CALCIUM GLUCONATE
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CALCIUM GLUCONATE INJECTION Initial U.S. Approval: 1941
fb40eba7-04e5-40dc-8a95-5f45e7bd70bc
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 27, 2024
Somerset Therapeutics, LLC
DUNS: 079947873
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
CALCIUM GLUCONATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
CALCIUM GLUCONATE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Container Label (50 mL)

Carton Label (50 mL) (25s Pack)
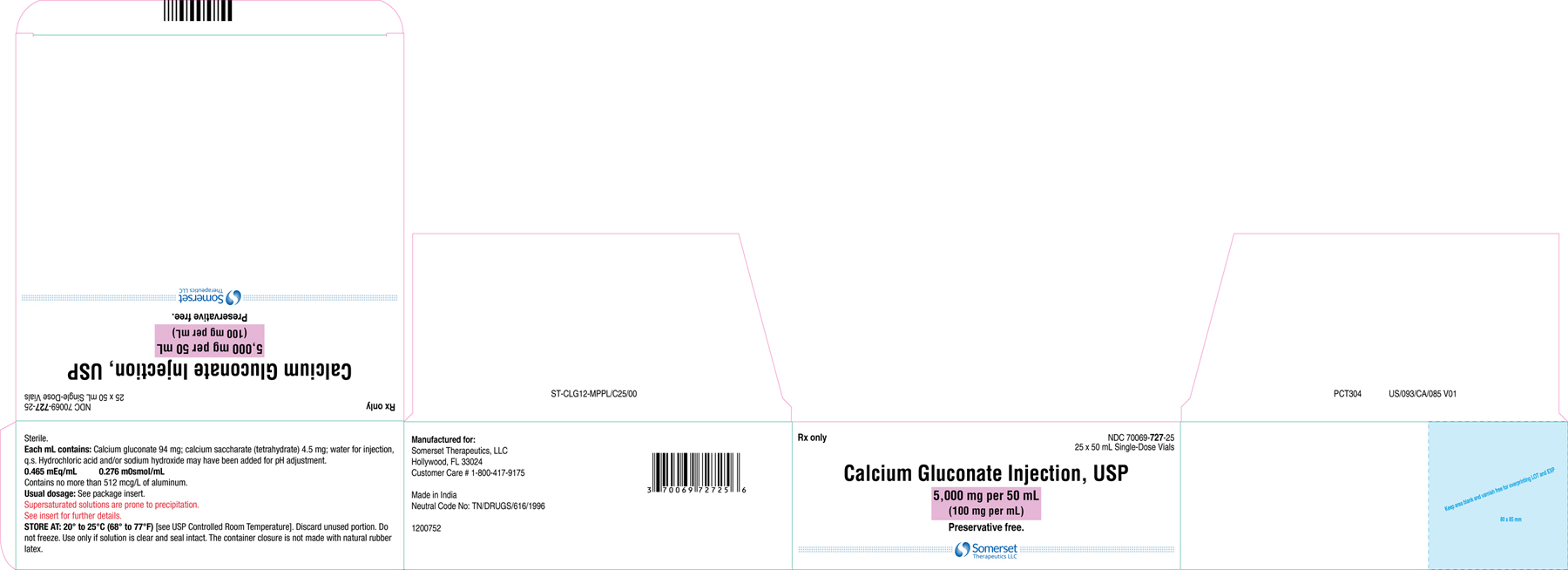
Carton Label (50 mL) (10s Pack)
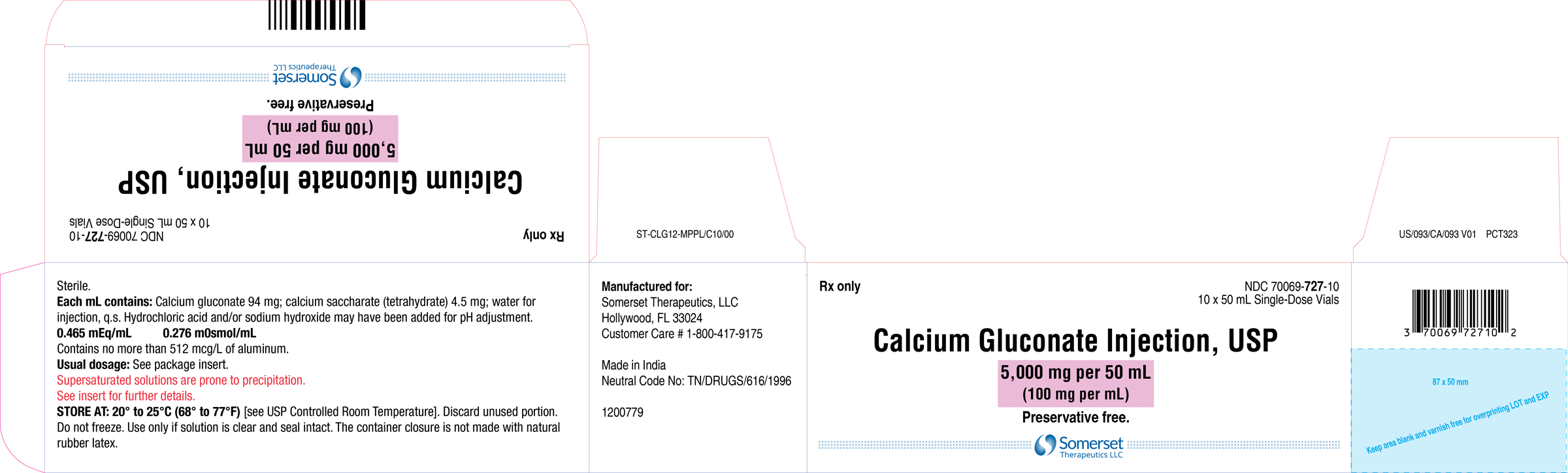
Container Label (100 mL)

Carton Label (100 mL) (20s Pack)

Carton Label (100 mL) 10s Pack
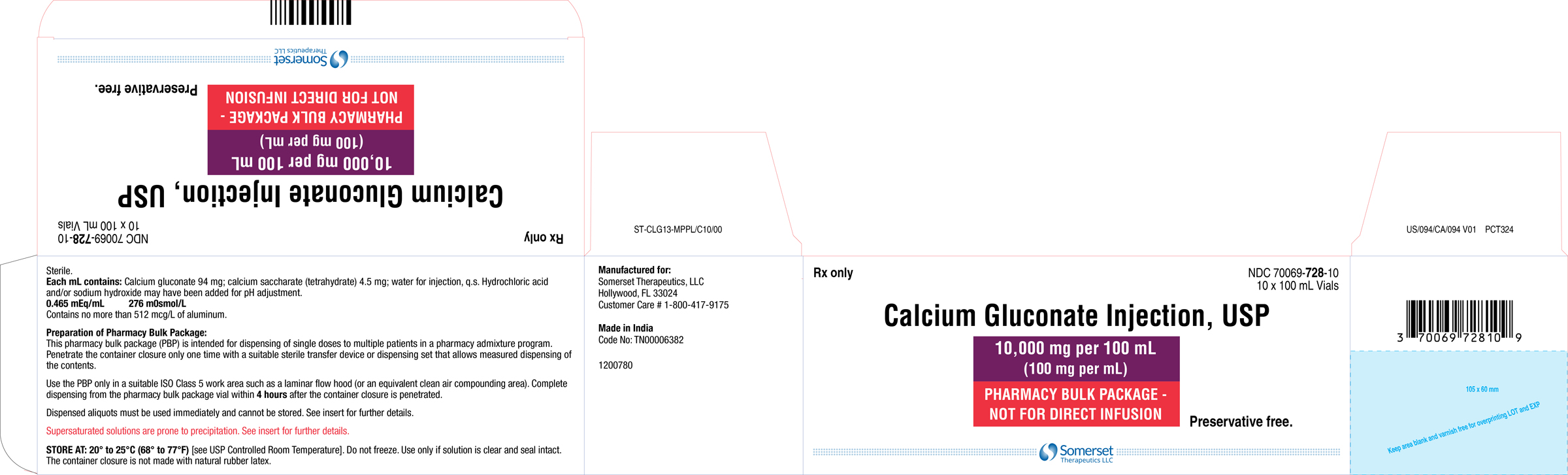
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Calcium gluconate injection is indicated for pediatric and adult patients for the treatment of acute symptomatic hypocalcemia.
Limitations of Use
The safety of calcium gluconate injection for long term use has not been established.
- Calcium gluconate injection is a form of calcium indicated for pediatric and adult patients for the treatment of acute symptomatic hypocalcemia. (1)
- Limitations of Use: The safety of calcium gluconate injection for long term use has not been established. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Calcium gluconate injection is contraindicated in:
- Hypercalcemia
- Neonates (28 days of age or younger) receiving ceftriaxone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypercalcemia (4)
- Neonates (28 days of age or younger) receiving ceftriaxone (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are also described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Arrhythmias with concomitant cardiac glycoside use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- End-organ damage due to intravascular ceftriaxone-calcium precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Tissue necrosis and calcinosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiac arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of calcium gluconate were identified in the literature. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Vasodilation, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, syncope, cardiac arrest
Administration site reactions: Local soft tissue inflammation, local necrosis, calcinosis cutis and calcification due to extravasation
The most common adverse events with calcium gluconate injection are local soft tissue inflammation and necrosis, calcinosis cutis and calcification that are related to extravasation. Other adverse events include vasodilation, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmia, syncope, and cardiac arrest. (6) (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Somerset Therapeutics, LLC at 1-800-417-9175 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Cardiac Glycosides
Hypercalcemia increases the risk of digoxin toxicity, while digoxin may be therapeutically ineffective in the presence of hypocalcemia. Synergistic arrhythmias may occur if calcium and cardiac glycosides are administered together. Avoid administration of calcium gluconate injection in patients receiving cardiac glycosides; if considered necessary, administer calcium gluconate injection slowly in small amounts and monitor ECG closely during administration.
7.2 Calcium Channel Blockers
Administration of calcium may reduce the response to calcium channel blockers.
7.3 Drugs that may cause Hypercalcemia
Vitamin D, vitamin A, thiazide diuretics, estrogen, calcipotriene and teriparatide administration may cause hypercalcemia. Monitor plasma calcium concentrations in patients taking these drugs concurrently.
- Cardiac Glycoside: Synergistic arrhythmias may occur if calcium and cardiac glycosides are administered together. (7.1)
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Administration of calcium may reduce the response. (7.2)
- Drugs that may cause hypercalcemia: Vitamin D, vitamin A, thiazide diuretics, estrogen, calcipotriene and teriparatide administration may cause hypercalcemia. Monitor plasma calcium concentrations in patients taking these drugs concurrently. (7.3)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Calcium gluconate injection, USP is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow, solution available in the following:
- Single dose vial: 5,000 mg per 50 mL (100 mg per mL)
- Pharmacy bulk package: 10,000 mg per 100 mL (100 mg per mL)
Each mL of calcium gluconate injection, USP contains 9.3 mg (0.465 mEq) of elemental calcium.
Calcium Gluconate Injection, USP: (3) (3)
- Single-dose vial: 5,000 mg per 50 mL (100 mg per mL)
- Pharmacy bulk package: 10,000 mg per 100 mL (100 mg per mL)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk summary
Limited available data with calcium gluconate injection use in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes. There are risks to the mother and the fetus associated with hypocalcemia in pregnancy [see Clinical Considerations].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal risk
Maternal hypocalcemia can result in an increased rate of spontaneous abortion, premature and dysfunctional labor, and possibly preeclampsia.
Fetal/Neonatal adverse reactions
Infants born to mothers with hypocalcemia can have associated fetal and neonatal hyperparathyroidism, which in turn can cause fetal and neonatal skeletal demineralization, subperiosteal bone resorption, osteitis fibrosa cystica and neonatal seizures. Infants born to mothers with hypocalcemia should be carefully monitored for signs of hypocalcemia or hypercalcemia, including neuromuscular irritability, apnea, cyanosis and cardiac rhythm disorders.
8.2 Lactation
Risk summary
Calcium is present in human milk as a natural component of human milk. It is not known whether intravenous administration of calcium gluconate injection can alter calcium concentration in human milk. There are no data on the effects of calcium gluconate injection on the breastfed infant, or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for calcium gluconate injection and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from calcium gluconate injection or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of calcium gluconate injection have been established in pediatric patients for the treatment of acute, symptomatic hypocalcemia.
Pediatric approval for calcium gluconate injection, including doses, is not based on adequate and well-controlled clinical studies. Safety and dosing recommendations in pediatric patients are based on published literature and clinical experience [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Concomitant use of ceftriaxone and calcium gluconate injection is contraindicated in neonates (28 days of age or younger) due to reports of fatal outcomes associated with the presence of lung and kidney ceftriaxone- calcium precipitates. In patients older than 28 days of age, ceftriaxone and calcium gluconate injection may be administered sequentially, provided the infusion lines are thoroughly flushed between infusions with a compatible fluid [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. This product contains up to 512 mcg/L aluminum which may be toxic, particularly for premature neonates due to immature renal function. Parenteral administration of aluminum greater than 4 to 5 mcg/kg/day is associated with central nervous system and bone toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In general dose selection for an elderly patient should start at the lowest dose of the recommended dose range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Renal Impairment
For patients with renal impairment, initiate calcium gluconate injection at the lowest dose of the recommended dose ranges across all age groups. Monitor serum calcium levels every 4 hours [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Hepatic function does not impact the availability of ionized calcium after calcium gluconate intravenous administration. Dose adjustment in hepatically impaired patients may not be necessary.
- Geriatric use: Dosing in elderly patients should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosage range. (8.5)
- Renal impairment: Initiate with the lower limit of the dosage range and monitor serum calcium levels every 4 hours. (8.6, 2.4)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of calcium gluconate injection may result in hypercalcemia. Symptoms of hypercalcemia typically develop when the total serum calcium concentration is ≥12 mg/dL. Neurologic symptoms include depression, weakness, fatigue, and confusion at lower levels, with patients experiencing hallucinations, disorientation, hypotonicity, seizures, and coma. Effects on the kidney include diminished ability to concentrate urine and diuresis.
If overdose of calcium gluconate injection occurs immediately discontinue administration and provide supportive treatments to restore intravascular volume as well as promote calcium excretion in the urine if necessary.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Calcium gluconate injection, USP is a sterile, preservative-free, nonpyrogenic, supersaturated solution of calcium gluconate, a form of calcium, for intravenous use.
Calcium gluconate is calcium D-gluconate (1:2) monohydrate. The structural formula is:
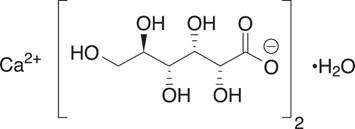
Molecular formula: C12H22CaO14• H2O
Molecular weight: 448.39
Solubility in water: 3.5 g/100 mL at 25°C
Calcium gluconate injection, USP is available as 5,000 mg per 50 mL (100 mg per mL) in a single-dose vial, or 10,000 mg per 100 mL (100 mg per mL) in a pharmacy bulk package.
Each mL of calcium gluconate injection, USP contains 100 mg of calcium gluconate (equivalent to 94 mg of calcium gluconate and 4.5 mg of calcium saccharate tetrahydrate), hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment (6.0 to 8.2) and sterile water for injection, q.s. It contains no antimicrobial agent.
Each mL of calcium gluconate injection, USP contains 9.3 mg (0.465 mEq) of elemental calcium.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been conducted to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of calcium gluconate injection. Calcium gluconate was not mutagenic with or without metabolic activation in the Ames test with Salmonella typhimurium (strains TA-1535, TA-1537, and TA-1538) or Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Strain D4). Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with calcium gluconate administered by the intravenous route.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Calcium gluconate injection, USP is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution supplied as follows:
|
** Calcium Gluconate Total Product** |
** Carton NDC and Package Configuration** |
** Vial NDC** |
|
5,000 mg calcium gluconate per 50 mL (100 mg per mL) |
70069-** 727** -25 |
70069-** 727** -01 |
|
70069-** 727** -10 | ||
|
10,000 mg calcium gluconate per 100 mL (100 mg per mL) |
70069-** 728** -20 |
70069-** 728** -01 |
|
70069-** 728** -10 |
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
Preservative Free. Discard any unused portion in the single-dose vial immediately or the pharmacy bulk package vial within 4 hours after initial closure puncture.
Each dose dispensed from the pharmacy bulk package vial must be used immediately.
The diluted solution must be used immediately.
**NOTE:**Supersaturated solutions are prone to precipitation. The precipitate, if present, may be dissolved by warming the vial to 60° to 80°C, with occasional agitation, until the solution becomes clear. Shake vigorously. Allow to cool to room temperature before dispensing. Use injection only if clear immediately prior to use.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Advise the patient that the risks associated with infusion including local tissue inflammation, local necrosis and calcinosis. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
SPL UNCLASSIFIED
Manufactured for:
Somerset Therapeutics, LLC
Hollywood, FL 33024
Made in India
Neutral Code No: (50 mL) TN/DRUGS/616/1996
Neutral Code No: (100 mL) TN00006382
1200778
ST- CLG-MPPL/P/01
US/LF/062 V02
PLF185/01
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Intravenous administration of calcium gluconate increases serum ionized calcium level. Calcium gluconate dissociates into ionized calcium in plasma. Ionized calcium and gluconate are normal constituents of body fluids.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Calcium gluconate injection is 100% bioavailable following intravenous injection.
Metabolism
Calcium itself does not undergo direct metabolism. The release of ionized calcium from intravenous administration of calcium gluconate is direct and does not seem to be affected by the first pass through the liver.
Distribution
Calcium in the body is distributed mainly in skeleton (99%). Only 1% of the total body calcium is distributed within the extracellular fluids and soft tissues. About 50% of total serum calcium is in the ionized form and represents the biologically active part. 8% to 10% serum calcium is bound to organic and inorganic acid and approximately 40% is protein-bound (primarily to albumin).
Elimination
Studies have shown a relationship between urinary calcium excretion and the intravenous administration of calcium gluconate, with a significant increase in urinary calcium excretion observed after the intravenous administration of calcium gluconate.
