceptibility to darunavir have been selected in cell culture and obtained from subjects treated with PREZISTA/ritonavir. Darunavir-resistant virus derived in cell culture from wild-type HIV-1 had 21- to 88-fold decreased susceptibility to darunavir and developed 2 to 4 of the following amino acid substitutions S37D, R41E/T, K55Q, H69Q, K70E, T74S, V77I, or I85V in the protease. Selection in cell culture of darunavir resistant HIV-1 from nine HIV-1 strains harboring multiple PI resistance-associated mutations resulted in the overall emergence of 22 mutations in the protease gene, coding for amino acid substitutions L10F, V11I, I13V, I15V, G16E, L23I, V32I, L33F, S37N, M46I, I47V, I50V, F53L, L63P, A71V, G73S, L76V, V82I, I84V, T91A/S, and Q92R, of which L10F, V32I, L33F, S37N, M46I, I47V, I50V, L63P, A71V, and I84V were the most prevalent. These darunavir-resistant viruses had at least eight protease substitutions and exhibited 50- to 641-fold decreases in darunavir susceptibility with final EC 50values ranging from 125 nM to 3461 nM.
Clinical trials of PREZISTA/ritonavir in treatment-experienced subjects: In a pooled analysis of the 600/100 mg PREZISTA/ritonavir twice daily arms of trials TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, TMC114-C215, and the control arms of etravirine trials TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216, the amino acid substitutions V32I and I54L or M developed most frequently on PREZISTA/ritonavir in 41% and 25%, respectively, of the treatment-experienced subjects who experienced virologic failure, either by rebound or by never being suppressed (less than 50 copies/mL). Other substitutions that developed frequently in PREZISTA/ritonavir virologic failure isolates occurred at amino acid positions V11I, I15V, L33F, I47V, I50V, and L89V. These amino acid substitutions were associated with decreased susceptibility to darunavir; 90% of the virologic failure isolates had a greater than 7-fold decrease in susceptibility to darunavir at failure. The median darunavir phenotype (fold change from reference) of the virologic failure isolates was 4.3-fold at baseline and 85-fold at failure. Amino acid substitutions were also observed in the protease cleavage sites in the Gag polyprotein of some PREZISTA/ritonavir virologic failure isolates. In trial TMC114-C212 of treatment-experienced pediatric subjects, the amino acid substitutions V32I, I54L and L89M developed most frequently in virologic failures on PREZISTA/ritonavir.
In the 96-week as-treated analysis of the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C214, the percent of virologic failures (never suppressed, rebounders and discontinued before achieving suppression) was 21% (62/298) in the group of subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily compared to 32% (96/297) of subjects receiving lopinavir/ritonavir 400/100 mg twice daily. Examination of subjects who failed on PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily and had post-baseline genotypes and phenotypes showed that 7 subjects (7/43; 16%) developed PI substitutions on PREZISTA/ritonavir treatment resulting in decreased susceptibility to darunavir. Six of the 7 had baseline PI resistance-associated substitutions and baseline darunavir phenotypes greater than 7. The most common emerging PI substitutions in these virologic failures were V32I, L33F, M46I or L, I47V, I54L, T74P and L76V. These amino acid substitutions were associated with 59- to 839-fold decreased susceptibility to darunavir at failure. Examination of individual subjects who failed in the comparator arm on lopinavir/ritonavir and had post-baseline genotypes and phenotypes showed that 31 subjects (31/75; 41%) developed substitutions on lopinavir treatment resulting in decreased susceptibility to lopinavir (greater than 10-fold) and the most common substitutions emerging on treatment were L10I or F, M46I or L, I47V or A, I54V and L76V. Of the 31 lopinavir/ritonavir virologic failure subjects, 14 had reduced susceptibility (greater than 10-fold) to lopinavir at baseline.
In the 48-week analysis of the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C229, the number of virologic failures (including those who discontinued before suppression after Week 4) was 26% (75/294) in the group of subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily compared to 19% (56/296) of subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily. Examination of isolates from subjects who failed on PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily and had post- baseline genotypes showed that 8 subjects (8/60; 13%) had isolates that developed IAS-USA defined PI resistance-associated substitutions compared to 5 subjects (5/39; 13%) on PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily. Isolates from 2 subjects developed PI resistance associated substitutions associated with decreased susceptibility to darunavir; 1 subject isolate in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily arm, developed substitutions V32I, M46I, L76V and I84V associated with a 24-fold decreased susceptibility to darunavir, and 1 subject isolate in the PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily arm developed substitutions L33F and I50V associated with a 40-fold decreased susceptibility to darunavir. In the PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily and PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily groups, isolates from 7 (7/60; 12%) and 4 (4/42; 10%) virologic failures, respectively, developed decreased susceptibility to an NRTI included in the treatment regimen.
Clinical trials of PREZISTA/ritonavir in treatment-naïve subjects: In the 192-week as-treated analysis censoring those who discontinued before Week 4 of the Phase 3 trial TMC114-C211, the percentage of virologic failures (never suppressed, rebounders and discontinued before achieving suppression) was 22% (64/288) in the group of subjects receiving PREZISTA/ritonavir 800/100 mg once daily compared to 29% (76/263) of subjects receiving lopinavir/ritonavir 800/200 mg per day. In the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm, emergent PI resistance- associated substitutions were identified in 11 of the virologic failures with post-baseline genotypic data (n=43). However, none of the darunavir virologic failures had a decrease in darunavir susceptibility (greater than 7-fold change) at failure. In the comparator lopinavir/ritonavir arm, emergent PI resistance-associated substitutions were identified in 17 of the virologic failures with post-baseline genotypic data (n=53), but none of the lopinavir/ritonavir virologic failures had decreased susceptibility to lopinavir (greater than 10-fold change) at failure. The reverse transcriptase M184V substitution and/or resistance to emtricitabine, which was included in the fixed background regimen, was identified in 4 virologic failures from the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm and 7 virologic failures in the lopinavir/ritonavir arm.
Cross-resistance
Cross-resistance among PIs has been observed. Darunavir has a less than 10-fold decreased susceptibility in cell culture against 90% of 3309 clinical isolates resistant to amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir and/or tipranavir showing that viruses resistant to these PIs remain susceptible to darunavir.
Darunavir-resistant viruses were not susceptible to amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir or saquinavir in cell culture. However, six of nine darunavir-resistant viruses selected in cell culture from PI-resistant viruses showed a fold change in EC 50values less than 3 for tipranavir, indicative of limited cross-resistance between darunavir and tipranavir. In trials TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215, 34% (64/187) of subjects in the PREZISTA/ritonavir arm whose baseline isolates had decreased susceptibility to tipranavir (tipranavir fold change greater than 3) achieved less than 50 copies/mL serum HIV-1 RNA levels at Week 96. Of the viruses isolated from subjects experiencing virologic failure on PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily (greater than 7-fold change), 41% were still susceptible to tipranavir and 10% were susceptible to saquinavir while less than 2% were susceptible to the other protease inhibitors (amprenavir, atazanavir, indinavir, lopinavir or nelfinavir).
In trial TMC114-C214, the 7 PREZISTA/ritonavir virologic failures with reduced susceptibility to darunavir at failure were also resistant to the approved PIs (fos)amprenavir, atazanavir, lopinavir, indinavir, and nelfinavir at failure. Six of these 7 were resistant to saquinavir and 5 were resistant to tipranavir. Four of these virologic failures were already PI-resistant at baseline.
Cross-resistance between darunavir and nucleoside/nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors, non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, fusion inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor antagonists, or integrase inhibitors is unlikely because the viral targets are different.
Baseline Genotype/Phenotype and Virologic Outcome Analyses
Genotypic and/or phenotypic analysis of baseline virus may aid in determining darunavir susceptibility before initiation of PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg twice daily therapy. The effect of baseline genotype and phenotype on virologic response at 96 weeks was analyzed in as-treated analyses using pooled data from the Phase 2b trials (Trials TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215) (n=439). The findings were confirmed with additional genotypic and phenotypic data from the control arms of etravirine trials TMC125-C206 and TMC125-C216 at Week 24 (n=591).
Diminished virologic responses were observed in subjects with 5 or more baseline IAS-defined primary protease inhibitor resistance-associated substitutions (D30N, V32I, L33F, M46I/L, I47A/V, G48V, I50L/V, I54L/M, L76V, V82A/F/L/S/T, I84V, N88S, L90M) (see Table 17).
Table 17: Response to PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg Twice Daily by Baseline Number of IAS-Defined Primary PI Resistance-Associated Substitutions: As-treated Analysis of Trials TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215
IAS-defined primary PI substitutions |
Proportion of subjects with <50 copies/mL at Week 96 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Overall |
de novoENF |
Re-used/No ENF | |
|
ENF=enfuvirtide | |||
|
All |
44% (192/439) |
54% (61/112) |
40% (131/327) |
|
0 – 4 |
50% (162/322) |
58% (49/85) |
48% (113/237) |
|
5 |
22% (16/74) |
47% (9/19) |
13% (7/55) |
|
≥6 |
9% (3/32) |
17% (1/6) |
8% (2/26) |
IAS Primary PI Substitutions (2008): D30N, V32I, L33F, M46I/L, I47A/V, G48V, I50L/V, I54L/M, L76V, V82A/F/L/S/T, I84V, N88S, L90M.
The presence at baseline of two or more of the substitutions V11I, V32I, L33F, I47V, I50V, I54L or M, T74P, L76V, I84V or L89V was associated with a decreased virologic response to PREZISTA/ritonavir. In subjects not taking enfuvirtide de novo, the proportion of subjects achieving viral load less than 50 plasma HIV-1 RNA copies/mL at 96 weeks was 59%, 29%, and 12% when the baseline genotype had 0–1, 2 and greater than or equal to 3 of these substitutions, respectively.
Baseline darunavir phenotype (shift in susceptibility relative to reference) was shown to be a predictive factor of virologic outcome. Response rates assessed by baseline darunavir phenotype are shown in Table 18. These baseline phenotype groups are based on the select patient populations in the trials TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215, and are not meant to represent definitive clinical susceptibility breakpoints for PREZISTA/ritonavir. The data are provided to give clinicians information on the likelihood of virologic success based on pre-treatment susceptibility to darunavir.
Table 18: Response (HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL at Week 96) to PREZISTA/ritonavir 600/100 mg Twice Daily by Baseline Darunavir Phenotype and by Use of Enfuvirtide: As-treated Analysis of Trials TMC114-C213, TMC114-C202, and TMC114-C215|
Baseline DRV phenotype |
Proportion of subjects with <50 copies/mL at Week 96 | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
All |
de novoENF |
Re-used/No ENF | |
|
ENF=enfuvirtide | |||
|
Overall |
175/417 (42%) |
61/112 (54%) |
131/327 (40%) |
|
0 – 7 |
148/270 (55%) |
44/65 (68%) |
104/205 (51%) |
|
>7 – 20 |
16/53 (30%) |
7/17 (41%) |
9/36 (25%) |
|
>20 |
11/94 (12%) |
6/23 (26%) |
5/71 (7%) |