Silodosin
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SILODOSIN CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SILODOSIN CAPSULES. SILODOSIN capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
322ce16e-485f-4fd2-bb30-6b4776bc9e85
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 30, 2023
Alembic Pharmaceuticals Limited
DUNS: 650574663
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Silodosin
PRODUCT DETAILS
INGREDIENTS (11)
Silodosin
PRODUCT DETAILS
INGREDIENTS (10)
Drug Labeling Information
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Orthostatic Effects
Postural hypotension, with or without symptoms (e.g., dizziness) may develop when beginning silodosin capsules treatment. As with other alpha-blockers, there is potential for syncope. Patients should be cautioned about driving, operating machinery, or performing hazardous tasks when initiating therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6), Use in Specific Populations (8.5), Clinical Pharmacology (12.2), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.2 Renal Impairment
In a clinical pharmacology study, plasma concentrations (AUC and Cmax) of silodosin were approximately three times higher in subjects with moderate renal impairment compared with subjects with normal renal function, while half-lives of silodosin doubled in duration. The dose of silodosin capsules should be reduced to 4 mg in patients with moderate renal impairment. Exercise caution and monitor such patients for adverse events[ see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Silodosin capsules are contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment[ see Contraindications (4)].
5.3 Hepatic Impairment
Silodosin capsule has not been tested in patients with severe hepatic impairment, and therefore, should not be prescribed to such patients [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.4 Pharmacokinetic Drug-Drug Interactions
In a drug interaction study, co-administration of a single 8 mg dose of silodosin capsules with 400 mg ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, caused a 3.8-fold increase in maximum plasma silodosin concentrations and 3.2-fold increase in silodosin exposure (i.e., AUC). Concomitant use of ketoconazole or other strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, clarithromycin, ritonavir) is therefore contraindicated [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.5 Pharmacodynamic Drug-Drug Interactions
The pharmacodynamic interactions between silodosin and other alpha-blockers have not been determined. However, interactions may be expected, and silodosin capsules should not be used in combination with other alpha-blockers [see Drug Interactions (7.3)].
A specific pharmacodynamic interaction study between silodosin and antihypertensive agents has not been performed. However, patients in the Phase 3 clinical studies taking concomitant antihypertensive medications with silodosin capsules did not experience a significant increase in the incidence of syncope, dizziness, or orthostasis. Nevertheless, exercise caution during concomitant use with antihypertensives and monitor patients for possible adverse events [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Drug Interactions (7.6)].
Caution is also advised when alpha-adrenergic blocking agents including silodosin capsules are co-administered with PDE5 inhibitors. Alpha-adrenergic blockers and PDE5 inhibitors are both vasodilators that can lower blood pressure. Concomitant use of these two drug classes can potentially cause symptomatic hypotension [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
5.6 Carcinoma of the Prostate
Carcinoma of the prostate and BPH cause many of the same symptoms. These two diseases frequently co-exist. Therefore, patients thought to have BPH should be examined prior to starting therapy with silodosin capsules to rule out the presence of carcinoma of the prostate.
5.7 Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome
Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome has been observed during cataract surgery in some patients on alpha-1 blockers or previously treated with alpha-1 blockers. This variant of small pupil syndrome is characterized by the combination of a flaccid iris that billows in response to intraoperative irrigation currents; progressive intraoperative miosis despite preoperative dilation with standard mydriatic drugs; and potential prolapse of the iris toward the phacoemulsification incisions. Patients planning cataract surgery should be told to inform their ophthalmologist that they are taking silodosin capsules [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.8 Laboratory Test Interactions
No laboratory test interactions were observed during clinical evaluations. Treatment with silodosin capsules for up to 52 weeks had no significant effect on prostate-specific antigen (PSA).
- Postural hypotension, with or without symptoms (e.g., dizziness), may develop when beginning silodosin capsules treatment. (5.1)
- In patients with moderate renal impairment, silodosin capsules dose should be reduced to 4 mg once daily. (5.2)
- Silodosin capsules should not be used in combination with other alpha-blockers. (5.5)
- Examine patients thought to have BPH prior to starting therapy with silodosin capsules to rule out the presence of carcinoma of the prostate. (5.6)
- Inform patients planning cataract surgery to notify their ophthalmologist that they are taking silodosin capsules because of the possibility of Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS). (5.7)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Silodosin is a selective antagonist of alpha-1 adrenoreceptors. The chemical
name of silodosin is
1-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-5-[(2R)-2-({2-[2-(2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)phenoxy]ethyl}amino)propyl]-2,3-dihydro-1H-indole-7-carboxamide
and the molecular formula is C25H32F3N3O4 with a molecular weight of 495.53.
The structural formula of silodosin is:
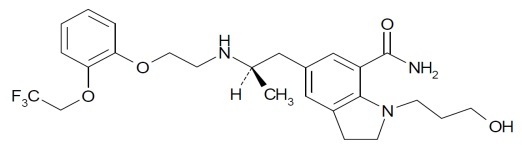
Silodosin is a white to pale yellow powder that melts at approximately 105 to 109°C. It is freely soluble in acetic acid, freely soluble in alcohol and very slightly to practically soluble in water.
Each silodosin capsules 4 mg capsule for oral administration contains 4 mg silodosin, and the following inactive ingredients: pregelatinized starch, sucrose, sodium lauryl sulfate and magnesium stearate. The size #3 hard gelatin capsules contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsules are printed with edible gold ink containing shellac, propylene glycol and iron oxide yellow.
Each silodosin capsules 8 mg capsule for oral administration contains 8 mg silodosin, and the following inactive ingredients: pregelatinized starch, sucrose, sodium lauryl sulfate and magnesium stearate. The size #1 hard gelatin capsules contain gelatin and titanium dioxide. The capsules are printed with edible green ink containing shellac, propylene glycol, iron oxide yellow FD&C Blue No. 1 Aluminum Lake.
