PAROXETINE HYDROCHLORIDE
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Paroxetine HCL CR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for . (paroxetine) extended-release tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1992
087ff0d3-1761-47ea-a8c1-7c4cb679af97
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 22, 2025
Apotex Corp
DUNS: 845263701
Products 6
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
paroxetine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
paroxetine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
paroxetine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
paroxetine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
paroxetine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
paroxetine hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (17)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel
NDC 60505-3675-3
Paroxetine HCl
** Controlled-Release Tablets**
37.5 mg
30 tablets
Rx only
Federal Law requires dispensing ofparoxetine hydrochloride controlled-release tablets**** with the Medication Guide provided with this bottle.
Store at or below 25°C (77°F) [see USP].
Each controlled-release tablet contains paroxetine hydrochloride equivalent to 37.5 mg paroxetine.
Dosage: See accompanying prescribing information.
**Important:**Use safety closures when dispensing this product unless otherwise directed by physician or requested by purchaser.
Made in Canada

CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of paroxetine in the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), panic disorder (PD), social anxiety disorder (SAD), and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) is unknown, but is presumed to be linked to potentiation of serotonergic activity in the central nervous system resulting from inhibition of neuronal reuptake of serotonin (5-HT).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Studies at clinically relevant doses in humans have demonstrated that paroxetine blocks the uptake of serotonin into human platelets. In vitro studies in animals also suggest that paroxetine is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of neuronal serotonin reuptake (SSRI) and has only very weak effects on norepinephrine and dopamine neuronal reuptake.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Tablets of Paroxetine HCL CR contain a degradable polymeric matrix designed to control the dissolution rate of paroxetine over a period of approximately 4 to 5 hours. In addition to controlling the rate of drug release in vivo, an enteric coat delays the start of drug release until tablets of Paroxetine HCL CR have left the stomach.
Paroxetine extended-release tablets are completely absorbed after oral dosing of a solution of the hydrochloride salt. In a study in which normal male and female subjects (n = 23) received single oral doses of Paroxetine HCL CR at 4 dosage strengths (12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, and 50 mg), paroxetine Cmax and AUC0-inf increased disproportionately with dose (as seen also with immediate‑release formulations). Mean Cmax and AUC0-inf values at these doses were 2, 5.5, 9, and 12.5 ng/mL, and 121, 261, 338, and 540 ng·hr. /mL, respectively. Tmax was observed typically between 6 and 10 hours post‑dose, reflecting a reduction in absorption rate compared with immediate‑release formulations. The bioavailability of 25 mg Paroxetine HCL CR is not affected by food.
Distribution
Paroxetine distributes throughout the body, including the CNS, with only 1% remaining in the plasma.
Approximately 95% and 93% of paroxetine is bound to plasma protein at 100 ng/mL and 400 ng/mL, respectively. Under clinical conditions, paroxetine concentrations would normally be less than 400 ng/mL. Paroxetine does not alter the in vitro protein binding of phenytoin or warfarin.
Elimination
Metabolism
The mean elimination half-life of paroxetine was 15 to 20 hours throughout a range of single doses of Paroxetine HCL CR (12.5 mg, 25 mg, 37.5 mg, and 50 mg). During repeated administration of Paroxetine HCL CR (25 mg once daily), steady state was reached within 2 weeks (i.e., comparable to immediate‑release formulations). In a repeat‑dose study in which normal male and female subjects (n = 23) received Paroxetine HCL CR (25 mg daily), mean steady state Cmax, Cmin, and AUC0-24 values were 30 ng/mL, 20 ng/mL, and 550 ng·hr./mL, respectively.
Based on studies using immediate‑release formulations, steady‑state drug exposure based on AUC0-24 was several‑fold greater than would have been predicted from single‑dose data. The excess accumulation is a consequence of the fact that 1 of the enzymes that metabolizes paroxetine is readily saturable.
In steady‑state dose proportionality studies involving elderly and nonelderly patients, at doses of the immediate‑release formulation of 20 mg to 40 mg daily for the elderly and 20 mg to 50 mg daily for the nonelderly, some nonlinearity was observed in both populations, again reflecting a saturable metabolic pathway (Figure 3).
Paroxetine is extensively metabolized after oral administration. The principal metabolites are polar and conjugated products of oxidation and methylation, which are readily cleared. Conjugates with glucuronic acid and sulfate predominate, and major metabolites have been isolated and identified. Data indicate that the metabolites have no more than 1/50 the potency of the parent compound at inhibiting serotonin uptake. The metabolism of paroxetine is accomplished in part by CYP2D6. Saturation of this enzyme at clinical doses appears to account for the nonlinearity of paroxetine kinetics with increasing dose and increasing duration of treatment. The role of this enzyme in paroxetine metabolism also suggests potential drug‑drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Excretion
Approximately 64% of a 30 mg oral solution dose of paroxetine was excreted in the urine with 2% as the parent compound and 62% as metabolites over a 10‑day post‑dosing period. About 36% was excreted in the feces (probably via the bile), mostly as metabolites and less than 1% as the parent compound over the 10‑day post‑dosing period.
The elimination half-life is approximately 15 to 20 hours after a single dose of Paroxetine HCL CR. Paroxetine metabolism is mediated in part by CYP2D6, and the metabolites are primarily excreted in the urine and to some extent in the feces. Pharmacokinetic behavior of paroxetine has not been evaluated in subjects who are deficient in CYP2D6 (poor metabolizers).
Drug Interaction Studies
There are clinically significant, known drug interactions between paroxetine and other drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Figure 1. Impact of Paroxetine on the Pharmacokinetics of Co-Administered Drugs (log scale)
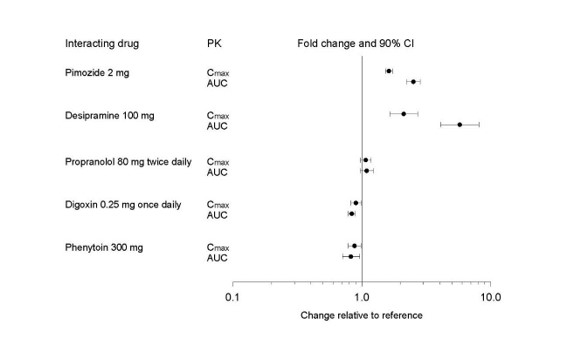
Figure 2. Impact of Co-Administered Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Paroxetine
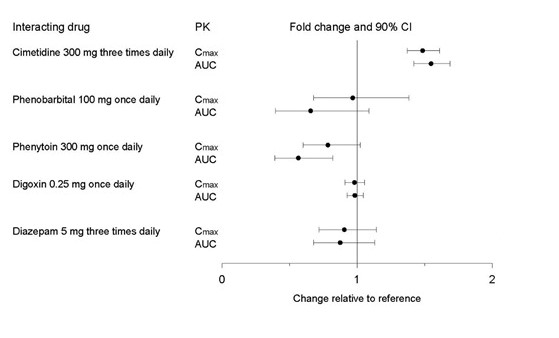
Theophylline: Reports of elevated theophylline levels associated with immediate‑release paroxetine treatment have been reported. While this interaction has not been formally studied, it is recommended that theophylline levels be monitored when these drugs are concurrently administered.
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome CYP3A4
An in vivo interaction study involving the coadministration under steady‑state conditions of paroxetine and terfenadine, a substrate for CYP3A4, revealed no effect of paroxetine on terfenadine pharmacokinetics. In addition, in vitro studies have shown ketoconazole, a potent inhibitor of CYP3A4 activity, to be at least 100 times more potent than paroxetine as an inhibitor of the metabolism of several substrates for this enzyme, including terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, triazolam, and cyclosporine. Paroxetine’s extent of inhibition of CYP3A4 activity is not expected to be of clinical significance.
Specific Populations
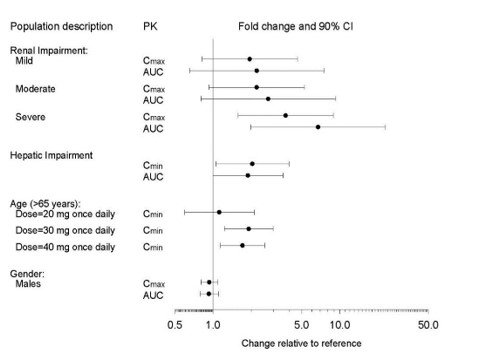
The impact of specific populations on the pharmacokinetics of paroxetine are shown in Figure 3
Figure 3. Impact of Specific Population on the Pharmacokinetics of Paroxetine (log scale)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Paroxetine HCL CR USP, contains paroxetine hydrochloride, an SSRI. It is the hydrochloride salt of a phenylpiperidine compound identified chemically as (-)-trans-4R-(4'-fluorophenyl)-3S-[(3',4'-methylenedioxyphenoxy) methyl] piperidine hydrochloride hemihydrate and has the empirical formula of C19H20FNO3·HCl·1/2H2O. The molecular weight is 374.8 g/mol (329.4 g/mol as free base). The structural formula of paroxetine hydrochloride is:
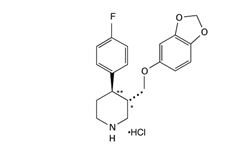
Paroxetine hydrochloride is an odorless, off‑white powder, having a melting point range of 120°C to 138°C and a solubility of 5.4 mg/mL in water.
Paroxetine HCL CR tablets, USP are intended for oral administration. Each extended‑release tablet contains 12.5 mg, 25 mg, or 37.5 mg paroxetine equivalent to 14.25 mg, 28.51 mg, or 42.76 mg of paroxetine hydrochloride, respectively. One layer of the tablet consists of a degradable barrier layer and the other contains the active material in a hydrophilic matrix.
Inactive ingredients consist of glyceryl behenate, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, methacrylic acid copolymer type C, polyethylene glycols, polysorbate 80, polyvinylpyrrolidone, silicon dioxide, sodium lauryl sulfate, talc, titanium dioxide, triethyl citrate and the following colorants: D&C Red No. 30 aluminum lake (25 mg), D&C Yellow No. 10 aluminum lake (12.5 mg), FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake (37.5 mg), FD&C Yellow No. 6 aluminum lake (12.5 mg), red ferric oxide (25 mg) and Yellow ferric oxide (12.5 mg and 37.5 mg).
