Vosevi
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VOSEVI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VOSEVI. VOSEVI (sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir) tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2017
17ffc094-8ca7-45d2-80d8-fd043bc9a221
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 14, 2024
Gilead Sciences, Inc.
DUNS: 185049848
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
SOFOSBUVIR, VELPATASVIR, and VOXILAPREVIR
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (19)
Drug Labeling Information
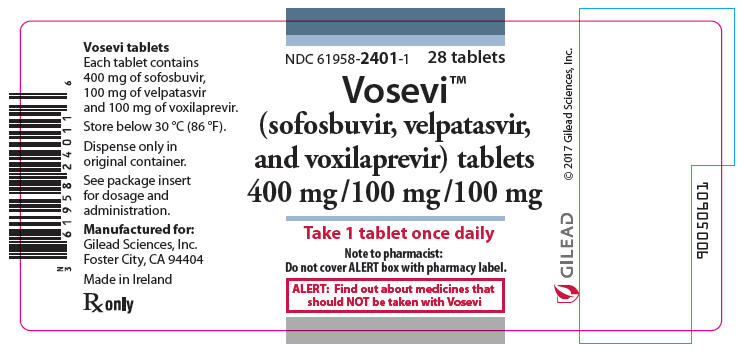
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 28 Tablet Bottle Label
NDC 61958-2401-1
28 tablets
Vosevi™
(sofosbuvir, velpatasvir,
and voxilaprevir) tablets
400 mg / 100 mg / 100 mg
Take 1 tablet once daily
Note to pharmacist:
Do not cover ALERT box with pharmacy label.
ALERT: Find out about medicines that
should NOT be taken with Vosevi
BOXED WARNING SECTION
WARNING: RISK OF HEPATITIS B VIRUS REACTIVATION IN PATIENTS COINFECTED WITH
HCV AND HBV
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation has been reported, in some cases resulting in fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, and death. (5.1)
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
VOSEVI is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) who have [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Studies (14)]:
- genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 infection and have previously been treated with an HCV regimen containing an NS5A inhibitor.
- genotype 1a or 3 infection and have previously been treated with an HCV regimen containing sofosbuvir without an NS5A inhibitor.
- Additional benefit of VOSEVI over sofosbuvir/velpatasvir was not shown in adults with genotype 1b, 2, 4, 5, or 6 infection previously treated with sofosbuvir without an NS5A inhibitor.
VOSEVI is a fixed-dose combination of sofosbuvir, a hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleotide analog NS5B polymerase inhibitor, velpatasvir, an HCV NS5A inhibitor, and voxilaprevir, an HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor, and is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with chronic HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A) who have (1, 2.2, 14):
- genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 infection and have previously been treated with an HCV regimen containing an NS5A inhibitor.
- genotype 1a or 3 infection and have previously been treated with an HCV regimen containing sofosbuvir without an NS5A inhibitor.
- Additional benefit of VOSEVI over sofosbuvir/velpatasvir was not shown in adults with genotype 1b, 2, 4, 5, or 6 infection previously treated with sofosbuvir without an NS5A inhibitor.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
VOSEVI is contraindicated with rifampin [see Drug Interactions (7.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Coadministration with rifampin. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in labeling:
- Serious Symptomatic Bradycardia When Coadministered with Amiodarone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse Reactions in HCV-Infected Subjects without Cirrhosis or with Compensated Cirrhosis
The adverse reactions data for VOSEVI were derived from two Phase 3 clinical trials (POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4) that evaluated a total of 445 subjects infected with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 HCV, without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A), who received VOSEVI for 12 weeks. VOSEVI was studied in placebo- and active-controlled (sofosbuvir/velpatasvir) trials [see Clinical Studies (14.1 and 14.2)].
The proportion of subjects who permanently discontinued treatment due to adverse events was 0.2% for subjects who received VOSEVI for 12 weeks.
The most common adverse reactions (adverse events assessed as causally related by the investigator and at least 10%) were headache, fatigue, diarrhea, and nausea in subjects treated with VOSEVI for 12 weeks.
Table 2 lists adverse reactions (adverse events assessed as causally related by the investigator, all grades) observed in at least 5% of subjects receiving 12 weeks of treatment with VOSEVI in the Phase 3 clinical trials. The side-by- side tabulation is to simplify presentation; direct comparison across trials should not be made due to differing trial designs.
Table 2 Adverse Reactions (All Grades) Reported in ≥5% of Subjects With HCV Without Cirrhosis or With Compensated Cirrhosis Receiving VOSEVI in POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4|
POLARIS-1 |
POLARIS-4 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VOSEVI |
Placebo |
VOSEVI |
SOF/VEL | |
|
Headache |
21% |
14% |
23% |
23% |
|
Fatigue |
17% |
15% |
19% |
23% |
|
Diarrhea |
13% |
9% |
14% |
3% |
|
Nausea |
13% |
7% |
10% |
3% |
|
Asthenia |
6% |
4% |
4% |
6% |
|
Insomnia |
6% |
3% |
3% |
1% |
In POLARIS-1, of the subjects receiving VOSEVI who experienced adverse reactions, 99% were mild or moderate (Grade 1 or 2) in severity. In POLARIS-4, of the subjects receiving VOSEVI who experienced adverse reactions, all the reported adverse reactions were mild or moderate (Grade 1 or 2) in severity.
Less Common Adverse Reactions Reported in Clinical Trials
The following adverse reactions occurred in less than 5% of subjects without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis treated with VOSEVI for 12 weeks and are included because of a potential causal relationship.
Rash: In the POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4 trials, rash occurred in less than 1% and 2% of subjects treated with VOSEVI, respectively. Rash was reported in 1% of subjects treated with placebo in POLARIS-1 and was not reported by any subject taking sofosbuvir/velpatasvir in POLARIS-4. No serious adverse reactions of rash occurred, and all rashes were mild or moderate in severity.
Depression: In the POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4 trials, depressed mood occurred in less than 1% and 1% of subjects treated with VOSEVI, respectively. Depressed mood was not reported by any subject taking placebo in POLARIS-1 and was reported in 1% of subjects treated with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir in POLARIS-4. No serious adverse reactions of depressed mood occurred and all events were mild or moderate in severity.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Lipase Elevations: Isolated, asymptomatic lipase elevations of greater than 3×ULN were observed in POLARIS-1 in 2% of subjects treated with VOSEVI and 3% of subjects treated with placebo, and in POLARIS-4 in 2% of subjects treated with VOSEVI and less than 1% of subjects treated with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
Creatine Kinase: Isolated, asymptomatic creatine kinase elevations greater than or equal to 10×ULN were reported in POLARIS-1 in 1% of subjects treated with VOSEVI and 1% of subjects treated with placebo, and in POLARIS-4 in less than 1% of subjects treated with VOSEVI and no subjects treated with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir.
Total bilirubin: Increases in total bilirubin less than or equal to 1.5×ULN were observed in subjects treated with VOSEVI due to inhibition of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3 by voxilaprevir: 4% and 6% of subjects without cirrhosis in POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4, respectively; and 7% and 13% of subjects with compensated cirrhosis in POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4, respectively. No subjects experienced jaundice and total bilirubin levels decreased after completing VOSEVI treatment.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of sofosbuvir-containing regimens. Because postmarketing reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hepatobiliary Disorders
Hepatic decompensation, hepatic failure with NS3/4A protease inhibitor- containing regimens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Cardiac Disorders
Serious symptomatic bradycardia has been reported in patients taking amiodarone who initiated treatment with a sofosbuvir-containing regimen [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Skin rashes, sometimes with blisters or angioedema-like swelling
Angioedema
- The most common adverse reactions (incidence greater than or equal to 10%, all grades) observed with treatment with VOSEVI for 12 weeks were headache, fatigue, diarrhea, and nausea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Gilead Sciences, Inc. at 1-800-GILEAD-5 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Potential for Other Drugs to Affect VOSEVI
Sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir are substrates of drug transporters P-gp and BCRP while GS-331007 (predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir) is not. Voxilaprevir is also a substrate of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. In vitro, slow metabolic turnover of velpatasvir by CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4 and of voxilaprevir by CYP1A2, CYP2C8, and primarily CYP3A4 was observed.
Drugs that are inducers of P-gp and/or moderate to strong inducers of CYP2B6, CYP2C8, or CYP3A4 (e.g., St. John's wort, carbamazepine) may significantly decrease plasma concentrations of sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and/or voxilaprevir leading to reduced therapeutic effect of VOSEVI. The use of these agents with VOSEVI is not recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. VOSEVI may be coadministered with P-gp, BCRP, and CYP inhibitors. The use of OATP inhibitors which may substantially increase exposure of voxilaprevir (e.g., cyclosporine) with VOSEVI is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Potential for VOSEVI to Affect Other Drugs
Velpatasvir and voxilaprevir are inhibitors of drug transporters P-gp, BCRP, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3. Velpatasvir is also an inhibitor of OATP2B1. Coadministration of VOSEVI with drugs that are substrates of these transporters may alter the exposure of such drugs. Coadministration of VOSEVI with BCRP substrates (e.g., methotrexate, mitoxantrone, imatinib, irinotecan, lapatinib, rosuvastatin, sulfasalazine, topotecan) is not recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Established and Potentially Significant Drug Interactions
Clearance of HCV infection with direct acting antivirals may lead to changes in hepatic function, which may impact the safe and effective use of concomitant medications. For example, altered blood glucose control resulting in serious symptomatic hypoglycemia has been reported in diabetic patients in postmarketing case reports and published epidemiological studies. Management of hypoglycemia in these cases required either discontinuation or dose modification of concomitant medications used for diabetes treatment.
Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (e.g., International Normalized Ratio [INR] in patients taking warfarin, blood glucose levels in diabetic patients) or drug concentrations of concomitant medications such as cytochrome P450 substrates with a narrow therapeutic index (e.g., certain immunosuppressants) is recommended to ensure safe and effective use. Dose adjustments of concomitant medications may be necessary.
Table 3 provides a listing of established or potentially clinically significant drug interactions. The drug interactions described are based on studies conducted with either VOSEVI, the components of VOSEVI (sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and/or voxilaprevir), or are predicted drug interactions that may occur with VOSEVI [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 3 Potentially Significant Drug Interactions: Alteration in Dose or Regimen May Be Recommended Based on Drug Interaction Studies or Predicted Interaction*|
Concomitant Drug Class: Drug Name |
Effect on Concentration† |
Clinical Effect/Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Acid Reducing Agents: |
↓ velpatasvir |
Velpatasvir solubility decreases as pH increases. Drugs that increase gastric pH are expected to decrease concentration of velpatasvir. |
|
Antacids (e.g., aluminum and magnesium hydroxide) |
Separate antacid and VOSEVI administration by 4 hours. | |
|
H2-receptor antagonists (e.g., famotidine)‡ |
H2-receptor antagonists may be administered simultaneously with or staggered from VOSEVI at a dose that does not exceed doses comparable with famotidine 40 mg twice daily. | |
|
Proton-pump inhibitors (e.g., omeprazole)‡ |
Omeprazole 20 mg can be administered with VOSEVI. Use with other proton pump- inhibitors has not been studied. | |
|
Antiarrhythmics: | ||
|
amiodarone |
Effect on amiodarone, sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir concentrations unknown |
Coadministration of amiodarone with VOSEVI may result in serious symptomatic bradycardia. The mechanism of this effect is unknown. Coadministration of amiodarone with VOSEVI is not recommended; if coadministration is required, cardiac monitoring is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
|
digoxin‡ |
↑ digoxin |
Therapeutic concentration monitoring of digoxin is recommended when coadministered with VOSEVI. Refer to digoxin prescribing information for monitoring and dose modification recommendations for concentration increases with unclear magnitude. |
|
Anticoagulants: | ||
|
dabigatran etexilate‡ |
↑ dabigatran |
Clinical monitoring of dabigatran is recommended when coadministered with VOSEVI. Refer to dabigatran etexilate prescribing information for dose modification recommendations in the setting of moderate renal impairment. |
|
Anticonvulsants: | ||
|
carbamazepine‡ |
↓ sofosbuvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
|
Antimycobacterials: | ||
|
rifampin‡ |
↓ sofosbuvir |
Coadministration with rifampin is contraindicated**[see Contraindications (4)].** |
|
rifabutin‡ |
↓ sofosbuvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
|
Antiretrovirals: | ||
|
atazanavir‡ |
↑ voxilaprevir |
Coadministration of VOSEVI with atazanavir- or lopinavir-containing regimens is not recommended. |
|
tipranavir/ritonavir |
↓ sofosbuvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. The effect on voxilaprevir is unknown. |
|
efavirenz‡ |
↓ velpatasvir |
Coadministration of VOSEVI with efavirenz-containing regimens is not recommended. |
|
tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (tenofovir DF)‡ |
↑ tenofovir |
Monitor for tenofovir-associated adverse reactions in patients receiving VOSEVI concomitantly with a regimen containing tenofovir DF. Refer to the prescribing information of the tenofovir DF-containing product for recommendations on renal monitoring. |
|
Herbal Supplements: | ||
|
St. John's wort |
↓ sofosbuvir |
Coadministration is not recommended. |
|
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: | ||
|
pravastatin‡ |
↑ pravastatin |
Coadministration of VOSEVI with pravastatin has been shown to increase the concentration of pravastatin, which is associated with increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Pravastatin may be administered with VOSEVI at a dose that does not exceed pravastatin 40 mg. |
|
rosuvastatin‡ |
↑ rosuvastatin |
Coadministration of VOSEVI with rosuvastatin may significantly increase the concentration of rosuvastatin which is associated with increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Coadministration of VOSEVI with rosuvastatin is not recommended. |
|
pitavastatin |
↑ pitavastatin |
Coadministration with VOSEVI may increase the concentration of pitavastatin and is not recommended, due to an increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. |
|
atorvastatin‡ |
↑ atorvastatin |
Coadministration with VOSEVI may increase the concentrations of atorvastatin, fluvastatin, lovastatin, and simvastatin. Increased statin concentrations may increase the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Use the lowest approved statin dose. If higher doses are needed, use the lowest necessary statin dose based on a risk/benefit assessment. |
|
Immunosuppressants: | ||
|
cyclosporine‡ |
↑ voxilaprevir |
Coadministration of voxilaprevir with cyclosporine has been shown to substantially increase the plasma concentration of voxilaprevir, the safety of which has not been established. Coadministration of VOSEVI with cyclosporine is not recommended. |
7.4 Drugs without Clinically Significant Interactions with VOSEVI
Based on drug interaction studies conducted with the components of VOSEVI (sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and/or voxilaprevir) or VOSEVI, no clinically significant drug interactions have been observed with the following drugs [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]:
- VOSEVI: cobicistat, darunavir, elvitegravir, emtricitabine, ethinyl estradiol/norgestimate, gemfibrozil, rilpivirine, ritonavir, tenofovir alafenamide, voriconazole
- Sofosbuvir/velpatasvir: dolutegravir, ketoconazole, raltegravir
- Sofosbuvir: methadone, tacrolimus
- P-gp inducers and/or moderate to strong CYP inducers (e.g., St. John's wort, carbamazepine): May decrease concentrations of sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and/or voxilaprevir. Use of VOSEVI with P-gp inducers and/or moderate to strong CYP inducers is not recommended. (5.4, 7)
- Consult the full prescribing information prior to use for potential drug interactions. (4, 5.3, 5.4, 7)
- Clearance of HCV infection with direct acting antivirals may lead to changes in hepatic function, which may impact safe and effective use of concomitant medications. Frequent monitoring of relevant laboratory parameters (INR or blood glucose) and dose adjustments of certain concomitant medications may be necessary. (7.3)
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: 11/2019 | ||
|
Patient Information | |||
|
What is the most important information I should know about VOSEVI? | |||
|
What is VOSEVI?
It is not known if VOSEVI is safe and effective in children. | |||
|
Do not take VOSEVI: if you also take any medicines that contain rifampin (Rifater®, Rifamate®, Rimactane®, Rifadin®) | |||
|
Before taking VOSEVI, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take,
including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal
supplements. VOSEVI and other medicines may affect each other. This can cause
you to have too much or not enough VOSEVI or other medicines in your body.
This may affect the way VOSEVI or your other medicines work or may cause side
effects.
| |||
|
How should I take VOSEVI?
| |||
|
What are the possible side effects of VOSEVI? *Hepatitis B virus (HBV) reactivation. See "What is the most important information I should know about VOSEVI?" *In people who had or have advanced liver problems before starting treatment with VOSEVI: rare risk of worsening liver problems, liver failure and death. Your healthcare provider will check you for signs and symptoms of worsening liver problems during treatment with VOSEVI. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following signs and symptoms: | |||
|
| ||
|
*Slow heart rate (bradycardia). VOSEVI treatment may result in slowing of the heart rate along with other symptoms when taken with amiodarone (Cordarone®, Nexterone®, Pacerone®), a medicine used to treat certain heart problems. In some cases, bradycardia has led to death or the need for a heart pacemaker when amiodarone is taken with medicines similar to VOSEVI that contain sofosbuvir. Get medical help right away if you take amiodarone with VOSEVI and get any of the following symptoms: | |||
|
| ||
These are not all the possible side effects of VOSEVI. | |||
|
How should I store VOSEVI?
Keep VOSEVI and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of VOSEVI | |||
|
What are the ingredients in VOSEVI? |
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Dosage and Administration, Renal Impairment (2.3) |
11/2019 |
|
Warnings and Precautions, Risk of Hepatic Decompensation/Failure in Patients with Evidence of Advanced Liver Disease (5.2) |
09/2019 |
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Each VOSEVI tablet contains 400 mg of sofosbuvir, 100 mg of velpatasvir, and
100 mg of voxilaprevir. The tablets are beige, capsule-shaped, film-coated,
and debossed with "GSI" on one side and
" " on the other
side.
" on the other
side.
Tablets: 400 mg sofosbuvir, 100 mg velpatasvir, and 100 mg voxilaprevir (3)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
No specific antidote is available for overdose with VOSEVI. If overdose occurs the patient must be monitored for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with VOSEVI consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. Hemodialysis can efficiently remove the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir, GS-331007, with an extraction ratio of 53%. Hemodialysis is unlikely to result in significant removal of velpatasvir or voxilaprevir since velpatasvir and voxilaprevir are highly bound to plasma protein.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
VOSEVI is a fixed-dose combination tablet containing sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, and voxilaprevir for oral administration. Sofosbuvir is a nucleotide analog HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitor, velpatasvir is an NS5A inhibitor, and voxilaprevir is an NS3/4A protease inhibitor.
Each tablet contains 400 mg sofosbuvir, 100 mg velpatasvir, and 100 mg of voxilaprevir. The tablets include the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, copovidone, croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and microcrystalline cellulose. The tablets are film-coated with a coating material containing the following inactive ingredients: ferrosoferric oxide, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide.
Sofosbuvir: The IUPAC name for sofosbuvir is (S)-Isopropyl 2-((S)-(((2R,3R,4R,5R)-5-(2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-1(2H)-yl)-4-fluoro-3-hydroxy-4-methyltetrahydrofuran-2-yl)methoxy)-(phenoxy)phosphorylamino)propanoate. It has a molecular formula of C22H29FN3O9P and a molecular weight of 529.45. It has the following structural formula:
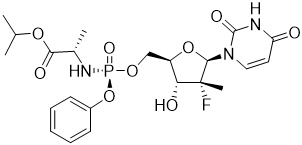
Sofosbuvir is a white to off-white crystalline solid with a solubility of at least 2 mg/mL across the pH range of 2–7.7 at 37 °C and is slightly soluble in water.
Velpatasvir: The IUPAC name for velpatasvir is Methyl {(1R)-2-[(2S,4S)-2-(5-{2-[(2S,5S)-1-{(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}-5-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-1,11-dihydro[2]benzopyrano[4',3':6,7]naphtho[1,2-d]imidazol-9-yl}-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-4-(methoxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl}carbamate. It has a molecular formula of C49H54N8O8 and a molecular weight of 883.0. It has the following structural formula:
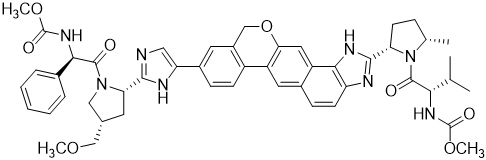
Velpatasvir is practically insoluble (less than 0.1 mg/mL) above pH 5, slightly soluble (3.6 mg/mL) at pH 2, and soluble (greater than 36 mg/mL) at pH 1.2.
Voxilaprevir: The IUPAC name for voxilaprevir is (1aR,5S,8S,9S,10R,22aR)-5-tert- butyl-N-{(1R,2R)-2-(difluoromethyl)-1-[(1-methylcyclopropanesulfonyl) carbamoyl]cyclopropyl}-9-ethyl-18,18-difluoro-14-methoxy-3,6-dioxo-1,1a,3,4,5,6,9,10,18,19,20,21,22,22a-tetradecahydro-8H-7,10-methanocyclopropa[18,19][1,10,3,6]dioxadiazacyclononadecino[11,12-b]quinoxaline-8-carboxamide. It has a molecular formula of C40H52F4N6O9S and a molecular weight of 868.9. It has the following structural formula:
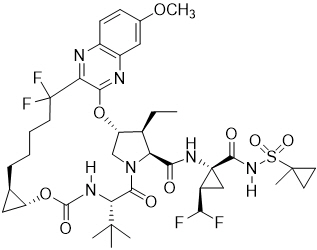
Voxilaprevir is a white to light brown solid. It is slightly hygroscopic to hygroscopic. Voxilaprevir is practically insoluble (less than 0.1 mg/mL) below pH 6.8.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured and distributed by:
Gilead Sciences, Inc.
Foster City, CA 94404
VOSEVI, ATRIPLA, GENVOYA, HARVONI, and ODEFSEY are trademarks of Gilead Sciences, Inc., or its related companies. All other trademarks referenced herein are the property of their respective owners.
© 2019 Gilead Sciences, Inc. All rights reserved.
209195-GS-003
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Description of Clinical Trials
The efficacy of VOSEVI was evaluated in two Phase 3 trials in DAA-experienced subjects with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis, as summarized in Table 8.
Table 8 Trials Conducted With VOSEVI in DAA-Experienced Subjects With HCV Infection|
Trial |
Population |
Study Arms and Comparator Groups |
|---|---|---|
|
DAA: direct-acting antiviral; SOF: sofosbuvir; VEL: velpatasvir | ||
| ||
|
POLARIS-1* |
Genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 NS5A inhibitor-experienced†, |
VOSEVI 12 weeks (263) |
|
POLARIS-4‡ |
Genotype 1, 2, 3, or 4 DAA-experienced§ who have not received an NS5A
inhibitor, |
VOSEVI 12 weeks (182) |
Serum HCV RNA values were measured during the clinical trials using the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS Taqman HCV test (version 2.0) with a lower limit of quantification (LLOQ) of 15 IU/mL. Sustained virologic response (SVR12), defined as HCV RNA less than LLOQ at 12 weeks after the cessation of treatment, was the primary endpoint in both trials. Relapse is defined as HCV RNA greater than or equal to LLOQ after end-of-treatment response among subjects who completed treatment. On-treatment virologic failure is defined as breakthrough, rebound, or non-response.
14.2 Clinical Trials in HCV DAA-Experienced Subjects
NS5A Inhibitor-Experienced Adults Without Cirrhosis or With Compensated Cirrhosis (POLARIS-1)
POLARIS-1 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial that evaluated 12 weeks of treatment with VOSEVI compared with 12 weeks of placebo in DAA-experienced subjects with genotype 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis who previously failed a regimen containing an NS5A inhibitor. Subjects with genotype 1 HCV infection were randomized 1:1 to each group. Subjects with genotype 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6 HCV infection were enrolled to the VOSEVI group. Randomization was stratified by the presence or absence of cirrhosis.
Demographics and baseline characteristics were generally balanced across treatment groups. Of the 415 treated subjects, the median age was 59 years (range: 27 to 84); 77% of the subjects were male; 81% were White; 14% were Black; 6% were Hispanic or Latino; 33% had a baseline body mass index at least 30 kg/m2; the majority of subjects had genotype 1 (72%) or genotype 3 (19%) HCV infection; 82% had a non-CC IL28B genotype (CT or TT); 74% had baseline HCV RNA levels at least 800,000 IU/mL; and 41% had compensated cirrhosis. In the POLARIS-1 trial, prior DAA regimens contained the following NS5A inhibitors: ledipasvir (51%), daclatasvir (27%), ombitasvir (11%), velpatasvir (7%), and elbasvir (3%).
Table 9 presents the SVR12 by HCV genotype for the POLARIS-1 trial. No subjects in the placebo group achieved SVR12.
Table 9 POLARIS-1 Trial: Virologic Outcomes by HCV Genotype in VOSEVI- Treated Subjects Without Cirrhosis or With Compensated Cirrhosis (12 Weeks After Treatment)|
VOSEVI 12 Weeks | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Total |
GT-1 |
GT-2 |
GT-3 |
GT-4 |
GT-5 |
GT-6 | |||
|
GT-1a (N=101) |
GT-1b (N=45) |
Total† (N=150) | |||||||
|
GT: genotype | |||||||||
| |||||||||
|
SVR12 |
96% |
96% |
100% |
97% |
100% |
95% |
91% |
100% |
100% |
|
Outcome for Subjects without SVR | |||||||||
|
On-Treatment Virologic Failure |
<1% |
1% |
0/45 |
1% |
0/5 |
0/78 |
0/22 |
0/1 |
0/6 |
|
Relapse‡ |
2% |
1% |
0/45 |
1% |
0/5 |
5% |
5% |
0/1 |
0/6 |
|
Other§ |
1% |
2% |
0/45 |
1% |
0/5 |
0/78 |
5% |
0/1 |
0/6 |
DAA-Experienced Adults Without Cirrhosis or With Compensated Cirrhosis Who Had Not Received An NS5A Inhibitor (POLARIS-4)
POLARIS-4 was a randomized, open-label trial that evaluated 12 weeks of treatment with VOSEVI and 12 weeks of treatment with SOF/VEL in subjects with genotype 1, 2, 3, or 4 HCV infection without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis who had previously failed a HCV DAA-containing regimen that did not include an NS5A inhibitor. Subjects whose only DAA exposure was an NS3/4A protease inhibitor were excluded. Subjects with genotype 1, 2, or 3 HCV infection were randomized 1:1 to each group. Randomization was stratified by HCV genotype and by the presence or absence of cirrhosis. Subjects with genotype 4 HCV infection were enrolled to the VOSEVI group. No subjects with genotype 5 or 6 were enrolled.
Demographics and baseline characteristics were generally balanced across treatment groups. Of the 333 treated subjects, the median age was 58 years (range: 24 to 85); 77% of the subjects were male; 87% were White, 9% were Black; 8% were Hispanic or Latino; 35% had a baseline body mass index at least 30 kg/m2; 81% had non-CC IL28B genotypes (CT or TT); 75% had baseline HCV RNA levels at least 800,000 IU/mL; and 46% had compensated cirrhosis. In the POLARIS-4 trial, prior DAA regimens contained sofosbuvir (85%) with the following: peginterferon alfa and ribavirin or ribavirin (69%), HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor (boceprevir, simeprevir, or telaprevir; 15%), and investigational DAA (<1%). Of the 15% of subjects without prior sofosbuvir exposure, most received investigational HCV DAAs or approved HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors, with or without peginterferon alfa and ribavirin.
Treatment with VOSEVI for 12 weeks resulted in numerically higher SVR12 rates than treatment with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir for 12 weeks in subjects with HCV genotype 1a and 3 infection. Comparable SVR12 rates were observed in subjects with HCV genotype 1b and 2 infection treated with VOSEVI for 12 weeks or with sofosbuvir/velpatasvir for 12 weeks. No comparison data are available for HCV genotypes 4, 5, and 6. Given these data, the additional benefit of VOSEVI has not been shown over sofosbuvir/velpatasvir for these genotypes and VOSEVI is only indicated for the treatment of HCV genotypes 1a or 3 infection in adults who previously received sofosbuvir without an NS5A inhibitor.
Table 10 presents the comparative virologic outcome data for HCV genotype 1, 2, and 3 subjects with prior exposure to a sofosbuvir-containing regimen.
Table 10 POLARIS-4 Trial: Virologic Outcomes by HCV Genotype in VOSEVI-Treated Subjects* and SOF/VEL-Treated Subjects* Without Cirrhosis or With Compensated Cirrhosis (12 Weeks After Treatment)|
*Subjects with prior exposure to a SOF-containing regimen |
VOSEVI |
SOF/VEL |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
Overall (Genotypes 1, 2, and 3) | ||
|
SVR12 |
97% (135/139) |
88% (110/125) |
|
Not achieving SVR12 | ||
|
On-treatment virologic failure |
0% (0/139) |
1% (1/125) |
|
Relapse* |
1% (1/139) |
10% (13/124) |
|
Other† |
2% (3/139) |
1% (1/125) |
|
Genotype 1 | ||
|
SVR12 |
96% (52/54) |
85% (34/40) |
|
Not achieving SVR12 | ||
|
On-treatment virologic failure |
0% (0/54) |
0% (0/40) |
|
Relapse* |
2% (1/54) |
13% (5/40) |
|
Other† |
2% (1/54) |
3% (1/40) |
|
Genotype 1a | ||
|
SVR12 |
97% (35/36) |
82% (23/28) |
|
Not achieving SVR12 | ||
|
On-treatment virologic failure |
0% (0/36) |
0% (0/28) |
|
Relapse* |
3% (1/36) |
18% (5/28) |
|
Other† |
0% (0/36) |
0% (0/28) |
|
Genotype 1b | ||
|
SVR12 |
94% (17/18) |
92% (11/12) |
|
Not achieving SVR12 | ||
|
On-treatment virologic failure |
0% (0/18) |
0% (0/12) |
|
Relapse* |
0% (0/18) |
0% (0/12) |
|
Other† |
6% (1/18) |
8% (1/12) |
|
Genotype 2 | ||
|
SVR12 |
100% (31/31) |
97% (32/33) |
|
Not achieving SVR12 | ||
|
On-treatment virologic failure |
0% (0/31) |
3% (1/33) |
|
Relapse* |
0% (0/31) |
0% (0/32) |
|
Other† |
0% (0/31) |
0% (0/33) |
|
Genotype 3 | ||
|
SVR12 |
96% (52/54) |
85% (44/52) |
|
Not achieving SVR12 | ||
|
On-treatment virologic failure |
0% (0/54) |
0% (0/52) |
|
Relapse* |
0% (0/54) |
15% (8/52) |
|
Other† |
4% (2/54) |
0% (0/52) |
In POLARIS-4, VOSEVI was administered for 12 weeks to 18 HCV genotype 4 subjects (with or without cirrhosis) who had prior exposure to a SOF- containing regimen without an NS5A inhibitor. All subjects achieved SVR12.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Patients Coinfected with HCV and HBV
Inform patients that HBV reactivation can occur in patients coinfected with HBV during or after treatment of HCV virus infection. Advise patients to tell their healthcare provider if they have a history of hepatitis B infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Risk of Hepatic Decompensation/Failure in Patients with Evidence of Advanced Liver Disease
Advise patients to seek medical evaluation immediately for symptoms of worsening liver problems such as nausea, tiredness, yellowing of the skin or white part of the eyes, bleeding or bruising more easily than normal, confusion, loss of appetite, diarrhea, dark or brown urine, dark or bloody stool, swelling of the stomach area (abdomen) or pain in the upper right side of the stomach area, sleepiness, or vomiting of blood [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Serious Symptomatic Bradycardia When Coadministered with Amiodarone
Advise patients to seek medical evaluation immediately for symptoms of bradycardia such as near-fainting or fainting, dizziness or lightheadedness, malaise, weakness, excessive tiredness, shortness of breath, chest pain, confusion, or memory problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Adverse Reactions (6.2), and Drug Interactions (7.3)].
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that VOSEVI may interact with other drugs. Advise patients to report to their healthcare provider the use of any other prescription or nonprescription medication or herbal products including St. John's wort [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Administration
Advise patients to take VOSEVI once daily on a regular dosing schedule with food. Inform patients that it is important not to miss or skip doses and to take VOSEVI for the duration that is recommended by the physician.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
No adequate human data are available to establish whether or not VOSEVI poses a risk to pregnancy outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of adverse developmental outcomes was observed with the components of VOSEVI (sofosbuvir, velpatasvir, or voxilaprevir) at exposures greater than those in humans at the recommended human dose (RHD) [see Data]. During organogenesis in the mouse, rat, and rabbit, systemic exposures (AUC) of velpatasvir were approximately 23 (mice), 4 (rats), and 0.5 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD, while exposures of voxilaprevir were approximately 141 (rats) and 4 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD. Exposures of the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir (GS-331007) were approximately 6 (rats) and 16 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD. In rat pre/postnatal development studies, maternal systemic exposures (AUC) for each component of VOSEVI were approximately 7 (sofosbuvir metabolite GS-331007), 3 (velpatasvir), and 238 (voxilaprevir) times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Data
Sofosbuvir: Sofosbuvir was administered orally to pregnant rats (up to 500 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (up to 300 mg/kg/day) on gestation days 6 to 18 and 6 to 19, respectively, and also to rats (oral doses up to 500 mg/kg/day) from gestation day 6 to lactation/post-partum day 20. No significant effects on embryo-fetal (rats and rabbits) or pre/postnatal (rats) development were observed at the highest doses tested. The systemic exposures (AUC) of the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir (GS-331007) during gestation were approximately 6 (rats) and 16 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Velpatasvir: Velpatasvir was administered orally to pregnant mice (up to 1000 mg/kg/day), rats (up to 200 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (up to 300 mg/kg/day) from gestation days 6 to 15, 6 to 17, and 7 to 20, respectively, and also to rats (oral doses up to 200 mg/kg) on gestation day 6 to lactation/post-partum day 20. No significant effects on embryo-fetal (mice, rats, and rabbits) or pre/postnatal (rats) development were observed at the highest doses tested. The systemic exposures (AUC) of velpatasvir during gestation were approximately 23 (mice), 4 (rats), and 0.5 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Voxilaprevir: Voxilaprevir was administered orally to pregnant rats (up to 100 mg/kg/day) and rabbits (up to 600 mg/kg/day) from gestation days 6 to 17, and 7 to 19, respectively, and also to rats (oral doses up to 100 mg/kg) on gestation day 6 to lactation/post-partum day 20. No significant effects on embryo-fetal (rats and rabbits) or pre/postnatal (rats) development were observed at the highest doses tested. The systemic exposures (AUC) of voxilaprevir during gestation were approximately 141 (rats) and 4 (rabbits) times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether the components of VOSEVI and its metabolites are present in human breast milk, affect human milk production, or have effects on the breastfed infant. When the components of VOSEVI were administered to lactating rats, GS-331007 (the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir) and velpatasvir were detected in milk, while voxilaprevir was detected in the plasma of nursing pups likely due to the presence of voxilaprevir in milk. No significant effects of any of the drugs were observed in nursing rat pups [see Data].
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for VOSEVI and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from VOSEVI or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Sofosbuvir: No significant effects of sofosbuvir on growth or postnatal development were observed in nursing pups at the highest dose tested in rats. Maternal systemic exposure (AUC) of the predominant circulating metabolite of sofosbuvir (GS-331007) was approximately 7 times the exposure in humans at the RHD, with exposure of approximately 2% that of maternal exposure observed in nursing pups on lactation day 10. In a lactation study, sofosbuvir metabolites (primarily GS-331007) were excreted into the milk of lactating rats following administration of a single oral dose of sofosbuvir (20 mg/kg) on lactation day 2, with milk concentrations of approximately 10% that of maternal plasma concentrations observed 1 hour post-dose.
Velpatasvir: No significant effects of velpatasvir on growth or postnatal development were observed in nursing pups at the highest dose tested in rats. Maternal systemic exposure (AUC) of velpatasvir was approximately 3 times the exposure in humans at the RHD. Velpatasvir was present in the milk (approximately 173% that of maternal plasma concentrations) of lactating rats following a single oral dose of velpatasvir (30 mg/kg), and systemic exposure (AUC) in nursing pups was approximately 4% that of maternal exposure on lactation day 10.
Voxilaprevir: No significant effects of voxilaprevir on growth or postnatal development were observed in nursing pups at the highest dose tested in rats. Maternal systemic exposure (AUC) of voxilaprevir was approximately 238 times the exposure in humans at the RHD, with exposure of approximately 58% that of maternal exposure observed in nursing pups on lactation day 10.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of VOSEVI have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical trials of VOSEVI included 74 subjects aged 65 and over (17% of total number of subjects in the POLARIS-1 and POLARIS-4 Phase 3 clinical trials). No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. No dosage adjustment of VOSEVI is warranted in geriatric patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VOSEVI is recommended for patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment, including ESRD requiring dialysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
No dosage adjustment of VOSEVI is recommended for patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh A). VOSEVI is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B or C) due to the higher exposures of voxilaprevir (up to 6-fold in non-HCV infected subjects); the safety and efficacy have not been established in HCV-infected patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Postmarketing cases of hepatic decompensation/failure have been reported in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Sofosbuvir: Sofosbuvir was not genotoxic in a battery of in vitro or in vivo assays, including bacterial mutagenicity, chromosome aberration using human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and in vivo mouse micronucleus assays.
Sofosbuvir was not carcinogenic in a 2-year mouse study (up to 200 mg/kg/day in males and 600 mg/kg/day in females) and in a 2-year rat study (up to 750 mg/kg/day), resulting in exposures of the predominant circulating metabolite GS-331007 of approximately 4 and 17 times (in male and female mice, respectively) and 9 times (in rats) the exposure in humans at the recommended human dose (RHD).
Velpatasvir: Velpatasvir was not genotoxic in a battery of in vitro or in vivo assays, including bacterial mutagenicity, chromosome aberration using human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and in vivo rat micronucleus assays.
Velpatasvir was not carcinogenic in a 6-month rasH2 transgenic mouse study (up to 1000 mg/kg/day) and a 2-year rat carcinogenicity study (up to 200 mg/kg/day). The exposure of VEL in the 2-year rat study was approximately 6 times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Voxilaprevir: Voxilaprevir was not genotoxic in a battery of in vitro or in vivo assays, including bacterial mutagenicity, chromosome aberration using human peripheral blood lymphocytes, and in vivo rat micronucleus assays.
Carcinogenicity studies for voxilaprevir have not been conducted.
Impairment of Fertility
Sofosbuvir: Sofosbuvir had no effects on embryo-fetal viability or on fertility when evaluated in rats. At the highest dose tested, AUC exposure to the predominant circulating metabolite GS-331007 was approximately 4 times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Velpatasvir: Velpatasvir had no effects on embryo-fetal viability or on fertility when evaluated in rats. At the highest dose tested, velpatasvir exposure was approximately 4 times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
Voxilaprevir: Voxilaprevir had no effects on embryo-fetal viability or on fertility when evaluated in rats. At the highest dose tested, voxilaprevir exposure was approximately 149 times the exposure in humans at the RHD.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each VOSEVI tablet contains 400 mg of sofosbuvir, 100 mg of velpatasvir, and
100 mg of voxilaprevir. The tablets are beige, capsule-shaped, film-coated,
and debossed with "GSI" on one side and
" " on the other
side. Each bottle contains 28 tablets (NDC 61958-2401-1), polyester coil,
silica gel desiccant, and is closed with a child-resistant closure.
" on the other
side. Each bottle contains 28 tablets (NDC 61958-2401-1), polyester coil,
silica gel desiccant, and is closed with a child-resistant closure.
Store below 30 °C (86 °F). Dispense only in original container.
