TPOXX
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TPOXX safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TPOXX. TPOXX (tecovirimat) capsules, for oral use TPOXX (tecovirimat) injection for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2018
fce826ab-4d6a-4139-a2ee-a304a913a253
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 12, 2023
SIGA Technologies, Inc.
DUNS: 932651516
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
tecovirimat monohydrate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
tecovirimat monohydrate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (1)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypoglycemia When Co-Administered with Repaglinide
Co-administration of repaglinide and tecovirimat may cause mild to moderate hypoglycemia. Monitor blood glucose and monitor for hypoglycemic symptoms when administering TPOXX with repaglinide [see Drug Interactions (7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
In a drug interaction study, 10 of 30 healthy subjects experienced mild (6 subjects) or moderate (4 subjects) hypoglycemia following co-administration of repaglinide (2 mg) and TPOXX. Symptoms resolved in all subjects after intake of food and/or oral glucose.
5.2 Risks of Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Excipient for Patients with Renal
Insufficiency and Pediatric Patients < 2 Years of Age
Patients with renal insufficiency
TPOXX Injection: In healthy patients and in patients with mild to severe renal insufficiency, the majority of an 8 g dose of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (per 200 mg tecovirimat/20 mL solution) is eliminated in the urine. It is known that clearance of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin is reduced in patients with mild, moderate, and severe renal impairment, resulting in higher exposure to hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin; in these patients, half-life values are increased over normal values by approximately two-, four-, and six-fold, respectively. In these patients, successive infusions may result in accumulation of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin until steady state is reached.
In patients with mild (defined as creatinine clearance 60-89 mL/min) and moderate (defined as creatinine clearance 30-59 mL/min) renal impairment, TPOXX Injection should be used with caution. Creatinine clearance should be closely monitored and, if renal toxicity is suspected, consideration should be given to administering TPOXX orally if possible or to using an alternative medication. TPOXX Injection is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance 30 mL/min) [see Contraindictions (4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Pediatric patients
TPOXX Injection: In pediatric patients less than 2 years of age, there are limited data regarding the use of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Given that renal tubular function rapidly matures over the first few years of life, clearance of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin may be reduced in young pediatric patients, resulting in higher exposure to hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. TPOXX Injection should be used with caution in this population given that animal studies have shown potential for nephrotoxicity at very high exposure levels of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Given the potential for drug accumulation due to renal immaturity in pediatric patients less than 2 years, monitoring of renal function after treatment is recommended [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Hypoglycemia: Co-administration with repaglinide may cause hypoglycemia. Monitor blood glucose and monitor for hypoglycemic symptoms during co- administration. (5.1)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of TPOXX on Other Drugs
Tecovirimat is a weak inducer of cytochrome P450 (CYP)3A and a weak inhibitor of CYP2C8 and CYP2C19. However, the effects are not expected to be clinically relevant for most substrates of those enzymes based on the magnitude of interactions and the duration of treatment of TPOXX. See Table 5 for clinical recommendations for select sensitive substrates.
7.2 Established Drug Interactions
Table 5 provides a listing of established or significant drug interactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 5: Significant Drug Interactions|
a ↓ = decrease, ↑ = increase b These interactions have been studied in healthy adults. | ||
|
Concomitant Drug Class: |
Effect on |
Clinical Effect/Recommendation |
|
Blood Glucose-Lowering Agent: | ||
|
Repaglinideb |
↑ repaglinide |
Monitor blood glucose and monitor for |
|
CNS Depressant: | ||
|
Midazolamb |
↓ midazolam |
Monitor for effectiveness of midazolam. |
7.3 Drugs Without Clinically Significant Interactions With TPOXX
Based on a drug interaction study, no clinically significant drug interactions have been observed when TPOXX is co-administered with bupropion, flurbiprofen, or omeprazole [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.4 Vaccine Interactions
No vaccine-drug interaction studies have been performed in human subjects. Some animal studies have indicated that co-administration of TPOXX at the same time as live smallpox vaccine (vaccinia virus) may reduce the immune response to the vaccine. The clinical impact of this interaction on vaccine efficacy is unknown.
Consult the full prescribing information prior to and during treatment for potential drug interactions. (5.1, 7, 12.3)
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
TPOXX Capsule
How Supplied
Each TPOXX capsule contains 200 mg of tecovirimat. TPOXX capsules are hard gelatin with an opaque orange body imprinted in white ink with “SIGA” followed by the SIGA logo followed by “®”, and an opaque black cap imprinted in white ink with "ST-246®", containing white to off-white powder. Each bottle contains 42 capsules (NDC 50072-200-42) with an induction seal and child-resistant cap.
Storage and Handling
Store capsules in the original bottle at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
TPOXX Injection
How Supplied
TPOXX injection is supplied in a 30 mL single-dose vial as a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution for intravenous administration containing 200 mg/20 mL (10 mg/mL) of tecovirimat (NDC 50072-010-30). This solution is intended for dilution with either 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride injection or 5% (w/v) dextrose injection solution. The vial stopper is not made with natural rubber latex. The vials are packed in cartons of seven vials. Short-term (up to 24 hours) storage and handling at an ambient temperature is acceptable.
Storage and Handling
Store TPOXX injection in a refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) Do not freeze.
The diluted solution(s) of TPOXX injection with either 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride (normal saline) or 5% (w/v) dextrose solution should be used within 4 hours of preparation if stored at room temperature or within 24 hours of preparation if stored at 2°C to 8°C [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on the use of tecovirimat in pregnant individuals to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, and other adverse maternal and fetal outcomes.
In animal reproduction studies, no embryofetal developmental toxicity was observed in mice during the period of organogenesis at tecovirimat exposures (area under the curve [AUC]) up to 23 times higher than human exposure at the recommended human dose (RHD). In rabbits, no embryofetal developmental toxicity was observed during organogenesis at tecovirimat exposures (AUC) less than human exposures at the RHD. In a mouse pre-/post-natal development study, no toxicities were observed at maternal tecovirimat exposures up to 24 times higher than human exposure at the RHD (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown, and the estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is higher than the general population. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Tecovirimat was administered orally to pregnant mice at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day from gestation Days 6-15. No embryofetal toxicities were observed at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day (approximately 23 times higher than human exposure at the RHD).
Tecovirimat was administered orally to pregnant rabbits at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day from gestation Days 6-19. No embryofetal toxicities were observed at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (0.4 times the human exposure at the RHD).
In the pre-/post-natal development study, tecovirimat was administered orally to pregnant mice at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day from gestation Day 6 to post- natal Day 20. No toxicities were observed at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day (approximately 24 times higher than human exposure at the RHD).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Because of the potential for variola virus transmission through direct contact with the breastfed infant, breastfeeding is not recommended in patients with smallpox. There are no data on the presence of tecovirimat in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or on milk production. Tecovirimat was present in animal milk (see Data). When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely to be present in human milk.
Data
In a lactation study at doses up to 1,000 mg/kg/day, mean tecovirimat milk to plasma ratios up to approximately 0.8 were observed at 6 and 24 hours post- dose when administered orally to mice on lactation Day 10 or 11.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
There are no data on the effect of tecovirimat on human fertility. Decreased fertility due to testicular toxicity was observed in male mice [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
As in adults, the effectiveness of TPOXX in pediatric patients is based solely on efficacy studies in animal models of orthopoxvirus disease. As exposure of healthy pediatric subjects to TPOXX with no potential for direct clinical benefit is not ethical, pharmacokinetic simulation was used to derive dosing regimens that are predicted to provide pediatric patients with exposures comparable to the observed exposure in adults receiving 600 mg orally twice daily (every 12 hours) or 200 mg intravenously twice daily (every 12 hours). The dosage for pediatric patients is based on weight [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
TPOXX Injection:
There are limited data regarding the use of hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, an ingredient in TPOXX injection, in pediatric patients less than 2 years of age. Given the potential for drug accumulation due to renal immaturity in pediatric patients less than 2 years, monitoring of renal function after treatment is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of TPOXX did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether the safety profile of TPOXX is different in this population compared to younger subjects. Of the 359 subjects in the clinical study of TPOXX, 10% (36/359) were ≥ 65 years of age, and 1% (4/359) were ≥ 75 years of age. No alteration of dosing is needed for patients ≥ 65 years of age [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
TPOXX Capsules:
No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild, moderate or severe renal impairment or patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
TPOXX Injection:
Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, an ingredient in TPOXX injection, when administered intravenously, is eliminated through glomerular filtration. No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild (creatinine clearance 60-89 mL/min) or moderate (creatinine clearance 30-59 mL/min) renal impairment. TPOXX Injection is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance below 30 mL/min) [see Contraindictions (4)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild, moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child Pugh Class A, B, or C) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Lactation: Breastfeeding is not recommended in patients with smallpox. (8.2)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
TPOXX capsules and TPOXX injection contains tecovirimat, an inhibitor of the orthopoxvirus VP37 envelope wrapping protein.
TPOXX (tecovirimat) capsules, for oral use are immediate release capsules containing tecovirimat monohydrate equivalent to 200 mg of tecovirimat for oral administration. The capsules include the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and sodium lauryl sulfate. The capsule shell is composed of gelatin, FD&C blue #1, FD&C red #3, FD&C yellow #6, and titanium dioxide.
TPOXX (tecovirimat) injection, for intravenous use is a sterile, colorless to pale yellow solution free of visible particles that is intended for intravenous use following dilution. Tecovirimat injection is available in a single-dose vial containing 200 mg/20 mL (10 mg/mL) of tecovirimat and 8,000 mg (400 mg/mL) of Hydroxypropyl Betadex, NF (hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin) and Water for Injection, USP/NF.
Tecovirimat monohydrate is a white to off-white crystalline solid with the chemical name Benzamide, N-[(3aR,4R,4aR,5aS,6S,6aS)-3,3a,4,4a,5,5a,6,6a-octahydro-1,3-dioxo-4,6 ethenocycloprop[f]isoindol-2(1H)-yl]-4-(trifluoromethyl), rel-(monohydrate). The chemical formula is C19H15F3N2O3·H2O representing a molecular weight of 394.35 g/moL. The molecular structure is as follows:
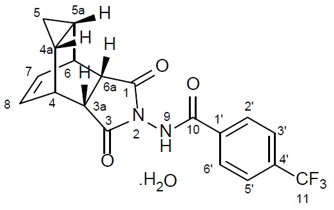
Tecovirimat monohydrate is practically insoluble in water and across the pH range of 2.0-6.5 (< 0.1 mg/mL).
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with tecovirimat.
Tecovirimat was not genotoxic in in vitro or in vivo assays, including a bacterial reverse mutation assay, a mammalian mutagenicity assay in mouse lymphoma L5178Y/TK± cells, and in an in vivo mouse micronucleus study.
Impairment of Fertility
In a fertility and early embryonic development study in mice, no effects of tecovirimat on female fertility were observed at tecovirimat exposures (AUC) approximately 24 times higher than human exposure at the RHD. In male mice, decreased male fertility associated with testicular toxicity (increased percent abnormal sperm and decreased sperm motility) was observed at 1,000 mg/kg/day (approximately 24 times the human exposure at the RHD).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
In a repeat-dose toxicology study in dogs, convulsions (tonic and clonic) were observed in one animal within 6 hours of a single dose of 300 mg/kg (approximately 4 times higher than the highest observed human exposure at the RHD based on Cmax). Electroencephalography (EEG) findings in this animal were consistent with seizure activity during the observed convulsions. Tremors, which were considered non-adverse, were observed at 100 mg/kg/dose (similar to the highest observed human exposure at the RHD based on Cmax), although no convulsions or EEG findings were observed at this dose.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Overview
The effectiveness of TPOXX for treatment of smallpox disease has not been determined in humans because adequate and well-controlled field trials have not been feasible, and inducing smallpox disease in humans to study the drug’s efficacy is not ethical. Therefore, the effectiveness of TPOXX for treatment of smallpox disease was established based on results of adequate and well- controlled animal efficacy studies of non-human primates and rabbits infected with non-variola orthopoxviruses. Survival rates observed in the animal studies may not be predictive of survival rates in clinical practice.
Study Design
Efficacy studies were conducted in cynomolgus macaques infected with monkeypox virus, and New Zealand white (NZW) rabbits infected with rabbitpox virus. The primary efficacy endpoint for these studies was survival. In non-human primate studies, cynomolgus macaques were lethally challenged intravenously with 5 x 107 plaque-forming units of monkeypox virus; tecovirimat was administered orally once daily at a dose level of 10 mg/kg for 14 days, starting at Day 4, 5 or 6 post-challenge. In rabbit studies, NZW rabbits were lethally challenged intradermally with 1,000 plaque-forming units of rabbitpox virus; tecovirimat was administered orally once daily for 14 days at a dose level of 40 mg/kg, starting at Day 4 post-challenge. The timing of tecovirimat dosing in these studies was intended to assess efficacy when treatment is initiated after animals have developed clinical signs of disease, specifically dermal pox lesions in cynomolgus macaques, and fever in rabbits. Clinical signs of disease were evident in some animals at Day 2-3 post-challenge but were evident in all animals by Day 4 post-challenge. Survival was monitored for 3-6 times the mean time to death for untreated animals in each model.
Study Results
Treatment with tecovirimat for 14 days resulted in statistically significant improvement in survival relative to placebo, except when given to cynomolgus macaques starting at Day 6 post-challenge (Table 8).
Table 8: Survival Rates in Tecovirimat Treatment Studies in Cynomolgus Macaques and NZW Rabbits Exhibiting Clinical Signs of Orthopoxvirus Disease|
aDay post-challenge tecovirimat treatment was initiated bp-value is from 1-sided Boschloo Test (with Berger-Boos modification of gamma = 0.000001) compared to placebo cSurvival percentage in tecovirimat treated animals minus survival percentage in placebo treated animals dExact 95% confidence interval based on the score statistic of difference in survival rates eA placebo control group was not included in this study. KEY: NA = Not Applicable | |||||
|
Treatment |
Survival Percentage |
p-value****b |
Survival Rate | ||
|
Placebo |
Tecovirimat | ||||
|
Cynomolgus Macaques | |||||
|
Study 1 |
Day 4 |
0% (0/7) |
80% (4/5) |
0.0038 |
80% (20.8%, 99.5%) |
|
Study 2 |
Day 4 |
0% (0/6) |
100% (6/6) |
0.0002 |
100% (47.1%, 100%) |
|
Study 3 |
Day 4 |
0% (0/3) |
83% (5/6) |
0.0151 |
83% (7.5%, 99.6%) |
|
Day 5 |
83% (5/6) |
0.0151 |
83% (7.5%, 99.6%) | ||
|
Day 6 |
50% (3/6) |
0.1231 |
50% (-28.3%, 90.2%) | ||
|
NZW Rabbits | |||||
|
Study 4 |
Day 4 |
0% (0/10) |
90% (9/10) |
< 0.0001 |
90% (50.3%, 99.8%) |
|
Study 5 |
Day 4 |
NAe |
88% (7/8) |
NA |
NA |
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Efficacy Based on Animal Models Alone
Inform patients that the efficacy of TPOXX is based solely on efficacy studies demonstrating a survival benefit in animals and that the effectiveness of TPOXX has not been tested in humans with smallpox disease [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Important Dosage and Administration Information
Advise patients to take TPOXX capsules as directed within 30 minutes of eating a full meal containing moderate or high fat with 6-8 oz. of water [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Inform patients to take TPOXX for the entire duration without missing or skipping a dose [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Inform patients who cannot swallow capsules to refer to the Instructions for Use [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that TPOXX may interact with other drugs. Advise patients to report to their healthcare provider the use of other prescription drugs. Co- administration of TPOXX with repaglinide may cause hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
TPOXX injection: Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin, a required component of TPOXX injection, is eliminated through glomerular filtration. Therefore, in patients with severe renal impairment (defined as creatinine clearance below 30 mL/min), the use of TPOXX injection is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. In patients with mild (defined as creatinine clearance 60-89 mL/min) and moderate (defined as creatinine clearance 30-59 mL/min) renal impairment, TPOXX injection should be used with caution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Lactation
Instruct individuals with smallpox not to breastfeed their infant because of the risk of passing variola virus to the breastfed infant [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
TPOXX capsules Manufactured by:
Catalent Pharma Solutions, LLC
1100 Enterprise Drive
Winchester, KY 40391
TPOXX injection manufactured by:
Patheon Manufacturing Services LLC
5900 Martin Luther King Jr. Highway
Greenville, NC 27834
Distributed by:
SIGA Technologies, Inc.
4575 SW Research Way, Suite 110
Corvallis, OR 97333
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Issued: 05/2022 | |
|
PATIENT INFORMATION | ||
|
TPOXX (Tē-Pox or Tee-pahx) |
TPOXX (Tē-Pox or Tee-pahx) | |
|
What is TPOXX?
| ||
|
Who should not receive TPOXX injection? | ||
|
Before taking or receiving TPOXX, tell your healthcare provider about all of your or your child’s medical conditions, including if you or your child:
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you or your child
take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and
herbal supplements. | ||
|
How should I take TPOXX?
TPOXX capsules:
TPOXX Injection for Intravenous Infusion (IV) TPOXX injection is given to you or your child by intravenous (IV) infusion into a vein slowly over 6 hours using an infusion pump by a health care provider. | ||
|
What are the possible side effects of TPOXX? *Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Low blood sugar can happen when TPOXX is taken or received with repaglinide, a medicine used to treat type 2 diabetes. Tell your healthcare provider if you get any of the following symptoms of low blood sugar: | ||
|
• headache |
• dizziness |
• weakness |
|
The most common side effects of TPOXX capsules include: | ||
|
• headache |
• stomach pain | |
|
The most common side effects of TPOXX injection include: | ||
|
• reactions at the site of your IV infusion | ||
|
These are not all the possible side effects of TPOXX. | ||
|
How should I store TPOXX?
Keep TPOXX and all other medicines out of the reach of children. | ||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of TPOXX. | ||
|
What are the ingredients in TPOXX? TPOXX capsules manufactured by: Catalent Pharma Solutions 1100 Enterprise Drive Winchester, KY 40391 TPOXX injection manufactured by: Patheon Manufacturing Services LLC 5900 Martin Luther King Jr. Highway Greenville, NC 27834 Distributed By: SIGA Technologies, Inc. 4575 SW Research Way, Suite 110 Corvallis, OR 97333 For more information, go to www.SIGA.com or call 1-888-899-3472. |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Instructions
It is recommended that patients 13 kg and above initiate oral treatment with TPOXX capsules if possible. If patients are unable to take oral TPOXX capsules or Drug-Food Preparation, treatment may be initiated with TPOXX injection as a 6 hour intravenous (IV) infusion. If IV treatment is necessary, conversion from IV to oral TPOXX is recommended as soon as oral treatment can be tolerated [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. In patients receiving an IV infusion, the first dose of oral treatment should be given at the time of and in place of the next scheduled IV dosing.
In patients receiving an oral treatment who subsequently require IV treatment, the first dose of IV infusion should be given at the time of and in place of the next scheduled oral dosing.
TPOXX capsules
Take TPOXX capsules within 30 minutes after a full meal containing moderate or high fat.
Missed Dose
If a dose of oral TPOXX is missed, the patient should take the dose as soon as possible and anytime up to 8 hours prior to the next scheduled dose. If less than 8 hours remain before the next scheduled dose, do not take the missed dose, and resume dosing at the next scheduled dose.
TPOXX injection
Administer TPOXX injection by IV infusion over 6 hours via an infusion pump. Must dilute TPOXX Injection prior to use [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
2.2 Testing Before Initiating and During Treatment with TPOXX Injection
Determine creatinine clearance in all patients before starting TPOXX injection and monitor while receiving TPOXX injection as clinically appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Contraindictions (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4, 8.6)].
2.3 TPOXX Oral Dosage for Pediatric Patients Weighing at Least 13 kg and
Adults
The recommended dosage of TPOXX capsules in pediatric patients weighing at least 13 kg and adults is displayed in Table 1 below.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage and Preparation Instructions for TPOXX Capsules in Pediatric Patients Weighing at Least 13 kg and Adults|
aTPOXX capsules should be taken within 30 minutes after a full meal containing moderate or high fat [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] | ||
|
Body Weight |
Oral Dosage for 14 Days****a | |
|
Dosage (Number of Capsules) |
Drug Food Preparation for Patients Who Cannot Swallow Capsules | |
|
13 kg to less than 25 kg |
200 mg (1 capsule) every 12 hours |
Carefully open the required number of capsules and mix contents of capsule(s) of TPOXX with 30 mL of liquid (e.g., milk, chocolate milk) or soft food (e.g., apple sauce, yogurt). The entire mixture should be administered within 30 minutes of its preparation. |
|
25 kg to less than 40 kg |
400 mg (2 capsules) every 12 hours | |
|
40 kg to less than 120 kg |
600 mg (3 capsules) every 12 hours | |
|
120 kg and above |
600 mg (3 capsules) every 8 hours |
2.4 Renal Impairment
TPOXX injection is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance below 30 mL per minute [see Contraindictions (4)].
2.5 Dosage and Administration of TPOXX Injection for Intravenous Infusion
The recommended dosage of TPOXX injection in pediatric patients weighing at least 3 kg and adults is displayed in Table 2 below.
TPOXX injection is supplied in a single-dose clear glass vial containing 200 mg/20 mL (10 mg/mL). Parenteral drug products must be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. To administer:
- Use aseptic technique when preparing TPOXX injection.
- Withdraw the quantity of TPOXX injection (Table 2), add this volume to the syringe then dilute with two equal parts of either 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride injection (normal saline) or 5% (w/v) dextrose injection in a syringe of suitable size. Injection with diluents other than 0.9% sodium chloride or 5% dextrose solution has not been studied.NOT FOR IV BOLUS INJECTION. Do not use prefilled infusion bags for product preparation and administration.
- The diluted TPOXX injection may be stored refrigerated (2°C - 8°C) for up to 24 hours or at room temperature (15°C - 25°C) for up to 4 hours.
- Gently swirl the syringe of in-use solution prior to inserting into the syringe pump and infuse over 6 hours every 12 hours for 14 days.
- Do not re-use the single-dose vial once it has been punctured.
|
aPatients weighing at least 13 kg should be switched to TPOXX Capsules to complete the 14 day treatment course as soon as oral therapy can be tolerated. b10 mg/mL TPOXX solution containing 40% hydroxypropyl betadex (8 g per vial) with water for injection [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3)] cDiluent is either 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride injection or 5% (w/v) dextrose injection solution. dDepending on size of syringe available with syringe pump system, two separate syringes may be needed for each 6 hour administration. | |||
|
Body Weight |
Dosage for up to 14 days |
Volume of TPOXX Injection****b |
Volume of Diluent****c |
|
3 kg to less than 35 kg |
6 mg/kg every 12 hours by intravenous infusion over 6 hoursa |
0.6 mL/kg |
1.2 mL/kg |
|
35 kg to less than 120 kg |
200 mg every 12 hours by intravenous infusion over 6 hours |
20 mL |
40 mL |
|
120 kg and aboved |
300 mg every 12 hours by intravenous infusion over 6 hours |
30 mL |
60 mL |
- Pediatric and Adult Patients weighing 40 kg or more (2.3) (Oral Dosing):
- 40 kg to less than 120 kg: 600 mg of TPOXX every 12 hours for 14 days
- 120 kg or more: 600 mg of TPOXX every 8 hours for 14 days
- Pediatrics and adult patients weighing 13 kg or more and those who cannot swallow capsules (2.3) (Oral Dosing): TPOXX Capsules can be administered by carefully opening the number of capsule noted below and mixing and administering the entire contents in 30 mL of liquid (e.g., milk, chocolate milk) or soft food (e.g., apple sauce, yogurt):
- 13 kg to less than 25 kg: 200 mg (1 Capsule) of TPOXX every 12 hours for 14 days
- 25 kg to less than 40 kg: 400 mg (2 Capsules) of TPOXX every 12 hours for 14 days
- 40 kg to less than 120 kg: 600 mg (3 Capsules) of TPOXX every 12 hours for 14 days
- 120 kg or more: 600 mg (3 capsules) every 8 hours for 14 days
- Patients weighing 3 kg and above (2.5) (Intravenous Dosing):
- 3 kg to less than 35 kg: 6 mg/kg every 12 hours by intravenous infusion over 6 hours for up to 14 days
- 35 kg to less than 120 kg: 200 mg every 12 hours by intravenous infusion over 6 hours for up to 14 days
- 120 kg and above: 300 mg every 12 hours by intravenous infusion over 6 hours for up to 14 days
- Pediatric patients weighing 13 kg or more should be switched to TPOXX Capsules to complete the 14-day treatment course as soon as oral therapy can be tolerated.
- Administration Instruction for TPOXX Capsules: Take within 30 minutes after a full meal containing moderate or high fat. (2.1, 2.3)
- Administration Instructions for TPOXX Injection: Infuse over 6 hours via infusion pump. (2.5)
- See Full Prescribing Information for additional information on the administration and preparation of TPOXX Capsules and Injection. (2)
