DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE TIMOLOL MALEATE
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE AND TIMOLOL MALEATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE AND TIMOLOL MALEATE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION. DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE AND TIMOLOL MALEATE ophthalmic solution, for topical ophthalmic use Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
02d89d37-cbca-4e06-83ef-2a10f988f1ea
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 13, 2023
Florida Pharmaceutical Products, LLC
DUNS: 084014259
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
dorzolamide hydrochloride timolol maleate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 71921-226-10
Florida Pharmaceutical Products, LLC
Dorzolamide HCl/ Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP, 22.3 mg/6.8 mg per
mL.
10 mL in 10 mL Bottle (Container) Label
Rx

NDC 71921-226-10
Florida Pharmaceutical Products, LLC
Dorzolamide HCl/ Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP, 22.3 mg/6.8 mg per mL.
10 mL Carton Label
Rx

CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Asthma, COPD
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
4.2 Sinus Bradycardia, AV Block, Cardiac Failure, Cardiogenic Shock
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with sinus bradycardia, second or third degree atrioventricular block, overt cardiac failure, and cardiogenic shock [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
4.3 Hypersensitivity
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients with:
- Bronchial asthma or a history of bronchial asthma, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (4.1)
- Sinus bradycardia, second or third degree atrioventricular block, overt cardiac failure, cardiogenic shock. (4.2)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product. (4.3, 5.3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potentiation of Respiratory Reactions Including Asthma
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains timolol maleate, a beta-adrenergic blocking agent; and although administered topically, is absorbed systemically. Therefore, the same types of adverse reactions that are attributable to systemic administration of beta-adrenergic blocking agents may occur with topical administration. For example, severe respiratory reactions, including death due to bronchospasm in patients with asthma, and rarely death in association with cardiac failure, have been reported following systemic or ophthalmic administration of timolol maleate [see Contraindications (4.1)].
5.2 Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation may be essential for support of the circulation in individuals with diminished myocardial contractility, and its inhibition by beta-adrenergic receptor blockade may precipitate more severe failure.
In patients without a history of cardiac failure continued depression of the myocardium with beta-blocking agents over a period of time can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure. At the first sign or symptom of cardiac failure, dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution should be discontinued [see Contraindications (4.2)].
5.3 Sulfonamide Hypersensitivity
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains dorzolamide, a sulfonamide; and although administered topically, it is absorbed systemically. Therefore, the same types of adverse reactions that are attributable to sulfonamides may occur with topical administration of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Fatalities have occurred, although rarely, due to severe reactions to sulfonamides including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and other blood dyscrasias. Sensitization may recur when a sulfonamide is readministered irrespective of the route of administration. If signs of serious reactions or hypersensitivity occur, discontinue the use of this preparation [see Contraindications (4.3)].
5.4 Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (e.g., chronic bronchitis, emphysema) of mild or moderate severity, bronchospastic disease, or a history of bronchospastic disease (other than bronchial asthma or a history of bronchial asthma, in which dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is contraindicated) should, in general, not receive beta- blocking agents, including dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution [see Contraindications (4.1)].
5.5 Increased Reactivity to Allergens
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of atopy or a history of severe anaphylactic reactions to a variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic challenge with such allergens. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat anaphylactic reactions.
5.6 Potentiation of Muscle Weakness
Beta-adrenergic blockade has been reported to potentiate muscle weakness consistent with certain myasthenic symptoms (e.g., diplopia, ptosis, and generalized weakness). Timolol has been reported rarely to increase muscle weakness in some patients with myasthenia gravis or myasthenic symptoms.
5.7 Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents should be administered with caution in patients subject to spontaneous hypoglycemia or to diabetic patients (especially those with labile diabetes) who are receiving insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
5.8 Masking of Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may mask certain clinical signs (e.g., tachycardia) of hyperthyroidism. Patients suspected of developing thyrotoxicosis should be managed carefully to avoid abrupt withdrawal of beta- adrenergic blocking agents that might precipitate a thyroid storm.
5.9 Renal and Hepatic Impairment
Dorzolamide has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl <30 mL/min). Because dorzolamide and its metabolite are excreted predominantly by the kidney, dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is not recommended in such patients.
Dorzolamide has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment and should therefore be used with caution in such patients.
5.10 Impairment of Beta-Adrenergically Mediated Reflexes During Surgery
The necessity or desirability of withdrawal of beta-adrenergic blocking agents prior to major surgery is controversial. Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade impairs the ability of the heart to respond to beta-adrenergically mediated reflex stimuli. This may augment the risk of general anesthesia in surgical procedures. Some patients receiving beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents have experienced protracted severe hypotension during anesthesia. Difficulty in restarting and maintaining the heartbeat has also been reported. For these reasons, in patients undergoing elective surgery, some authorities recommend gradual withdrawal of beta-adrenergic receptor blocking agents.
If necessary during surgery, the effects of beta-adrenergic blocking agents may be reversed by sufficient doses of adrenergic agonists.
5.11 Corneal Endothelium
Carbonic anhydrase activity has been observed in both the cytoplasm and around the plasma membranes of the corneal endothelium. There is an increased potential for developing corneal edema in patients with low endothelial cell counts. Caution should be used when prescribing dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution to this group of patients.
5.12 Bacterial Keratitis
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial.
- Potentiation of Respiratory Reactions Including Asthma (5.1)
- Cardiac Failure (5.2)
- Sulfonamide Hypersensitivity (5.3)
- Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (5.4)
- Increased Reactivity to Allergens (5.5)
- Potentiation of Muscle Weakness (5.6)
- Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus (5.7)
- Masking of Thyrotoxicosis (5.8)
- Renal and Hepatic Impairment (5.9)
- Impairment of Beta-Adrenergically Mediated Reflexes During Surgery (5.10)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution was evaluated in 1,035 patients with elevated intraocular pressure treated for open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension for up to 15 months. Approximately 5% of all patients discontinued therapy because of adverse reactions.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions occurring in up to 30% of patients were taste perversion (bitter, sour, or unusual taste) or ocular burning and/or stinging. The following adverse reactions were reported in 5 to15% of patients: conjunctival hyperemia, blurred vision, superficial punctate keratitis or eye itching.
The following adverse reactions were reported in 1 to 5% of patients: abdominal pain, back pain, blepharitis, bronchitis, cloudy vision, conjunctival discharge, conjunctival edema, conjunctival follicles, conjunctival injection, conjunctivitis, corneal erosion, corneal staining, cortical lens opacity, cough, dizziness, dryness of eyes, dyspepsia, eye debris, eye discharge, eye pain, eye tearing, eyelid edema, eyelid erythema, eyelid exudate/scales, eyelid pain or discomfort, foreign body sensation, glaucomatous cupping, headache, hypertension, influenza, lens nucleus coloration, lens opacity, nausea, nuclear lens opacity, pharyngitis, post- subcapsular cataract, sinusitis, upper respiratory infection, urinary tract infection, visual field defect, vitreous detachment.
Other adverse reactions that have been reported with the individual components are listed below:
Dorzolamide 2%
Angioedema, asthenia/fatigue, bronchospasm, contact dermatitis, epistaxis, eyelid crusting, ocular discomfort, photophobia, signs and symptoms of ocular allergic reaction, transient myopia.
Timolol (ocular administration)
Body as a Whole: Asthenia/fatigue; Cardiovascular: Arrhythmia, syncope, cerebral ischemia, worsening of angina pectoris, palpitation, cardiac arrest, pulmonary edema, edema, claudication, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and cold hands and feet; Digestive: Anorexia, abdominal pain; Immunologic: Systemic lupus erythematosus; Nervous System/Psychiatric: Increase in signs and symptoms of myasthenia gravis, somnolence, insomnia, nightmares, behavioral changes and psychic disturbances including confusion, hallucinations, anxiety, disorientation, nervousness, and memory loss; Skin: Alopecia, psoriasiform rash or exacerbation of psoriasis; Hypersensitivity: Signs and symptoms of systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, and localized and generalized rash; Respiratory: Bronchospasm (predominantly in patients with pre-existing bronchospastic disease); Endocrine: Masked symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients; Special Senses: Ptosis, decreased corneal sensitivity, cystoid macular edema, visual disturbances including refractive changes and diplopia, pseudopemphigoid, and tinnitus; Urogenital: Retroperitoneal fibrosis, decreased libido, impotence, and Peyronie’s disease; Musculoskeletal: Myalgia.
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: bradycardia, cardiac failure, cerebral vascular accident, chest pain, choroidal detachment following filtration surgery, depression, diarrhea, dry mouth, dyspnea, heart block, hypotension, iridocyclitis, myocardial infarction, nasal congestion, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, paresthesia, photophobia, respiratory failure, skin rashes, urolithiasis, and vomiting.
Timolol (oral administration)
The following additional adverse reactions have been reported in clinical experience with ORAL timolol maleate or other ORAL beta-blocking agents and may be considered potential effects of ophthalmic timolol maleate: Allergic: Erythematous rash, fever combined with aching and sore throat, laryngospasm with respiratory distress; Body as a Whole: Extremity pain, decreased exercise tolerance, weight loss; Cardiovascular: Worsening of arterial insufficiency, vasodilatation; Digestive: Gastrointestinal pain, hepatomegaly, mesenteric arterial thrombosis, ischemic colitis; Hematologic: Nonthrombocytopenic purpura; thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis; Endocrine: Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia; Skin: Pruritus, skin irritation, increased pigmentation, sweating; Musculoskeletal: Arthralgia; NervousSystem/Psychiatric: Vertigo, local weakness, diminished concentration, reversible mental depression progressing to catatonia, an acute reversible syndrome characterized by disorientation for time and place, emotional lability, slightly clouded sensorium, and decreased performance on neuropsychometrics; Respiratory: Rales, bronchial obstruction; Urogenital: Urination difficulties.
The most frequently reported adverse reactions were taste perversion (bitter, sour, or unusual taste) or ocular burning and/or stinging in up to 30% of patients. Conjunctival hyperemia, blurred vision, superficial punctate keratitis or eye itching were reported between 5 to 15% of patients. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Florida Pharmaceutical Products, LLCat 1-800-315-0985****or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects. Developmental toxicity studies with dorzolamide hydrochloride in rabbits at oral doses of ≥ 2.5 mg/kg/day (37 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose) revealed malformations of the vertebral bodies. These malformations occurred at doses that caused metabolic acidosis with decreased body weight gain in dams and decreased fetal weights. No treatment-related malformations were seen at 1 mg/kg/day (15 times the recommended human ophthalmic dose).
Teratogenicity studies with timolol in mice, rats, and rabbits at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day (7,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose) demonstrated no evidence of fetal malformations. Although delayed fetal ossification was observed at this dose in rats, there were no adverse effects on postnatal development of offspring. Doses of 1,000 mg/kg/day (142,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose) were maternotoxic in mice and resulted in an increased number of fetal resorptions. Increased fetal resorptions were also seen in rabbits at doses of 14,000 times the systemic exposure following the maximum recommended human ophthalmic dose, in this case without apparent maternotoxicity.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether dorzolamide is excreted in human milk. Timolol maleate has been detected in human milk following oral and ophthalmic drug administration. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions from dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in nursing infants, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution have been established when administered individually in pediatric patients aged 2 years and older. Use of these drug products in these children is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in children and adults. Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients below the age of 2 years have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, USP is the combination of a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and a topical beta- adrenergic receptor blocking agent.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride is described chemically as: (4S-trans)-4-(ethylamino)-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide monohydrochloride. Dorzolamide hydrochloride is optically active. The specific rotation is:
[a] 25°C (C=1, water) = ~ -17°.
405nm
Its empirical formula is C10H16N2O4S3•HCl and its structural formula is:
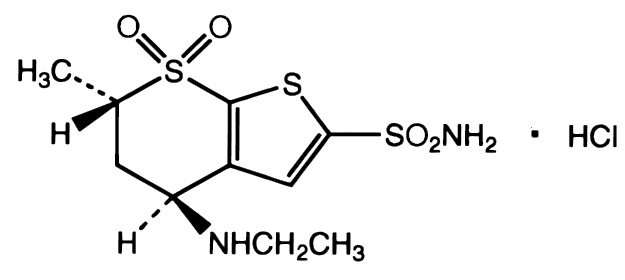
Dorzolamide hydrochloride has a molecular weight of 360.91. It is a white to off-white, crystalline powder, which is soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol and ethanol.
Timolol maleate is described chemically as: (-)-1-(tert- butylamino)-3-[(4-morpholino-1,2,5-thiadiazol-3-yl)oxy]-2-propanol maleate (1:1) (salt). Timolol maleate possesses an asymmetric carbon atom in its structure and is provided as the levo-isomer. The optical rotation of timolol maleate is:
[a] 25°C in 1N HCl (C = 5) = -12.2° (-11.7° to -12.5°).
405 nm
Its molecular formula is C13H24N4O3S•C4H4O4 and its structural formula is:
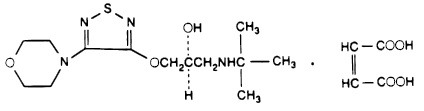
Timolol maleate has a molecular weight of 432.50. It is a white, odorless, crystalline powder which is soluble in water, methanol, and alcohol. Timolol maleate is stable at room temperature.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, USP is supplied as a sterile, isotonic, buffered, slightly viscous, aqueous solution. The pH of the solution is approximately 5.65, and the osmolarity is 242 to 323 mOsM. Each mL of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, USP contains 20 mg dorzolamide (equivalent to 22.26 mg of dorzolamide hydrochloride) and 5 mg timolol (equivalent to 6.83 mg timolol maleate). Inactive ingredients are sodium citrate, hydroxyethyl cellulose, sodium hydroxide, mannitol, and water for injection. Benzalkonium chloride 0.0075% is added as a preservative.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is comprised of two components: Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate. Each of these two components decreases elevated intraocular pressure, whether or not associated with glaucoma, by reducing aqueous humor secretion. Elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor in the pathogenesis of optic nerve damage and glaucomatous visual field loss. The higher the level of intraocular pressure, the greater the likelihood of glaucomatous field loss and optic nerve damage.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride is an inhibitor of human carbonic anhydrase II. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye decreases aqueous humor secretion, presumably by slowing the formation of bicarbonate ions with subsequent reduction in sodium and fluid transport. Timolol maleate is a beta1 and beta2 (non-selective) adrenergic receptor blocking agent that does not have significant intrinsic sympathomimetic, direct myocardial depressant, or local anesthetic (membrane-stabilizing) activity. The combined effect of these two agents administered as dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution twice daily results in additional intraocular pressure reduction compared to either component administered alone, but the reduction is not as much as when dorzolamide administered three times daily and timolol twice daily are administered concomitantly. [See Clinical Studies (14)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Dorzolamide Hydrochloride
When topically applied, dorzolamide reaches the systemic circulation. To assess the potential for systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibition following topical administration, drug and metabolite concentrations in RBCs and plasma and carbonic anhydrase inhibition in RBCs were measured. Dorzolamide accumulates in RBCs during chronic dosing as a result of binding to CA-II. The parent drug forms a single N-desethyl metabolite, which inhibits CA-II less potently than the parent drug but also inhibits CA-I. The metabolite also accumulates in RBCs where it binds primarily to CA-I. Plasma concentrations of dorzolamide and metabolite are generally below the assay limit of quantitation (15nM). Dorzolamide binds moderately to plasma proteins (approximately 33%).
Dorzolamide is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine; the metabolite also is excreted in urine. After dosing is stopped, dorzolamide washes out of RBCs nonlinearly, resulting in a rapid decline of drug concentration initially, followed by a slower elimination phase with a half-life of about four months.
To simulate the systemic exposure after long-term topical ocular administration, dorzolamide was given orally to eight healthy subjects for up to 20 weeks. The oral dose of 2 mg twice daily closely approximates the amount of drug delivered by topical ocular administration of dorzolamide 2% three times daily. Steady state was reached within 8 weeks. The inhibition of CA-II and total carbonic anhydrase activities was below the degree of inhibition anticipated to be necessary for a pharmacological effect on renal function and respiration in healthy individuals.
Timolol Maleate
In a study of plasma drug concentrations in six subjects, the systemic exposure to timolol was determined following twice daily topical administration of timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5%. The mean peak plasma concentration following morning dosing was 0.46 ng/mL.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Potential for Exacerbation of Asthma and COPD
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may cause severe worsening of asthma and COPD symptoms including death due to bronchospasm. Advise patients with bronchial asthma, a history of bronchial asthma, or severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease not to take this product. [see Contraindications (4.1)].
Potential of Cardiovascular Effects
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may cause worsening of cardiac symptoms. Advise patients with sinus bradycardia, second or third degree atrioventricular block, or cardiac failure not to take this product. [see Contraindications (4.2)].
Sulfonamide Reactions
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains dorzolamide (which is a sulfonamide) and, although administered topically, is absorbed systemically. Therefore the same types of adverse reactions that are attributable to sulfonamides may occur with topical administration, including severe skin reactions. Advise patients that if serious or unusual reactions or signs of hypersensitivity occur, they should discontinue the use of the product and seek their physician's advice. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Handling Ophthalmic Solutions
Instruct patients that ocular solutions, if handled improperly or if the tip of the dispensing container contacts the eye or surrounding structures, can become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Intercurrent Ocular Conditions
Advise patients that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician’s advice concerning the continued use of the present multidose container.
Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart.
Contact Lens Use
Advise patients that dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains benzalkonium chloride which may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Contact lenses should be removed prior to administration of the solution. Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes following administration of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.

Manufactured For:
Florida Pharmaceutical Products, LLC
Boca Raton, FL 33487
Toll-free # 1-800-315-0985
Manufactured by:
Indoco Remedies Limited
Verna, Goa-403722, India.
Revised: June 2023
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
SPL MEDGUIDE SECTION
Patient Information about
Dorzolamide Hydrochloride-Timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP
** (door-ZOLE-ah-mide hye-droe-klor-ide tye-MOE-lawl MAL-ee-ate)**
What is****dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution?
****Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is a prescription eye drop that contains two medicines, dorzolamide hydrochloride called an ophthalmic carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and timolol maleate called a beta-blocker.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is used to lower high pressure in the eye in people with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension when a beta-blocking medicine alone does not work to control the eye pressure.
It is not known if dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is safe and effective in children 2 years of age and younger.
Do not use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution if you:
- have or have had asthma.
- have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) which includes emphysema, chronic bronchitis or both.
- have heart problems including a slow heartbeat, heart block, heart failure, or your heart muscle suddenly becomes weak due to a severe heart attack or other heart problem that caused heart damage (cardiogenic shock).
- are allergic to any of the ingredients in dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. See the end of this Patient Information leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
Before using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have or have had allergies to sulfa drugs
- have a history of anaphylactic reactions to allergens
- have atopy (genetic disposition to develop allergic reactions)
- have or have had muscle weakness or myasthenia gravis
- have diabetes
- have thyroid disease
- have or have had kidney or liver problems
- plan to have any type of surgery
- wear contact lenses
- are using any other eye drops
- have an eye infection or eye trauma
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution will harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. You and your healthcare provider will decide if you should use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution while you are pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution passes into breastmilk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may affect the way medicines work, and other medicines may affect how dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution works. Do not start a new medicine without first talking to your healthcare provider. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for a list of medicines you are using, if you are not sure. Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution?
- See the complete Instructions for Use at the end of this Patient Information leaflet for detailed instructions about the right way to use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- Use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Use 1 drop of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution in the affected eye or both eyes if needed, 2 times each day. 1 drop in the morning and 1 drop in the evening.
- If you are using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution with another eyedrop, wait at least 5 minutes before or after using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- If you have eye surgery or have any problems with your eye such as trauma or an infection, talk to your healthcare provider about continuing to use the bottle (multidose) that contains dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution contains a preservative called benzalkonium chloride. The preservative may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. If you wear contact lenses, remove them before using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. The lenses can be placed back into your eyes 15 minutes after using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- Do not touch your eye or eyelid with the dropper tip. Eye medicines, not handled the right way, can become contaminated by bacteria that can cause eye infections. Serious damage to the eye and followed by loss of vision may happen from using contaminated eye medicines. If you thinkyour dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution medicine may be contaminated, or if you develop an eye infection, contact your healthcare provider right away about continuing to use your bottle of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- If you use too much dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution you may have dizziness, headaches, shortness of breath, slow heartbeats, or problems breathing. If you have any of these symptoms call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution?
Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution may cause serious side effects, including:
*severe breathing problems. These breathing problems can happen in people who have asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or heart failure and can cause death. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have breathing problems while using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. *heart failure. This can happen in people who already have heart failure and in people who have never had heart failure before. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these symptoms of heart failure while taking dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution:
- shortness of breath
- irregular heartbeat (palpitations)
- swelling of your ankles or feet
- sudden weight gain
*serious sulfa (sulfonamide) reactions. Serious reactions including death can happen in people who are allergic to sulfonamide medicines like one of the medicines in dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Other serious reactions can include:
- severe skin reactions
- liver problems
- blood problems
Stop using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution and call your healthcare provider or get emergency help right away if you get any of these symptoms of an allergic reaction:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*increased allergic reactions. People who have a genetic history of developing allergies (atopy) or who have a history of severe anaphylactic reactions from different allergens may have increased allergic reactions while taking beta-blockers, like one of the medicines in dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Your usual dose of epinephrine used to treat your anaphylactic reactions may not work as well.Stop using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution and call your healthcare provider or get emergency help right away if you get any of these symptoms of an allergic reaction:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
*worsening muscle weakness. Muscle weakness symptoms including double vision or drooping eyelids can happen while using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Muscle weakness can get worse in people who already have problems with muscle weakness like myasthenia gravis. *swelling of eye. Some people with low counts of certain types of cells in the eye have developed corneal edema when using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Call your healthcare provider if you have swelling in your eyes.
The most common side effects of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution include:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
These are not all the possible side effects of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088
How should I store dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution?
- Store at 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
- Protect from light. *Do not use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution after the expiration date on the bottle.
Keep dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution and all medicine out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet.
Do not use dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution?
Active ingredients: dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate
Inactive ingredients: sodium citrate, hydroxyethylcellulose, sodium hydroxide, mannitol, water for injection and benzalkonium chloride added as a preservative.
This Patient Package Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
06/2023
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Dorzolamide Hydrochloride and timolol Maleate Ophthalmic Solution, USP
(door-ZOLE-ah-mide hye-droe-klor-ide tye-MOE-lawl MAL-ee-ate)
for topical ophthalmic use****
Read this Instructions for Use before you start using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
Important Information:
*Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution is for use in the eye.
- If you are using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution with another eyedrop, wait at least 5 minutes before or after using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- If you wear contact lenses, remove them before using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. The lenses can be placed back into your eyes15 minutes after using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. *Do not touch your eye or eyelid with the dropper tip. Eye medicines, not handled the right way, can become contaminated by bacteria that can cause eye infections. Serious damage to the eye and followed by loss of vision may happen from using contaminated eye medicines.If you think your dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution medicine may be contaminated, or if you develop an eye infection, contact your healthcare provider right away about continuing to use your bottle of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- Wash your hands before each use to make sure you do not infect your eyes while using dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
- Before using the eyedrops for the first time, be sure the tamper-evident ring around the cap is not broken. If the tamper-evident ring is broken, call your pharmacist to get a new bottle of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution.
Step 1. Tear off tamper-evident ring.
Step 2. To open the dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution bottle, unscrew the cap by turning counterclockwise.
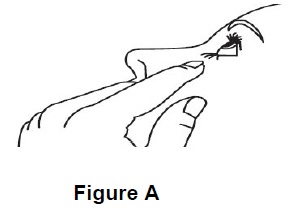
Step 3. Tilt your head back. Gently pull your lower eyelid downwards to form a pocket between your eyelid and your eye, look up (See Figure A).
****
**Step 4.**Turn the dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution bottle upside down.
Step 5. Place the dropper tip of the dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution bottle close to your eye but be careful not to touch your eye with it. Gently press the dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution bottle lightly with your thumb or index finger until 1 drop of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution falls into your eye (See Figure B).
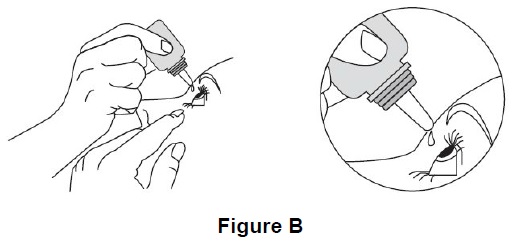
Step 6. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 with the other eye if instructed to do so by
your healthcare provider.
Step 7. Replace the cap by turning until it is firmly touching the bottle.
Do not overtighten the cap.
Step 8. If you use contact lenses,wait at least 15 minutes before
placing them back into your eyes.
• The dropper tip is made to give a single drop of dorzolamide hydrochloride
and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution. Do not enlarge the hole of the
dropper tip.
• After you have used all of your doses of dorzolamide hydrochloride and
timolol maleate ophthalmic solution, there will be some dorzolamide
hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution left in the bottle.
• There is an extra amount of dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate
ophthalmic solution that has been added to the bottle. You will get the full
amount of Dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution
that your doctor prescribed.
•Do not try to remove the extra dorzolamide hydrochloride and timolol
maleate ophthalmic solution medicine from the bottle.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug
Administration
TEAR AND DISCARD RING BEFORE USE.
Do not use if tear-off ring is missing or broken.
Manufactured For:
Florida Pharmaceutical Products, LLC
Boca Raton, FL 33487
Toll-free # 1-800-315-0985
Manufactured by:
Indoco Remedies Limited
Verna, Goa-403722, India.
Revised: June 2023
