CYSTEINE HYDROCHLORIDE
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP. Initial U.S. Approval: 1971
cbf70fc3-14b3-4c17-8de8-acba1e12ac95
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Apr 29, 2022
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
DUNS: 005083209
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
cysteine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (4)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
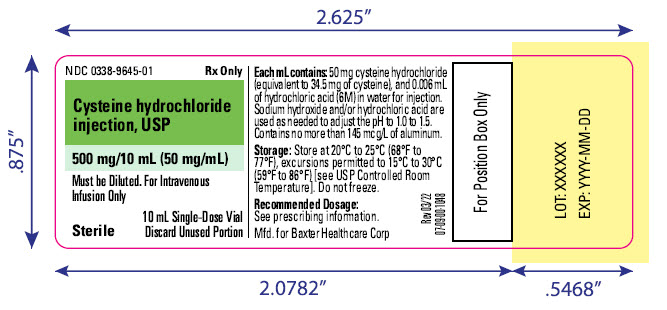
NDC 0338-9645-01
Rx only
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL)
Must be Diluted. For Intravenous
Infusion Only
Sterile
10 mL Single-Dose Vial
Discard Unused Portion
Each mL contains: 50 mg cysteine hydrochloride
(equivalent to 34.5 mg of cysteine), and 0.006 mL
of hydrochloric acid (6M) in water for injection.
Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid are
used as needed to adjust the pH to 1.0 to 1.5.
Contains no more than 145 mcg/l of aluminum.
Storage: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to
77°F ), excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C
(59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
Recommended Dosage:
****See prescribing information.
Mfd. for Baxter Healthcare Corp
Rev 03/22
07-09-00-1048
For Position Box Only
LOT: XXXXXX
EXP: YYYY-MM-DD
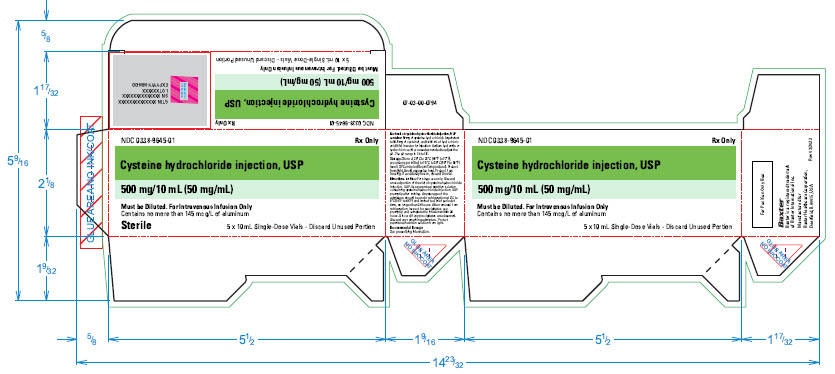
NDC 0338-9645-01
Rx Only
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL)
Must be Diluted. For Intravenous Infusion Only
5 x 10 mL Single-Dose Vials – Discard Unused Portion
Reserved for 2D barcode
GTIN XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
SN XXXXXXXXXXXXXX
LOT XXXXXX
EXP YYY-MD-DD
NDC 0338-9645-01
Rx Only
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL)
Must be Diluted. For Intravenous Infusion Only
****Contains no more than 145 mcg/L of aluminum
Sterile
5 x 10 mL Single-Dose Vials – Discard Unused Portion
07-03-00-0794
Each mL of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP
contains: 50mg of cysteine hydrochloride (equivalent
to 34.5 mg of cysteine), and 0.006 mL of hydrochloric
acid (6M) in water for injection. Sodium hydroxide or
hydrochloric acid are used as needed to adjust the
pH. The pH range is 1.0 to 1.5.
Storage: Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F ),
excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F )
[see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect
from light. Avoid excessive heat. Protect from
freezing. If accidently frozen, discard the vial.
Directions for Use: For single use only. Discard
unused portion of the vial of cysteine hydrochloride
injection, USP. Use parenteral nutrition solution
containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP
promptly after mixing. Any storage of the
admixture should be under refrigeration at 2°C to
8°C (36°F to 46°F) and limited to brief period of
time, no longer than 24 hours. After removal from
refrigeration, inspect for precipitates, use
promptly, and complete the infusion within 24
hours. Discard if any precipitates are observed.
Discard any remaining admixture. Protect
parenteral nutrition solution from light.
Recommended Dosage:
See prescribing information.
NDC 0338-9645-01
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL)
Must be Diluted. For Intravenous Infusion Only
****Contains no more than 145 mcg/L of aluminum
5 x 10 mL Single-Dose Vials- Discard Unused Portion
For Position Only Box
Baxter
Baxter is a registered trademark
of Baxter International Inc.
Manufactured for
Baxter Healthcare Corporation,
Deerfield, IL 60015, USA
Rev 03/2022
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is indicated for use as an additive to amino acids solutions to meet nutritional requirements of neonates (preterm and term infants less than one month of age) requiring total parenteral nutrition.
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is a sulfur-containing amino acid indicated for use as an additive to amino acids solutions to meet nutritional requirements of neonates (preterm and term infants less than one month of age) requiring total parenteral nutrition. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is contraindicated in:
•
Patients with known hypersensitivity to one or more amino acids.
•
Patients with inborn errors of amino acid metabolism due to risk of severe metabolic or neurologic complications.
•
Patients with pulmonary edema or acidosis due to low cardiac output.
•
Hypersensitivity to one or more amino acids (4)
•
Inborn errors of amino acid metabolism (4)
•
Pulmonary edema or acidosis due to low cardiac output (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the prescribing information:
•
Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Increased BUN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Acid-base imbalance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Hepatobiliary disorders [see Warning and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Adverse reactions with the use of cysteine hydrochloride injection were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
•
Metabolic acidosis
•
Local infusion site reactions, including a warm sensation, erythema, phlebitis, and thrombosis at the infusion site
•
Generalized flushing, fever, and nausea
Most common adverse reactions are local reactions (warm sensation, erythema, phlebitis, and thrombosis at the infusion site), generalized flushing, fever, nausea, and metabolic acidosis. (6)
**To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactBaxter Healthcare Corporation at 1-866-888-2472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or **www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) cysteine hydrochloride, USP as a clear, colorless, sterile solution in a single-dose vial.
Injection: 500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) cysteine hydrochloride, USP in a single- dose vial. (3)
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Information
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is for intravenous infusion after dilution and admixing use only. Prior to administration, cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP must be diluted and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions.
The resulting solution is for intravenous infusion into a central or peripheral vein. The choice of a central or peripheral venous route should depend on the osmolarity of the final infusate. Solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsm/L or greater must be infused through a central catheter [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Preparation and Administration Information
•
Prior to administration, cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP must be diluted and used as an admixture in parenteral nutrition solutions.
•
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is to be prepared only in a suitable work area such as a laminar flow hood (or an equivalent clean air compounding area). The key factor in the preparation is careful aseptic technique to avoid inadvertent touch contamination during mixing of solutions and addition of other nutrients.
•
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is for addition to amino acid solutions prior to further admixing with dextrose injection using a parenteral nutrition container.
•
Calcium and phosphate ratios must be considered. Excess addition of calcium and phosphate, especially in the form of mineral salts, may result in the formation of calcium phosphate precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
•
Use a dedicated line for parenteral nutrition solutions.
•
Intravenous lipid emulsions can be infused concurrently into the same vein as cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP-containing amino acid and dextrose solutions by a Y-connector located near the infusion site; flow rates of each solution should be controlled separately by infusion pumps.
•
For administration, use a 0.22 micron in-line filter.
•
To prevent air embolism, use a non-vented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set, avoid multiple connections, do not connect flexible containers in series, fully evacuate residual gas in the container prior to administration, do not pressurize the flexible container to increase flow rates, and if administration is controlled by a pumping device, turn off pump before the container runs dry.
•
Visually inspect the diluted parenteral nutrition solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP for particulate matter and discoloration before admixing, after admixing, after removal from refrigeration, and prior to administration. The solution should be clear and there should be no precipitates. A slight yellow color does not alter the quality and efficacy of this product.
2.3 Preparation Instructions for Admixing Using a Parenteral Nutrition
Container
•
Remove cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP vial from the carton and inspect for particulate matter.
•
Transfer the required amount of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP to an amino acid solution using strict aseptic techniques to avoid microbial contamination.
•
The amino acid solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP can then be used to prepare admixtures in the parenteral nutrition container using strict aseptic techniques.
•
Amino acids solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP may be mixed with dextrose injection. The following proper mixing sequence must be followed to minimize pH related problems:
1.
Transfer dextrose injection to the parental nutrition pooling container
2.
Transfer phosphate salt
3.
Transfer cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP-containing amino acid solution
4.
Transfer electrolytes
5.
Transfer trace elements
•
Use gentle agitation during admixing to minimize localized concentration effects; shake containers gently after each addition.
•
For automated compounding, refer to Instructions for Use of the applicable compounder.
•
Because additives may be incompatible, evaluate all additions to the parenteral nutrition container for compatibility and stability of the resulting preparation. Consult with pharmacist, if available. Questions about compatibility may be directed to Baxter Healthcare Corporation. If it is deemed advisable to introduce additives to the parenteral nutrition container, use aseptic technique.
•
Inspect the final parenteral nutrition solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP to ensure that precipitates have not formed during mixing or on addition of additives. Discard if any precipitates are observed.
Stability and Storage
•
For single use only. Discard unused portion of the vial of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP.
•
Use parenteral nutrition solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP promptly after mixing. Any storage of the admixture should be under refrigeration at 2ºC to 8ºC (36ºF to 46ºF) and limited to a brief period of time, no longer than 24 hours. After removal from refrigeration, inspect for precipitates, use promptly, and complete the infusion within 24 hours. Discard if any precipitates are observed.
•
Discard any remaining admixture.
•
Protect parenteral nutrition solution from light.
2.4 Dosing Considerations
The dosage of the final parenteral nutrition solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP must be based on the concentrations of all components in the solution and the recommended nutritional requirements [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. Consult the prescribing information of all added components to determine the recommended nutritional requirements.
The dosage of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP should be individualized based on the patient’s clinical condition (ability to adequately metabolize amino acids), body weight and nutritional/fluid requirements, as well as additional energy given orally/enterally to the patient. Prior to initiating parenteral nutrition, the following patient information should be reviewed: review of all medications, gastrointestinal function and laboratory data (such as electrolytes (including magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus), glucose, urea/creatinine, liver panel, and complete blood count.
Prior to administration of parenteral nutrition solution containing cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP, correct severe fluid, electrolyte and acid-base disorders.
2.5 Recommended Dosage for Neonates
The recommended dosage and volume of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is based upon the recommended daily protein (amino acid) requirements.
Table 1. Recommended Daily Dosage of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP in Neonates (Preterm and Term Infants Less Than One Month of Age)
| |||
|
Dosage |
Protein*** Requirement** |
Dosage |
Volume |
|
Neonates |
3 to 4 |
22 |
0.44 |
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP contains 50 mg/mL of cysteine hydrochloride (equivalent to 34.5 mg/mL of cysteine). Therefore, the recommended dosage of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP provides 15 mg cysteine/gram of amino acids for neonates.
•
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is for intravenous infusion after dilution and admixing only. (2.1)
•
See full prescribing information for information on preparation, administration, and instructions for use. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4)
•
The recommended dosage in neonates is based upon the recommended daily protein (amino acid) requirements: 22 mg cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP/g amino acids. The corresponding volume is 0.44 mL cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP/g amino acids. (2.5)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
In the event of over hydration or solute overload, re-evaluate the patient and institute appropriate corrective measures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.7)].
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP for use as an additive to amino acid solutions to meet nutritional requirements is not indicated for use in adults. Appropriate administration of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is not expected to cause major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with cysteine hydrochloride.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is used as an additive to amino acid solutions to meet nutritional requirements of neonates requiring total parenteral nutrition and is not indicated for use in adults. There are no data on the presence of cysteine hydrochloride in human or animal milk or the effects on milk production. Data available on the effects of cysteine hydrochloride on infants, either directly or through breastmilk, do not suggest a significant risk of adverse reactions from exposure.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is indicated for use as an additive to amino acid solutions to meet the nutritional requirements of neonates, including preterm infants, requiring total parenteral nutrition. The safety profile for cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP use in neonates includes risks of acid-base imbalance and hepatobiliary dysfunction.
Acid-base imbalance, including metabolic acidosis, and liver dysfunction may occur with cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP administration in preterm infants. Frequent clinical and laboratory assessments are necessary to monitor and manage fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, liver tests, and acid- base balance during parenteral nutrition therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hyperammonemia is of special significance in neonates. This reaction appears to be related to a deficiency of the urea cycle amino acids of genetic or product origin. It is essential that blood ammonia be measured during treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Because of immature renal function, neonates including preterm infants, receiving prolonged parenteral nutrition with cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP may be at higher risk of aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP (cysteine hydrochloride injection) is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution for intravenous use supplied as 500 mg/10 mL cysteine hydrochloride, USP in a single-dose vial.
Each mL of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP contains 50 mg of cysteine hydrochloride, (equivalent to 34.5 mg of cysteine), and 0.006 mL of hydrochloric acid (6M) in water for injection. Sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid are used as needed to adjust the pH. The pH range of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP is 1.0 to 1.5.
The active ingredient is cysteine hydrochloride. The chemical name of cysteine hydrochloride is L-cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate. Its molecular formula is C3H7NO2S • HCI • H2O and molecular weight is 175.63. The chemical structure of L-cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate is depicted below:
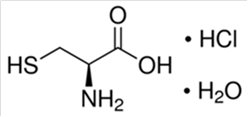
Cysteine hydrochloride is a white crystalline powder soluble in water. Cysteine is a sulfur-containing amino acid and is prone to oxidation when exposed to air in aqueous solution, which may convert cysteine to insoluble cystine resulting in precipitation over time.
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP contains no more than 145 mcg/L of aluminum.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Endogenous cysteine is synthesized from methionine by the enzyme, cystathionase, via the trans-sulfuration pathway, and serves as a precursor substrate for both glutathione and taurine. Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP provides cysteine to the systemic circulation of neonates who require parenteral nutrition and cannot synthesize adequate quantities of cysteine due to deficient cystathionase activity.
REFERENCES SECTION
15 REFERENCES
1. Ayers P. et al. A.S.P.E.N. Parenteral Nutrition Handbook, 2nd ed. 2014 pg. 123 and 124.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform caregivers or home healthcare providers of the following risks of cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP:
•
Pulmonary embolism due to pulmonary vascular precipitates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Vein damage and thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Increased BUN [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Acid-base imbalance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Hepatobiliary disorders [see Warning and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Aluminum toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Monitoring and laboratory tests [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Manufactured for:
Baxter Healthcare Corporation,
Deerfield, IL 60015, USA
Baxter is a registered trademark of Baxter International Inc.
Rev. 04/22
07-19-00-4043
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP (cysteine hydrochloride injection) is a clear, colorless, sterile and nonpyrogenic solution supplied as follows:
500 mg/10 mL (50 mg/mL) of cysteine hydrochloride, USP in single-dose vials
(NDC 0338-
9645-01), packaged as 5 vials per carton (NDC 0338-9645-01)
Store cysteine hydrochloride injection, USP at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F);
excursions
permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from light. Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing. If
accidentally frozen, discard
the vial.
Vial stoppers are not made with natural rubber latex.
For storage of admixed solution see Dosage and Administration (2.3)
