Fluticasone Propionate and Salmeterol
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS.Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder, for oral inhalation useInitial U.S. Approval: 2000
6eb6ddac-fa26-43b3-bf3e-5b7b58138fdc
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 19, 2023
Prasco Laboratories
DUNS: 065969375
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
fluticasone propionate and salmeterol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (3)
fluticasone propionate and salmeterol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (3)
fluticasone propionate and salmeterol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (3)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 66993-586-97
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS Inhalation Powder
500 mcg /50 mcg
PRASCO
Rx Only
FOR ORAL INHALATION ONLY
Each blister contains 500 mcg of fluticasone propionate and 72.5 mcg of salmeterol xinafoate, equivalent to 50 mcg of salmeterol base, with lactose.
1 DISKUS Inhalation Device
Containing 1 Foil Strip of 60 Blisters
62000000089843 Rev. 9/23

WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Asthma-Related Events – Hospitalizations, Intubations, Death
Use of LABA as monotherapy (without ICS) for asthma is associated with an increased risk of asthma-related death [see Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial (SMART)]. Available data from controlled clinical trials also suggest that use of LABA as monotherapy increases the risk of asthma-related hospitalization in pediatric and adolescent patients. These findings are considered a class effect of LABA monotherapy. When LABA are used in fixed- dose combination with ICS, data from large clinical trials do not show a significant increase in the risk of serious asthma‑related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death) compared with ICS alone (see Serious Asthma-Related Events with Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-acting Beta2-adrenergic Agonists).
Serious Asthma-Related Events with Inhaled Corticosteroid/Long-acting Beta2-adrenergic Agonists
Four (4) large, 26-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled clinical safety trials were conducted to evaluate the risk of serious asthma-related events when LABA were used in fixed-dose combination with ICS compared with ICS alone in subjects with asthma. Three (3) trials included adult and adolescent subjects aged 12 years and older: 1 trial compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol inhalation powder with fluticasone propionate inhalation powder [see Clinical Studies (14.1)], 1 trial compared mometasone furoate/formoterol with mometasone furoate, and 1 trial compared budesonide/formoterol with budesonide. The fourth trial included pediatric subjects aged 4 to 11 years and compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol inhalation powder with fluticasone propionate inhalation powder [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The primary safety endpoint for all 4 trials was serious asthma-related events (hospitalizations, intubations, death). A blinded adjudication committee determined whether events were asthma related.
The 3 adult and adolescent trials were designed to rule out a risk margin of 2.0, and the pediatric trial was designed to rule out a risk margin of 2.7. Each individual trial met its pre-specified objective and demonstrated non- inferiority of ICS/LABA to ICS alone. A meta-analysis of the 3 adult and adolescent trials did not show a significant increase in risk of a serious asthma-related event with ICS/LABA fixed-dose combination compared with ICS alone (Table 1). These trials were not designed to rule out all risk for serious asthma-related events with ICS/LABA compared with ICS.
Table 1. Meta-analysis of Serious Asthma-Related Events in Subjects with Asthma Aged 12 Years and Older|
ICS = Inhaled Corticosteroid, LABA = Long-acting Beta2-adrenergic Agonist. | |||
|
ICS/LABA **(n = 17,537)**a |
ICS **(n = 17,552)**a |
ICS/LABA vs. ICS Hazard Ratio **(95% CI)**b | |
|
Serious asthma-related eventc |
116 |
105 |
1.10 (0.85, 1.44) |
|
2 |
0 | |
|
1 |
2 | |
|
115 |
105 |
The pediatric safety trial included 6,208 pediatric subjects aged 4 to 11 years who received ICS/LABA (fluticasone propionate/salmeterol inhalation powder) or ICS (fluticasone propionate inhalation powder). In this trial, 27/3,107 (0.9%) subjects randomized to ICS/LABA and 21/3,101 (0.7%) subjects randomized to ICS experienced a serious asthma-related event. There were no asthma-related deaths or intubations. ICS/LABA did not show a significantly increased risk of a serious asthma-related event compared with ICS based on the pre-specified risk margin (2.7), with an estimated hazard ratio of time to first event of 1.29 (95% CI: 0.73, 2.27).
Salmeterol Multicenter Asthma Research Trial (SMART)
A 28-week, placebo-controlled, U.S. trial that compared the safety of salmeterol with placebo, each added to usual asthma therapy, showed an increase in asthma-related deaths in subjects receiving salmeterol (13/13,176 in subjects treated with salmeterol versus 3/13,179 in subjects treated with placebo; relative risk: 4.37 [95% CI: 1.25, 15.34]). Use of background ICS was not required in SMART. The increased risk of asthma-related death is considered a class effect of LABA monotherapy.
5.2 Deterioration of Disease and Acute Episodes
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should not be initiated in patients during rapidly deteriorating or potentially life-threatening episodes of asthma or COPD. Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS has not been studied in subjects with acutely deteriorating asthma or COPD. The initiation of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS in this setting is not appropriate.
Serious acute respiratory events, including fatalities, have been reported when salmeterol, a component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, has been initiated in patients with significantly worsening or acutely deteriorating asthma. In most cases, these have occurred in patients with severe asthma (e.g., patients with a history of corticosteroid dependence, low pulmonary function, intubation, mechanical ventilation, frequent hospitalizations, previous life‑threatening acute asthma exacerbations) and in some patients with acutely deteriorating asthma (e.g., patients with significantly increasing symptoms; increasing need for inhaled, short‑acting beta2-agonists; decreasing response to usual medications; increasing need for systemic corticosteroids; recent emergency room visits; deteriorating lung function). However, these events have occurred in a few patients with less severe asthma as well. It was not possible from these reports to determine whether salmeterol contributed to these events.
Increasing use of inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists is a marker of deteriorating asthma. In this situation, the patient requires immediate reevaluation with reassessment of the treatment regimen, giving special consideration to the possible need for replacing the current strength of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS with a higher strength, adding additional ICS, or initiating systemic corticosteroids. Patients should not use more than 1 inhalation twice daily of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS.
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should not be used for the relief of acute symptoms, i.e., as rescue therapy for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm. Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS has not been studied in the relief of acute symptoms and extra doses should not be used for that purpose. Acute symptoms should be treated with an inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonist.
When beginning treatment with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, patients who have been taking oral or inhaled, short-acting beta2-agonists on a regular basis (e.g., 4 times a day) should be instructed to discontinue the regular use of these drugs.
5.3 Excessive Use of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS and Use with
Other Long-acting Beta2-agonists
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should not be used more often than recommended, at higher doses than recommended, or in conjunction with other medicines containing LABA, as an overdose may result. Clinically significant cardiovascular effects and fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs. Patients using Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should not use another medicine containing a LABA (e.g., salmeterol, formoterol fumarate, arformoterol tartrate, indacaterol) for any reason.
5.4 Local Effects of Inhaled Corticosteroids
In clinical trials, the development of localized infections of the mouth and pharynx with Candida albicans has occurred in subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS. When such an infection develops, it should be treated with appropriate local or systemic (i.e., oral) antifungal therapy while treatment with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS continues, but at times therapy with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS may need to be interrupted. Advise the patient to rinse his/her mouth with water without swallowing following inhalation to help reduce the risk of oropharyngeal candidiasis.
5.5 Pneumonia
Physicians should remain vigilant for the possible development of pneumonia in patients with COPD as the clinical features of pneumonia and exacerbations frequently overlap.
Lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia, have been reported in patients with COPD following the inhaled administration of corticosteroids, including fluticasone propionate and fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS. In 2 replicate 1-year trials in 1,579 subjects with COPD, there was a higher incidence of pneumonia reported in subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg (7%) than in those receiving salmeterol 50 mcg (3%). The incidence of pneumonia in the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS was higher in subjects older than 65 years (9%) compared with the incidence in subjects younger than 65 years (4%). [See Adverse Reactions (6.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.5).]
In a 3-year trial in 6,184 subjects with COPD, there was a higher incidence of pneumonia reported in subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg compared with placebo (16% with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, 14% with fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, 11% with salmeterol 50 mcg, and 9% with placebo). Similar to what was seen in the 1-year trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg, the incidence of pneumonia was higher in subjects older than 65 years (18% with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg versus 10% with placebo) compared with subjects younger than 65 years (14% with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg versus 8% with placebo). [See Adverse Reactions (6.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.5).]
5.6 Immunosuppression
Persons who are using drugs that suppress the immune system are more susceptible to infections than healthy individuals. Chickenpox and measles, for example, can have a more serious or even fatal course in susceptible children or adults using corticosteroids. In such children or adults who have not had these diseases or been properly immunized, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure. How the dose, route, and duration of corticosteroid administration affect the risk of developing a disseminated infection is not known. The contribution of the underlying disease and/or prior corticosteroid treatment to the risk is also not known. If a patient is exposed to chickenpox, prophylaxis with varicella zoster immune globulin (VZIG) may be indicated. If a patient is exposed to measles, prophylaxis with pooled intramuscular immunoglobulin (IG) may be indicated. (See the respective package inserts for complete VZIG and IG prescribing information.) If chickenpox develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
ICS should be used with caution, if at all, in patients with active or quiescent tuberculosis infections of the respiratory tract; systemic fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; or ocular herpes simplex.
5.7 Transferring Patients from Systemic Corticosteroid Therapy
Particular care is needed for patients who have been transferred from systemically active corticosteroids to ICS because deaths due to adrenal insufficiency have occurred in patients with asthma during and after transfer from systemic corticosteroids to less systemically available ICS. After withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids, a number of months are required for recovery of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) function.
Patients who have been previously maintained on 20 mg or more of prednisone (or its equivalent) may be most susceptible, particularly when their systemic corticosteroids have been almost completely withdrawn. During this period of HPA suppression, patients may exhibit signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency when exposed to trauma, surgery, or infection (particularly gastroenteritis) or other conditions associated with severe electrolyte loss. Although Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS may control asthma symptoms during these episodes, in recommended doses it supplies less than normal physiological amounts of glucocorticoid systemically and does NOT provide the mineralocorticoid activity that is necessary for coping with these emergencies.
During periods of stress or a severe asthma attack, patients who have been withdrawn from systemic corticosteroids should be instructed to resume oral corticosteroids (in large doses) immediately and to contact their physicians for further instruction. These patients should also be instructed to carry a warning card indicating that they may need supplementary systemic corticosteroids during periods of stress or a severe asthma attack.
Patients requiring oral corticosteroids should be weaned slowly from systemic corticosteroid use after transferring to Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. Prednisone reduction can be accomplished by reducing the daily prednisone dose by 2.5 mg on a weekly basis during therapy with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. Lung function (mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1] or morning peak expiratory flow [AM PEF]), beta-agonist use, and asthma symptoms should be carefully monitored during withdrawal of oral corticosteroids. In addition, patients should be observed for signs and symptoms of adrenal insufficiency, such as fatigue, lassitude, weakness, nausea and vomiting, and hypotension.
Transfer of patients from systemic corticosteroid therapy to Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS may unmask allergic conditions previously suppressed by the systemic corticosteroid therapy (e.g., rhinitis, conjunctivitis, eczema, arthritis, eosinophilic conditions).
During withdrawal from oral corticosteroids, some patients may experience symptoms of systemically active corticosteroid withdrawal (e.g., joint and/or muscular pain, lassitude, depression) despite maintenance or even improvement of respiratory function.
5.8 Hypercorticism and Adrenal Suppression
Fluticasone propionate, a component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, will often help control asthma symptoms with less suppression of HPA function than therapeutically equivalent oral doses of prednisone. Since fluticasone propionate is absorbed into the circulation and can be systemically active at higher doses, the beneficial effects of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS in minimizing HPA dysfunction may be expected only when recommended dosages are not exceeded and individual patients are titrated to the lowest effective dose. A relationship between plasma levels of fluticasone propionate and inhibitory effects on stimulated cortisol production has been shown after 4 weeks of treatment with fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol. Since individual sensitivity to effects on cortisol production exists, physicians should consider this information when prescribing Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS.
Because of the possibility of significant systemic absorption of ICS in sensitive patients, patients treated with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should be observed carefully for any evidence of systemic corticosteroid effects. Particular care should be taken in observing patients postoperatively or during periods of stress for evidence of inadequate adrenal response.
It is possible that systemic corticosteroid effects such as hypercorticism and adrenal suppression (including adrenal crisis) may appear in a small number of patients who are sensitive to these effects. If such effects occur, Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should be reduced slowly, consistent with accepted procedures for reducing systemic corticosteroids, and other treatments for management of asthma symptoms should be considered.
5.9 Drug Interactions with Strong Cytochrome P450 3A4 Inhibitors
The use of strong cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) inhibitors (e.g., ritonavir, atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, saquinavir, ketoconazole, telithromycin) with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS is not recommended because increased systemic corticosteroid and increased cardiovascular adverse effects may occur [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.10 Paradoxical Bronchospasm and Upper Airway Symptoms
As with other inhaled medicines, Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS can produce paradoxical bronchospasm, which may be life threatening. If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs following dosing with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, it should be treated immediately with an inhaled, short-acting bronchodilator; Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS should be discontinued immediately; and alternative therapy should be instituted. Upper airway symptoms of laryngeal spasm, irritation, or swelling, such as stridor and choking, have been reported in patients receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS.
5.11 Immediate Hypersensitivity Reactions
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., urticaria, angioedema, rash, bronchospasm, hypotension), including anaphylaxis, may occur after administration of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. There have been reports of anaphylactic reactions in patients with severe milk protein allergy after inhalation of powder products containing lactose; therefore, patients with severe milk protein allergy should not use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS [see Contraindications (4)].
5.12 Cardiovascular and Central Nervous System Effects
Excessive beta-adrenergic stimulation has been associated with seizures, angina, hypertension or hypotension, tachycardia with rates up to 200 beats/min, arrhythmias, nervousness, headache, tremor, palpitation, nausea, dizziness, fatigue, malaise, and insomnia [see Overdosage (10.2)]. Therefore, Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, like all products containing sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with cardiovascular disorders, especially coronary insufficiency, cardiac arrhythmias, and hypertension.
Salmeterol, a component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, can produce a clinically significant cardiovascular effect in some patients as measured by pulse rate, blood pressure, and/or symptoms. Although such effects are uncommon after administration of salmeterol at recommended doses, if they occur, the drug may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta-agonists have been reported to produce electrocardiogram (ECG) changes, such as flattening of the T wave, prolongation of the QTc interval, and ST segment depression. The clinical significance of these findings is unknown. Large doses of inhaled or oral salmeterol (12 to 20 times the recommended dose) have been associated with clinically significant prolongation of the QTc interval, which has the potential for producing ventricular arrhythmias. Fatalities have been reported in association with excessive use of inhaled sympathomimetic drugs.
5.13 Reduction in Bone Mineral Density
Decreases in bone mineral density (BMD) have been observed with long-term administration of products containing ICS. The clinical significance of small changes in BMD with regard to long-term consequences such as fracture is unknown. Patients with major risk factors for decreased bone mineral content, such as prolonged immobilization, family history of osteoporosis, postmenopausal status, tobacco use, advanced age, poor nutrition, or chronic use of drugs that can reduce bone mass (e.g., anticonvulsants, oral corticosteroids), should be monitored and treated with established standards of care. Since patients with COPD often have multiple risk factors for reduced BMD, assessment of BMD is recommended prior to initiating Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS and periodically thereafter. If significant reductions in BMD are seen and Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS is still considered medically important for that patient’s COPD therapy, use of medicine to treat or prevent osteoporosis should be strongly considered.
2-Year Fluticasone Propionate Trial
A 2-year trial in 160 subjects (females aged 18 to 40 years, males 18 to 50) with asthma receiving chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)-propelled fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol 88 or 440 mcg twice daily demonstrated no statistically significant changes in BMD at any time point (24, 52, 76, and 104 weeks of double-blind treatment) as assessed by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry at lumbar regions L1 through L4.
3-Year Bone Mineral Density Trial
Effects of treatment with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg or salmeterol 50 mcg on BMD at the L1-L4 lumbar spine and total hip were evaluated in 186 subjects with COPD (aged 43 to 87 years) in a 3-year double- blind trial. Of those enrolled, 108 subjects (72 males and 36 females) were followed for the entire 3 years. BMD evaluations were conducted at baseline and at 6-month intervals. Conclusions cannot be drawn from this trial regarding BMD decline in subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS versus salmeterol due to the inconsistency of treatment differences across gender and between lumbar spine and total hip.
In this trial there were 7 non-traumatic fractures reported in 5 subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS and 1 non-traumatic fracture in 1 subject treated with salmeterol. None of the non-traumatic fractures occurred in the vertebrae, hip, or long bones.
3-Year Survival Trial
Effects of treatment with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, salmeterol 50 mcg, or placebo on BMD was evaluated in a subset of 658 subjects (females and males aged 40 to 80 years) with COPD in the 3-year survival trial. BMD evaluations were conducted at baseline and at 48, 108, and 158 weeks. Conclusions cannot be drawn from this trial because of the large number of dropouts (>50%) before the end of the follow-up and the maldistribution of covariates among the treatment groups that can affect BMD.
Fracture risk was estimated for the entire population of subjects with COPD in the survival trial (N = 6,184). The probability of a fracture over 3 years was 6.3% for fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS, 5.4% for fluticasone propionate, 5.1% for salmeterol, and 5.1% for placebo.
5.14 Effect on Growth
Orally inhaled corticosteroids may cause a reduction in growth velocity when administered to pediatric patients. Monitor the growth of pediatric patients receiving Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS routinely (e.g., via stadiometry). To minimize the systemic effects of orally inhaled corticosteroids, including Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, titrate each patient’s dosage to the lowest dosage that effectively controls his/her symptoms [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
5.15 Glaucoma and Cataracts
Glaucoma, increased intraocular pressure, and cataracts have been reported in patients with asthma and COPD following the long-term administration of ICS, including fluticasone propionate, a component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. Consider referral to an ophthalmologist in patients who develop ocular symptoms or use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS long term.
Effects of treatment with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, salmeterol 50 mcg, or placebo on development of cataracts or glaucoma was evaluated in a subset of 658 subjects with COPD in the 3-year survival trial. Ophthalmic examinations were conducted at baseline and at 48, 108, and 158 weeks. Conclusions about cataracts cannot be drawn from this trial because the high incidence of cataracts at baseline (61% to 71%) resulted in an inadequate number of subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, who were eligible and available for evaluation of cataracts at the end of the trial (n = 53). The incidence of newly diagnosed glaucoma was 2% with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, 5% with fluticasone propionate, 0% with salmeterol, and 2% with placebo.
5.16 Eosinophilic Conditions and Churg-Strauss Syndrome
In rare cases, patients on inhaled fluticasone propionate, a component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, may present with systemic eosinophilic conditions. Some of these patients have clinical features of vasculitis consistent with Churg-Strauss syndrome, a condition that is often treated with systemic corticosteroid therapy. These events usually, but not always, have been associated with the reduction and/or withdrawal of oral corticosteroid therapy following the introduction of fluticasone propionate. Cases of serious eosinophilic conditions have also been reported with other ICS in this clinical setting. Physicians should be alert to eosinophilia, vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients. A causal relationship between fluticasone propionate and these underlying conditions has not been established.
5.17 Coexisting Conditions
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, like all medicines containing sympathomimetic amines, should be used with caution in patients with convulsive disorders or thyrotoxicosis and in those who are unusually responsive to sympathomimetic amines. Doses of the related beta2-adrenoceptor agonist albuterol, when administered intravenously, have been reported to aggravate preexisting diabetes mellitus and ketoacidosis.
5.18 Hypokalemia and Hyperglycemia
Beta-adrenergic agonist medicines may produce significant hypokalemia in some patients, possibly through intracellular shunting, which has the potential to produce adverse cardiovascular effects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The decrease in serum potassium is usually transient, not requiring supplementation. Clinically significant changes in blood glucose and/or serum potassium were seen infrequently during clinical trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS at recommended doses.
•
LABA monotherapy increases the risk of serious asthma-related events. (5.1)
•
Do not initiate in acutely deteriorating asthma or COPD. Do not use to treat acute symptoms. (5.2)
•
Do not use in combination with an additional medicine containing a LABA because of risk of overdose. (5.3)
•
Candida albicans infection of the mouth and pharynx may occur. Monitor patients periodically. Advise the patient to rinse his/her mouth with water without swallowing after inhalation to help reduce the risk. (5.4)
•
Increased risk of pneumonia in patients with COPD. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of pneumonia. (5.5)
•
Potential worsening of infections (e.g., existing tuberculosis; fungal, bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections; ocular herpes simplex). Use with caution in patients with these infections. More serious or even fatal course of chickenpox or measles can occur in susceptible patients. (5.6)
•
Risk of impaired adrenal function when transferring from systemic corticosteroids. Taper patients slowly from systemic corticosteroids if transferring to Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. (5.7)
•
Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression may occur with very high dosages or at the regular dosage in susceptible individuals. If such changes occur, discontinue Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS slowly. (5.8)
•
If paradoxical bronchospasm occurs, discontinue Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS and institute alternative therapy. (5.10)
•
Use with caution in patients with cardiovascular or central nervous system disorders because of beta-adrenergic stimulation. (5.12)
•
Assess for decrease in bone mineral density initially and periodically thereafter. (5.13)
•
Monitor growth of pediatric patients. (5.14)
•
Glaucoma and cataracts may occur with long-term use of inhaled corticosteroids. Consider referral to an ophthalmologist in patients who develop ocular symptoms or use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS long term. (5.15)
•
Be alert to eosinophilic conditions, hypokalemia, and hyperglycemia. (5.16, 5.18)
•
Use with caution in patients with convulsive disorders, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus, and ketoacidosis. (5.17)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Use of LABA may result in the following:
•
Serious asthma-related events – hospitalizations, intubations, death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Cardiovascular and central nervous system effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
Systemic and local corticosteroid use may result in the following:
•
Candida albicans infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
•
Pneumonia in patients with COPD [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Immunosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Hypercorticism and adrenal suppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
•
Reduction in bone mineral density [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
•
Growth effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
•
Glaucoma and cataracts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience in Asthma
Adult and Adolescent Subjects Aged 12 Years and Older
The incidence of adverse reactions associated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS in Table 2 is based upon two 12-week, placebo- controlled, U.S. clinical trials (Trials 1 and 2). A total of 705 adult and adolescent subjects (349 females and 356 males) previously treated with salmeterol or ICS were treated twice daily with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS (100/50- or 250/50-mcg doses), fluticasone propionate inhalation powder (100- or 250-mcg doses), salmeterol inhalation powder 50 mcg, or placebo. The average duration of exposure was 60 to 79 days in the active treatment groups compared with 42 days in the placebo group.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS with ≥3% Incidence and More Common than Placebo in Adult and Adolescent Subjects with Asthma|
Adverse Event |
Fluticasone Propionate/ 100/50 mcg (n = 92) % |
Fluticasone Propionate/ 250/50 mcg (n = 84) % |
Fluticasone Propionate 100 mcg (n = 90) % |
Fluticasone Propionate 250 mcg (n = 84) % |
Salmeterol 50 mcg (n = 180) % |
Placebo (n = 175) % |
|
Ear, nose, and throat | ||||||
|
27 |
21 |
29 |
25 |
19 |
14 |
|
13 |
10 |
7 |
12 |
8 |
6 |
|
7 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
8 |
5 |
|
4 |
5 |
6 |
1 |
3 |
4 |
|
5 |
2 |
2 |
4 |
<1 |
<1 |
|
1 |
4 |
2 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Lower respiratory | ||||||
|
4 |
4 |
4 |
10 |
6 |
3 |
|
2 |
8 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
3 |
6 |
0 |
0 |
3 |
2 |
|
Neurology | ||||||
|
12 |
13 |
14 |
8 |
10 |
7 |
|
Gastrointestinal | ||||||
|
4 |
6 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
|
4 |
1 |
0 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
4 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
1 |
1 |
|
3 |
0 |
3 |
1 |
2 |
2 |
|
Non-site specific | ||||||
|
3 |
0 |
1 |
4 |
0 |
1 |
|
Musculoskeletal | ||||||
|
4 |
2 |
1 |
5 |
3 |
3 |
The types of adverse reactions and events reported in Trial 3, a 28-week, non-U.S. clinical trial in 503 subjects previously treated with ICS who were treated twice daily with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 500 mcg and salmeterol inhalation powder 50 mcg used concurrently, or fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 500 mcg, were similar to those reported in Table 2.
Additional Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions not previously listed, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, that were reported more frequently by subjects with asthma treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS compared with subjects treated with placebo include the following: lymphatic signs and symptoms; muscle injuries; fractures; wounds and lacerations; contusions and hematomas; ear signs and symptoms; nasal signs and symptoms; nasal sinus disorders; keratitis and conjunctivitis; dental discomfort and pain; gastrointestinal signs and symptoms; oral ulcerations; oral discomfort and pain; lower respiratory signs and symptoms; pneumonia; muscle stiffness, tightness, and rigidity; bone and cartilage disorders; sleep disorders; compressed nerve syndromes; viral infections; pain; chest symptoms; fluid retention; bacterial infections; unusual taste; viral skin infections; skin flakiness and acquired ichthyosis; disorders of sweat and sebum.
Pediatric Subjects Aged 4 to 11 Years
The safety data for pediatric subjects aged 4 to 11 years is based upon 1 U.S. trial of 12 weeks’ treatment duration. A total of 203 subjects (74 females and 129 males) who were receiving ICS at trial entry were randomized to either fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg or fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 100 mcg twice daily. Common adverse reactions (≥3% and greater than placebo) seen in the pediatric subjects but not reported in the adult and adolescent clinical trials include: throat irritation and ear, nose, and throat infections.
Laboratory Test Abnormalities
Elevation of hepatic enzymes was reported in ≥1% of subjects in clinical trials. The elevations were transient and did not lead to discontinuation from the trials. In addition, there were no clinically relevant changes noted in glucose or potassium.
6.2 Clinical Trials Experience in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Short-term (6 Months to 1 Year) Trials
The short-term safety data are based on exposure to fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg twice daily in one 6-month and two 1-year clinical trials. In the 6-month trial, a total of 723 adult subjects (266 females and 457 males) were treated twice daily with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg, fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 250 mcg, salmeterol inhalation powder, or placebo. The mean age of the subjects was 64, and the majority (93%) was Caucasian. In this trial, 70% of the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS reported an adverse reaction compared with 64% on placebo. The average duration of exposure to fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg was 141.3 days compared with 131.6 days for placebo. The incidence of adverse reactions in the 6-month trial is shown in Table 3.
Table 3. Overall Adverse Reactions with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg with ≥3% Incidence in Subjects with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Associated with Chronic Bronchitis|
Adverse Event |
Fluticasone Propionate/ (n = 178) % |
Fluticasone Propionate (n = 183) % |
Salmeterol (n = 177) % |
Placebo (n = 185) % |
|
Ear, nose, and throat | ||||
|
10 |
6 |
3 |
1 |
|
8 |
5 |
4 |
7 |
|
5 |
3 |
<1 |
0 |
|
3 |
8 |
5 |
3 |
|
Lower respiratory | ||||
|
6 |
4 |
3 |
3 |
|
Neurology | ||||
|
16 |
11 |
10 |
12 |
|
4 |
<1 |
3 |
2 |
|
Non-site specific | ||||
|
4 |
3 |
0 |
3 |
|
3 |
2 |
2 |
3 |
|
Musculoskeletal | ||||
|
9 |
8 |
12 |
9 |
|
3 |
3 |
1 |
1 |
In the two 1-year trials, fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg was compared with salmeterol in 1,579 subjects (863 males and 716 females). The mean age of the subjects was 65 years, and the majority (94%) was Caucasian. To be enrolled, all of the subjects had to have had a COPD exacerbation in the previous 12 months. In this trial, 88% of the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS and 86% of the subjects treated with salmeterol reported an adverse event. The most common events that occurred with a frequency of >5% and more frequently in the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, nasal congestion, back pain, sinusitis, dizziness, nausea, pneumonia, candidiasis, and dysphonia. Overall, 55 (7%) of the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS and 25 (3%) of the subjects treated with salmeterol developed pneumonia.
The incidence of pneumonia was higher in subjects older than 65 years, 9% in the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS compared with 4% in the subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS younger than 65 years. In the subjects treated with salmeterol, the incidence of pneumonia was the same (3%) in both age groups. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.5).]
Long-term (3 Years) Trial
The safety of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg was evaluated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter, international, 3-year trial in 6,184 adult subjects with COPD (4,684 males and 1,500 females). The mean age of the subjects was 65 years, and the majority (82%) was Caucasian. The distribution of adverse events was similar to that seen in the 1-year trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg. In addition, pneumonia was reported in a significantly increased number of subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg and fluticasone propionate 500 mcg (16% and 14%, respectively) compared with subjects treated with salmeterol 50 mcg or placebo (11% and 9%, respectively). When adjusted for time on treatment, the rates of pneumonia were 84 and 88 events per 1,000 treatment-years in the groups treated with fluticasone propionate 500 mcg and with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, respectively, compared with 52 events per 1,000 treatment-years in the salmeterol and placebo groups. Similar to what was seen in the 1-year trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg, the incidence of pneumonia was higher in subjects older than 65 years (18% with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg versus 10% with placebo) compared with subjects younger than 65 years (14% with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg versus 8% with placebo). [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.5).]
Additional Adverse Reactions
Other adverse reactions not previously listed, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, that were reported more frequently by subjects with COPD treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS compared with subjects treated with placebo include the following: syncope; ear, nose, and throat infections; ear signs and symptoms; laryngitis; nasal congestion/blockage; nasal sinus disorders; pharyngitis/throat infection; hypothyroidism; dry eyes; eye infections; gastrointestinal signs and symptoms; oral lesions; abnormal liver function tests; bacterial infections; edema and swelling; viral infections.
Laboratory Abnormalities
There were no clinically relevant changes in these trials. Specifically, no increased reporting of neutrophilia or changes in glucose or potassium was noted.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse reactions reported from clinical trials, the following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of any formulation of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol, fluticasone propionate, and/or salmeterol regardless of indication. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or causal connection to fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS, fluticasone propionate, and/or salmeterol or a combination of these factors.
Cardiac Disorders
Arrhythmias (including atrial fibrillation, extrasystoles, supraventricular tachycardia), ventricular tachycardia.
Endocrine Disorders
Cushing’s syndrome, Cushingoid features, growth velocity reduction in children/adolescents, hypercorticism.
Eye Disorders
Glaucoma.
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Abdominal pain, dyspepsia, xerostomia.
Immune System Disorders
Immediate and delayed hypersensitivity reaction (including very rare anaphylactic reaction). Very rare anaphylactic reaction in patients with severe milk protein allergy.
Infections and Infestations
Esophageal candidiasis.
Metabolic and Nutrition Disorders
Hyperglycemia, weight gain.
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue, and Bone Disorders
Arthralgia, cramps, myositis, osteoporosis.
Nervous System Disorders
Paresthesia, restlessness.
Psychiatric Disorders
Agitation, aggression, depression. Behavioral changes, including hyperactivity and irritability, have been reported very rarely and primarily in children.
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders
Dysmenorrhea.
Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders
Chest congestion; chest tightness; dyspnea; facial and oropharyngeal edema, immediate bronchospasm; paradoxical bronchospasm; tracheitis; wheezing; reports of upper respiratory symptoms of laryngeal spasm, irritation, or swelling such as stridor or choking.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Ecchymoses, photodermatitis.
Vascular Disorders
Pallor.
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥3%) include:
•
Asthma: Upper respiratory tract infection or inflammation, pharyngitis, dysphonia, oral candidiasis, bronchitis, cough, headaches, nausea and vomiting. (6.1)
•
COPD: Pneumonia, oral candidiasis, throat irritation, dysphonia, viral respiratory infections, headaches, musculoskeletal pain. (6.2)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Prasco Laboratories at 1-866-525-0688 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or [www.fda.gov/medwatch](https://www.fda.gov/safety/medwatch-fda-safety- information-and-adverse-event-reporting-program).
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder 100/50 mcg, Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder 250/50 mcg, and Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder 500/50 mcg are combinations of fluticasone propionate and salmeterol xinafoate.
One active component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS is fluticasone propionate, a corticosteroid having the chemical name S-(fluoromethyl) 6α,9-difluoro-11β,17-dihydroxy-16α-methyl-3-oxoandrosta-1,4-diene-17β-carbothioate, 17-propionate and the following chemical structure:

Fluticasone propionate is a white powder with a molecular weight of 500.6, and the empirical formula is C25H31F3O5S. It is practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide and dimethylformamide, and slightly soluble in methanol and 95% ethanol.
The other active component of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS is salmeterol xinafoate, a beta2-adrenergic bronchodilator. Salmeterol xinafoate is the racemic form of the 1-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid salt of salmeterol. It has the chemical name 4-hydroxy-α1-[[[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino]methyl]-1,3-benzenedimethanol, 1-hydroxy-2-naphthalenecarboxylate and the following chemical structure:

Salmeterol xinafoate is a white powder with a molecular weight of 603.8, and the empirical formula is C25H37NO4•C11H8O3. It is freely soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in ethanol, chloroform, and isopropanol; and sparingly soluble in water.
Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS is a purple plastic inhaler containing a foil blister strip. Each blister on the strip contains a white powder mix of micronized fluticasone propionate (100, 250, or 500 mcg) and micronized salmeterol xinafoate salt (72.5 mcg, equivalent to 50 mcg of salmeterol base) in 12.5 mg of formulation containing lactose monohydrate (which contains milk proteins). After the inhaler is activated, the powder is dispersed into the airstream created by the patient inhaling through the mouthpiece.
Under standardized in vitro test conditions, Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS delivers 93, 233, and 465 mcg of fluticasone propionate and 45 mcg of salmeterol base per blister from Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder 100/50 mcg, Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder 250/50 mcg, and Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder 500/50 mcg, respectively, when tested at a flow rate of 60 L/min for 2 seconds.
In adult subjects with obstructive lung disease and severely compromised lung function (mean FEV1 20% to 30% of predicted), mean peak inspiratory flow (PIF) through the DISKUS inhaler was 82.4 L/min (range: 46.1 to 115.3 L/min).
Inhalation profiles for adolescent (N = 13, aged 12 to 17 years) and adult (N = 17, aged 18 to 50 years) subjects with asthma inhaling maximally through the DISKUS inhaler show mean PIF of 122.2 L/min (range: 81.6 to 152.1 L/min). Inhalation profiles for pediatric subjects with asthma inhaling maximally through the DISKUS inhaler show a mean PIF of 75.5 L/min (range: 49.0 to 104.8 L/min) for the 4-year-old subject set (N = 20) and 107.3 L/min (range: 82.8 to 125.6 L/min) for the 8-year-old subject set (N = 20).
The actual amount of drug delivered to the lung will depend on patient factors, such as inspiratory flow profile.
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
PATIENT INFORMATION Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder for oral inhalation use | |
|
What is Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS? • o o • • • o o o | |
|
Do not use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS: • • • • | |
|
Before using Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS and certain other medicines may interact with each other. This may cause serious side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take antifungal or anti-HIV medicines. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | |
|
How should I use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS? Read the step-by-step instructions for using Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS at the end of this Patient Information. • • • • • • • • • • • • o o o o o o o | |
|
What are the possible side effects of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS? Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS can cause serious side effects, including: • • | |
|
• • • |
• • • |
|
• • Symptoms of adrenal insufficiency include: | |
|
• • • |
• • |
|
• • | |
|
• • |
• • |
|
• | |
|
• • |
• |
|
• | |
|
• |
• |
|
• • • • Common side effects of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS include: Asthma: | |
|
• • • • |
• • • • |
|
In children with asthma, infections in the ear, nose, and throat are common. COPD: | |
|
• • • |
• • • |
|
These are not all the possible side effects of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |
|
How should I store Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS? • • • Keep Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |
|
General information about the safe and effective use of Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS that was written for health professionals. | |
|
What are the ingredients in Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS? Active ingredients: fluticasone propionate, salmeterol xinafoate Inactive ingredient: lactose monohydrate (contains milk proteins) For more information about Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS, call 1-866-525-0688. Trademarks are owned by or licensed to the GSK group of companies. Manufactured for: Prasco Laboratories Mason, OH 45040 USA Manufactured by: GlaxoSmithKline Durham, NC 27701 ©2023 GSK group of companies or its licensor. ADD-PS:7PIL | |
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: July 2023 |
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
|
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhalation powder for oral inhalation use | |
|
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment. Your Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhaler
Important information about your Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhaler: • • • • • How to use your Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS inhaler Follow these steps every time you use Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. Step 1. Open your Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS. • Step 2. Slide the lever until you hear it click. • | |
|
|
Figure C |
|
• Follow the instructions below so you will not accidentally waste a dose: • • • Step 3. Inhale your medicine. • • | |
|
Figure D |
Figure E |
|
• • • Step 4. Close the DISKUS. •
Figure F • | |
|
Step 5. Rinse your mouth. •
The counter on top of the DISKUS shows you how many doses are left. After you have taken55 doses, the numbers5 to0 will show in red.** See Figure H.**These numbers warn you there are only a few doses left and are a reminder to get a refill.
• • • • • • • • • |
|
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: July 2023 |
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Asthma
Adult and Adolescent Subjects Aged 12 Years and Older
In clinical trials comparing fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS with its individual components, improvements in most efficacy endpoints were greater with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS than with the use of either fluticasone propionate or salmeterol alone. In addition, clinical trials showed similar results between fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS and the concurrent use of fluticasone propionate plus salmeterol at corresponding doses from separate inhalers.
Trials Comparing Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS with Fluticasone Propionate Alone or Salmeterol Alone: Three (3) double-blind, parallel-group clinical trials were conducted with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS in 1,208 adult and adolescent subjects (aged 12 years and older, baseline FEV1 63% to 72% of predicted normal) with asthma that was not optimally controlled on their current therapy. All treatments were inhalation powders given as 1 inhalation from the DISKUS inhaler twice daily, and other maintenance therapies were discontinued.
Trial 1: Clinical Trial with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg: This placebo-controlled, 12-week, U.S. trial compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg with its individual components, fluticasone propionate 100 mcg and salmeterol 50 mcg. The trial was stratified according to baseline asthma maintenance therapy; subjects were using either ICS (n = 250) (daily doses of beclomethasone dipropionate 252 to 420 mcg; flunisolide 1,000 mcg; fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol 176 mcg; or triamcinolone acetonide 600 to 1,000 mcg) or salmeterol (n = 106). Baseline FEV1 measurements were similar across treatments: fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg, 2.17 L; fluticasone propionate 100 mcg, 2.11 L; salmeterol, 2.13 L; and placebo, 2.15 L.
Predefined withdrawal criteria for lack of efficacy, an indicator of worsening asthma, were utilized for this placebo-controlled trial. Worsening asthma was defined as a clinically important decrease in FEV1 or PEF, increase in use of VENTOLIN (albuterol, USP) Inhalation Aerosol, increase in night awakenings due to asthma, emergency intervention or hospitalization due to asthma, or requirement for asthma medication not allowed by the protocol. As shown in Table 4, statistically significantly fewer subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg were withdrawn due to worsening asthma compared with fluticasone propionate, salmeterol, and placebo.
Table 4. Percent of Subjects Withdrawn due to Worsening Asthma in Subjects Previously Treated with Either Inhaled Corticosteroids or Salmeterol (Trial 1)|
Fluticasone Propionate/ Salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg (n = 87) |
Fluticasone Propionate 100 mcg (n = 85) |
Salmeterol 50 mcg (n = 86) |
Placebo (n = 77) |
|
3% |
11% |
35% |
49% |
The FEV1 results are displayed in Figure 1. Because this trial used predetermined criteria for worsening asthma, which caused more subjects in the placebo group to be withdrawn, FEV1 results at Endpoint (last available FEV1 result) are also provided. Subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg had significantly greater improvements in FEV1 (0.51 L, 25%) compared with fluticasone propionate 100 mcg (0.28 L, 15%), salmeterol (0.11 L, 5%), and placebo (0.01 L, 1%). These improvements in FEV1 with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS were achieved regardless of baseline asthma maintenance therapy (ICS or salmeterol).
Figure 1. Mean Percent Change from Baseline in FEV1 in Subjects with Asthma Previously Treated with Either Inhaled Corticosteroids or Salmeterol (Trial 1)
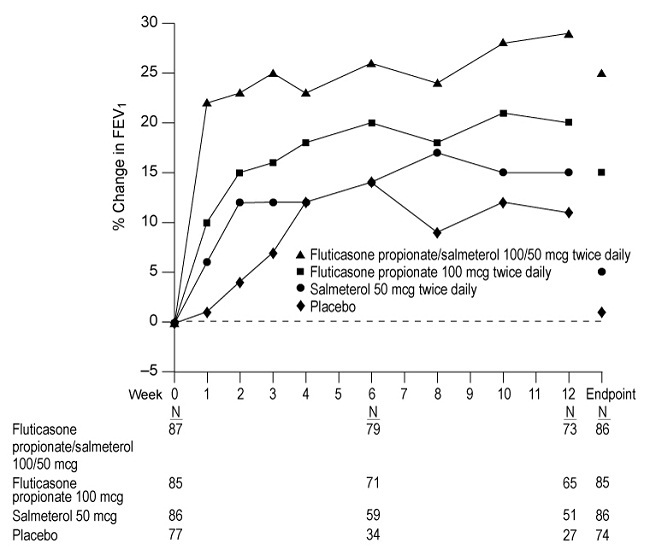
The effect of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg on morning and evening PEF endpoints is shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Peak Expiratory Flow Results for Subjects with Asthma Previously Treated with Either Inhaled Corticosteroids or Salmeterol (Trial 1)|
AM PEF = morning peak expiratory flow, PM PEF = evening peak expiratory flow. | ||||
|
a Change from baseline = change from baseline at Endpoint (last available data). | ||||
|
Efficacy Variable****a |
Fluticasone Propionate/ 100/50 mcg (n = 87) |
Fluticasone Propionate 100 mcg (n = 85) |
Salmeterol 50 mcg (n = 86) |
Placebo (n = 77) |
|
AM PEF (L/min) | ||||
|
393 |
374 |
369 |
382 |
|
53 |
17 |
-2 |
-24 |
|
PM PEF (L/min) | ||||
|
418 |
390 |
396 |
398 |
|
35 |
18 |
-7 |
-13 |
The subjective impact of asthma on subjects’ perception of health was evaluated through use of an instrument called the Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ) (based on a 7-point scale where 1 = maximum impairment and 7 = none). Subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg had clinically meaningful improvements in overall asthma-specific quality of life as defined by a difference between groups of ≥0.5 points in change from baseline AQLQ scores (difference in AQLQ score of 1.25 compared with placebo).
Trial 2: Clinical Trial with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg: This placebo-controlled, 12-week, U.S. trial compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg with its individual components, fluticasone propionate 250 mcg and salmeterol 50 mcg, in 349 subjects with asthma using ICS (daily doses of beclomethasone dipropionate 462 to 672 mcg; flunisolide 1,250 to 2,000 mcg; fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol 440 mcg; or triamcinolone acetonide 1,100 to 1,600 mcg). Baseline FEV1 measurements were similar across treatments: fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg, 2.23 L; fluticasone propionate 250 mcg, 2.12 L; salmeterol, 2.20 L; and placebo, 2.19 L.
Efficacy results in this trial were similar to those observed in Trial 1. Subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg had significantly greater improvements in FEV1 (0.48 L, 23%) compared with fluticasone propionate 250 mcg (0.25 L, 13%), salmeterol (0.05 L, 4%), and placebo (decrease of 0.11 L, decrease of 5%). Statistically significantly fewer subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg were withdrawn from this trial for worsening asthma (4%) compared with fluticasone propionate (22%), salmeterol (38%), and placebo (62%). In addition, fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg was superior to fluticasone propionate, salmeterol, and placebo for improvements in morning and evening PEF. Subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg also had clinically meaningful improvements in overall asthma- specific quality of life as described in Trial 1 (difference in AQLQ score of 1.29 compared with placebo).
Trial 3: Clinical Trial with Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg: This 28-week, non-U.S. trial compared fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg with fluticasone propionate 500 mcg alone and concurrent therapy (salmeterol 50 mcg plus fluticasone propionate 500 mcg administered from separate inhalers) twice daily in 503 subjects with asthma using ICS (daily doses of beclomethasone dipropionate 1,260 to 1,680 mcg; budesonide 1,500 to 2,000 mcg; flunisolide 1,500 to 2,000 mcg; or fluticasone propionate inhalation aerosol 660 to 880 mcg [750 to 1,000 mcg inhalation powder]). The primary efficacy parameter, morning PEF, was collected daily for the first 12 weeks of the trial. The primary purpose of weeks 13 to 28 was to collect safety data.
Baseline PEF measurements were similar across treatments: fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, 359 L/min; fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, 351 L/min; and concurrent therapy, 345 L/min. Morning PEF improved significantly with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg compared with fluticasone propionate 500 mcg over the 12-week treatment period. Improvements in morning PEF observed with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg were similar to improvements observed with concurrent therapy.
Onset of Action and Progression of Improvement in Asthma Control: The onset of action and progression of improvement in asthma control were evaluated in the 2 placebo-controlled U.S. trials. Following the first dose, the median time to onset of clinically significant bronchodilatation (≥15% improvement in FEV1) in most subjects was seen within 30 to 60 minutes. Maximum improvement in FEV1 generally occurred within 3 hours, and clinically significant improvement was maintained for 12 hours (Figure 2). Following the initial dose, predose FEV1 relative to Day 1 baseline improved markedly over the first week of treatment and continued to improve over the 12 weeks of treatment in both trials. No diminution in the 12-hour bronchodilator effect was observed with either fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg (Figures 2 and 3) or fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg as assessed by FEV1 following 12 weeks of therapy.
Figure 2. Percent Change in Serial 12-Hour FEV1 in Subjects with Asthma Previously Using Either Inhaled Corticosteroids or Salmeterol (Trial 1)
First Treatment Day
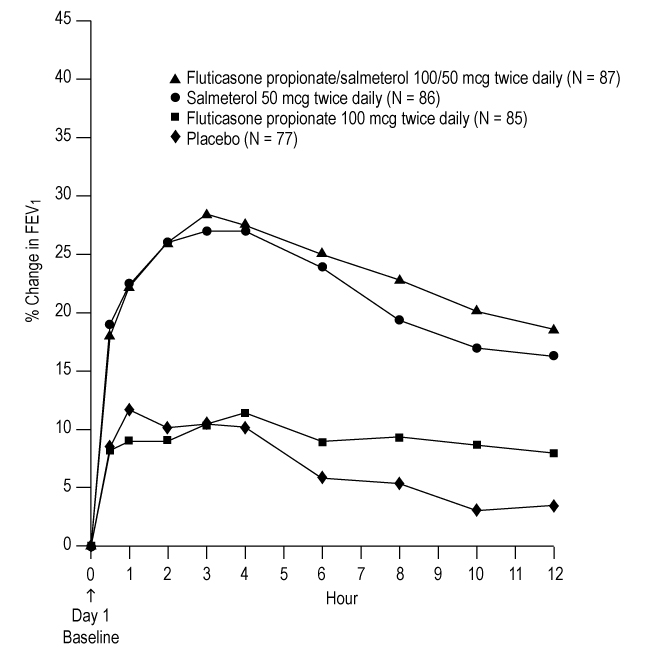
Figure 3. Percent Change in Serial 12-Hour FEV1 in Subjects with Asthma Previously Using Either Inhaled Corticosteroids or Salmeterol (Trial 1)
Last Treatment Day (Week 12)
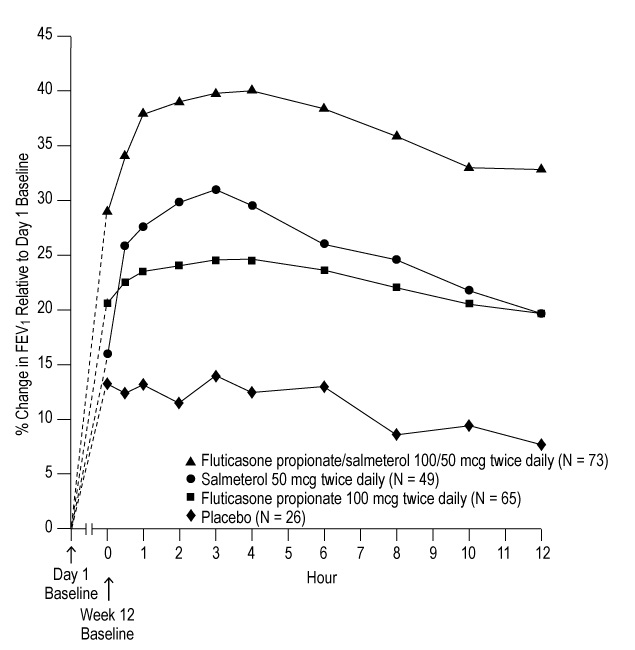
Reduction in asthma symptoms and use of rescue VENTOLIN Inhalation Aerosol and improvement in morning and evening PEF also occurred within the first day of treatment with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS, and continued to improve over the 12 weeks of therapy in both trials.
Pediatric Subjects
In a 12-week U.S. trial, fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg twice daily was compared with fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 100 mcg twice daily in 203 children with asthma aged 4 to 11 years. At trial entry, the children were symptomatic on low doses of ICS (beclomethasone dipropionate 252 to 336 mcg/day; budesonide 200 to 400 mcg/day; flunisolide 1,000 mcg/day; triamcinolone acetonide 600 to 1,000 mcg/day; or fluticasone propionate 88 to 250 mcg/day). The primary objective of this trial was to determine the safety of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg compared with fluticasone propionate inhalation powder 100 mcg in this age group; however, the trial also included secondary efficacy measures of pulmonary function. Morning predose FEV1 was obtained at baseline and Endpoint (last available FEV1 result) in children aged 6 to 11 years. In subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg, FEV1 increased from 1.70 L at baseline (n = 79) to 1.88 L at Endpoint (n = 69) compared with an increase from 1.65 L at baseline (n = 83) to 1.77 L at Endpoint (n = 75) in subjects receiving fluticasone propionate 100 mcg.
The findings of this trial, along with extrapolation of efficacy data from subjects aged 12 years and older, support the overall conclusion that fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg is efficacious in the treatment of asthma in subjects aged 4 to 11 years.
Safety and Efficacy Trials Comparing Fluticasone Propionate/Salmeterol DISKUS with Fluticasone Propionate
Serious Asthma-Related Events: Two 26-week, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, active comparator trials were conducted to compare the safety and efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS with fluticasone propionate inhalation powder in adult and adolescent subjects (Trial 4, NCT01475721) and in pediatric subjects aged 4 to 11 years (Trial 5, NCT01462344). The primary safety objective of both trials was to evaluate whether the addition of salmeterol xinafoate to fluticasone propionate therapy (fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS) was non-inferior to ICS fluticasone propionate in terms of the risk of a serious asthma-related event (hospitalization, endotracheal intubation, and death). The trials were designed to rule out pre-defined risk margins for serious asthma‑related events of 2.0 for Trial 4 and 2.7 for Trial 5. A blinded adjudication committee determined whether events were asthma related.
Trial 4 enrolled subjects with moderate to severe persistent asthma with a history of asthma‑related hospitalization or at least 1 asthma exacerbation in the previous year treated with systemic corticosteroids. A total of 11,679 adult and adolescent subjects [5,834 receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg, fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg, or fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg and 5,845 receiving fluticasone propionate inhalation powder (100, 250, or 500 mcg)] were included. Trial 5 enrolled subjects with a diagnosis of asthma and a history of at least 1 asthma exacerbation in the previous year treated with systemic corticosteroid. A total of 6,208 subjects aged 4 to 11 years [3,107 receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 100/50 mcg or fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg and 3,101 receiving fluticasone propionate inhalation powder (100 or 250 mcg)] were included. In both trials, subjects with life-threatening asthma were excluded. In Trials 4 and 5, fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS was non-inferior to fluticasone propionate in terms of time to first serious asthma‑related events based on the pre-specified risk margins, with estimated hazard ratios of 1.03 (95% CI: 0.64, 1.66) and 1.29 (95% CI: 0.73, 2.27), respectively (Table 6).
Table 6. Serious Asthma-Related Events in the 26-Week Trials 4 and 5|
a Number of subjects with event that occurred within 6 months after the first
use of study drug or 7 days after the last date of study drug treatment,
whichever date was later. Subjects can have one or more events, but only the
first event was counted for analysis. A blinded adjudication committee
determined whether events were asthma related. | ||||
|
Adult and Adolescent Subjects |
Pediatric Subjects | |||
|
Fluticasone Propionate/ (n = 5,834) |
Fluticasone Propionate (n = 5,845) |
Fluticasone Propionate/ (n = 3,107) |
Fluticasone Propionate Inhalation Powder (n = 3,101) | |
|
Serious asthma-related event (hospitalization, endotracheal intubation, and death)a |
34 (0.6%) |
33 (0.6%) |
27 (0.9%) |
21 (0.7%) |
|
Hazard ratio (Fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS/fluticasone propionate) |
1.03 (0.64-1.66)b |
1.29 (0.73-2.27)b | ||
|
Asthma-related death |
0 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Asthma-related intubation (endotracheal) |
0 |
2 |
0 |
0 |
|
Asthma-related hospitalization (≥24-hour stay) |
34 |
33 |
27 |
21 |
Effect on Exacerbation: Trials 4 and 5 included time to first exacerbation as a secondary endpoint, where exacerbation was defined as a deterioration of asthma requiring the use of systemic corticosteroids for at least 3 days or an in-patient hospitalization or emergency department visit due to asthma that required systemic corticosteroids. In Trials 4 and 5, the hazard ratio for the time to first asthma exacerbation for fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS relative to fluticasone propionate inhalation powder was 0.79 (95% CI: 0.70, 0.89) and 0.86 (95% CI: 0.73, 1.01), respectively. The difference in exacerbations was primarily driven by a reduction in those requiring systemic corticosteroids only.
14.2 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg and fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg in the treatment of subjects with COPD was evaluated in 6 randomized, double-blind, parallel-group clinical trials in adult subjects aged 40 years and older. These trials were primarily designed to evaluate the efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS on lung function (3 trials), exacerbations (2 trials), and survival (1 trial).
Lung Function
Two (2) of the 3 clinical trials primarily designed to evaluate the efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS on lung function were conducted in 1,414 subjects with COPD associated with chronic bronchitis. In these 2 trials, all the subjects had a history of cough productive of sputum that was not attributable to another disease process on most days for at least 3 months of the year for at least 2 years. The trials were randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, 24-week treatment duration. One (1) trial evaluated the efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg compared with its components fluticasone propionate 250 mcg and salmeterol 50 mcg and with placebo, and the other trial evaluated the efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg compared with its components fluticasone propionate 500 mcg and salmeterol 50 mcg and with placebo. Trial treatments were inhalation powders given as 1 inhalation from the DISKUS inhaler twice daily. Maintenance COPD therapies were discontinued, with the exception of theophylline. The subjects had a mean pre-bronchodilator FEV1 of 41% and 20% reversibility at trial entry. Percent reversibility was calculated as 100 times (FEV1 post-albuterol minus FEV1 pre-albuterol)/FEV1 pre- albuterol.
Improvements in lung function (as defined by predose and postdose FEV1) were significantly greater with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS than with fluticasone propionate, salmeterol, or placebo. The improvement in lung function with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg was similar to the improvement seen with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg.
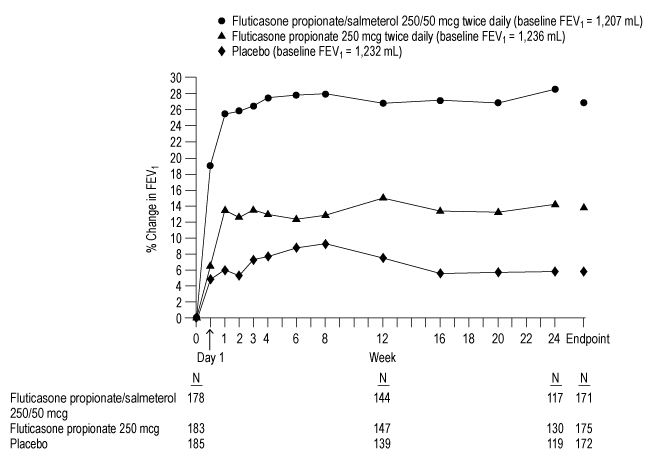
Figures 4 and 5 display predose and 2-hour postdose, respectively, FEV1 results for the trial with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg. To account for subject withdrawals during the trial, FEV1 at Endpoint (last evaluable FEV1) was evaluated. Subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg had significantly greater improvements in predose FEV1 at Endpoint (165 mL, 17%) compared with salmeterol 50 mcg (91 mL, 9%) and placebo (1 mL, 1%), demonstrating the contribution of fluticasone propionate to the improvement in lung function with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS (Figure 4). Subjects receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg had significantly greater improvements in postdose FEV1 at Endpoint (281 mL, 27%) compared with fluticasone propionate 250 mcg (147 mL, 14%) and placebo (58 mL, 6%), demonstrating the contribution of salmeterol to the improvement in lung function with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS (Figure 5).
Figure 4. Predose FEV1: Mean Percent Change from Baseline in Subjects with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Figure 5. Two-Hour Postdose FEV1: Mean Percent Changes from Baseline over Time in Subjects with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
The third trial was a 1-year trial that evaluated fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, salmeterol 50 mcg, and placebo in 1,465 subjects. The subjects had an established history of COPD and exacerbations, a pre-bronchodilator FEV1 <70% of predicted at trial entry, and 8.3% reversibility. The primary endpoint was the comparison of pre-bronchodilator FEV1 in the groups receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg or placebo. Subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg had greater improvements in FEV1 (113 mL, 10%) compared with fluticasone propionate 500 mcg (7 mL, 2%), salmeterol (15 mL, 2%), and placebo (-60 mL, -3%).
Exacerbations
Two (2) trials were primarily designed to evaluate the effect of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg on exacerbations. In these 2 trials, exacerbations were defined as worsening of 2 or more major symptoms (dyspnea, sputum volume, and sputum purulence) or worsening of any 1 major symptom together with any 1 of the following minor symptoms: sore throat, colds (nasal discharge and/or nasal congestion), fever without other cause, and increased cough or wheeze for at least 2 consecutive days. COPD exacerbations were considered of moderate severity if treatment with systemic corticosteroids and/or antibiotics was required and were considered severe if hospitalization was required.
Exacerbations were also evaluated as a secondary outcome in the 1- and 3-year trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg. There was not a symptomatic definition of exacerbation in these 2 trials. Exacerbations were defined in terms of severity requiring treatment with antibiotics and/or systemic corticosteroids (moderately severe) or requiring hospitalization (severe).
The 2 exacerbation trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg were identical trials designed to evaluate the effect of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg and salmeterol 50 mcg, each given twice daily, on exacerbations of COPD over a 12-month period. A total of 1,579 subjects had an established history of COPD (but no other significant respiratory disorders). Subjects had a pre-bronchodilator FEV1 of 33% of predicted, a mean reversibility of 23% at baseline, and a history of ≥1 COPD exacerbation in the previous year that was moderate or severe. All subjects were treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg twice daily during a 4-week run-in period prior to being assigned trial treatment with twice-daily fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg or salmeterol 50 mcg. In both trials, treatment with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg resulted in a significantly lower annual rate of moderate/severe COPD exacerbations compared with salmeterol (30.5% reduction [95% CI: 17.0, 41.8], P<0.001) in the first trial and (30.4% reduction [95% CI: 16.9, 41.7], P<0.001) in the second trial. Subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg also had a significantly lower annual rate of exacerbations requiring treatment with oral corticosteroids compared with subjects treated with salmeterol (39.7% reduction [95% CI: 22.8, 52.9], P<0.001) in the first trial and (34.3% reduction [95% CI: 18.6, 47.0], P<0.001) in the second trial. Secondary endpoints including pulmonary function and symptom scores improved more in subjects treated with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg than with salmeterol 50 mcg in both trials.
Exacerbations were evaluated in the 1- and the 3-year trials with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg as 1 of the secondary efficacy endpoints. In the 1-year trial, the group receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg had a significantly lower rate of moderate and severe exacerbations compared with placebo (25.4% reduction compared with placebo [95% CI: 13.5, 35.7]) but not when compared with its components (7.5% reduction compared with fluticasone propionate [95% CI: -7.3, 20.3] and 7% reduction compared with salmeterol [95% CI: -8.0, 19.9]). In the 3-year trial, the group receiving fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg had a significantly lower rate of moderate and severe exacerbations compared with each of the other treatment groups (25.1% reduction compared with placebo [95% CI: 18.6, 31.1], 9.0% reduction compared with fluticasone propionate [95% CI: 1.2, 16.2], and 12.2% reduction compared with salmeterol [95% CI: 4.6, 19.2]).
There were no trials conducted to directly compare the efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg on exacerbations. Across trials, the reduction in exacerbations seen with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg was not greater than the reduction in exacerbations seen with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 250/50 mcg.
Survival
A 3-year multicenter, international trial evaluated the efficacy of fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg compared with fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, salmeterol 50 mcg, and placebo on survival in 6,112 subjects with COPD. During the trial subjects were permitted usual COPD therapy with the exception of other ICS and long-acting bronchodilators. The subjects were aged 40 to 80 years with an established history of COPD, a pre- bronchodilator FEV1 <60% of predicted at trial entry, and <10% of predicted reversibility. Each subject who withdrew from double-blind treatment for any reason was followed for the full 3-year trial period to determine survival status. The primary efficacy endpoint was all-cause mortality. Survival with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg was not significantly improved compared with placebo or the individual components (all-cause mortality rate 12.6% fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS versus 15.2% placebo). The rates for all-cause mortality were 13.5% and 16.0% in the groups treated with salmeterol 50 mcg and fluticasone propionate 500 mcg, respectively. Secondary outcomes, including pulmonary function (post- bronchodilator FEV1), improved with fluticasone propionate/salmeterol DISKUS 500/50 mcg, salmeterol 50 mcg, and fluticasone propionate 500 mcg compared with placebo.








