Iclusig
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ICLUSIG safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ICLUSIG. ICLUSIG (ponatinib) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2012
16d804b6-4957-43ee-b18c-3b36ec37c5ac
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 26, 2024
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
DUNS: 039997266
Products 4
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
ponatinib hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
ponatinib hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
ponatinib hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
ponatinib hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 63020-536-30
ICLUSIG®
(ponatinib) tablets
10 mg
Each tablet contains 10 mg ponatinib
equivalent to 10.68 mg ponatinib HCl
Dispense Attached Medication Guide
30 tablets
Rx only
Takeda

BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: ARTERIAL OCCLUSIVE EVENTS, VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLIC EVENTS, HEART
FAILURE, and HEPATOTOXICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
*Arterial occlusive events (AOEs), including fatalities, have occurred in ICLUSIG-treated patients. AOEs included fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, stenosis of large arterial vessels of the brain, severe peripheral vascular disease, and the need for urgent revascularization procedures. Patients with and without cardiovascular risk factors, including patients age 50 years or younger, experienced these events. Monitor for evidence of AOEs. Interrupt or discontinue ICLUSIG based on severity. Consider benefit-risk to guide a decision to restart ICLUSIG. (2.2,5.1) *Venous thromboembolic events (VTEs) have occurred in ICLUSIG-treated patients. Monitor for evidence of VTEs. Interrupt or discontinue ICLUSIG based on severity (2.2,5.2). *Heart failure, including fatalities, occurred in ICLUSIG-treated patients. Monitor for heart failure and manage patients as clinically indicated. Interrupt or discontinue ICLUSIG for new or worsening heart failure (2.2,5.3). *Hepatotoxicity, liver failure and death have occurred in ICLUSIG-treated patients. Monitor liver function tests. Interrupt or discontinue ICLUSIG based on severity (2.2,5.4).
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
None.
None. (4)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on ICLUSIG
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Coadministration of ICLUSIG with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases ponatinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of ICLUSIG adverse reactions. Avoid coadministration of ICLUSIG with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If coadministration of ICLUSIG with strong CYP3A inhibitors cannot be avoided, reduce the ICLUSIG dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Coadministration of ICLUSIG with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases ponatinib plasma concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid coadministration of ICLUSIG with strong CYP3A inducers unless the benefit outweighs the risk of decreased ponatinib exposure. Monitor patients for reduced efficacy. Selection of concomitant medication with no or minimal CYP3A induction potential is recommended.
- Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Avoid coadministration or reduce ICLUSIG dose if coadministration cannot be avoided. (2.3, 7.1)
- Strong CYP3A Inducers: Avoid coadministration. (7.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Indications and Usage (1) |
3/2024 |
|
Dosage and Administration, Recommended Dosage (2.1) |
3/2024 |
|
Dosage and Administration, Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions (2.2) |
3/2024 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5) |
3/2024 |
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animals and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], ICLUSIG can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on ICLUSIG use in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of ponatinib to pregnant rats during organogenesis caused adverse developmental effects at doses lower than human exposures at the maximum recommended human dose of 45 mg/day (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Ponatinib was studied for effects on embryo-fetal development in pregnant rats given oral doses of 0.3 mg/kg/day, 1 mg/kg/day, and 3 mg/kg/day during organogenesis (25 rats per group). At the maternally toxic dose of 3 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the AUC in patients receiving the maximum recommended dose of 45 mg/day), ponatinib caused embryo-fetal toxicity as shown by increased resorptions, reduced body weight, external alterations, multiple soft tissue and skeletal alterations, and reduced ossification. Embryo-fetal toxicities also were observed at 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 24% the AUC in patients receiving the maximum recommended dose of 45 mg/day) and involved multiple fetal soft tissue and skeletal alterations, including reduced ossification.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of ponatinib in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ICLUSIG and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
ICLUSIG can cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating ICLUSIG.
Contraception
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ICLUSIG and for 3 weeks after the last dose.
Infertility
Females
Based on animal data, ponatinib may impair fertility in females of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. It is not known whether these effects on fertility are reversible.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ICLUSIG have not been established in pediatric patients.
Juvenile Animal Toxicity Data
A juvenile toxicity study in 15 day old rats was conducted with daily oral gavage administration of ponatinib at 0.75 mg/kg/day, 1.5 mg/kg/day, or 3 mg/kg/day for 21 days. There were no adverse effects of ponatinib on juvenile rat developmental parameters (vaginal opening, preputial separation or bone measurements) observed in this study. Once daily oral administration of 3 mg/kg/day ponatinib to juvenile rats beginning on Day 15 postpartum (pp) resulted in mortality related to inflammatory effects after 6 to 7 days following initiation of treatment. The dose of 3 mg/kg/day is approximately 0.32 times the maximum recommended human dose of 45 mg/day on a mg/m2 basis for a child.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 163 patients with Ph+ALL who received ICLUSIG in PhALLCON, 21% were 65 years and older and 7% were 75 years and older. Overall, no differences in efficacy of ICLUSIG were observed between patients 65 years of age or older compared to younger patients. AOEs occurred in 21% (7/34) of patients 65 years and older and 2.3% (3/129) of patients less than 65 years of age.
Of the 94 patients with CP-CML who received ICLUSIG at a starting dose of 45 mg in OPTIC, 17% were 65 years and older and 2.1% were 75 years and older. Patients aged 65 years and older had a lower ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS rate at 12 months (27%) as compared with patients less than 65 years of age (47%). AOEs occurred in 38% (6/16) of patients 65 years and older and 9% (7/78) of patients less than 65 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Of the 449 patients who received ICLUSIG in PACE, 35% were 65 years and older and 8% were 75 years and older. In patients with CP-CML, patients aged 65 years and older had a lower major cytogenetic response rate (40%) as compared with patients less than 65 years of age (65%). In patients with AP-CML, BP- CML, and Ph+ ALL, patients aged 65 years and older had a similar hematologic response rate (45%) as compared with patients less than 65 years of age (44%). AOEs occurred in 35% (54/155) of patients 65 years and older and in 21% (61/294) of patients less than 65 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Patients aged 65 years or older are more likely to experience adverse reactions including vascular occlusion, decreased platelet count, peripheral edema, increased lipase, dyspnea, asthenia, muscle spasms, and decreased appetite. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment are more likely to experience adverse reactions compared to patients with normal hepatic function. For patients with CP-CML, AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL receiving monotherapy, reduce the starting dose of ICLUSIG for patients with pre-existing hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A, B, or C). For patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL, dosage adjustment is not recommended when administering ICLUSIG to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). Clinical data in patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL with pre-existing moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) is not available and patients should be closely monitored for potential increased incidence of adverse reactions. Modify the ICLUSIG dosage in the event of adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The safety of multiple doses, or doses higher than 30 mg, has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment.
Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed. (8.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets, film-coated:
- 10 mg of ponatinib: Oval, white to off-white, biconvex, debossed "NZ" on one side and plain on the other side
- 15 mg of ponatinib: Round, white, biconvex, debossed "A5" on one side and plain on the other side
- 30 mg of ponatinib: Round, white, biconvex, debossed "C7" on one side and plain on the other side
- 45 mg of ponatinib: Round, white, biconvex, debossed "AP4" on one side and plain on the other side
Tablets: 10 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg and 45 mg. (3)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdoses with ICLUSIG were reported in clinical trials. One patient was estimated to have been administered 540 mg via nasogastric tube. Two hours after the overdosage, the patient had an uncorrected QT interval of 520 ms. Subsequent ECGs showed normal sinus rhythm with uncorrected QT intervals of 480 ms and 400 ms. The patient died 9 days after the overdosage from pneumonia and sepsis. Another patient self-administered 165 mg on Cycle 1 Day 2. The patient experienced fatigue and non-cardiac chest pain on Day 3. Multiple doses of 90 mg per day for 12 days in a patient resulted in pneumonia, systemic inflammatory response, atrial fibrillation, and a moderate pericardial effusion.
In the event of an overdosage, stop ICLUSIG, observe the patient and provide supportive treatment as appropriate.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
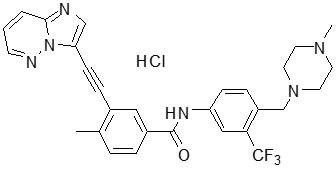
Ponatinib is a kinase inhibitor. The chemical name for ponatinib hydrochloride is 3-(imidazo[1,2-b]pyridazin-3-ylethynyl)-4-methyl-N-{4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)methyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl}benzamide hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C29H28ClF3N6O which corresponds to a formula weight of 569.02 g/mol. Its structure is shown below:
Ponatinib HCl is an off-white to yellow powder with pKa of 2.77 and 7.8. The solubility of ponatinib in pH 1.7, 2.7, and 7.5 buffers is 7790 mcg/mL, 3.44 mcg/mL, and 0.16 mcg/mL, respectively, indicating a decrease in solubility with increasing pH. Each tablet for oral administration contains 10 mg, 15 mg, 30 mg or 45 mg of ponatinib equivalent to 10.68 mg, 16.03 mg, 32.05 mg, and 48.08 mg of ponatinib hydrochloride with the following inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, sodium starch glycolate (type B), colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate and a tablet coating. The tablet coating consists of talc, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ponatinib is a kinase inhibitor. Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro tyrosine kinase activity of ABL and T315I mutant ABL with IC50 concentrations of 0.4 nM and 2.0 nM, respectively. Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro activity of additional kinases with IC50 concentrations between 0.1 nM and 20 nM, including members of the VEGFR, PDGFR, FGFR, EPH receptors and SRC families of kinases, and KIT, RET, TIE2, and FLT3. Ponatinib inhibited the in vitro viability of cells expressing native or mutant BCR::ABL, including T315I. In mice, treatment with ponatinib reduced the size of tumors expressing native or T315I mutant BCR::ABL when compared to controls.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In PACE, the dose intensity-safety relationship indicated that there are significant increases in Grade ≥3 adverse reactions (hypertension, thrombocytopenia, pancreatitis, neutropenia, rash, ALT increase, AST increase, lipase increase, myelosuppression) over the dose range of 15 mg to 45 mg. In addition to dose, increased age and history of ischemia, hypertension, diabetes, or hypercholesterolemia were also contributory factors to a higher incidence of AOEs.
In OPTIC, an exposure-response relationship between ponatinib exposure and molecular response rate at 12 months was observed. A relationship between higher ponatinib exposures and higher incidence of adverse reactions, including thrombocytopenia (Grade ≥3) and AOEs, was observed.
In vitro, there was no significant inhibition of platelet aggregation with ponatinib at concentrations seen clinically and up to 0.7 mcg/mL (1.23 μM).
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The QT interval prolongation potential of ICLUSIG was assessed in 39 patients with cancer who received ICLUSIG 30 mg, 45 mg, or 60 mg (0.67 to 1.33 times the approved maximum recommended starting dose) orally once daily. No large mean increase (i.e., >20 msec) in QTc interval was detected.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Ponatinib administered to patients with cancer exhibited approximately dose proportional increases in both steady-state Cmax and AUC over the dose range of 2 mg to 60 mg (0.04 to 1.33 times the approved maximum recommended starting dose). The mean (CV%) Cmax and AUC(0-24) of ICLUSIG 45 mg orally once daily at presumed steady-state in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies were 73 ng/mL (74%) and 1253 ng∙hr/mL (73%), respectively. The mean (CV%) Cmax and AUC(0-24) of ICLUSIG 30 mg orally once daily at presumed steady-state in patients with advanced hematologic malignancies were 65 ng/mL (28%) and 1080 ng∙hr/mL (29%), respectively. Exposure increased by approximately 90% (median) [range: 20% to 440%] between the first dose and presumed steady-state.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of ponatinib is unknown. Peak concentrations of ponatinib are observed within 6 hours after ICLUSIG oral administration.
Effect of Food
Following ingestion of either a high-fat (approximately 900 to 1000 calories
with approximately 150, 250, and 500 to 600 calories derived from protein,
carbohydrate, and fat, respectively) or low-fat meal (approximately 547
calories with approximately 56, 428 and 63 calories derived from protein,
carbohydrate, and fat, respectively) by 22 healthy volunteers, plasma
ponatinib exposures (AUC and Cmax) were not different when compared to fasting
conditions.
Distribution
Ponatinib is greater than 99% bound to plasma proteins in vitro. There was no plasma protein binding displacement of ponatinib (145 nM) in vitro by other highly protein bound medications (ibuprofen, nifedipine, propranolol, salicylic acid, and warfarin).
The mean (CV%) apparent steady-state volume of distribution is 1,223 liters (102%) following oral administration of ICLUSIG 45 mg orally once daily for 28 days in patients with cancer.
Elimination
The mean (range) terminal elimination half-life of ponatinib was approximately 24 (12 to 66) hours following ICLUSIG 45 mg orally once daily for 28 days in patients with cancer.
Metabolism
At least 64% of a dose undergoes Phase I and Phase II metabolism. CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent CYP2C8, CYP2D6 and CYP3A5 are involved in the Phase I metabolism of ponatinib in vitro. Ponatinib is also metabolized by esterases and/or amidases.
Excretion
Following a single oral dose of radiolabeled ponatinib, approximately 87% of the radioactive dose was recovered in the feces and approximately 5% in the urine.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of ponatinib were observed based on age (19 to 85 years), body weight (41 to 152 kg), and mild to moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 to 89 mL/min, estimated by the Cockcroft-Gault equation).
Patients with Renal Impairment
ICLUSIG has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment. Although renal excretion is not a major route of ponatinib elimination, the potential for severe renal impairment to affect hepatic elimination has not been determined.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
A single 30 mg oral dose of ICLUSIG was administered to subjects with normal hepatic function and to subjects with mild (Child-Pugh A), moderate (Child- Pugh B), and severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment. Compared to subjects with normal hepatic function, there was no trend of increased ponatinib exposure in subjects with hepatic impairment. There was an increased incidence of adverse reactions (e.g., gastrointestinal disorders, including a case of severe pancreatitis) in subjects with hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Strong CYP3A Inhibitors: Coadministration of ponatinib with multiple doses of ketoconazole (strong CYP3A inhibitor) increased the ponatinib AUC0-INF by 78% and Cmax by 47%.
Strong CYP3A Inducers: Coadministration of ponatinib with multiple doses of rifampin (strong CYP3A inducer) decreased the ponatinib AUC0-INF by 62% and Cmax by 42%.
Gastric Acid Reducing Agents: Coadministration of ponatinib with multiple doses of lansoprazole (proton pump inhibitor) decreased the ponatinib AUC0-INF by 6% and Cmax by 25%.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Ponatinib does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP3A, or CYP2D6 and does not induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, or CYP3A.
Transporter Systems: Ponatinib is a weak substrate for both P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP). Ponatinib is not a substrate for organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATP1B1, OATP1B3) and organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1).
Ponatinib inhibits P-gp, BCRP, and bile salt export pump (BSEP). Ponatinib does not inhibit OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, OCT2, or the organic anion transporters OAT1 and OAT3.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Lexington, MA 02421
ICLUSIG® and the ICLUSIG Logo® are registered trademarks of ARIAD
Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
TAKEDA® and the TAKEDA Logo® are registered trademarks of Takeda
Pharmaceutical Company Limited.
©2024 Takeda Pharmaceuticals U.S.A., Inc. All rights reserved.
ICL348 R10
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: March 2024 | ||
|
MEDICATION GUIDE | |||
|
What is the most important information I should know about ICLUSIG? | |||
|
| ||
|
Blood clots or blockage in your blood vessels can happen in people with or
without risk factors for heart and blood vessel disease, including people 50
years of age or younger. The most common risk factors for these problems are a
history of high blood pressure (hypertension), high cholesterol, and heart
disease. Blood clots or blockages in your blood vessels happen more often in
people as they get older, and in people with a history of decreased blood
flow, high blood pressure, diabetes, or high cholesterol.
See**"What are the possible side effects of ICLUSIG?"** for information about side effects. | |||
|
What is ICLUSIG? *Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (Ph+ ALL) * in combination with chemotherapy in newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL * alone in adults with Ph+ ALL who cannot receive any other kinase inhibitor medicines or who have a specific type of abnormal gene (T315I-positive) Ph+ ALL *Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
ICLUSIG is not for use to treat people with newly diagnosed chronic phase CML. | |||
|
Before you take ICLUSIG, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
| |||
|
| ||
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription medicines and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal
supplements. ICLUSIG and other medicines may affect each other causing side
effects. | |||
|
How should I take ICLUSIG?
| |||
|
What are the possible side effects of ICLUSIG?
| |||
|
| ||
|
*Fluid retention. Your body may hold too much fluid (fluid retention) which can be serious and may lead to death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these symptoms during treatment with ICLUSIG:
* swelling of your hands, ankles, feet, face, or all over your body
* weight gain
* shortness of breath and cough
*Irregular heartbeat. ICLUSIG may cause an irregular heartbeat. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you experience loss of consciousness, fainting, dizziness, chest pain or palpitations.
*Low blood cell counts. ICLUSIG may cause low blood cell counts, which can be severe. Your healthcare provider will check your blood counts regularly during treatment with ICLUSIG. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a fever or any signs of an infection while taking ICLUSIG. | |||
|
| ||
|
*Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS – also known as Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome). ICLUSIG may trigger a condition called RPLS. Call your healthcare provider right away if you get headaches, seizures, confusion, changes in vision or problems thinking. *Wound healing problems. Wound healing problems have happened in some people who take ICLUSIG. Tell your healthcare provider if you plan to have any surgery before or during treatment with ICLUSIG. * You should stop taking ICLUSIG at least 1 week before planned surgery. * Your healthcare provider should tell you when you may start taking ICLUSIG again after surgery. *A tear in your stomach or intestinal wall (perforation). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get: * severe pain in your stomach-area (abdomen) * swelling of the abdomen * high fever The most common side effects of ICLUSIG when given alone include: | |||
|
|
| |
|
The most common side effects of ICLUSIG when given with chemotherapy include: | |||
|
|
| |
|
Your healthcare provider may change your dose, temporarily stop, or
permanently stop treatment with ICLUSIG if you have certain side effects. | |||
|
How should I store ICLUSIG? | |||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of ICLUSIG | |||
|
What are the ingredients in ICLUSIG? |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Newly Diagnosed Ph+ ALL
The recommended starting dosage of ICLUSIG in combination with chemotherapy is 30 mg orally once daily with a reduction to 15 mg orally once daily upon achievement of MRD-negative (≤0.01% BCR::ABL1/ABL1) CR at the end of induction. Continue ICLUSIG in combination with chemotherapy for up to 20 cycles until loss of response or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14)].
For a description of dosing of agents administered in combination with ICLUSIG, [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Monotherapy for Ph+ ALL for Whom No Other Kinase Inhibitors Are Indicated or T315I-positive Ph+ ALL
The optimal dose of ICLUSIG has not been identified.
The recommended starting dosage of ICLUSIG is 45 mg orally once daily. Continue ICLUSIG until loss of response or unacceptable toxicity.
Consider discontinuing ICLUSIG if response has not occurred by 3 months.
CP-CML
The recommended starting dosage of ICLUSIG is 45 mg orally once daily with a reduction to 15 mg orally once daily upon achievement of ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS. Patients with loss of response can re-escalate the dose of ICLUSIG to a previously tolerated dosage of 30 mg or 45 mg orally once daily. Continue ICLUSIG until loss of response at the re-escalated dose or unacceptable toxicity.
Consider discontinuing ICLUSIG if hematologic response has not occurred by 3 months.
AP-CML and BP-CML
The optimal dose of ICLUSIG has not been identified.
The recommended starting dosage of ICLUSIG is 45 mg orally once daily. Consider reducing the dose of ICLUSIG for patients with accelerated phase (AP) CML who have achieved a major cytogenetic response. Continue ICLUSIG until loss of response or unacceptable toxicity.
Consider discontinuing ICLUSIG if response has not occurred by 3 months.
Administration
Advise patients of the following:
- ICLUSIG may be taken with or without food.
- Swallow tablets whole. Do not crush, break, cut or chew tablets.
- If a dose is missed, take the next dose at the regularly scheduled time the next day.
2.2 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dosage modifications of ICLUSIG for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1 and recommended dose reductions of ICLUSIG for adverse reactions are presented in Table 2.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage Modifications for ICLUSIG for Adverse Reactions|
Adverse Reaction |
Severity |
ICLUSIG Dosage Modifications |
|---|---|---|
|
Based on CTCAE v5.0: Grade 1 mild, Grade 2 moderate, Grade 3 severe, Grade 4
life-threatening | ||
|
AOE: cardiovascular or cerebrovascular |
Grade 1 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until resolved, then resume at same dose. |
|
Grade 2 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at next lower dose. | |
|
Grade 3 or 4 |
Discontinue ICLUSIG. | |
|
AOE: peripheral vascular and other |
Grade 1 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until resolved, then resume at same dose. |
|
Grade 2 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at same dose. | |
|
Grade 3 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at next lower dose. | |
|
Grade 4 |
Discontinue ICLUSIG. | |
|
Heart Failure |
Grade 2 or 3 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at next lower dose. |
|
Grade 4 |
Discontinue ICLUSIG. | |
|
Hepatotoxicity |
AST or ALT greater than 3 times ULN |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at next lower dose. |
|
AST or ALT at least 3 times ULN concurrent with bilirubin greater than 2 times ULN and alkaline phosphatase less than 2 times ULN |
Discontinue ICLUSIG. | |
|
Pancreatitis and Elevated Lipase |
Serum lipase greater than 1 to 1.5 times ULN |
Consider interrupting ICLUSIG until resolution, then resume at same dose. |
|
Serum lipase greater than 1.5 to 2 times ULN, 2 to 5 times ULN and asymptomatic, or asymptomatic radiologic pancreatitis |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1 (less than 1.5 times ULN), then resume at next lower dose. | |
|
Serum lipase greater than 2 to 5 times ULN and symptomatic, symptomatic Grade 3 pancreatitis, or serum lipase greater than 5 times ULN and asymptomatic |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until complete resolution of symptoms and after recovery of lipase elevation Grade 0 or 1, then resume at next lower dose. | |
|
Symptomatic pancreatitis and serum lipase greater than 5 times ULN |
Discontinue ICLUSIG. | |
|
Myelosuppression |
ANC less than 1 × 109/L |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until ANC at least 1.5 × 109/L and platelet at least 75 ×
109/L, then resume at same dose. |
|
Other Non-hematologic Adverse Reactions |
Grade 1 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until resolved, then resume at same dose. |
|
Grade 2 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at same dose. | |
|
Grade 3 or 4 |
Interrupt ICLUSIG until Grade 0 or 1, then resume at next lower dose. |
|
Dose Reduction |
Dosage for Patients with CP-CML |
Dosage for Patients with AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL Monotherapy |
Dosage for Patients with Newly Diagnosed Ph+ ALL |
|---|---|---|---|
|
First |
30 mg orally once daily |
30 mg orally once daily |
15 mg orally once daily |
|
Second |
15 mg orally once daily |
15 mg orally once daily |
10 mg orally once daily |
|
Third |
10 mg orally once daily |
Permanently discontinue ICLUSIG in patients unable to tolerate 15 mg orally once daily. |
Permanently discontinue ICLUSIG in patients unable to tolerate 10 mg orally once daily. |
|
Subsequent Reduction |
Permanently discontinue ICLUSIG in patients unable to tolerate 10 mg orally once daily. |
2.3 Dosage Modification for Coadministration of Strong CYP3A Inhibitors
Avoid coadministration of ICLUSIG with strong CYP3A inhibitors. If coadministration of a strong CYP3A inhibitor cannot be avoided, reduce the dosage of ICLUSIG as recommended in Table 3.
After the strong CYP3A inhibitor has been discontinued for 3 to 5 elimination half-lives, resume the ICLUSIG dosage that was tolerated prior to initiating the strong CYP3A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 3: Recommended ICLUSIG Dosage for Coadministration of Strong CYP3A Inhibitors|
Current ICLUSIG Dosage |
Recommended ICLUSIG Dosage with a Strong CYP3A Inhibitor |
|---|---|
|
45 mg orally once daily |
30 mg orally once daily |
|
30 mg orally once daily |
15 mg orally once daily |
|
15 mg orally once daily |
10 mg orally once daily |
|
10 mg orally once daily |
Avoid coadministration of ICLUSIG with a strong CYP3A inhibitor |
2.4 Dosage for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
For patients with CP-CML, AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL receiving monotherapy, reduce the starting dose of ICLUSIG from 45 mg orally once daily to 30 mg orally once daily in patients with pre-existing hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A, B, or C).
For patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL, no dosage adjustment is recommended when administering ICLUSIG to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child- Pugh A). Closely monitor patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) and modify the ICLUSIG dosage in the event of adverse reactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
- Recommended Dosage in Newly Diagnosed Ph+ ALL: Starting dose is 30 mg orally once daily in combination with chemotherapy, with a reduction to 15 mg once daily upon achievement of MRD-negative (≤0.01% BCR::ABL1/ABL1) CR at the end of induction. (2.1)
- Recommended Dosage in Monotherapy for Ph+ ALL for Whom No Other Kinase Inhibitors are Indicated or T315I-positive Ph+ ALL: Starting dose is 45 mg orally once daily. (2.1)
- Recommended Dosage in CP-CML: Starting dose is 45 mg orally once daily with a reduction to 15 mg once daily upon achievement of ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS. (2.1)
- Recommended Dosage in AP-CML and BP-CML: Starting dose is 45 mg orally once daily. (2.1)
- Hepatic Impairment: See the Full Prescribing Information for dosage modifications for hepatic impairment. (2.4)
- ICLUSIG may be taken with or without food. (2.1)
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 2 year carcinogenicity study, male and female rats were administered daily oral doses of ponatinib of 0.05 mg/kg/day, 0.1 mg/kg/day, 0.2 mg/kg/day and 0.2 mg/kg/day, 0.4 mg/kg/day, and 0.8 mg/kg/day, respectively. Exposures in animals at the highest dose tested were 0.3- to 0.8-fold the human exposure (based on AUC) at doses of 15 mg and 45 mg daily. Ponatinib induced a statistically significant increase in malignant squamous neoplasms of the clitoral gland in females at 0.8 mg/kg/day.
Ponatinib was not mutagenic in a bacterial mutagenesis (Ames) assay, was not clastogenic in a chromosome aberration assay in human lymphocytes, nor was it clastogenic in an in vivo mouse micronucleus assay at oral doses up to 2000 mg/kg.
Ponatinib may impair female fertility. In a fertility study in male and female rats, female fertility parameters were reduced at 1.5 mg/kg/day with exposure equivalent to 0.43 times and 1.23 times of human daily steady-state AUC at the maximum recommended human dose of 45 mg/day (AUC = 1296 h∙ng/mL) and 15 mg/day (451.8 h∙ng/mL), respectively. Evidence of pre- and post-implantation loss of embryos was observed in female rats. Although there were no effects on male fertility parameters in the rat fertility study, repeat dose toxicology studies in monkeys showed degeneration of epithelium of the testes in monkeys at exposures approximately 3.3 times the plasma drug exposure (AUC) in patients receiving the maximum recommended human dose of 45 mg/day.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Newly Diagnosed Ph+ ALL
The efficacy of ICLUSIG in combination with chemotherapy was evaluated in PhALLCON (NCT03589326), a randomized, active-controlled, multicenter, open- label trial of 245 patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL. Randomization was stratified by age at the time of induction therapy (18 to <45 years; ≥45 to <60 years; and ≥60 years). Patients were randomized (2:1) to receive either ICLUSIG 30 mg orally once daily (n=164) or imatinib 600 mg orally once daily (n=81) in combination with chemotherapy (imatinib in combination with chemotherapy is an unapproved regimen in adult patients). The ICLUSIG dose was reduced to 15 mg once daily after completion of the induction phase and achievement of MRD-negative complete remission (CR). If a patient lost MRD negativity at any time after dose reduction to 15 mg, re-escalation to 30 mg once daily was allowed. Only patients who achieved CR or CR with incomplete hematologic recovery (CRi) with MRD-negativity at the end of induction could continue study treatment at the investigator’s discretion.
Per protocol, patients were allowed to receive one cycle of optional prephase therapy excluding TKI prior to randomization to manage the acute disease during the screening period.
Patients were randomized to receive either ICLUSIG or imatinib in combination with 20 cycles of chemotherapy, followed by ICLUSIG or imatinib as single- agent therapy (ICLUSIG or imatinib as single-agent after chemotherapy for newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL is not an approved regimen). Each cycle lasted 28 days.
*Induction (Cycles 1 to 3): ICLUSIG 30 mgor imatinib 600 mg once daily in combination with: * Vincristine: 1.4 mg/m2 IV on Days 1 and 14; capped at 2 mgand * Dexamethasone: <60 years old – 40 mg orally on Days 1 to 4 and Days 11 to 14; ≥60 years old: 20 mg orally on Days 1 to 4 and Days 11 to 14.
*Consolidation (Cycles 4 to 9, alternating methotrexate and cytarabine): ICLUSIG 30 mg (or decreased to 15 mg if in MRD-negative CR)or imatinib 600 mg once daily in combination with: * Methotrexate (Cycles 4, 6, and 8): <60 years old – 1000 mg/m2 IV on Day 1; ≥60 years old – 250 mg/m2 IV, Day 1or * Cytarabine (Cycles 5, 7, and 9): <60 years old – 1000 mg/m2 IV every 12 hours on Days 1, 3, and 5; ≥60 years old – 250 mg/m2 IV every 12 hours on Days 1, 3, and 5
*Maintenance (Cycles 10 to 20): ICLUSIG 30 mg (or decreased to 15 mg if in MRD-negative CR)or imatinib 600 mg once daily in combination with: * Vincristine: 1.4 mg/m2 IV on Day 1 of each cycle; capped at 2 mgand * Prednisone: <60 years old – 200 mg orally on Days 1 to 5; ≥60 to 69 years old – 100 mg orally on Days 1 to 5; ≥70 years old – 50 mg orally on Days 1 to 5
Following combination therapy, patients continued to receive ICLUSIG or imatinib as single-agent therapy until relapse from CR, progressive disease (PD), hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), start of alternative therapy, or unacceptable toxicity.
The demographics and baseline disease characteristics of the randomized population are described in Table 11.
Table 11: Demographic and Disease Characteristics for PhALLCON|
Patient Characteristics at Entry |
ICLUSIG |
Imatinib |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Age (years) | ||
|
Median, years (range) |
54 (19 to 82) |
52 (19 to 75) |
|
Age Category, n (%) | ||
|
18 to <45 years |
58 (35%) |
29 (36%) |
|
45 to <60 years |
45 (27%) |
22 (27%) |
|
≥60 years |
61 (37%) |
30 (37%) |
|
Sex, n (%) | ||
|
Female |
90 (55%) |
43 (53%) |
|
Race, n (%) | ||
|
White |
104 (63%) |
62 (77%) |
|
Not reported |
28 (17%) |
2 (3%) |
|
Asian |
20 (12%) |
11 (14%) |
|
Black or African American |
9 (5%) |
4 (5%) |
|
ECOG Performance Status, n (%) | ||
|
0 |
72 (44%) |
33 (41%) |
|
1 |
85 (52%) |
43 (53%) |
|
2 |
7 (4%) |
5 (6%) |
|
Baseline BCR::ABL1 Dominant Variant | ||
|
p190 |
114 (70%) |
53 (65%) |
|
p210 |
40 (24%) |
25 (31%) |
|
Undetermined/not tested |
10 (6%) |
3 (4%) |
|
Prephase Therapy* |
74 (45%) |
41 (51%) |
|
Comorbidities, n (%) | ||
|
Hypertension |
58 (35%) |
30 (37%) |
|
Diabetes |
39 (24%) |
24 (30%) |
|
Dyslipidemia |
29 (18%) |
23 (28%) |
Among 244 treated patients, 96% completed induction (96% ICLUSIG, 95% imatinib), 84% received at least one cycle of consolidation (89% ICLUSIG, 75% imatinib), and 31% initiated maintenance (36% ICLUSIG, 21% imatinib). After completing combination therapy, 21% of patients received ICLUSIG and 9% received imatinib as single-agent therapy. The overall rate of HSCT was 34% (56/164) in the ICLUSIG arm versus 48% (39/81) in the imatinib arm.
Efficacy was based on the MRD-negative CR rate at the end of induction. The analysis population for MRD-negative CR included 232 randomized patients who had a baseline BCR::ABL1 dominant variant of p190 or p210 as determined by central laboratory tests (154 patients in the ICLUSIG arm and 78 in the imatinib arm). Efficacy results are summarized in Table 12.
Table 12: Efficacy Results in Patients with Ph+ ALL with Baseline BCR::ABL1 Dominant Variant of p190 or p210 in PhALLCON|
ICLUSIG |
Imatinib | |
|---|---|---|
|
MRD: minimal residual disease; CR: complete remission (complete response); BCR::ABL1: breakpoint cluster region-Abelson. | ||
| ||
|
MRD-negative CR******* at End of Induction** | ||
|
Achieved at the end of induction % (n/N) |
30% (46/154) |
12% (9/78) |
|
Risk difference (95% CI)† |
0.18 (0.08, 0.28) | |
|
p-value† |
0.0004 | |
|
CR**‡**** at End of Induction** % (n/N) |
79% (122/154) |
63% (49/78) |
The median duration of follow-up for overall survival was 20.4 months (95% CI: 18.4, 23.9) in the ICLUSIG arm and 18.1 months (95% CI: 13.9, 24.3) in the imatinib arm.
In the subset of patients who did not receive prephase therapy, MRD-negative CR at the end of induction was achieved by 31% of patients in the ICLUSIG arm compared to 16% of patients in the imatinib arm and CR at the end of induction was achieved by 84% and 61%, respectively.
Chronic Phase (CP) CML
The efficacy of ICLUSIG was evaluated in OPTIC (NCT02467270), a dose- optimization trial. Eligible patients had CP-CML whose disease was considered to be resistant or resistant/intolerant to at least 2 prior kinase inhibitors or who have the T315I mutation. T315I mutation testing was performed on peripheral blood by Sanger Sequencing of the p190 or p210 BCR::ABL region. Resistance in CP-CML while on a prior kinase inhibitor was defined as failure to achieve either a complete hematologic response (by 3 months), a minor cytogenetic response (by 6 months), or a major cytogenetic response (by 12 months), or development of a new BCR::ABL1 kinase domain mutation or new clonal evolution. Patients were required to have >1% BCR::ABL1IS (by real-time polymerase chain reaction) at trial entry. Patients received one of three starting dosages: 45 mg orally once daily, 30 mg orally once daily, or 15 mg orally once daily. Patients who received a starting dose of 45 mg or 30 mg had a dose reduction to 15 mg once daily upon achieving ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS. The major efficacy outcome measure was ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS at 12 months. The median duration of follow-up for the 45 mg cohort (N=94) was 27.0 months. Only the efficacy results for the recommended starting dose of 45 mg are described below.
A total of 282 patients received ICLUSIG: 94 received a starting dose of 45 mg, 94 received a starting dose of 30 mg, and 94 received a starting dose of 15 mg. Baseline demographic characteristics are described in Table 13 for patients who received a starting dose of 45 mg.
Table 13: Demographic and Disease Characteristics for OPTIC|
Patient Characteristics at Entry |
ICLUSIG |
|---|---|
|
Age | |
|
Median years (range) |
46 (19 to 81) |
|
Sex, n (%) | |
|
Male |
50 (53%) |
|
Race, n (%) | |
|
White |
73 (78%) |
|
Asian |
16 (17%) |
|
Other/Unknown |
4 (4%) |
|
Black or African American |
1 (1%) |
|
ECOG Performance Status, n (%) | |
|
ECOG 0 or 1 |
93 (99%) |
|
Disease History | |
|
Median time from diagnosis to first dose, years (range) |
5.5 (1 to 21) |
|
Resistant to Prior Kinase Inhibitor, n (%) |
92 (98%) |
|
Presence of one or more BCR::ABL kinase domain mutations, n (%) |
41 (44%) |
|
Number of Prior Kinase Inhibitors, n (%) | |
|
1 |
1 (1%) |
|
2 |
43 (46%) |
|
≥3 |
50 (53%) |
|
T315I mutation at baseline |
25 (27%) |
|
Comorbidities | |
|
Hypertension |
29 (31%) |
|
Diabetes |
5 (5%) |
|
Hypercholesterolemia |
3 (3%) |
|
History of ischemic heart disease |
3 (3%) |
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 14.
Table 14: Efficacy Results in Patients with CP-CML Who Received ICLUSIG at Starting Dose of 45 mg in OPTIC|
ICLUSIG | |
|---|---|
Þ | |
|
Molecular Response at 12 months† | |
|
Overall ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS Rate | |
|
% (n/N) |
44% (41/93) |
|
(95% CI)‡ |
(34%, 55%) |
|
Patients with T315I mutation | |
|
% (n/N) |
44% (11/25) |
|
(95% CI) |
(24%, 65%) |
|
Patients without T315I mutation | |
|
% (n/N) |
44% (29/66)§ |
|
(95% CI) |
(32%, 57%) |
|
Cytogenetic Response by 12 months | |
|
Major (MCyR)¶ | |
|
% (n/N) |
48% (44/91)# |
|
(95% CI) |
(38%, 59%) |
|
Patients with T315I mutation | |
|
% (n/N) |
52% (13/25) |
|
(95% CI) |
(31%, 72%) |
|
Patients without T315I mutation | |
|
% (n/N) |
46% (30/65)Þ |
|
(95% CI) |
(34%, 59%) |
Of the 45 patients who had a dose reduction after achieving ≤1% BCR::ABL1IS, 28 patients (62%) maintained their response at the reduced dose for at least 90 days. Of these 28 patients, 18 patients (64%) maintained the response for at least one year. Median duration of response (MR2) was not reached.
Chronic Phase (CP), Accelerated Phase (AP), Blast Phase (BP) CML and Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (Ph+ ALL)
The efficacy of ICLUSIG was evaluated in PACE (NCT01207440), a single-arm, open-label, international, multicenter trial. Eligible patients had CML and Ph+ ALL whose disease was considered to be resistant or intolerant to a prior kinase inhibitor. Patients were assigned to one of six cohorts based on disease phase (CP-CML, AP-CML, or BP-CML/Ph+ ALL), resistance or intolerance (R/I) to prior kinase inhibitors, and the presence of the T315I mutation. T315I mutation testing was performed on peripheral blood by Sanger Sequencing of the p190 or p210 BCR::ABL region.
Resistance in CP-CML while on a prior kinase inhibitor was defined as failure to achieve either a complete hematologic response (by 3 months), a minor cytogenetic response (by 6 months), or a major cytogenetic response (by 12 months). Patients with CP-CML who experienced a loss of response or development of a kinase domain mutation in the absence of a complete cytogenetic response or progression to AP-CML or BP-CML at any time on a prior kinase inhibitor were also considered resistant.
Resistance in AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL was defined as failure to achieve either a major hematologic response (by 3 months in AP-CML, and by 1 month in BP-CML and Ph+ ALL), loss of major hematologic response (at any time), or development of a kinase domain mutation in the absence of a complete major hematologic response while on a prior kinase inhibitor. Intolerance was defined as the discontinuation of a prior kinase inhibitor due to toxicities despite optimal management in the absence of a complete cytogenetic response in patients with CP-CML or major hematologic response for patients with AP- CML, BP-CML, or Ph+ ALL.
Patients were administered a starting dose of ICLUSIG 45 mg orally once daily.
The major efficacy outcome measure for patients with CP-CML was major cytogenetic response (MCyR), which included complete and partial cytogenetic responses (CCyR and PCyR). The major efficacy outcome measure for patients with AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL was major hematologic response (MaHR), defined as either a complete hematologic response (CHR) or no evidence of leukemia (NEL).
The trial enrolled 449 patients, of which 444 were eligible for efficacy analysis: 267 patients with CP-CML (R/I Cohort: N=203, T315I: N=64), 83 patients with AP-CML, 62 patients with BP-CML, and 32 patients with Ph+ ALL. Five patients were not eligible for efficacy analysis due to lack of confirmation of T315I mutation status, and these patients had not received prior dasatinib or nilotinib.
At study completion, the median duration of follow-up for the trial (all cohorts) was 40.5 months (range: 0.1 months to 79.5 months). The median duration of treatment was 35 months for patients with CP-CML, 21.1 months for patients with AP-CML, 3.2 months for patients with BP-CML and 2.9 months for patients with Ph+ ALL. Baseline demographic characteristics are described in Table 15.
Table 15: Demographic and Disease Characteristics for PACE|
Patient Characteristics at Entry |
Efficacy Population |
|---|---|
| |
|
Age | |
|
Median, years (range) |
59 (18 to 94) |
|
Sex, n (%) | |
|
Male |
236 (53%) |
|
Race, n (%) | |
|
White |
349 (79%) |
|
Asian |
57 (13%) |
|
Black or African American |
25 (6%) |
|
Other/Unknown |
13 (3%) |
|
ECOG Performance Status, n (%) | |
|
ECOG = 0 or 1 |
409 (92%) |
|
Disease History | |
|
Median time from diagnosis to first dose, years (range) |
6.1 (0.3 to 29) |
|
Resistant to Prior Kinase Inhibitor, n (%) |
374 (88%) |
|
Presence of one or more BCR::ABL kinase domain mutations*, n (%) |
244 (55%) |
|
Number of Prior Kinase Inhibitor, n (%) | |
|
1 |
29 (7%) |
|
2 |
166 (37%) |
|
≥3 |
249 (56%) |
|
T315I mutation at baseline |
128 (29%) |
|
Comorbidities | |
|
Hypertension |
159 (35%) |
|
Diabetes |
57 (13%) |
|
Hypercholesterolemia |
100 (22%) |
|
History of ischemic disease |
67 (15%) |
Efficacy results are summarized in Table 16 and Table 17.
Table 16: Efficacy of ICLUSIG in Patients with Resistant or Intolerant CP-CML in PACE|
Overall |
Cohort | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
R/I Cohort |
T315I Cohort | ||
| |||
|
Cytogenetic Response | |||
|
Major* (MCyR) |
55% |
51% |
70% |
|
Complete (CCyR) |
46% |
40% |
66% |
|
Major Molecular Response† |
40% |
35% |
58% |
In patients with CP-CML who achieved MCyR or MMR, the median time to response was 3 months (range: 1.8 to 12.3 months) and 6 months (range: 2 to 60.2 months), respectively. With a minimum follow-up of 60 months, the median durations of MCyR (range: 1 day to 70.1 months) and MMR (range: 1 day to 67.8 months) had not yet been reached.
Table 17: Efficacy of ICLUSIG in Patients with Resistant or Intolerant Advanced Disease (includes R/I and T315I Cohorts) in PACE|
AP-CML Overall |
BP-CML Overall |
Ph+ ALL Overall | |
|---|---|---|---|
| |||
|
Hematologic Response | |||
|
Major* (MaHR) |
57% |
31% |
41% |
|
(95% CI) |
(45%, 68%) |
(20%, 44%) |
(24%, 59%) |
|
Complete† (CHR) |
51% |
21% |
34% |
|
(95% CI) |
(39%, 62%) |
(12%, 33%) |
(19%, 53%) |
The median time to MaHR in patients with AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL was 0.8 months (range: 0.4 to 6.3 months), 1.0 month (range: 0.4 to 4 months), and 0.7 months (range: 0.4 to 6 months), respectively. The median duration of MaHR for patients with AP-CML, BP-CML, and Ph+ ALL was 14 months (range: 1.3 to 74.3 months), 6.5 months (range: 1.9 to 64.7 months), and 3.5 months (range: 1.9 to 13.7 months), respectively.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ICLUSIG tablets are available in the following configurations.
|
Strength |
NDC Number |
Description |
Presentation |
|---|---|---|---|
|
10 mg |
63020-536-30 |
oval, white to off-white, biconvex film-coated tablets with debossed "NZ" on one side and plain on the other side |
30 tablets in a wide-mouth white high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with a desiccant canister and induction sealed child resistant closure. |
|
15 mg |
63020-535-30 |
round, white, biconvex film-coated tablets with debossed "A5" on one side and plain on the other side |
30 tablets in a wide-mouth white high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with a desiccant canister and induction sealed child resistant closure. |
|
63020-535-60 |
60 tablets in a wide-mouth white high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with a desiccant canister and induction sealed child resistant closure. | ||
|
30 mg |
63020-533-30 |
round, white, biconvex film-coated tablets with debossed "C7" on one side and plain on the other side |
30 tablets in a wide-mouth white high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with a desiccant canister and induction sealed child resistant closure. |
|
45 mg |
63020-534-30 |
round, white, biconvex film-coated tablets with debossed "AP4" on one side and plain on the other side |
30 tablets in a wide-mouth white high density polyethylene (HDPE) bottle with a desiccant canister and induction sealed child resistant closure. |
Store ICLUSIG tablets at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Arterial Occlusive Events and Venous Thromboembolic Events
Inform patients that serious arterial thromboses (including arterial stenosis sometimes requiring revascularization) and VTEs have occurred. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider with any symptoms suggestive of a blood clot such as chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness on one side of the body, speech problems, leg pain, or leg swelling [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Heart Failure and Cardiac Arrhythmias
Inform patients of the possibility of heart failure, and abnormally slow or fast heart rates. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider if they experience symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, or fainting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.12)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the possibility of developing liver function abnormalities and serious hepatic toxicity. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if signs of liver failure occur, including jaundice, anorexia, bleeding or bruising [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hypertension
Inform patients of the possibility of new or worsening of existing hypertension. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for elevated blood pressure or if symptoms of hypertension occur including confusion, headache, dizziness, chest pain, or shortness of breath [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Pancreatitis
Inform patients of the possibility of developing pancreatitis that may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or abdominal discomfort, and to promptly report these symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Neuropathy
Inform patients of the possibility of developing peripheral or cranial neuropathy while being treated with ICLUSIG. Advise patients to report symptoms of neuropathy, such as hypoesthesia, hyperesthesia, paresthesia, discomfort, a burning sensation, neuropathic pain, or weakness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Ocular Toxicity
Inform patients of the possibility of ocular toxicity while being treated with ICLUSIG. Advise patients to report symptoms of ocular toxicity, such as blurred vision, dry eye, or eye pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Hemorrhage
Inform patients of the possibility of serious bleeding and to immediately contact their healthcare provider with any signs or symptoms suggestive of hemorrhage such as unusual bleeding or easy bruising [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Fluid Retention
Inform patients of the possibility of developing fluid retention and to contact their healthcare provider for symptoms such as leg swelling, abdominal swelling, weight gain, or shortness of breath [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Myelosuppression
Inform patients of the possibility of developing low blood cell counts; inform patients to report immediately should fever develop, particularly in association with any suggestion of infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Inform patients of the possibility of developing TLS and to immediately contact their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms associated with TLS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]. Advise patients to be adequately hydrated when taking ICLUSIG to reduce the risk of TLS.
Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome (RPLS – also known as Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome)
Inform patients of the possibility of developing Reversible Posterior Leukoencephalopathy Syndrome while being treated with ICLUSIG. Advise patients to report symptoms such as seizure, headache, decreased alertness, altered mental functioning, vision loss, and other visual and neurological disturbances [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
Impaired Wound Healing and Gastrointestinal Perforation
Inform patients that impaired wound healing and gastrointestinal fistula or perforation have been reported. Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider of any planned surgical procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with ICLUSIG and for 3 weeks after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with ICLUSIG and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential for reduced fertility from ICLUSIG [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Instructions for Taking ICLUSIG
Advise patients to take ICLUSIG exactly as prescribed and not to change their dose or to stop taking ICLUSIG unless they are told to do so by their healthcare provider. ICLUSIG may be taken with or without food. ICLUSIG tablets should be swallowed whole. Patients should not cut, crush or dissolve the tablets.
Patients should not take two doses at the same time to make up for a missed dose.
Advise patients not to drink grapefruit juice or eat grapefruit as it may increase the amount of ICLUSIG in their blood and therefore increase their risk of adverse reactions.
Lactose
Inform patients that ICLUSIG tablets contain lactose monohydrate.
